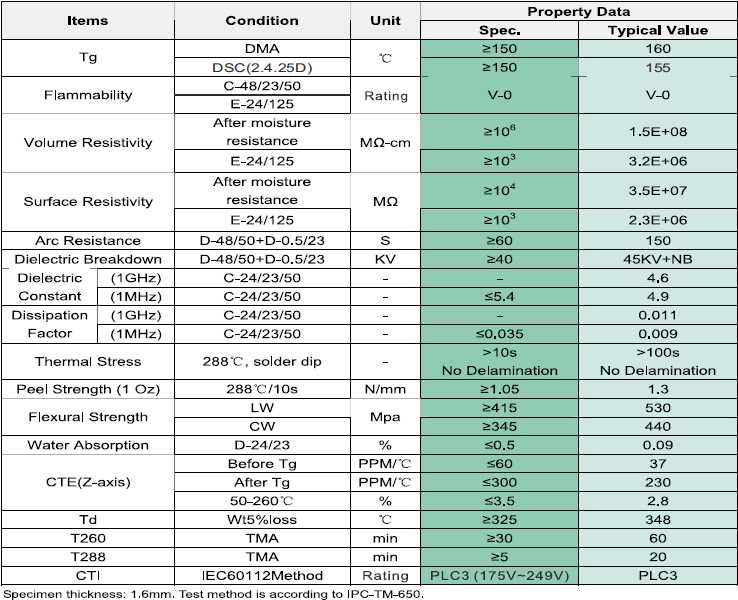
Unveiling the foundational essence of modern electronic circuitry lies in dissecting the quintessential manuscript that delineates its fabric and potential. Within the annals of technical documentation, there exists a trove of knowledge that orchestrates the symphony of connectivity, presenting a roadmap imbued with intricate details and vital statistics.
Delving into the marrow of this blueprint unveils a lexicon of critical parameters, an amalgamation of figures and characteristics that sculpt the very backbone of electronic infrastructure. These metrics, akin to the molecular codes of creation, dictate the behavior, resilience, and performance of the circuitry they govern.
Embark on a journey through the corridors of this technical parchment, where each line and symbol harbors significance, each notation a gateway to comprehension. Beyond the veil of jargon lies a realm where material properties, electrical characteristics, and thermal dynamics converge, shaping the destiny of every circuit etched upon its surface.
Understanding FR-4 Circuit Board Specifications: An In-Depth Exploration
In the realm of electronic engineering, delving into the intricate details of circuit board materials and specifications unveils a world of essential insights for designers and manufacturers alike. In this comprehensive guide, we embark on an exploration of the intricacies inherent in FR-4 circuit board documentation. Through deciphering these specifications, engineers gain a profound understanding of the material properties, performance characteristics, and manufacturing considerations vital for successful PCB design.
Deciphering Material Properties
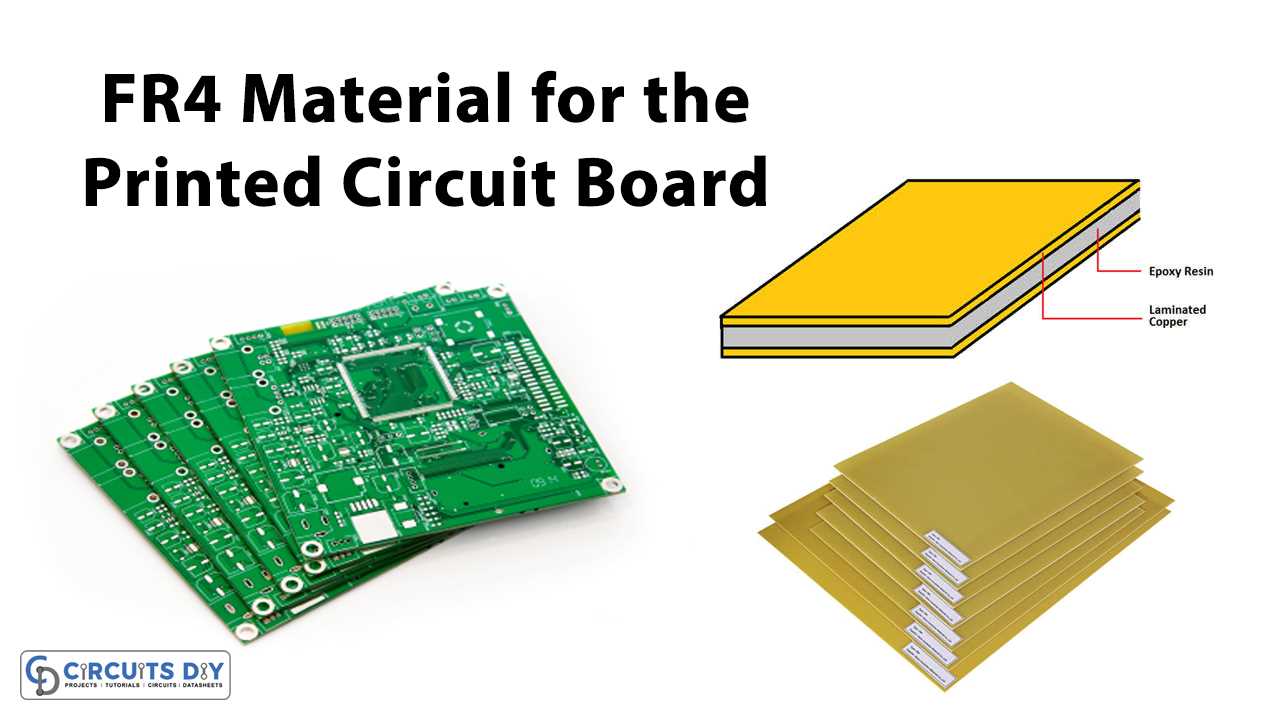
Within FR-4 circuit board datasheets lie a wealth of information regarding the material’s composition, mechanical properties, and thermal conductivity. By dissecting these details, engineers discern crucial aspects such as dielectric constant, glass transition temperature, and coefficient of thermal expansion. These properties profoundly influence the board’s performance under various environmental conditions and aid in selecting the most suitable substrate for specific applications.
Unraveling Performance Characteristics

Beyond material properties, FR-4 datasheets elucidate the performance characteristics essential for evaluating the circuit board’s reliability and functionality. Parameters like impedance control, signal integrity, and electrical conductivity play pivotal roles in ensuring optimal signal transmission and minimizing signal loss. By meticulously analyzing these specifications, engineers can fine-tune their designs to meet stringent performance requirements and mitigate potential issues arising from signal distortion or interference.
In essence, navigating FR-4 circuit board datasheets involves a meticulous examination of material properties and performance characteristics to inform intelligent design decisions and facilitate the seamless integration of electronic components. Through this comprehensive guide, engineers gain the proficiency to harness the full potential of FR-4 substrates, thereby advancing innovation and excellence in PCB design.
Deciphering FR-4 Circuit Board Specifications

In the realm of electronic components, navigating the intricate landscape of circuit board materials and their specifications is paramount for engineers and manufacturers alike. Understanding the nuances of FR-4 circuit board specifications can be akin to deciphering a complex code, where each parameter holds significance in the performance and functionality of the final product.
Understanding the Composition
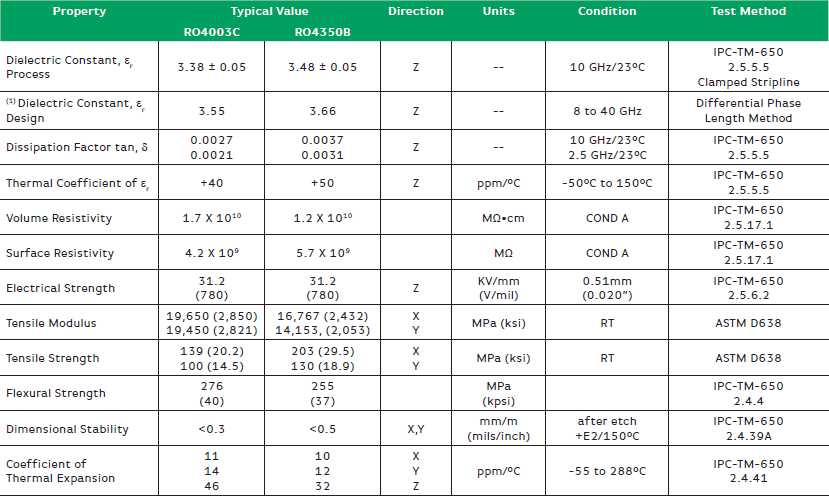
At the core of comprehending FR-4 circuit board specifications lies a grasp of its composition. Delving into the intricacies of the materials used unveils a tapestry of properties that influence the board’s thermal stability, mechanical strength, and electrical conductivity.
Decoding Performance Metrics

Beyond mere composition, deciphering FR-4 circuit board specifications entails a nuanced understanding of performance metrics. From dielectric constant to dissipation factor, each metric serves as a puzzle piece in gauging the board’s suitability for diverse applications, ranging from consumer electronics to aerospace endeavors.
Key Characteristics in FR-4 Circuit Board Specifications
In scrutinizing documentation for FR-4 circuit boards, one must navigate through a labyrinth of technical specifications. Understanding the nuances of these parameters is pivotal in ensuring optimal performance and compatibility within electronic systems.
Material Composition: The elemental constitution of the substrate profoundly influences the board’s thermal conductivity, dielectric constant, and mechanical properties. Comprehending the composition aids in predicting the board’s behavior under various operating conditions.
Thickness: The thickness of the substrate impacts the board’s rigidity, impedance, and signal integrity. Variances in thickness can affect the board’s suitability for specific applications, such as high-frequency designs or compact layouts.
Dielectric Constant (Dk): The dielectric constant delineates the material’s ability to store electrical energy under an applied voltage. A precise understanding of Dk facilitates impedance control and signal propagation, crucial for maintaining signal integrity.
Thermal Properties: Thermal conductivity, coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), and glass transition temperature (Tg) are pivotal parameters governing the board’s thermal performance. These properties dictate the board’s ability to dissipate heat and withstand temperature fluctuations without compromising structural integrity.
Surface Finish: The surface finish influences solderability, corrosion resistance, and electrical conductivity. Selecting an appropriate finish ensures robust solder joints and reliable electrical connections, essential for long-term reliability.
Copper Weight: The thickness of copper traces profoundly influences the board’s current-carrying capacity, impedance, and manufacturability. Balancing copper weight with design constraints is critical in optimizing electrical performance while adhering to cost considerations.
Flammability Rating: Understanding the flammability rating aids in assessing the board’s safety and compliance with industry standards. It provides insights into the material’s fire-resistant properties, essential for applications demanding stringent safety protocols.
Environmental Considerations: Factors such as moisture absorption, chemical resistance, and environmental certifications play a pivotal role in determining the board’s suitability for specific applications and operating environments. Evaluating these aspects ensures longevity and reliability in diverse usage scenarios.
Navigating FR-4 Material Properties
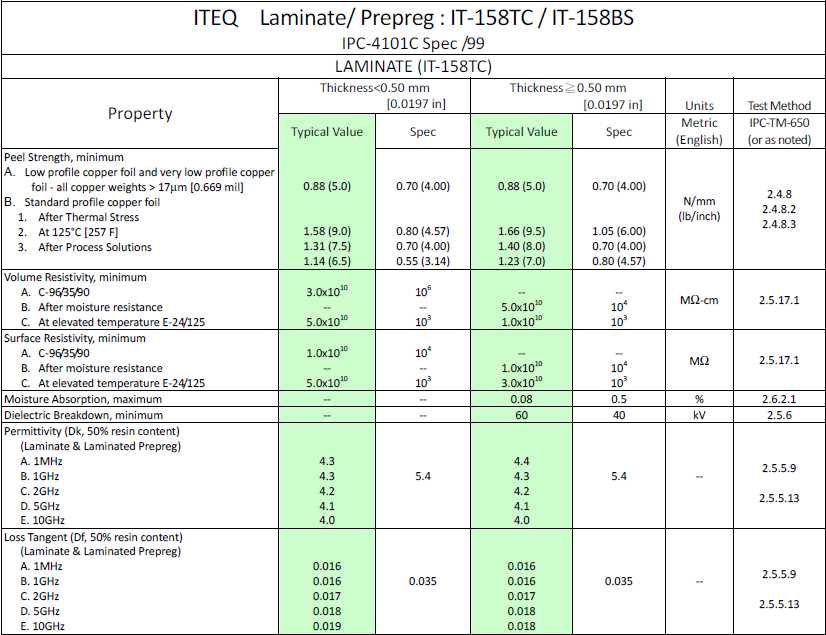
Exploring the intricate characteristics of the renowned substrate in electronics manufacturing entails a comprehensive understanding of its diverse material properties. This section delves into the nuanced facets of this ubiquitous material, shedding light on its mechanical, thermal, and electrical attributes crucial for a myriad of applications.
Understanding Mechanical Characteristics
Mechanical properties encompass a broad spectrum of traits defining the behavior of materials under various stresses and strains. In the realm of FR-4 substrates, these properties dictate its structural integrity, resilience to bending and flexing, and resistance to external forces. An exploration of its tensile strength, flexural modulus, and impact resistance elucidates its suitability for demanding environments across industries.
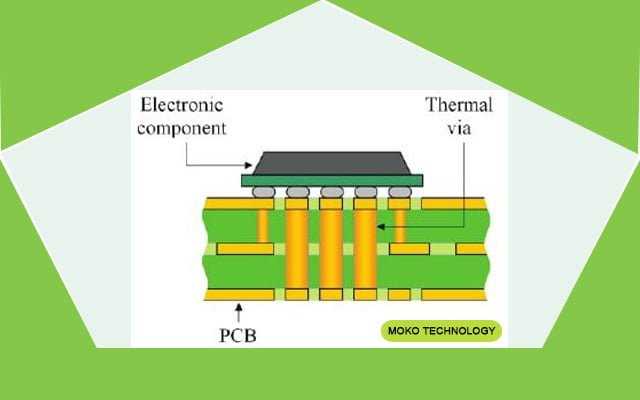
Analyzing Thermal Conductivity and Dissipation
Thermal conductivity forms a cornerstone in the realm of electronics, particularly in dissipating heat generated by components. Within FR-4 substrates, understanding thermal properties is paramount to ensuring efficient heat dissipation, preventing overheating, and maintaining optimal performance. Delving into parameters like thermal conductivity, coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), and glass transition temperature (Tg) unveils the substrate’s ability to mitigate thermal challenges in electronic assemblies.