Delve into the labyrinth of technological marvels, where circuits orchestrate symphonies of electrons, harmonizing in perfect unity to manifest innovation. In the realm of electronic exploration, one encounters a treasure trove of components, each bearing the potential to unlock the secrets of modern engineering.
Within this realm, one finds a cornerstone of electronic craftsmanship, a beacon illuminating the path toward precision and efficiency. This enigmatic entity, shrouded in a veil of intricacy, serves as the linchpin of countless electronic endeavors, guiding enthusiasts and professionals alike through the maze of circuitry.
Embark on a journey of discovery as we unravel the essence of this pivotal element, deciphering its intricacies and uncovering its boundless potential.
The Basics of Understanding MC1648P Specifications
Delving into the intricacies of electronic components often begins with deciphering their technical documentation. In this section, we will embark on a journey to unravel the fundamental aspects encapsulated within the specifications of the MC1648P device. By comprehending these key elements, one can gain valuable insights into its functionality and performance characteristics.
Functional Overview
At the core of comprehending the MC1648P lies a nuanced understanding of its operational principles. Through a detailed examination of its functional overview, one can discern the underlying mechanisms driving its behavior. This section elucidates the primary functions and operational modes of the device, shedding light on its versatility and applicability across various electronic circuits.
Performance Metrics
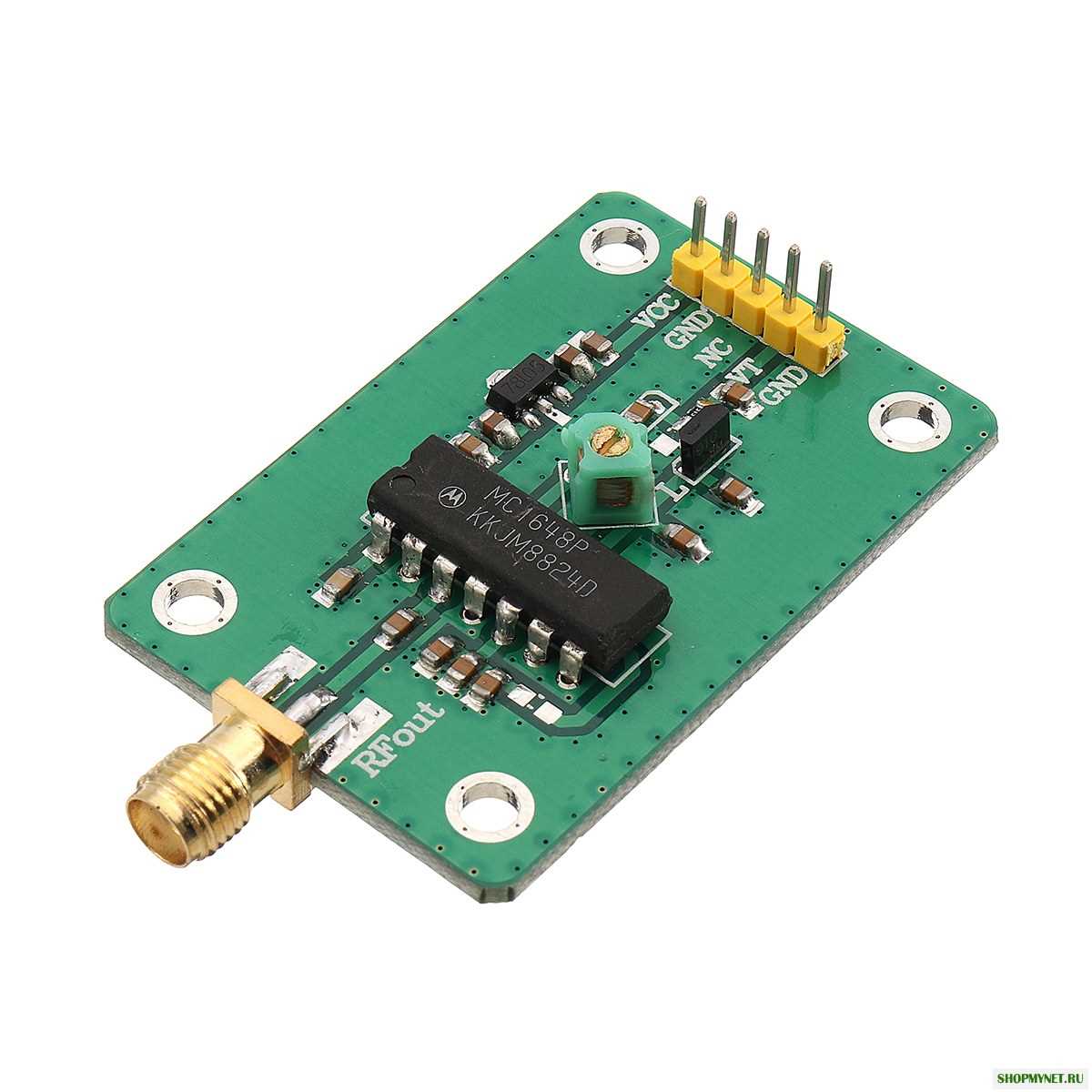
Quantifying the performance of the MC1648P entails an analysis of diverse metrics that define its efficacy in real-world applications. From frequency stability to output waveform integrity, each metric encapsulates crucial information regarding the device’s performance under distinct operating conditions. By scrutinizing these performance parameters, engineers can make informed decisions regarding its suitability for specific design requirements.
Understanding the Key Specifications
In delving into the intricacies of any electronic component, it is paramount to grasp the fundamental specifications that delineate its functionality and performance. Within the realm of semiconductor devices, comprehending these key parameters forms the cornerstone of informed decision-making and effective utilization.
Essential Performance Metrics
When evaluating a semiconductor component, several pivotal characteristics emerge as the linchpin of its operation. These metrics encapsulate vital aspects such as operational range, efficiency, and signal integrity, serving as the compass guiding engineers and enthusiasts alike through the labyrinth of technical intricacies.
Interpreting Technical Data

Beneath the veneer of technical jargon lies a trove of information awaiting decipherment. Decoding the language of specifications demands not only a keen eye for detail but also a holistic understanding of the interplay between different parameters. Through meticulous analysis and discernment, one can unlock the true potential encapsulated within the labyrinth of data sheets and technical documents.
Application Circuits and Configurations
In this section, we explore various application circuits and configurations for optimizing the performance and versatility of the component under discussion. Through these configurations, users can harness the full potential of the device in diverse settings and applications. By understanding the underlying principles and functionalities, engineers can tailor these circuits to suit specific requirements, thereby enhancing efficiency and functionality.
1. Signal Conditioning Circuits
- Signal conditioning circuits are paramount in preparing input signals for processing, ensuring compatibility and reliability.
- These circuits may include amplifiers, filters, and signal converters to adjust signal characteristics according to the application’s demands.
- By employing appropriate signal conditioning techniques, engineers can mitigate noise, improve signal-to-noise ratio, and enhance overall system performance.
2. Control and Modulation Circuits
- Control and modulation circuits play a pivotal role in regulating the operation and behavior of the system.
- These circuits facilitate precise control over parameters such as frequency, amplitude, and phase, crucial for achieving desired performance.
- Through modulation techniques like frequency modulation (FM) or amplitude modulation (AM), engineers can impart specific characteristics to the output signal, catering to diverse applications.
By exploring these application circuits and configurations, users can unlock the versatility and adaptability of the component, paving the way for innovative solutions across various domains.
Exploring the Applications of MC1648P Datasheet

Delve into the diverse realms of applications facilitated by the comprehensive insights provided within the specifications of the MC1648P component. This section elucidates the multifaceted utility of the data encapsulated within, transcending mere documentation to unveil a panorama of potential functionalities.
Embark on a journey through the myriad utilization scenarios offered by the MC1648P documentation. From its capacity to serve as a cornerstone in circuit design to its role in optimizing system performance, the datasheet furnishes an invaluable resource for engineers and enthusiasts alike.
| Application Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Electronic Circuit Design | Discover how the specifications delineated in the MC1648P datasheet empower engineers to architect intricate electronic systems, fostering innovation and efficiency. |
| Signal Processing | Explore the nuanced intricacies of signal manipulation and processing facilitated by the insights gleaned from the MC1648P documentation, enabling the refinement of communication and control systems. |
| Frequency Modulation | Unravel the applications of frequency modulation techniques, leveraging the guidelines provided within the MC1648P datasheet to achieve precision and reliability in frequency-based applications. |
| Oscillator Circuitry | Unlock the potential of oscillator circuitry configurations by harnessing the specifications outlined in the MC1648P datasheet, paving the way for stable and synchronized oscillations in diverse electronic systems. |
| Wireless Communication | Delve into the realm of wireless communication systems, leveraging the insights furnished by the MC1648P documentation to optimize performance and enhance connectivity in modern communication networks. |
By delving into the applications elucidated within the MC1648P datasheet, enthusiasts and professionals alike can harness its wealth of information to drive innovation, optimize performance, and unlock the full potential of electronic systems.
Usage in Electronic Oscillator Circuits

When delving into the realm of electronic oscillator circuits, it’s crucial to explore the application and integration of the component detailed within the referenced documentation. This section elucidates the practical utilization of the specified component, emphasizing its pivotal role in generating repetitive waveforms for various electronic systems.
Frequency Generation
One primary function entails facilitating the generation of precise and stable frequencies requisite for the operation of electronic devices. By harnessing the inherent characteristics of the component, electronic oscillator circuits can produce oscillations at desired frequencies, enabling synchronization within complex systems.
Signal Modulation
Beyond mere frequency generation, the component also contributes to signal modulation, allowing for the manipulation of waveforms to transmit information effectively. Through modulation techniques such as amplitude, frequency, or phase modulation, electronic oscillator circuits facilitate the encoding and decoding of data, vital in communication systems.
- Facilitates precise frequency generation.
- Enables signal modulation for data transmission.
- Essential component in electronic systems requiring stable oscillations.