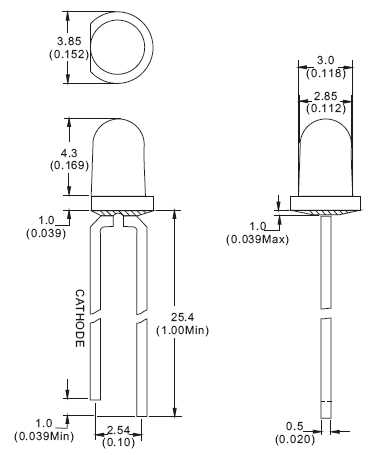
Delving into the intricacies of diminutive luminance components, this segment navigates through the specifications and functionalities of petite radiant elements. Offering a window into the world of compact brilliance, it ventures into the technical dimensions and operational capacities of these minute emissive entities.
Embark on a journey to uncover the nuances of these petite light sources, where we dissect the performance metrics, structural intricacies, and application potentials. Discover the underlying mechanics that govern the emission of light on a miniature scale, as we unravel the diverse facets of these diminutive luminous entities.
Join us as we traverse through the realm of miniature illumination, exploring the nuanced attributes and operational parameters that define these compact luminous modules. From their spectral characteristics to their efficacy in diverse applications, this exploration sheds light on the versatile capabilities encapsulated within these diminutive luminance components.
The Essentials of 5mm Light Emitting Diode Documentation
In the realm of illuminating components, there exists a wealth of information to navigate through when assessing the specifications of small-scale light-emitting diodes (LEDs). Understanding the foundational aspects of documentation associated with these compact luminous elements is crucial for informed decision-making and effective integration into various electronic applications.
Examining the intricacies of technical documents for 5mm LEDs involves delving into diverse parameters and performance metrics that illuminate their operational characteristics and potential applications. These documents serve as comprehensive guides, offering insights into the electrical, optical, and mechanical properties of these diminutive yet versatile light sources.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Electrical Characteristics | Details regarding voltage and current requirements, forward voltage drop, reverse voltage tolerance, and power dissipation. |
| Optical Specifications | Information on luminous intensity, viewing angle, wavelength, color rendering index (CRI), and radiant flux. |
| Mechanical Attributes | Physical dimensions, packaging type, lead configuration, and mounting options are outlined to facilitate proper integration into designs. |
| Environmental Considerations | Documentation may include details on operating and storage temperature ranges, moisture sensitivity level (MSL), and compliance with RoHS directives. |
By grasping the fundamentals encapsulated within 5mm LED datasheets, designers, engineers, and enthusiasts can discern the suitability of these luminous components for diverse projects, ranging from intricate circuitry to expansive lighting installations.
Understanding Specifications of Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs)
In the realm of lighting technology, comprehending the specifications of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) is paramount for informed decision-making and optimal performance. Delving into the intricacies of LED characteristics equips enthusiasts, engineers, and consumers alike with the knowledge necessary to discern the most suitable LED for their specific applications.
- Forward Voltage (VF): This parameter signifies the voltage required to turn on an LED and initiate light emission. Understanding the forward voltage aids in selecting appropriate power sources and ensuring efficient operation.
- Forward Current (IF): Representing the current flowing through the LED when it is in operation, the forward current directly influences the luminous intensity and longevity of the diode. Optimal forward current management is essential for maintaining LED performance and longevity.
- Luminous Intensity: This metric quantifies the brightness emitted by an LED and is typically measured in candelas (cd) or millicandelas (mcd). Grasping luminous intensity specifications facilitates the selection of LEDs suitable for various lighting applications, ranging from ambient illumination to indicator lights.
- Viewing Angle: Reflecting the angular spread of emitted light, the viewing angle dictates the coverage area illuminated by the LED. Different applications necessitate specific viewing angles to achieve desired lighting effects and coverage.
- Color Temperature: Characterizing the color appearance of emitted light, color temperature is measured in Kelvin (K). It determines whether the light emitted by an LED falls within the warm, neutral, or cool spectrum, enabling users to create atmospheres tailored to their preferences.
- Operating Temperature Range: Indicating the temperature range within which an LED can reliably function, the operating temperature range is crucial for assessing the suitability of LEDs for diverse environmental conditions. Understanding this specification ensures optimal performance and longevity of LEDs in various applications.
By delving into these key specifications, individuals gain a nuanced understanding of LED technology, empowering them to make informed decisions when selecting LEDs for their projects or applications.
Key Specifications in Specifications Sheets
In the realm of illuminated semiconductors, understanding the critical parameters delineated in product documentation is paramount. These essential metrics serve as the compass for engineers and designers navigating the intricacies of light-emitting diodes. Delving into the specifications of these devices illuminates crucial aspects guiding optimal utilization and performance.
1. Optical Characteristics
At the forefront of LED evaluation lie its optical characteristics, encapsulating luminous intensity, radiant flux, and viewing angle. Luminous intensity, measured in millicandelas (mcd), quantifies the brightness perceived by an observer, while radiant flux delineates the total luminous power emitted by the LED. The viewing angle dictates the spread of emitted light, crucial for applications necessitating specific illumination patterns.
2. Electrical Properties
Beyond luminosity, understanding the electrical properties is imperative for seamless integration into circuitry. Forward voltage (Vf) denotes the voltage drop across the LED when conducting current, crucial for determining appropriate power supply compatibility. Similarly, forward current (If) specifies the current magnitude necessary for optimal illumination, safeguarding against overdriving and potential degradation.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Forward Voltage (Vf) | The voltage drop across the LED when conducting current. |
| Forward Current (If) | The current magnitude necessary for optimal illumination. |
Interpreting Documentation for 5mm Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs)
In this section, we delve into the intricacies of understanding technical specifications provided for small-scale light-emitting components commonly known as 5mm LEDs. Navigating through the wealth of information presented in these documents can be daunting, but with a structured approach, one can extract valuable insights essential for informed decision-making and optimal utilization of these electronic components.
Deciphering Performance Characteristics
When scrutinizing documentation pertaining to 5mm LEDs, it’s imperative to discern the performance metrics provided. These metrics encapsulate vital aspects such as luminous intensity, forward voltage, viewing angle, and wavelength characteristics. Each parameter contributes uniquely to the LED’s behavior and performance within various applications.
Understanding Electrical Characteristics
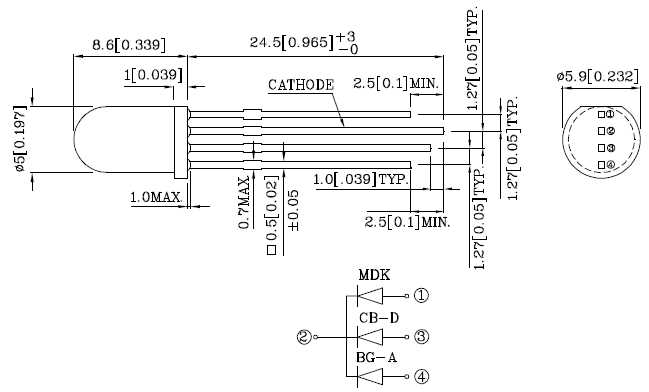
Equally significant are the electrical characteristics outlined in the datasheets. These specifications delineate the electrical properties governing the LED’s operation, encompassing parameters like forward current, reverse voltage, and power dissipation. Understanding these parameters is paramount for ensuring compatibility with driving circuits and safeguarding against potential operational issues.
By adeptly interpreting the documentation, one can glean comprehensive insights into the capabilities and limitations of 5mm LEDs, empowering effective integration into diverse electronic designs and illuminative applications.
Practical Application Insights
In this section, we delve into practical approaches and real-world insights concerning the utilization of the specified small light-emitting diodes (LEDs). Understanding how to effectively employ these components can significantly enhance the performance and efficiency of various electronic applications.
Optimizing Illumination
One key aspect to consider when integrating these miniature light sources is optimizing illumination. By strategically positioning and configuring the LEDs, engineers can achieve desired lighting effects while minimizing energy consumption. Experimenting with different arrangements and circuit designs can lead to innovative solutions for diverse lighting needs.
Enhancing Durability and Longevity
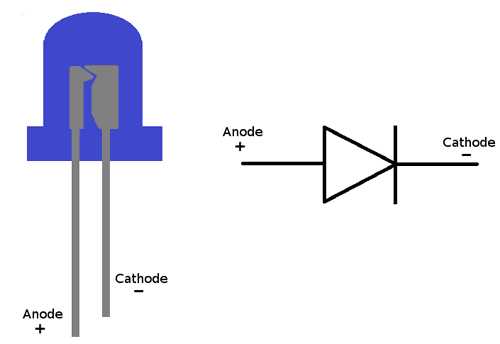
Another crucial consideration is ensuring the durability and longevity of LED-based systems. Implementing proper heat dissipation mechanisms and selecting robust materials can mitigate thermal stress and prolong the lifespan of the components. Moreover, incorporating protective measures against environmental factors such as moisture and vibration can bolster reliability in challenging operational conditions.
By applying these practical insights, developers can harness the full potential of small-scale LEDs in various applications, ranging from consumer electronics to industrial automation, fostering innovation and efficiency in the realm of electronics engineering.