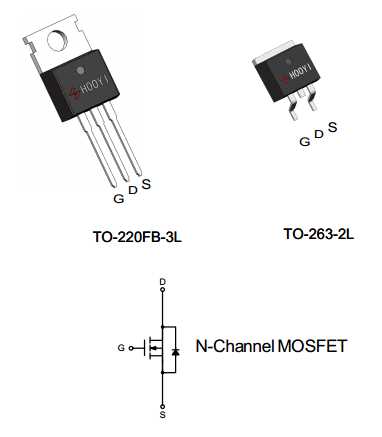
In the realm of electronic components, there exists a vital cornerstone that epitomizes innovation and efficiency, transcending mere circuits to redefine the very essence of power regulation and amplification.
Embedded within the intricate fabric of modern electronics, this enigmatic device, with its intricately woven network of conductive paths, is more than just a mere switch; it’s the orchestrator of electron flow, the guardian of voltage, and the sentinel of stability.
Steering away from the mundane, we delve into the essence of this technological marvel, exploring its myriad applications, intricacies, and performance benchmarks that shape the landscape of contemporary electronics.
Join us on a journey through the labyrinth of semiconductor mastery, where every electron tells a story, and every junction sparks a revelation.
Deciphering the 7934 MOSFET Documentation
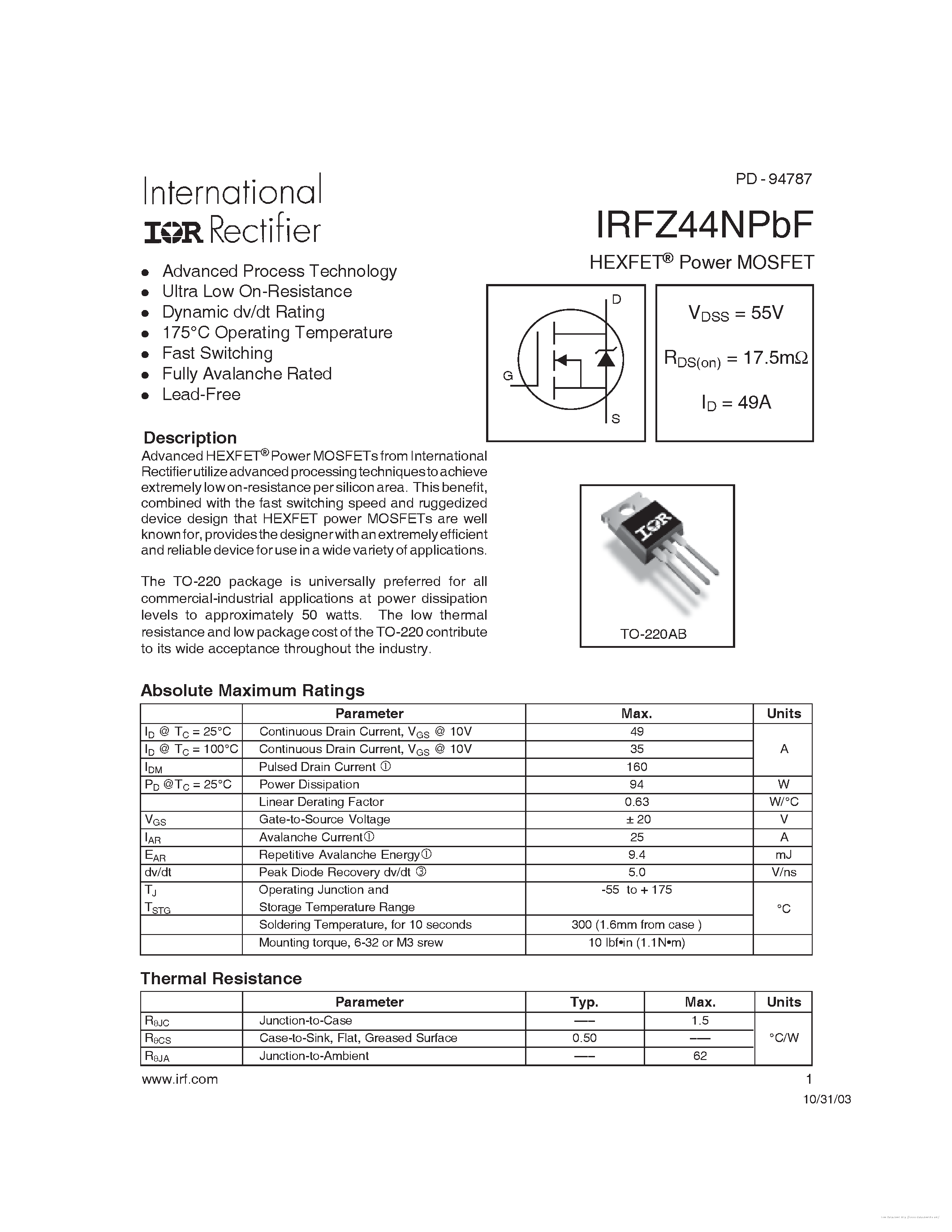
Within the intricate realm of semiconductor components lies a critical resource for engineers and enthusiasts alike: the comprehensive document outlining the specifications and characteristics of the 7934 MOSFET. This indispensable guide serves as a beacon, illuminating the operational intricacies and performance nuances of this essential electronic component.
Interpreting Functional Parameters
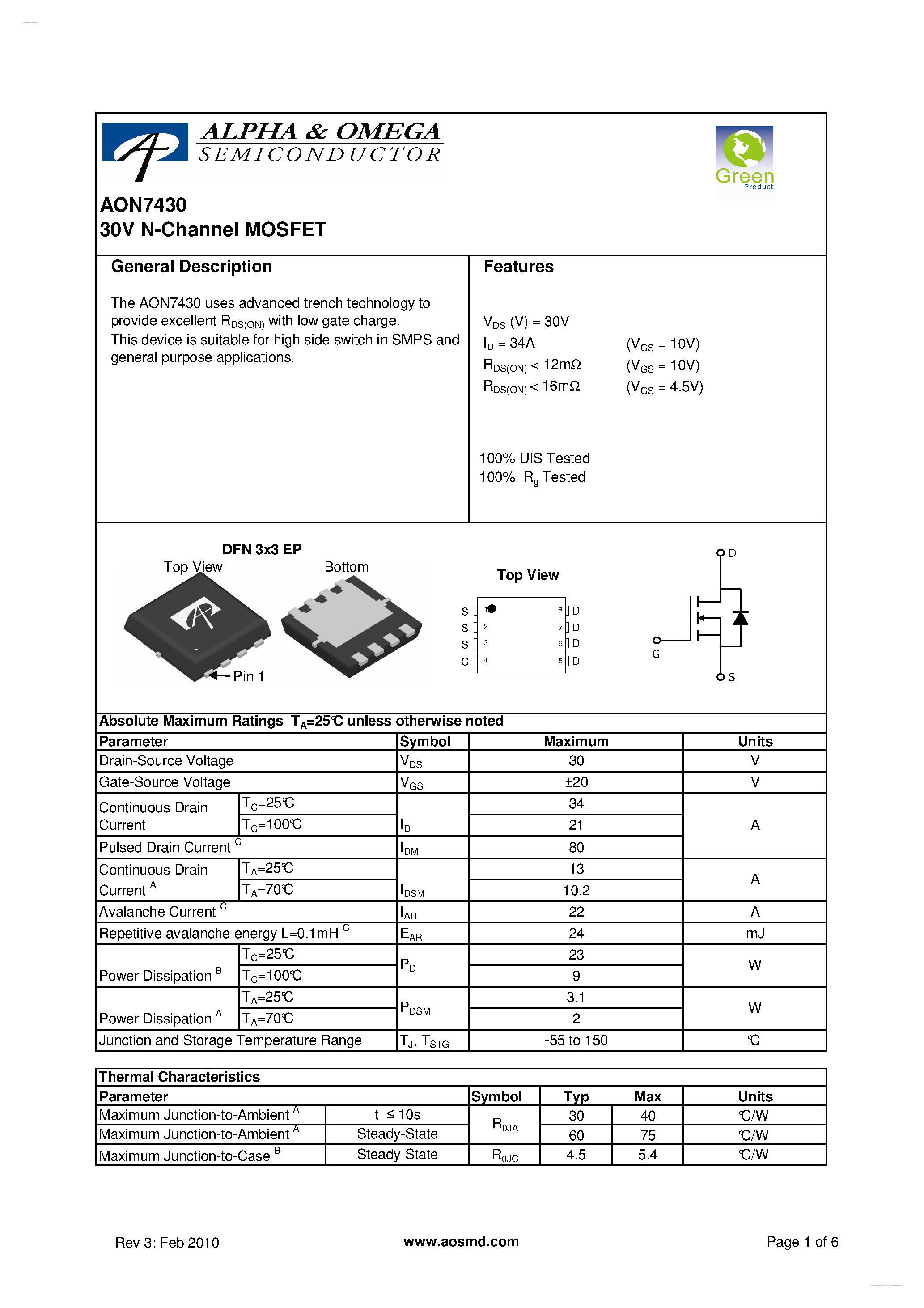
Embedded within the labyrinthine corridors of the datasheet are crucial insights into the functionality and operational capabilities of the 7934 MOSFET. By delving into the delineations of electrical parameters and performance metrics, one can unravel the intricate tapestry of its operational prowess and discern its suitability for diverse applications.
Exploring Application Considerations
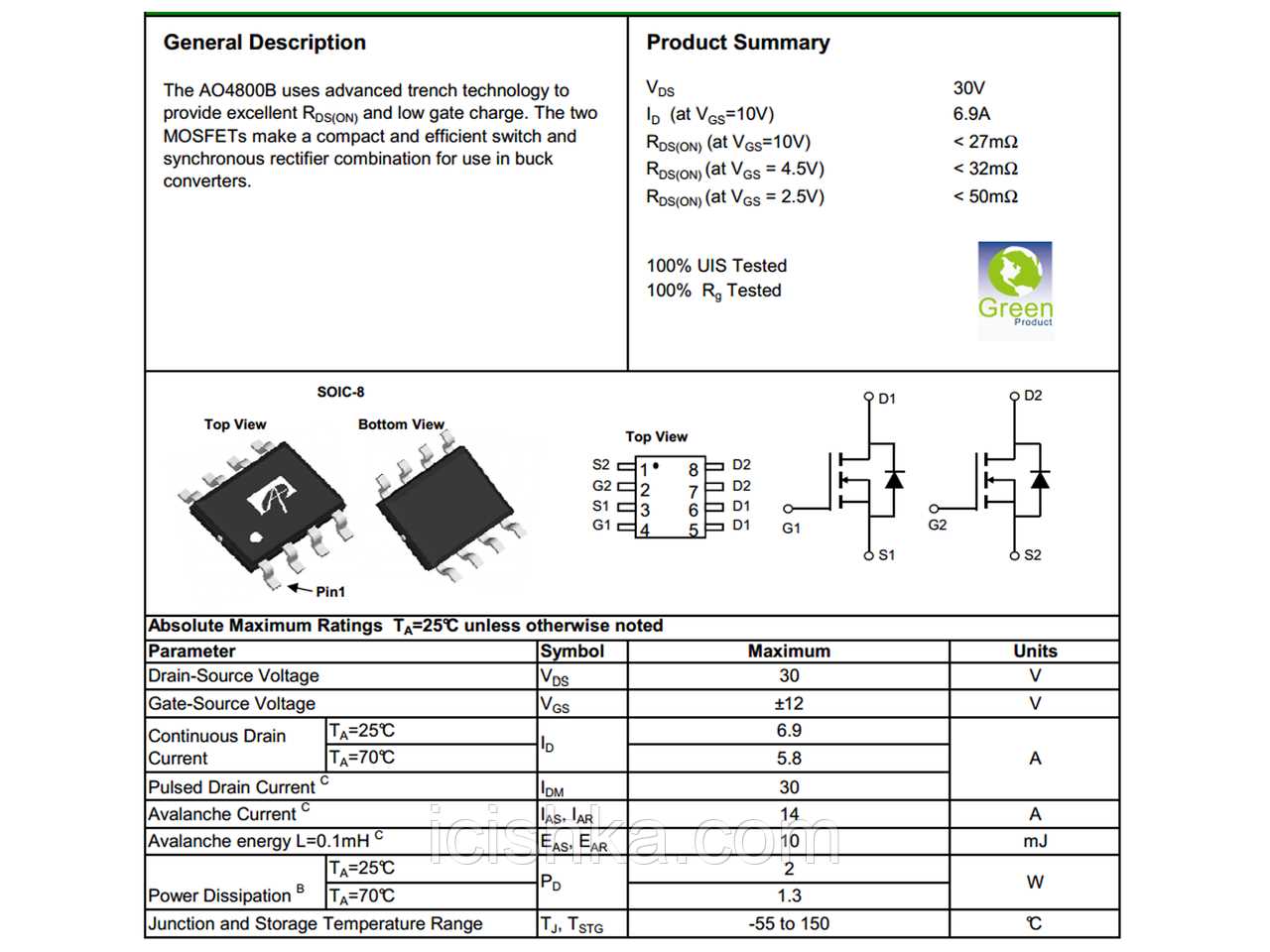
Beyond the realm of mere specifications lies a trove of information regarding the practical application of the 7934 MOSFET. This section elucidates the nuances of circuit design considerations, thermal management strategies, and compatibility assessments, offering invaluable guidance for engineers seeking to harness its potential within their projects.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Threshold Voltage | The voltage at which the MOSFET begins to conduct. |
| On-State Resistance | The resistance when the MOSFET is fully conducting. |
| Gate Charge | The amount of charge required to switch the MOSFET between on and off states. |
Key Specifications and Parameters
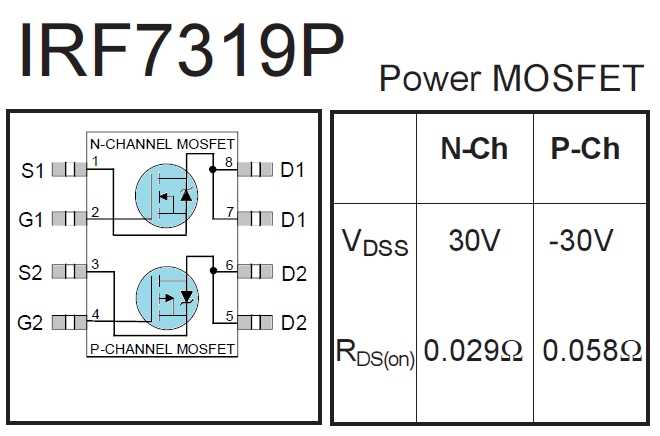
In this section, we delve into the fundamental characteristics and essential metrics that define the performance and functionality of the electronic component under scrutiny. Delving beyond nomenclature, we navigate through a spectrum of vital data points that encapsulate its operational prowess and applicative potential.
Electrical Properties:
Within the realm of electrical attributes, parameters such as voltage ratings, current capabilities, and resistance thresholds reign supreme. These metrics elucidate the component’s ability to withstand and manipulate electrical signals within a given circuit configuration.
Physical Dimensions:
Transitioning from the intangible realm of electrical specifications, we confront the tangible realm of physical dimensions. Ascertaining the spatial footprint, package type, and thermal characteristics, these dimensions delineate the component’s compatibility within diverse hardware architectures.
Performance Metrics:
Embarking on a journey through performance metrics, we unravel the intricacies of speed, efficiency, and reliability. From switching times to power dissipation, these metrics furnish a panoramic view of the component’s operational efficiency and endurance under varied load conditions.
Environmental Considerations:
Beyond the confines of intrinsic performance metrics, lies a terrain of environmental considerations. Temperature tolerances, moisture resistance, and compliance with industry standards furnish insights into the component’s adaptability to real-world operating conditions.
Application-specific Parameters:
Embracing the nuanced demands of diverse applications, we explore a repertoire of application-specific parameters. From frequency response to input/output capacitance, these parameters delineate the component’s suitability across a spectrum of specialized domains.
Conclusion:
Thus, through a meticulous examination of key specifications and parameters, we unravel the multifaceted persona of the electronic component, transcending mere nomenclature to unveil its intrinsic essence and applicative significance.
Application Considerations and Circuit Design
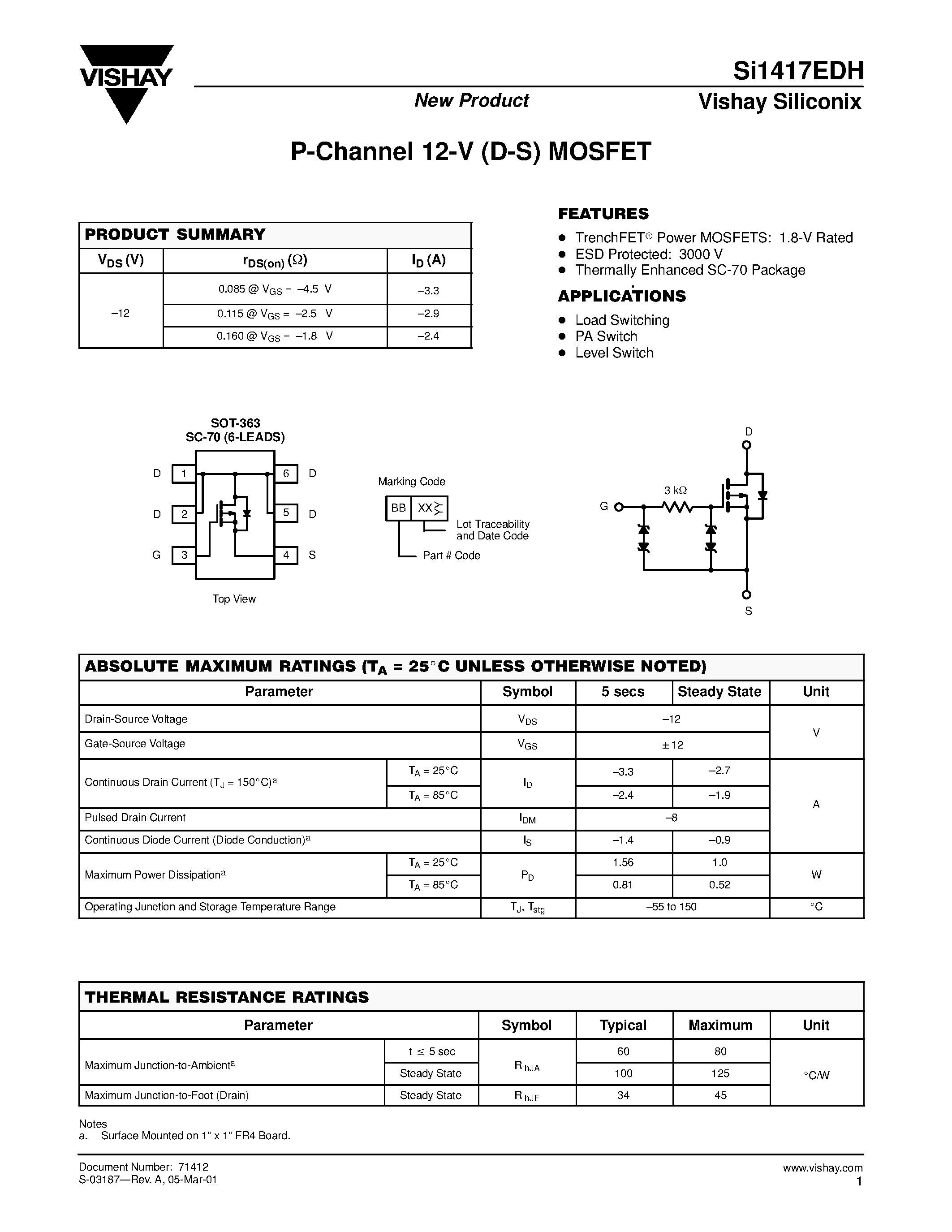
In the realm of electronic component integration and circuit optimization, thoughtful consideration of application requirements and meticulous circuit design are paramount. This section delves into the nuanced aspects of leveraging semiconductor devices effectively, exploring crucial factors beyond mere technical specifications.
Understanding Operational Environments
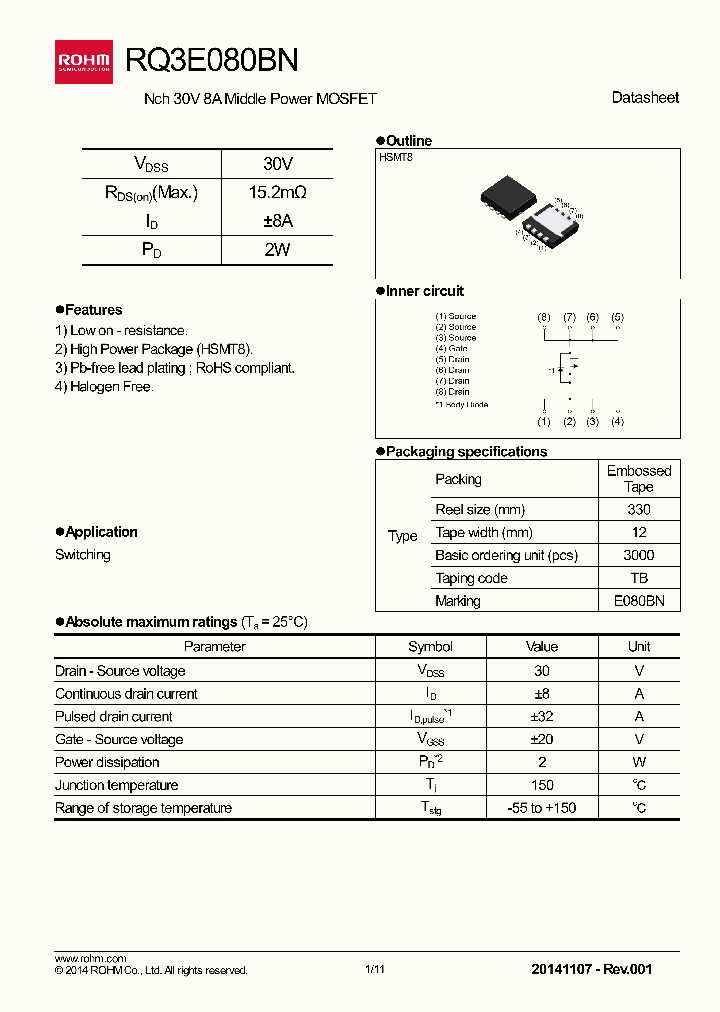
Operating conditions play a pivotal role in determining the efficacy and reliability of electronic circuits. Variations in temperature, voltage, and current demand meticulous attention, as they can significantly influence device performance and longevity. By comprehensively evaluating operational environments, engineers can tailor circuit designs to ensure robustness and stability across a spectrum of conditions.
Optimizing Performance and Efficiency
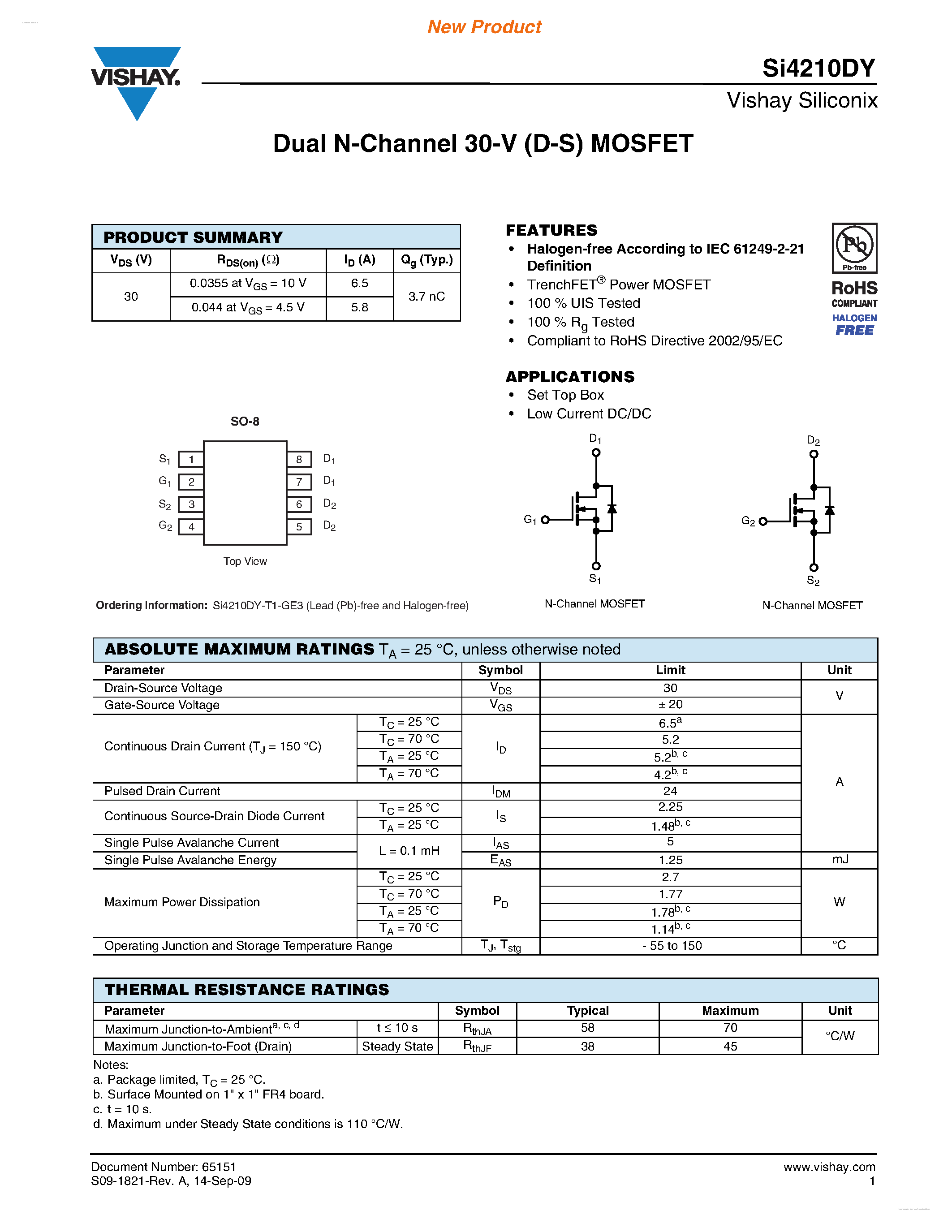
Efficient circuit design encompasses an intricate balance between performance and energy utilization. Maximizing functionality while minimizing power dissipation and heat generation is a perpetual pursuit in modern electronics. Through judicious component selection, layout optimization, and innovative design techniques, engineers endeavor to achieve optimal performance metrics without compromising on efficiency.
Thermal Management and Performance Optimization
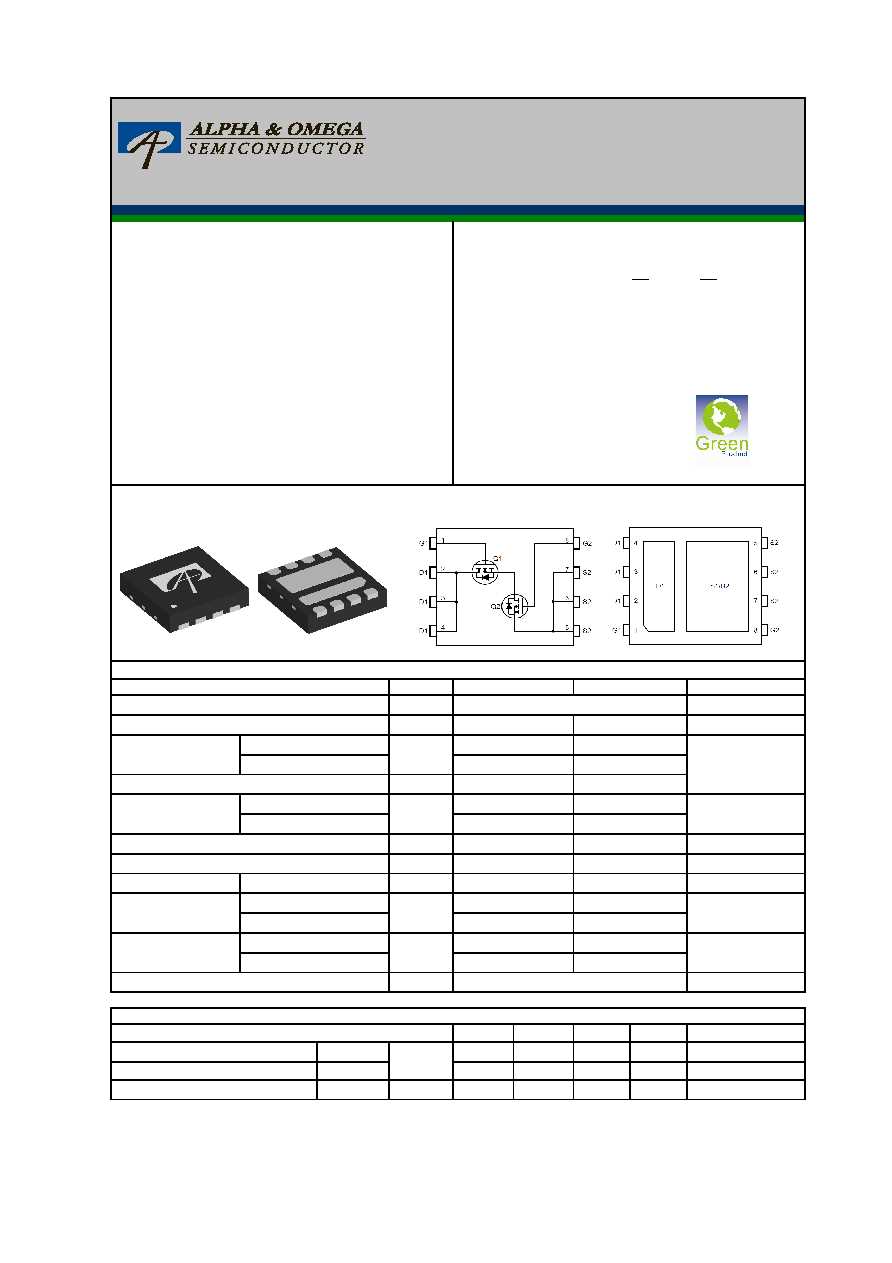
In the realm of semiconductor components, ensuring efficient thermal management is paramount for enhancing overall performance and reliability while extending the lifespan of electronic devices. This section delves into strategies aimed at regulating and optimizing temperature levels, thereby safeguarding against thermal-induced degradation and maximizing operational efficiency.
Understanding Heat Dissipation: One critical aspect of maintaining optimal performance lies in comprehending the mechanisms of heat dissipation within electronic systems. By grasping how heat is generated and distributed across components, engineers can devise targeted approaches to mitigate thermal stress and prevent detrimental effects on device functionality.
Implementing Effective Cooling Solutions: Efficient cooling solutions play a pivotal role in maintaining temperature equilibrium within electronic assemblies. Whether through active methods like fans and liquid cooling systems or passive techniques such as heat sinks and thermal pads, selecting appropriate cooling mechanisms is essential for preventing overheating and ensuring consistent performance under varying operational conditions.
Enhancing Thermal Conductivity: Optimizing the thermal conductivity of materials used in component design is instrumental in facilitating heat transfer away from sensitive areas. By incorporating materials with high thermal conductivity coefficients and employing advanced heat dissipation techniques like vapor chambers or phase-change materials, engineers can effectively manage temperature levels and bolster overall device efficiency.
Utilizing Thermal Modeling and Simulation: Employing sophisticated thermal modeling and simulation tools enables engineers to predict and analyze temperature distributions within electronic systems. By simulating thermal scenarios under different load conditions, designers can iteratively refine cooling strategies and optimize component layouts to ensure consistent performance and reliability across diverse operating environments.
Implementing Dynamic Thermal Management: Dynamic thermal management techniques, such as adaptive voltage scaling and frequency throttling, offer dynamic control over power consumption and heat generation in real-time. By dynamically adjusting operational parameters based on temperature feedback, electronic systems can effectively regulate thermal profiles and mitigate the risk of overheating without compromising performance.
Conclusion: In conclusion, effective thermal management is integral to optimizing the performance and longevity of semiconductor components in electronic systems. By adopting a multi-faceted approach encompassing heat dissipation, cooling solutions, material selection, simulation, and dynamic control strategies, engineers can ensure reliable operation and maximize the efficiency of electronic devices across a wide range of applications.