
When delving into the world of electrical components, it is crucial to have a solid understanding of technical documentation to ensure seamless integration and efficient operation. One such crucial component widely used in various electronic systems is the SPDT relay. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to deciphering the intricate details of SPDT relay datasheets, enabling engineers and enthusiasts to harness the full potential of this versatile device.
Within the realm of electrical engineering, the SPDT relay serves as a vital intermediary between control systems and load circuits. By utilizing an electromagnetically activated switch, this component allows the transfer of electrical signals from one circuit to another, effectively altering the system’s behavior. The relay is designed to provide reliable and efficient switching capabilities, making it an indispensable asset for a multitude of applications, ranging from automotive electronics to industrial automation.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the fundamental sections typically found in SPDT relay datasheets and decipher the essential information contained within. From pin diagrams to electrical characteristics, coil specifications to contact ratings, every aspect will be dissected to provide a clear understanding of the relay’s capabilities and limitations. By empowering you with this knowledge, we aim to pave the way for confident decision-making and successful implementation of SPDT relays in your projects.
The Basics of SPDT Relay: A Comprehensive Guide
In the world of electronic devices and circuitry, there exists a versatile component that plays a crucial role in controlling the flow of electrical currents. This component, known as a single-pole double-throw (SPDT) relay, is widely used in various applications to switch between two different circuits, making it an essential part of many electrical systems.
Understanding the Principles
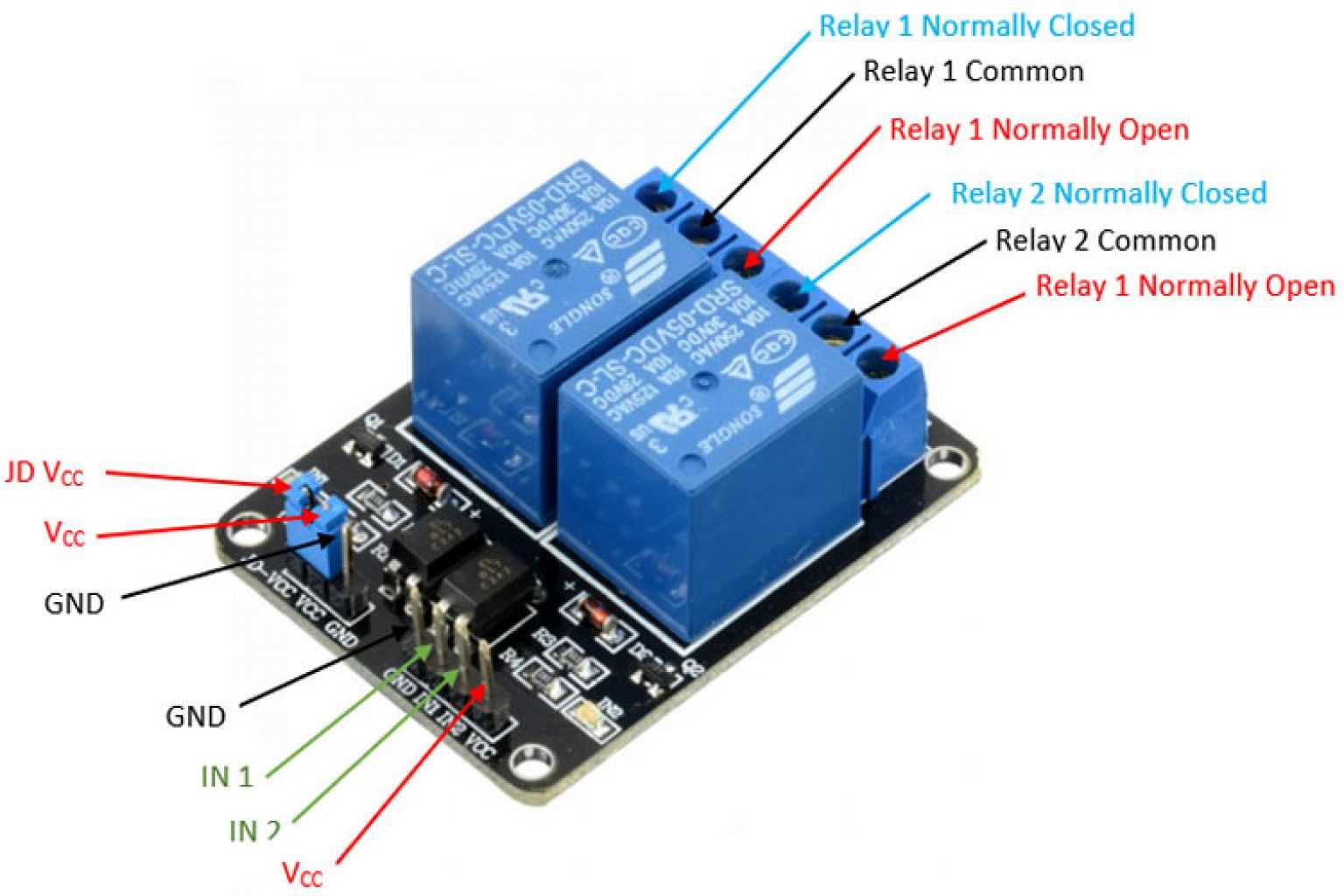
At its core, an SPDT relay consists of a coil, a set of common terminals, and a set of Normally Open (NO) and Normally Closed (NC) terminals. By applying an electrical current to the coil, a magnetic field is generated, causing the relay contacts to switch positions. This enables the connection of one circuit to either the NO or NC terminals, depending on the relay’s state.
The SPDT relay provides immense flexibility in controlling electrical currents, whether it be for switching between power sources, reversing motor polarity, or activating diverse mechanical devices. Its ability to handle both AC and DC voltages allows for compatibility with a wide range of applications, making it a popular choice in the field of electronics.
Applications and Usage
Due to its versatility, the SPDT relay finds extensive application in a variety of industries. In the automotive sector, it is utilized for powering headlamps, auxiliary lights, and turning on fans. Within the field of home automation, SPDT relays enable the control of lighting systems, HVAC units, and security systems.
Furthermore, the SPDT relay is widely employed in industrial automation for functions such as motor control, power distribution, and safety shutdowns. In telecommunications, it aids in signal routing, whereas in the field of renewable energy, it facilitates the switching between solar panels and storage systems.
Overall, the SPDT relay serves as a vital component in numerous applications, providing a reliable means of controlling electrical circuits and ensuring seamless functionality in complex systems.
Understanding the SPDT Relay Operation

In this section, we will explore the underlying principles behind the operation of single-pole, double-throw (SPDT) relays. By delving into the inner workings of these vital electronic components, we can gain a deeper understanding of how they facilitate the control and switching of electrical circuits without relying on overly technical jargon or complex data sheets.
The Principle of Switching

At its core, the SPDT relay operates on the principle of switching between two different positions in order to control the flow of electrical current. Similar to a crossroads where traffic can be directed in two different directions, the relay acts as an intelligent switch, allowing the circuit to be connected to one of two possible paths. This ability to redirect the path of electrical current provides a key advantage in various applications, enabling the relay to effectively control the operation of devices or systems.
The Functionality of Pole and Throw
Within the SPDT relay, there are two main components that work in concert to achieve the desired electrical switching: the pole and the throw. The pole refers to the common terminal that connects to either the normally closed (NC) or normally open (NO) terminal. Conversely, the throw corresponds to the alternate terminal to which the pole can be connected. By understanding the specific configurations for each of these terminals, we can decipher how the relay operates and functions in different scenarios.
NC Terminal: The normally closed terminal is the default position of the relay, where the pole is connected to the throw even when there is no external control input. This ensures that the circuit remains in its deactivated state, allowing current to flow through the normally closed contacts. The NC terminal is often associated with safety applications, where it provides fail-safe operation or emergency shutdown capabilities.
NO Terminal: On the other hand, the normally open terminal represents the alternative position of the relay, where the pole is disconnected from the throw until an external control signal is applied. This allows current to flow through the normally open contacts when the relay is activated, effectively completing the circuit in a controlled manner. The NO terminal is commonly utilized for enabling the operation of devices or activating specific functions within a system.
Understanding the SPDT relay operation empowers us to design and implement efficient and reliable control systems in various fields, ranging from automotive electronics to industrial automation. By grasping the fundamental principles of switching and the functionalities of pole and throw, we can make informed decisions in selecting and utilizing SPDT relays for diverse applications.
Exploring the SPDT Relay Datasheet: Key Specifications and Features

Delving into the technical details of a datasheet is crucial when it comes to understanding the capabilities and functionalities of a device. In this section, we will uncover the essential specifications and features of the Single Pole Double Throw (SPDT) relay. This versatile component plays a vital role in various electronic applications by providing switching functionality between two different circuits. By examining its key characteristics, engineers and enthusiasts can determine its suitability for specific projects.
A comprehensive examination of the SPDT relay datasheet requires an understanding of its electrical parameters. These parameters encompass factors such as contact ratings, coil voltage, and switching current. Contact ratings indicate the maximum permissible values for voltage and current that can be applied to the relay’s contacts. By evaluating these ratings, users can ensure the relay can handle the intended load without exceeding its capabilities. Coil voltage, on the other hand, determines the voltage required to energize the relay, enabling the switching operation. Additionally, switching current defines the maximum current that the relay can handle during its operation, highlighting its capacity to handle different electrical loads.
Aside from electrical parameters, the datasheet also provides insights into the mechanical characteristics of the SPDT relay. Mechanical endurance specifies the number of operations the relay can reliably perform before its performance begins to degrade. This parameter helps users estimate the relay’s lifespan and durability in real-world applications. Moreover, the datasheet may include details about the relay’s dimensions, pin layouts, and mounting options, aiding in integration and compatibility assessments.
Furthermore, understanding the operational principles of the SPDT relay is essential for efficient utilization. The datasheet offers information regarding the relay’s coil power consumption, activation time, and release time. Coil power consumption indicates the energy required to keep the coil energized during its operation, which becomes crucial in low-power applications. Activation time denotes the time required for the contacts to transition from one position to another upon energization, while release time represents the time taken for the contacts to return to their original state after de-energization. By analyzing these timings, users can select the appropriate relay for applications with specific timing requirements.
| Key Specifications | Features |
|---|---|
| Electrical Parameters | Mechanical Endurance |
| Coil Voltage | Dimensions |
| Switching Current | Pin Layouts |
| Contact Ratings | Mounting Options |
| Operational Principles | Coil Power Consumption |
| Activation Time | Release Time |
By thoroughly exploring the SPDT relay datasheet, designers and engineers gain valuable insights into its technical specifications and features. With a clear understanding of these details, they can confidently select the appropriate relay for their applications, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Application Examples and Benefits of using SPDT Relay

In this section, we will explore various examples of how SPDT relays can be used in different applications to provide several benefits. SPDT relays, also known as Single Pole Double Throw relays, are versatile electronic components that offer advantages such as flexibility, reliability, and compatibility with different types of devices.
1. Home automation and control systems

SPDT relays are commonly used in home automation and control systems to enable the switching of electrical devices. They can be employed in applications such as controlling lighting systems, HVAC systems, blinds, and motorized curtains. By using SPDT relays, homeowners can easily automate their homes and enhance convenience, energy efficiency, and security.
2. Industrial machinery and equipment
SPDT relays find extensive use in industrial machinery and equipment for their ability to switch high voltages and currents. They are often employed in motor control circuits, power distribution systems, and manufacturing processes. The benefits of using SPDT relays in industrial settings include improved control, reduced electrical noise, and enhanced safety.
Furthermore, SPDT relays can be utilized in automotive applications, telecommunications systems, power supplies, and many other fields where the switching of electrical signals and power is required. Their compact size, low power consumption, and long service life make them suitable for a wide range of devices and applications.
Overall, the application examples and benefits of using SPDT relays demonstrate their importance and effectiveness in various industries. These relays provide reliable and efficient switching solutions, allowing for the automation and control of electrical devices, improving system performance, and ensuring the safety and convenience of users.