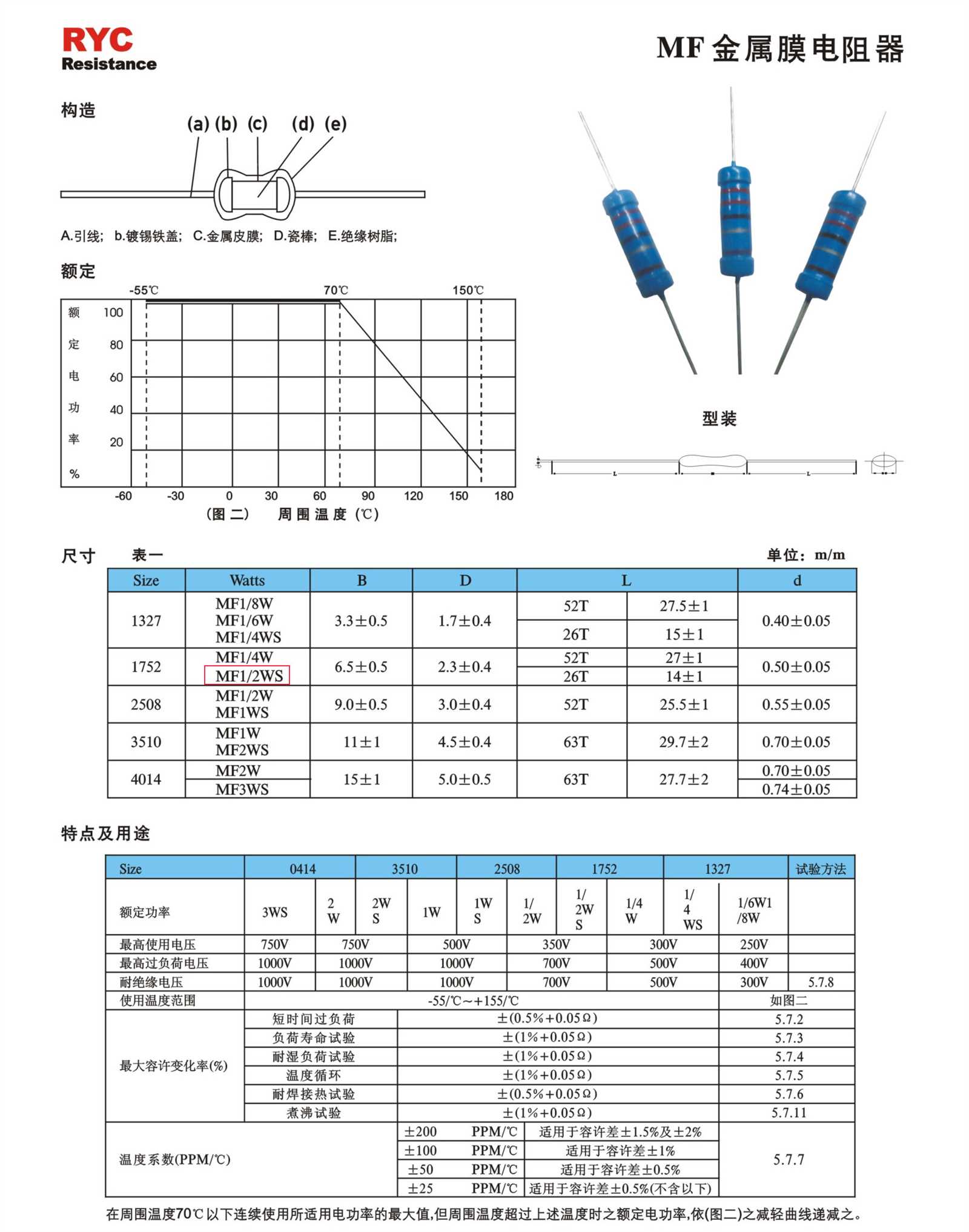
In the ever-evolving landscape of electronics, the successful integration of various components is crucial for the attainment of optimum performance. Among these essential elements, an individual component holds significant importance in establishing the desired functionality, reliability, and efficiency. This article aims to delve into the intricate realm of a specific electronic device, providing a comprehensive understanding of its characteristics and parameters.
When exploring the vast assortment of electronic components, it becomes evident that certain specifications play a pivotal role in determining their overall performance. With an array of possibilities to choose from, understanding the nuances of each component empowers engineers and technicians to make informed decisions during the design and implementation phases.
In this segment, we focus on a specific type of component without explicitly naming it. By examining the technical details of this indispensable element, we aim to provide invaluable insights into its features, capabilities, and potential applications. Through the utilization of synonymous phrases and terms, we will navigate through the intricacies without explicitly referring to it, ensuring a deeper understanding of its functionality and relevance in modern electronics.
Understanding the Basics of Rcr Resistors

In this section, we will explore the fundamental principles of Rcr resistors and gain a comprehensive understanding of their functionality and importance in electronic circuits.
Starting with the concept of electrical impedance, we will delve into the role of Rcr resistors in controlling current flow and regulating voltage levels within a circuit. We will explore how Rcr resistors resist the flow of electric current, dissipating energy in the form of heat, and how this resistance can be measured and quantified.
Next, we will examine the various types of Rcr resistors available in the market, including fixed resistors, variable resistors, and special-purpose resistors. We will highlight the advantages and applications of each type, emphasizing their versatility in different electronic devices and systems.
- We will explore the factors that determine the resistance value of an Rcr resistor, such as the resistivity of the material used, its length, cross-sectional area, and temperature coefficient.
- We will also discuss the different ways of representing and labeling Rcr resistors, including color coding, numerical codes, and datasheet specifications.
- Furthermore, we will touch upon the importance of selecting the appropriate power rating for an Rcr resistor to prevent overheating and ensure its longevity.
Lastly, we will explore common applications of Rcr resistors in various electronic circuits, such as voltage dividers, current limiting circuits, and signal conditioning circuits. We will provide practical examples and explanations to illustrate the role and significance of Rcr resistors in these applications.
By the end of this section, readers will have a solid grasp of the fundamentals of Rcr resistors, enabling them to confidently select, specify, and utilize these essential components in their electronic projects and designs.
Key Parameters and Specifications in RCR Resistor Datasheets
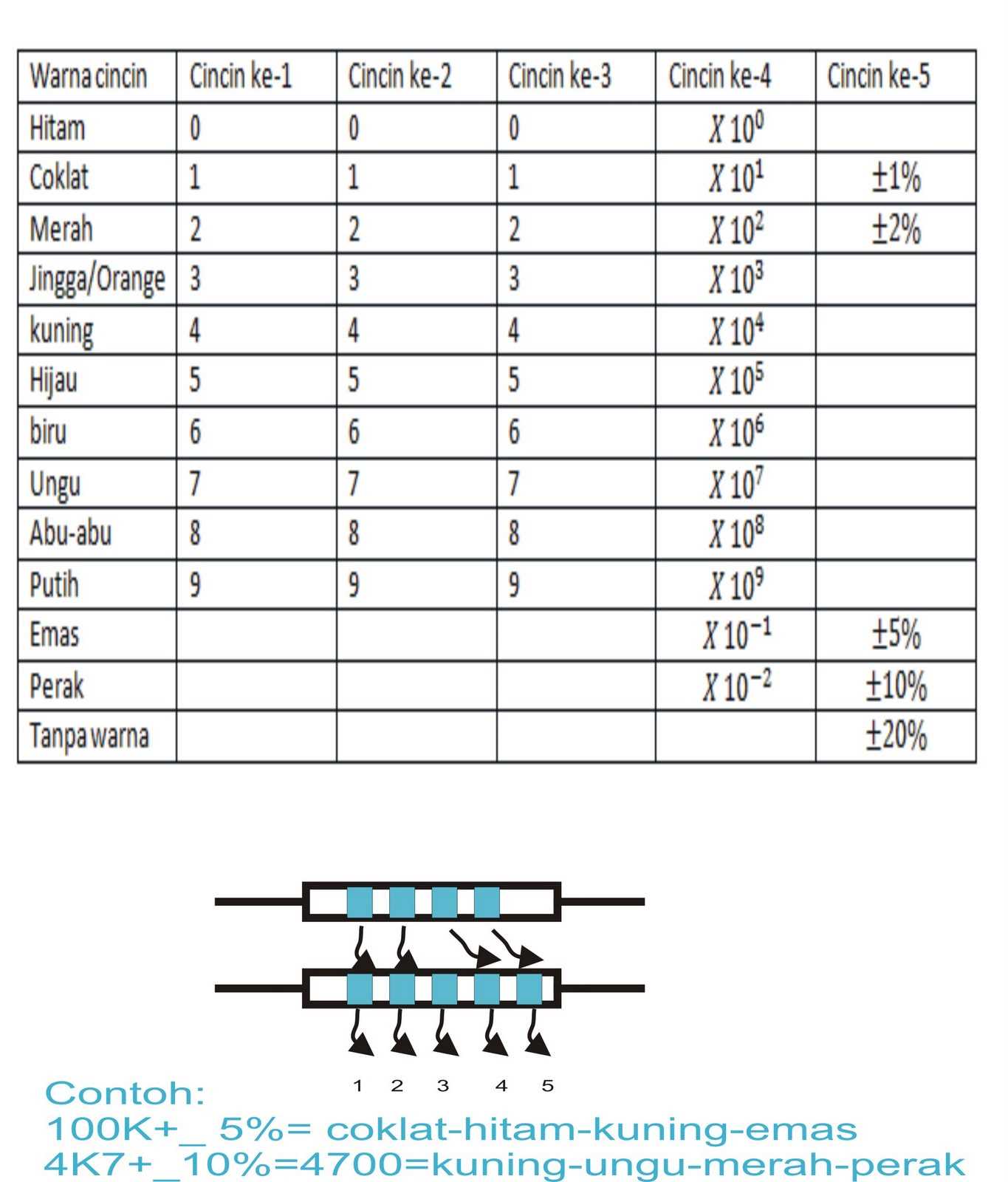
When analyzing RCR resistor datasheets, it is crucial to understand the key parameters and specifications that are provided. These details offer valuable insights into the performance and characteristics of the resistor, allowing engineers and designers to make informed decisions regarding its implementation in various electronic systems.
Resistance Value

One of the primary parameters specified in RCR resistor datasheets is the resistance value. This value indicates the extent to which the resistor opposes the flow of electric current. It is measured in ohms (Ω) and provides the foundation for determining the resistor’s functionality within a circuit.
Tolerance
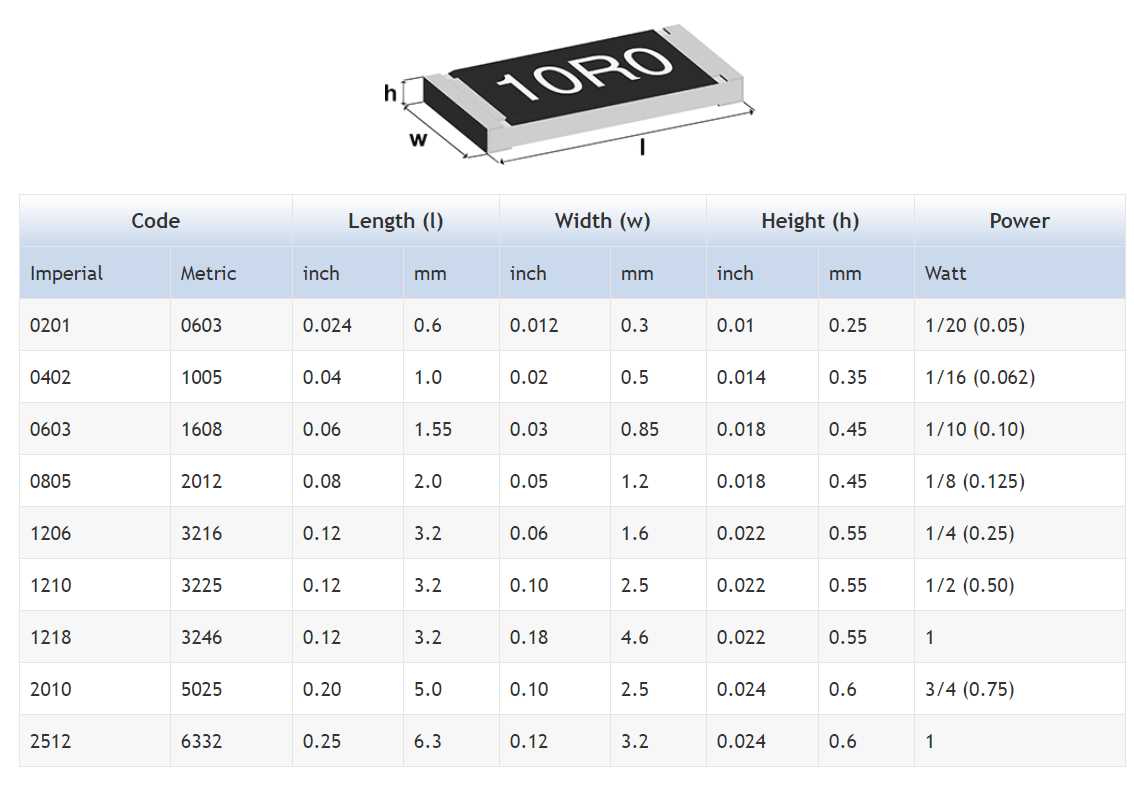
Tolerance refers to the permissible deviation from the specified resistance value. It is essential to consider this parameter to ensure accurate and reliable circuit performance. A lower tolerance indicates a resistor with greater precision in maintaining its specified resistance value, while a higher tolerance allows for a wider range of variability.
Temperature Coefficient of Resistance
An important characteristic to consider is the temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR). This value represents the rate at which the resistance of the resistor changes with temperature fluctuations. It is typically specified in parts per million per degree Celsius (ppm/°C) and determines the extent of resistance variation as the temperature changes.
Power Rating
The power rating of a resistor showcases its ability to dissipate heat without undergoing damage or failure. It indicates the maximum amount of power that a resistor can handle while maintaining its specified resistance value. Higher power ratings are essential for applications where the resistor may encounter higher current levels.
In conclusion, understanding the key parameters and specifications in RCR resistor datasheets is crucial for selecting the appropriate resistor for a given application. Components such as the resistance value, tolerance, temperature coefficient of resistance, and power rating provide essential information to ensure optimal performance and reliability within an electronic system.
Interpreting Rcr Resistor Datasheets for Proper Selection and Application
Understanding the information provided in datasheets is crucial for accurately selecting and effectively applying Rcr resistors. These documents contain valuable specifications and performance data that allow engineers and technicians to make informed decisions about which resistors are most suitable for their desired applications.
Deciphering Electrical Characteristics
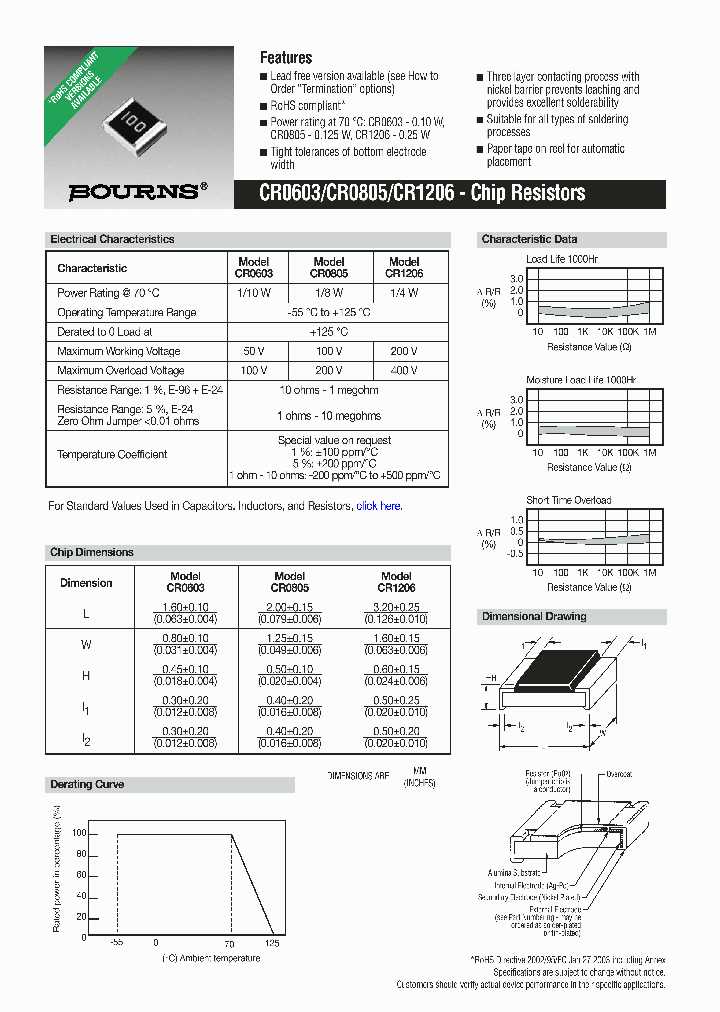
When examining Rcr resistor datasheets, it is important to pay attention to various electrical characteristics. Key parameters such as resistance value, tolerance, and power rating provide crucial information about a resistor’s performance and limitations.
Resistance value indicates the amount of opposition a resistor presents to the flow of electric current. Tolerance represents the range within which the actual resistance value may deviate from the stated nominal value. Power rating indicates the maximum amount of power a resistor can safely handle without overheating or getting damaged. Understanding these parameters helps in selecting resistors that can handle the voltage and current requirements of a specific circuit.
Identifying Physical Specifications
Physical dimensions and construction materials are also critical factors to consider. Rcr resistor datasheets often include information about size, shape, and mounting options. Additionally, material composition can affect the resistor’s reliability and performance under various environmental conditions.
Examining physical specifications is particularly important when working with space-constrained designs or when specific mounting techniques are required. A thorough understanding of these details ensures proper integration of the resistors into the overall circuit layout and minimizes the risk of mechanical or thermal issues.
Summary:
Effectively interpreting Rcr resistor datasheets involves analyzing electrical characteristics and physical specifications. By understanding the resistance value, tolerance, and power rating, engineers can select resistors that will behave as intended in their circuits. Additionally, paying attention to physical dimensions and materials ensures proper integration and reliable performance. It is essential to review and comprehend all the information provided in datasheets to make informed decisions and ultimately achieve optimal results in resistor selection and application.