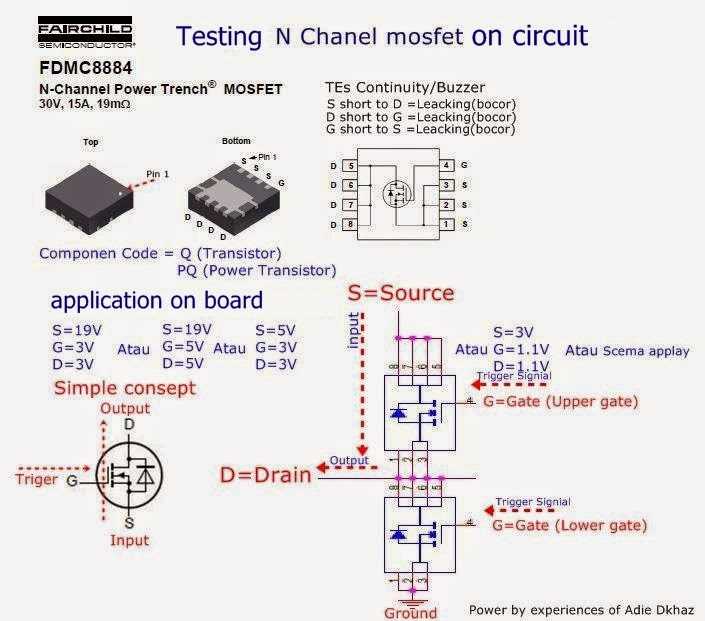
In the realm of electronic components, a treasure trove of technical insights awaits those who delve into the detailed documentation accompanying each device. This narrative unveils the intricate landscape of semiconductor exploration, where every nuanced detail holds significance in the intricate dance of electrical engineering.
Embark on a journey beyond the conventional understanding, where mere components transcend into the catalysts of innovation and precision. Within these pages lie not just specifications, but blueprints for creativity and mastery, inviting engineers to unlock the latent potential residing within every circuit and design.
Within these pages lie not just specifications, but blueprints for creativity and mastery, inviting engineers to unlock the latent potential residing within every circuit and design. By navigating through the labyrinth of technical jargon and graphical representations, one can decipher the secrets encoded within, transforming abstract concepts into tangible solutions.
Understanding Key Parameters in Power MOSFET Documentation
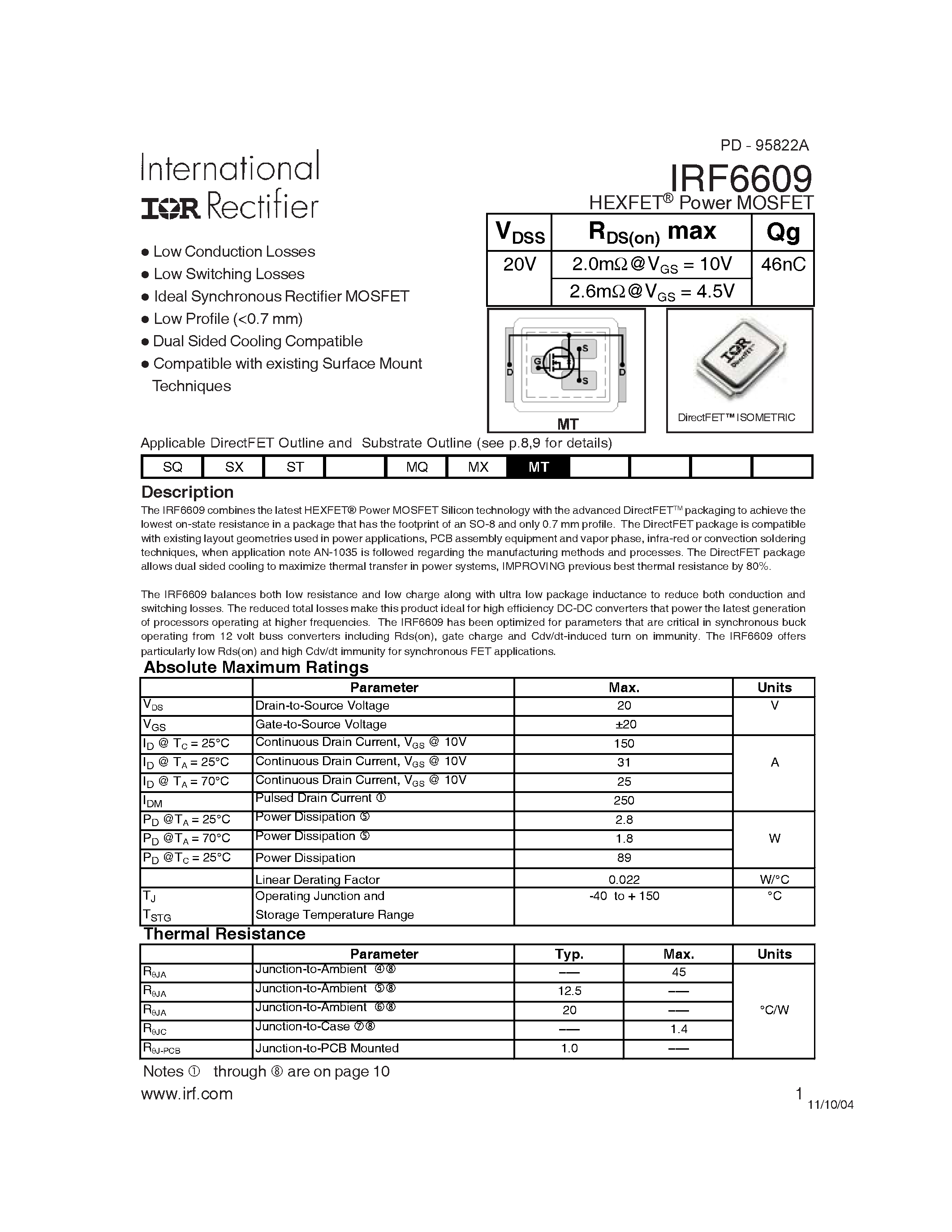
In the realm of electronic components, delving into the specifications of power MOSFETs is essential for engineers and enthusiasts alike. By comprehending the intricacies of these documents, one can unlock crucial insights into the performance and behavior of these semiconductor devices.
Let’s embark on a journey through the labyrinth of technical information provided in power MOSFET documentation. Within these datasheets lie a wealth of data encapsulating the capabilities and limitations of these devices. By deciphering the language of specifications, one can unveil the nuances that define their operation and potential applications.
- Threshold Voltage: This parameter serves as a pivotal indicator of a MOSFET’s operational characteristics, delineating the voltage at which the device begins to conduct current.
- Maximum Drain Current: Often denoted as ID(max), this specification delineates the upper limit of current that a MOSFET can effectively handle without succumbing to detrimental effects such as overheating or breakdown.
- On-Resistance: Represented by RDS(on), this parameter quantifies the resistance encountered when current flows through the MOSFET in its fully conducting state. Lower values denote higher efficiency and reduced power dissipation.
- Gate Charge: The gate charge specification, denoted as Qg, elucidates the amount of charge required to switch the MOSFET between its on and off states. Understanding this parameter is crucial for optimizing switching speeds and minimizing energy losses.
- Thermal Resistance: Thermal considerations play a vital role in the reliable operation of power MOSFETs. Thermal resistance parameters, such as junction-to-case (RθJC) and junction-to-ambient (RθJA), quantify the device’s ability to dissipate heat and maintain operational integrity under varying conditions.
These are just a few of the key parameters elucidated within power MOSFET datasheets. Each specification contributes to the holistic understanding of the device’s performance characteristics and aids in the selection of the most suitable component for a given application.
Deciphering the Specifications: Voltage, Current, and Power Ratings
In the realm of semiconductor components, comprehending the intricacies of technical specifications is paramount for optimal performance and safe operation. This section delves into unraveling the enigmatic details encapsulated within the specifications, shedding light on voltage tolerances, current handling capabilities, and power limitations of these electronic devices.
Understanding Voltage Ratings
Voltage, often described as electrical potential difference, serves as a fundamental parameter delineating the operational boundaries of semiconductor devices. Delving into the voltage specifications entails deciphering the permissible voltage levels across various terminals, encapsulating the device’s resilience against potential fluctuations and overvoltages. By comprehending these ratings, engineers can ensure the device operates within safe voltage thresholds, mitigating risks of electrical breakdown or performance degradation.
Decoding Current Ratings
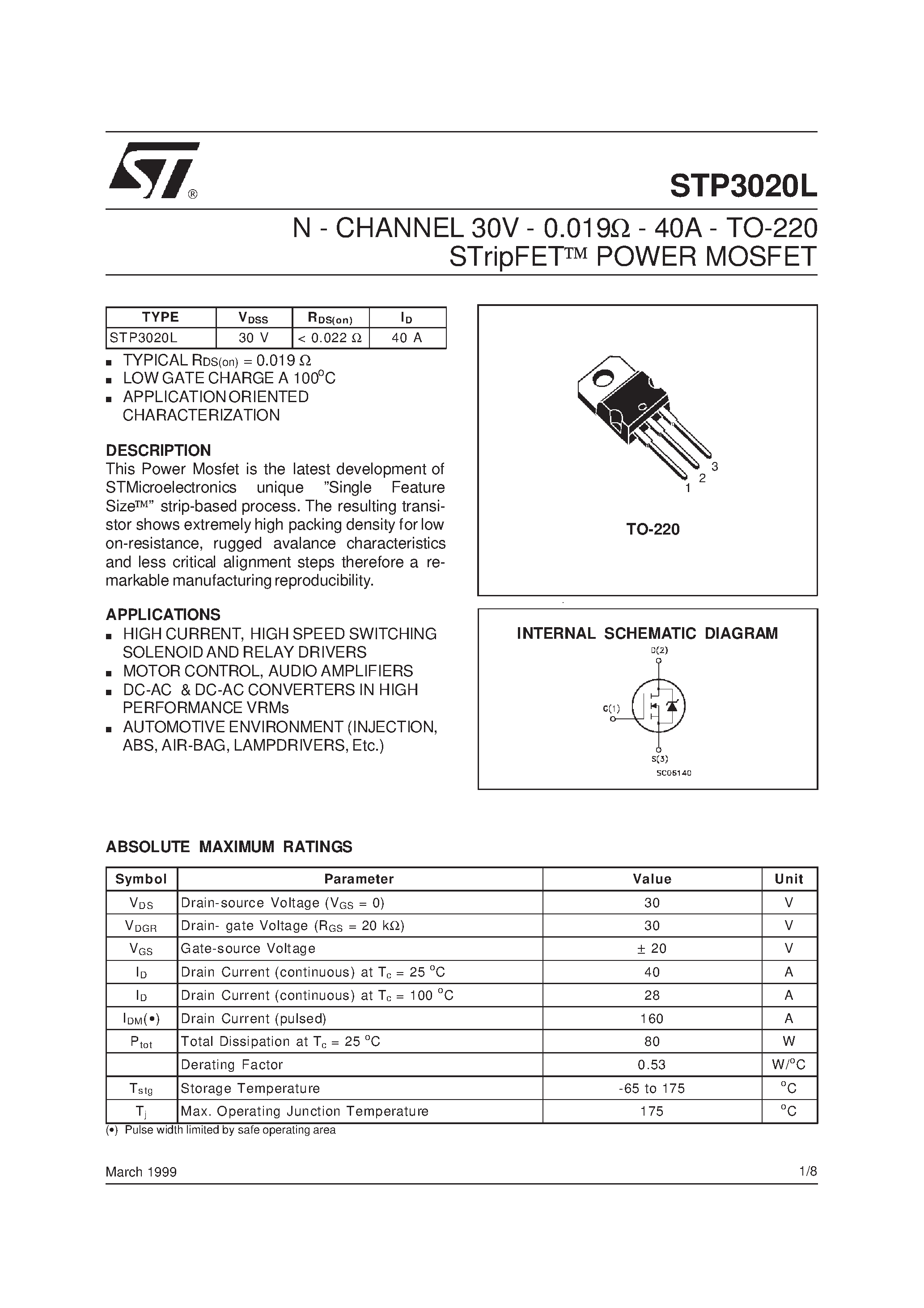
Current ratings stand as pivotal metrics defining the maximum current flow a semiconductor device can withstand or handle under specified conditions. Exploring these specifications involves unraveling the device’s capacity to channel electrical currents without succumbing to overheating or structural damage. Understanding current ratings enables engineers to design circuits that operate within the prescribed current limits, ensuring stability, efficiency, and longevity of the semiconductor components.
Unlocking Performance: Interpreting Thermal Characteristics of High-Power Semiconductor Devices
In the realm of cutting-edge electronics, understanding the thermal behavior of high-capacity semiconductor components is paramount for optimizing performance and ensuring reliability. This section delves into the intricate nuances of interpreting thermal characteristics of advanced semiconductor devices, shedding light on key parameters that dictate their operational efficiency and longevity.
Thermal Resistance: Unveiling the Heat Dissipation Capability
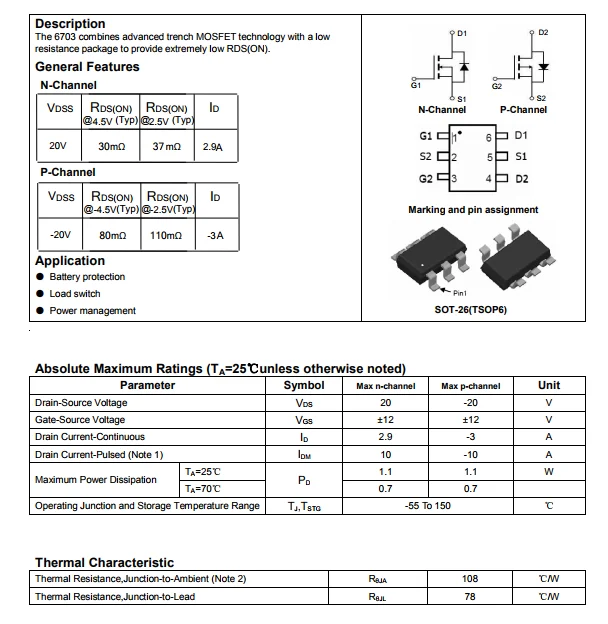
At the heart of every high-power semiconductor device lies its thermal resistance, a pivotal metric that elucidates the component’s ability to dissipate heat efficiently. By comprehending the intricacies of thermal resistance, engineers can fine-tune designs to enhance thermal management strategies, thereby maximizing device performance while mitigating the risks of overheating-induced malfunctions.
Temperature Ratings: Navigating Safe Operating Zones

Temperature ratings serve as guiding beacons for engineers, delineating the operational boundaries within which semiconductor devices can function reliably. By deciphering these ratings with precision, designers can chart pathways to optimize performance without breaching thermal thresholds, safeguarding devices against premature degradation and ensuring sustained functionality under demanding operating conditions.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | The measure of a device’s ability to dissipate heat efficiently, crucial for preventing overheating and maintaining optimal performance. |
| Temperature Ratings | Guiding thresholds that delineate safe operating zones, pivotal for ensuring device reliability and longevity under varied environmental conditions. |
Thermal Efficiency, Semiconductor Temperature, and Performance Adjustments
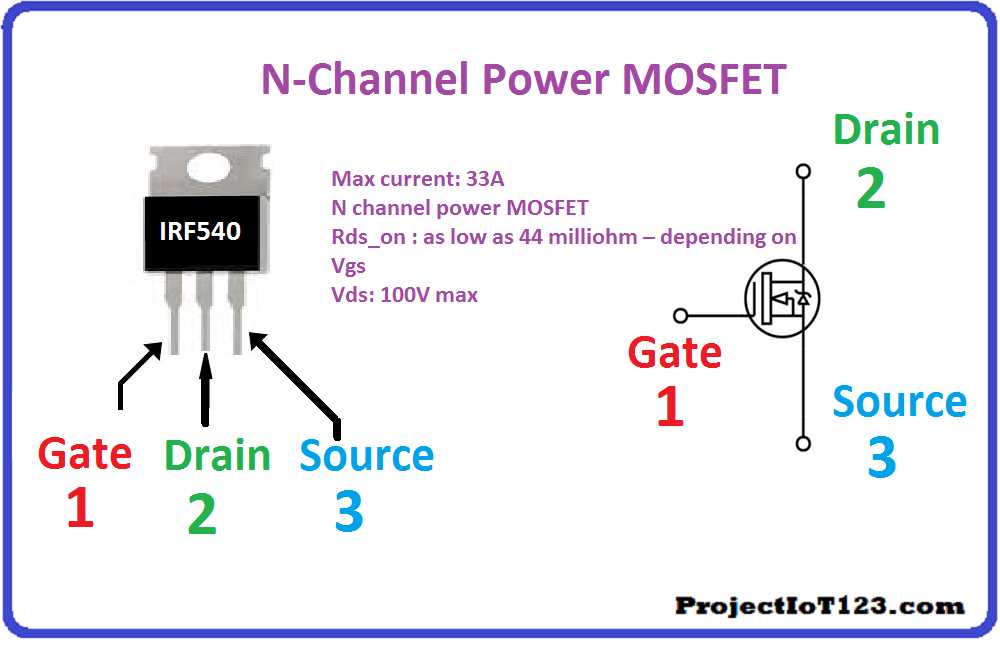
In the realm of semiconductor components, understanding the intricacies of thermal management is paramount. This section delves into crucial considerations surrounding thermal resistance, junction temperature, and derating. By comprehending these factors, engineers can optimize the operational performance and longevity of the component under varying environmental conditions.
Understanding Thermal Resistance
Thermal resistance serves as a pivotal metric in assessing the ability of a semiconductor device to dissipate heat efficiently. It delineates the device’s capability to conduct heat away from the junction to the ambient environment. A thorough grasp of thermal resistance aids in the selection of appropriate cooling mechanisms and ensures optimal device performance.
Junction Temperature and Derating
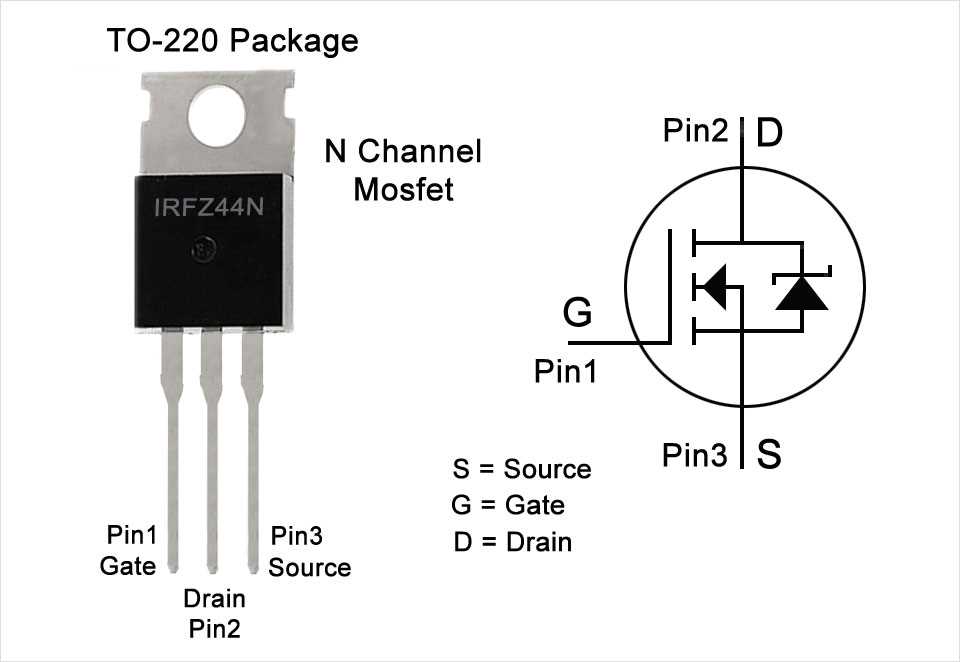
Junction temperature, the temperature at the heart of the semiconductor device, profoundly influences its reliability and operational characteristics. Derating, the process of adjusting operational parameters in response to temperature fluctuations, becomes imperative to maintain the device within its safe operating limits. By meticulously considering derating guidelines, engineers can mitigate the risk of device failure and enhance its overall reliability.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | Indicates the device’s ability to dissipate heat efficiently. |
| Junction Temperature | Defines the operating temperature at the semiconductor junction. |
| Derating | Process of adjusting operational parameters in response to temperature variations. |
Optimizing Design: Leveraging MOSFET Gate Drive Specifications
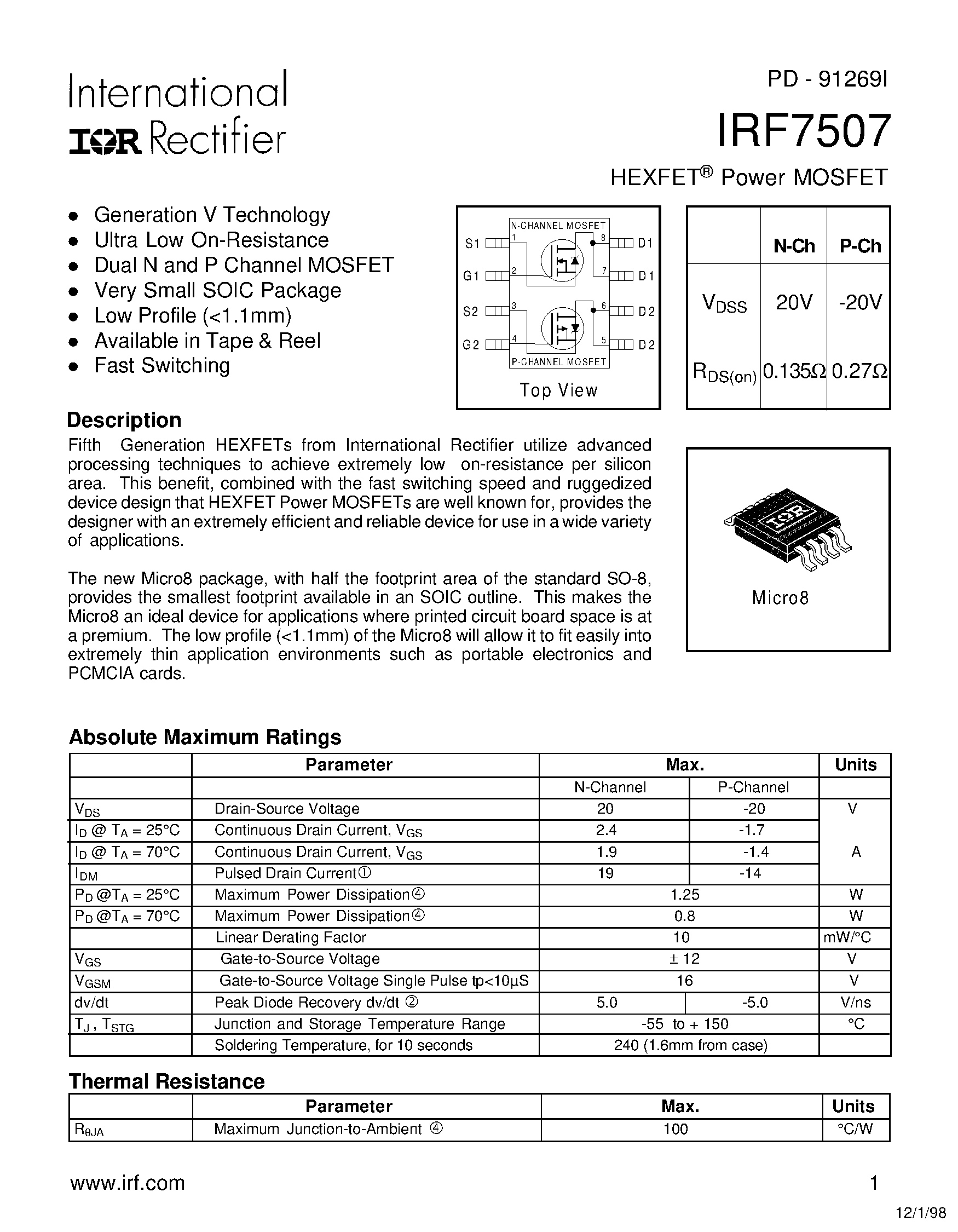
In the realm of electronic circuitry, the potency of a circuit’s performance often hinges upon the finesse with which its components are selected and configured. In this regard, the intricacies of MOSFET gate drive specifications stand out as pivotal elements in shaping the efficacy and efficiency of a design. This section delves into the art of harnessing MOSFET gate drive parameters to elevate the performance and reliability of electronic systems.
Understanding Gate Drive Parameters
Before delving into the nuances of optimization, it is imperative to grasp the essence of MOSFET gate drive specifications. These parameters encapsulate the electrical characteristics governing the interaction between the gate terminal of a MOSFET and the driving circuitry. From thresholds to capacitances, understanding these facets empowers designers to tailor their approaches for maximal efficacy.
- Threshold Voltage: The voltage level at which a MOSFET initiates conduction, influencing its turn-on behavior.
- Gate Charge: Reflects the amount of charge required to fully switch the MOSFET between its on and off states, affecting switching speed and efficiency.
- Gate Resistance: Determines the ease with which charge is delivered to or extracted from the gate, influencing switching losses and transient behavior.
- Gate-Source Capacitance: Governs the charge storage capacity of the gate, impacting switching speed and energy dissipation during transitions.
Optimizing Design Strategies
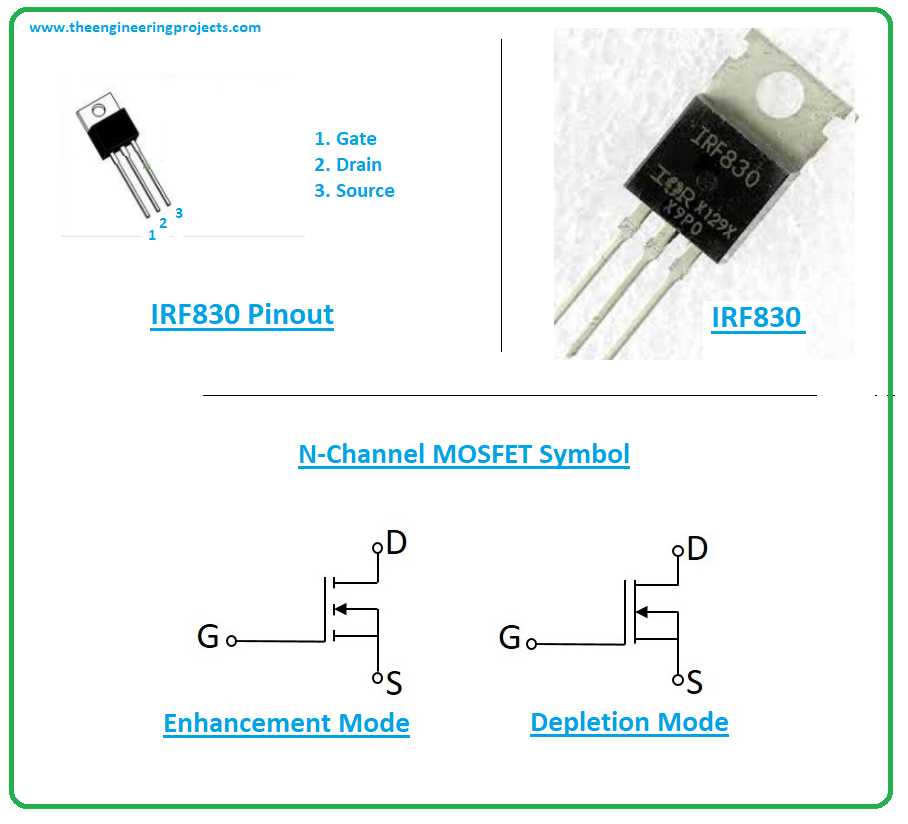
Armed with a comprehension of these gate drive parameters, designers can embark on a journey of optimization to enhance the performance and robustness of their circuits. By meticulously selecting components and configuring driving circuitry, several strategies emerge to streamline operation and mitigate potential pitfalls.
- Fine-Tuning Gate Resistance: Balancing gate resistance optimizes switching speed while minimizing ringing and overshoot, striking a delicate equilibrium for efficient operation.
- Optimal Gate Drive Voltage: Aligning the drive voltage with the MOSFET’s threshold voltage ensures swift turn-on while preventing excessive power dissipation, maximizing efficiency.
- Bypassing Capacitance Considerations: Strategically incorporating decoupling capacitors and minimizing parasitic capacitances mitigate voltage spikes and enhance transient response, bolstering reliability.
- Dynamic Gate Drive Control: Employing advanced techniques such as pulse-width modulation (PWM) enables dynamic adjustment of gate signals, facilitating precise control and adaptive operation.
By adopting these optimization strategies, designers can harness the full potential of MOSFET gate drive specifications, ushering in a new era of efficiency and performance in electronic designs.