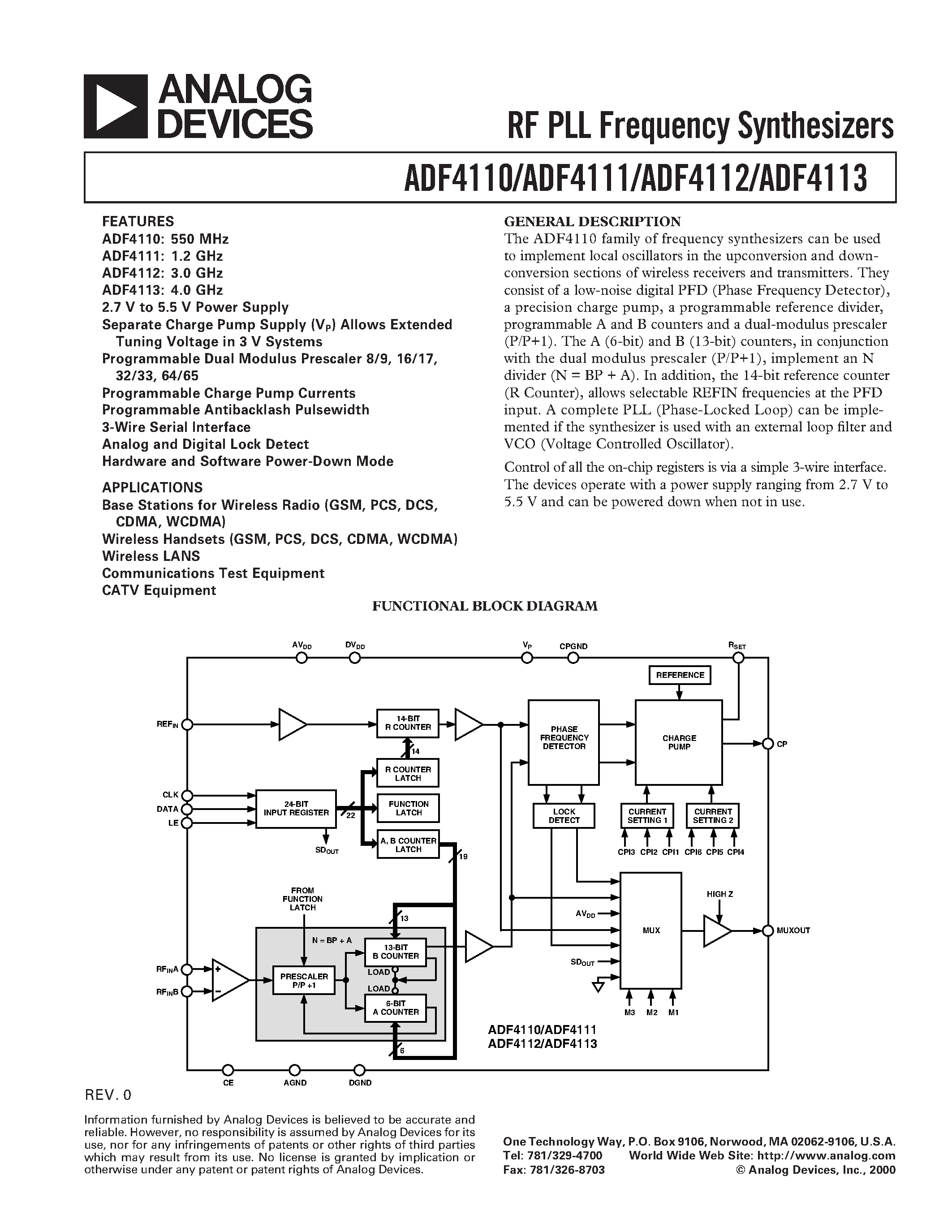
Imagine a technology that can synchronize different components of a complex electronic system, ensuring their seamless interaction and optimal performance. Picture a mechanism that can precisely adjust frequencies and durations, enabling data transmission at lightning-fast speeds. Meet the Phase-Locked Loop (PLL), the unsung hero of modern integrated circuit design.
With its ability to generate stable clock signals and suppress jitter, the PLL plays a vital role in numerous electronic applications, ranging from telecommunications to consumer electronics. This ingenious circuitry, often referred to as a frequency synthesizer, harnesses the power of feedback loops to lock the phase and frequency of an oscillator to a reference signal.
At the heart of the PLL lies a range of key components, including voltage-controlled oscillators (VCOs), phase detectors, and dividers. By intelligently manipulating these elements, the PLL ensures efficient communication between various devices, enabling them to share information seamlessly. With its versatility and adaptability, the PLL has become an indispensable tool for engineers seeking to optimize circuit performance and enhance system reliability.
In this article, we delve into the intricacies of PLL design, exploring its inner workings and the principles that drive its operation. We examine the various applications where PLLs are employed and delve into the critical parameters that engineers consider when selecting PLL components. By gaining a deeper understanding of the PLL’s capabilities and limitations, we can harness its power to push the boundaries of integrated circuit design and unlock new realms of technological advancement.
Understanding the Inner Workings of a Phase-Locked Loop
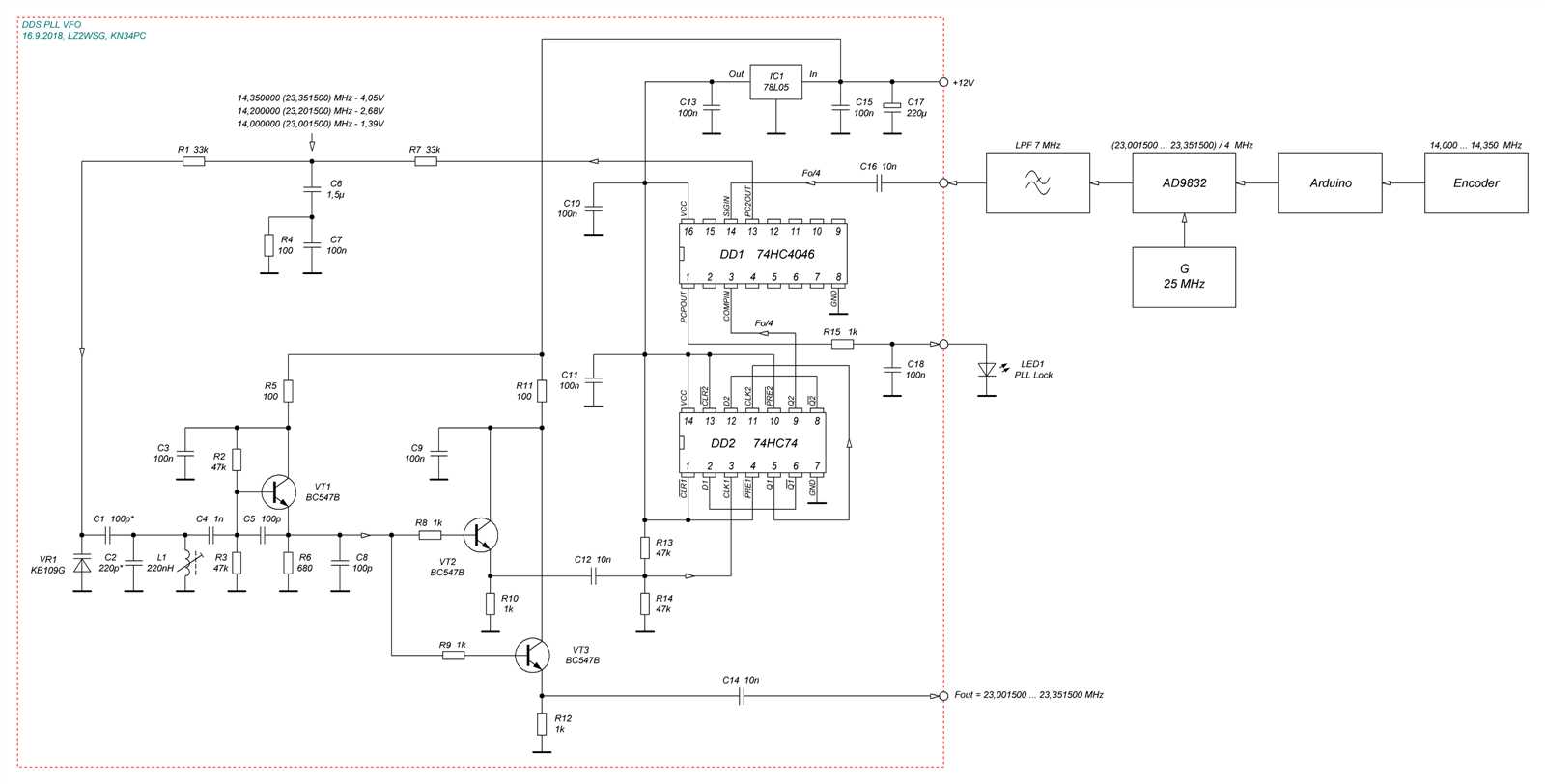
In the realm of electronic circuits, the phase-locked loop (PLL) is a fascinating and essential device with a multitude of applications. This section aims to delve into the intricate workings of a PLL and provide a comprehensive understanding of its inner mechanisms. By exploring the fundamental principles and functions behind a PLL, we can gain insight into its ability to synchronize signals, track and stabilize frequencies, and maintain a stable phase relationship between input and output signals.
The Importance of Frequency Synchronization
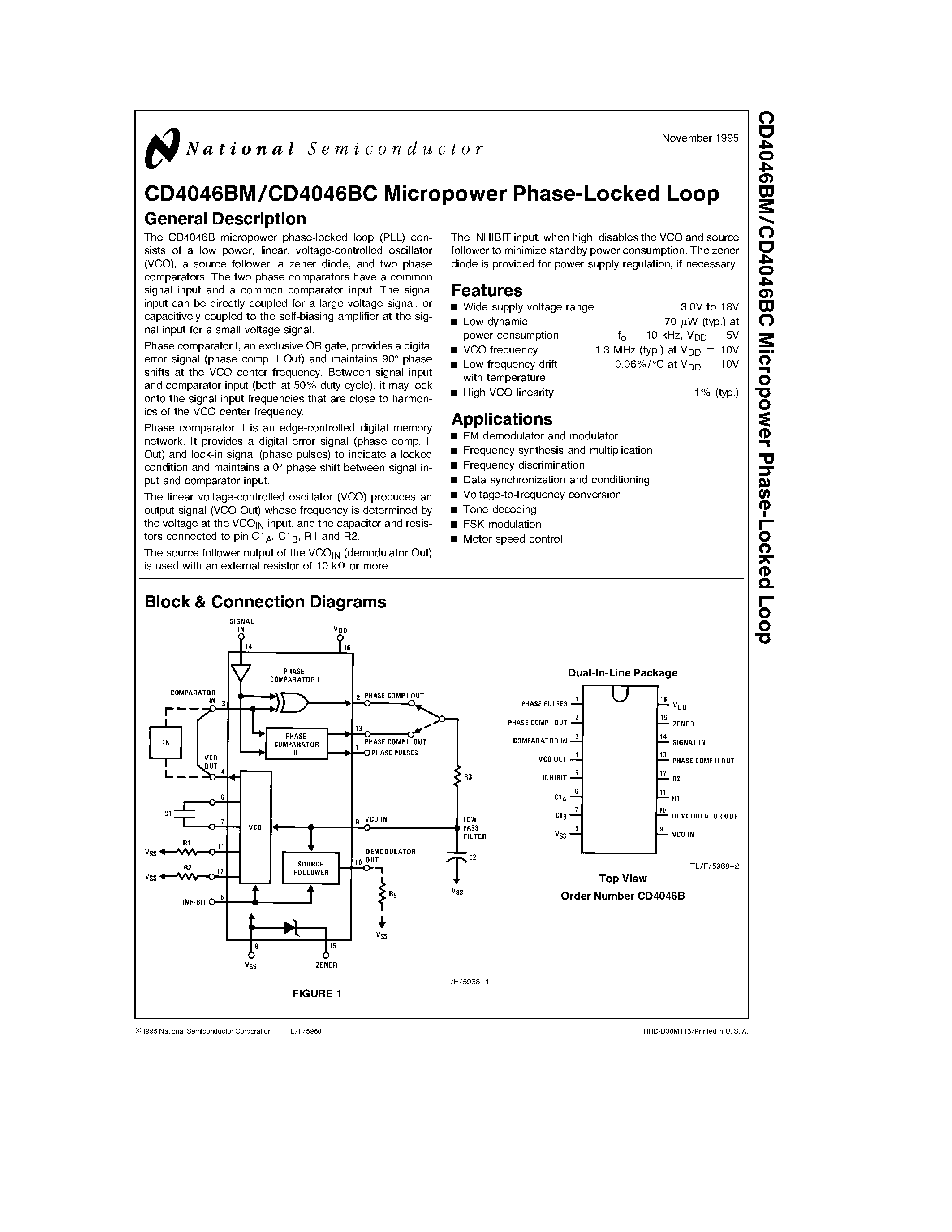
At its core, a PLL is designed to achieve frequency synchronization between an input signal and a reference signal. This synchronization is crucial in various applications where precise timing and reliable data transmission are paramount. Whether it is in communications systems, digital circuits, or even audio equipment, maintaining synchronized frequencies ensures accurate signal processing and optimal performance.
The Key Components of a PLL
A PLL consists of several key components that work together to achieve frequency synchronization. These components include a phase detector, a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO), and a low-pass filter. The phase detector, as the name suggests, compares the phases of the input and reference signals and produces an error voltage proportional to their phase difference. This error voltage is then filtered by the low-pass filter, resulting in a control voltage that is fed into the VCO. The VCO, in response to the control voltage, generates an output signal that adjusts its frequency to match the reference signal, thus achieving frequency synchronization.
The Importance of Phase-Locked Loops in Modern Technology
Phase-locked loops are integral to the operation of many modern electronic devices. They play a crucial role in applications such as frequency synthesis, clock recovery, demodulation, and phase modulation. By providing accurate frequency synchronization, PLLs enable the smooth operation of communication systems, data transmission, audio processing, and many other essential functions. Their versatility and reliability make them indispensable in various industries, ensuring the efficient and accurate performance of electronic systems.
In conclusion, understanding the inner workings of a phase-locked loop allows us to appreciate its significance in modern technology. By achieving frequency synchronization and maintaining stable phase relationships, PLLs enable the reliable processing of signals in a wide range of applications. This knowledge forms the foundation for further exploration and utilization of PLLs in various electronic circuits and systems.
Exploring the Different Applications of Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) Technology
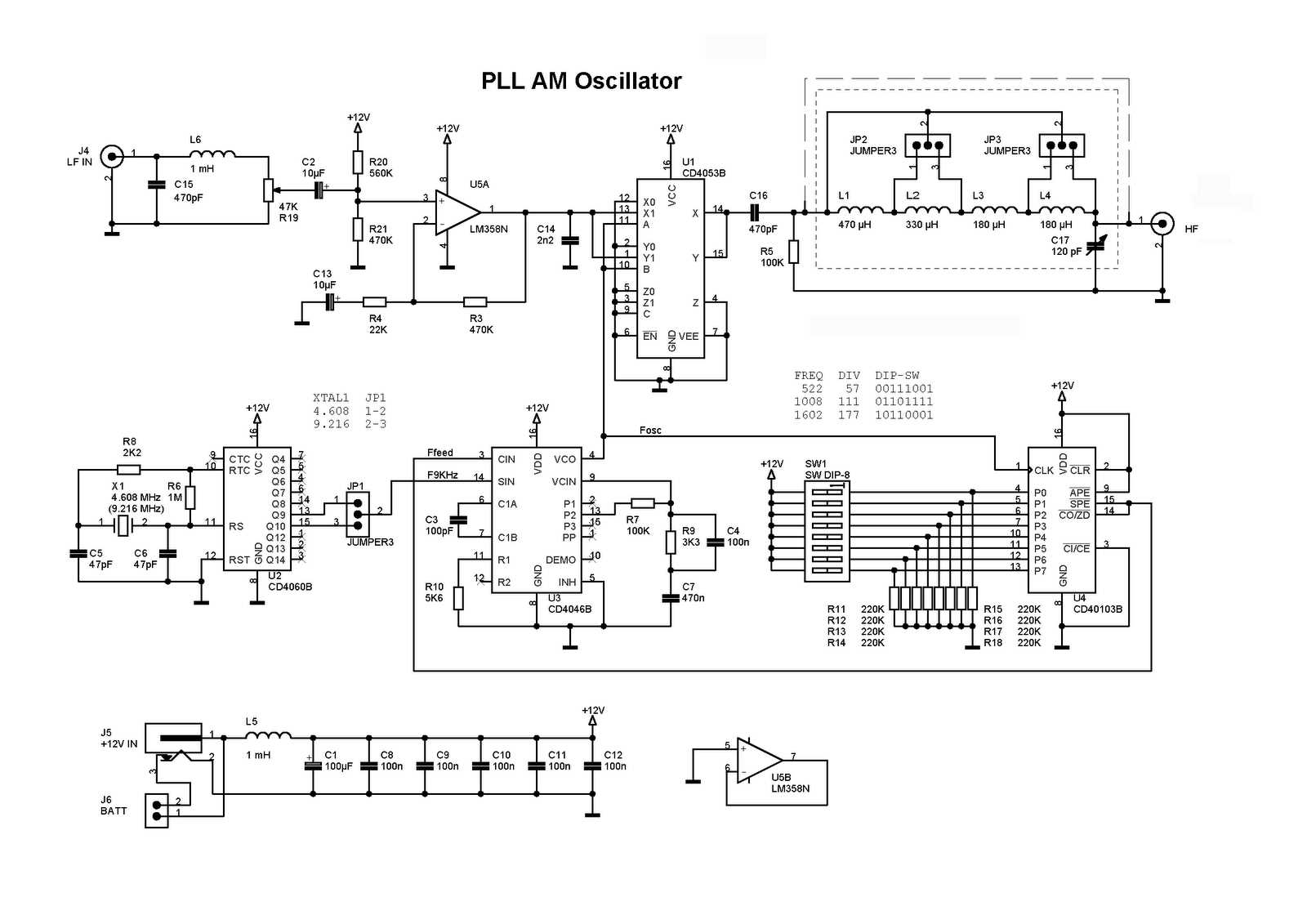
In the world of electronics and telecommunications, there exists a versatile technology that plays a crucial role in various applications without drawing much attention – Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) technology. This sophisticated technology, often referred to as a pivotal building block, offers a wide range of applications across different industries, from signal processing and communication systems to frequency synthesis and clock recovery. Let’s dive deeper into the diverse applications of PLL technology and explore the unique functions it performs in each field.
One notable application of this advanced technology is in the field of wireless communication systems. PLLs are used to demodulate signals, ensuring accurate clock recovery and maintaining synchronization between the transmitted and received signals. This plays a critical role in ensuring clear and uninterrupted voice communication, data transmission, and even in satellite communication systems.
PLL technology also finds relevance in frequency synthesis, which involves generating stable and precise frequency signals. By employing PLLs, frequency synthesis circuits can generate signals with minimal phase noise, making them suitable for applications such as radio transmitters, radar systems, and even high-speed data transfer. The ability to generate accurate and stable frequencies is particularly crucial in industries like aerospace and defense.
Furthermore, PLLs find application in clock recovery circuits. In digital systems, where many components rely on synchronized clock signals, PLL technology enables the recovery of clock signals from data streams. This ensures accurate synchronization of different components, avoiding data loss, and maintaining reliable operation in various applications such as integrated circuits, microprocessors, and data storage devices.
Another fascinating application of PLL technology is in the realm of signal processing. PLL-based circuits can be used as frequency dividers, phase comparators, and even as a means to generate controlled frequency sweeps. These functionalities find applications in areas such as software-defined radios, radar systems, frequency hopping systems, and many more.
- Wireless communication systems
- Frequency synthesis
- Clock recovery circuits
- Signal processing
In summary, PLL technology plays a versatile and integral role across numerous industrial sectors. From wireless communication systems to frequency synthesis, clock recovery circuits, and signal processing, PLLs contribute to the precise and reliable functioning of various electronic devices and systems. Understanding the diverse applications of PLLs allows for the advancement of technology and the development of innovative solutions to meet the evolving needs of different industries.
Tips for Selecting and Implementing the Right Pll for Your Project
Choosing and implementing a phase-locked loop (PLL) that meets the specific requirements of your project can be a critical task. This section provides valuable insights and recommendations for making informed decisions, without directly referencing the PLL or its datasheet.
Understand your project’s needs: Before selecting a PLL, it’s essential to thoroughly grasp your project’s requirements, such as frequency stability, signal noise, and input/output voltage compatibility. Consider the specific application and any unique challenges that may arise.
Evaluate performance characteristics: Investigate the various performance characteristics that are relevant to your project. Analyze factors like phase noise, spurious signals, jitter, and frequency stability. Familiarize yourself with the appropriate industry standards and specifications for these parameters.
Research available options: Explore the market to identify different PLL options that could potentially fulfill your project’s needs. Look beyond typical datasheets; examine industry literature, application notes, and technical resources to gain a comprehensive understanding of each PLL’s strengths and weaknesses.
Consider design constraints: Take into account any limitations or design constraints that may affect the PLL’s integration into your project. Factors such as power consumption, board space requirements, and temperature range capabilities should be carefully evaluated to ensure compatibility.
Seek expert advice: Consulting with experts or experienced engineers can provide valuable insights into selecting the right PLL for your project. Reach out to industry professionals, join online communities or forums, and engage in discussions to benefit from their knowledge and experience.
Perform thorough testing: Once you have selected a PLL, thoroughly test its performance in simulated or real-world scenarios. Verify that it meets the specifications and requirements identified earlier. Make iterative adjustments as needed to optimize its performance within your project.
This section equips you with the essential tips and considerations needed to navigate the selection and implementation process of a PLL for your project successfully. It emphasizes the importance of understanding project needs, evaluating performance characteristics, researching available options, considering design constraints, seeking expert advice, and performing thorough testing.