Within the realm of electronic components lies a fascinating entity, known for its ability to bridge the physical divide between circuits without direct electrical connection. This enigmatic device operates on the principle of optical transmission, leveraging light to convey signals across isolation barriers, thereby safeguarding sensitive circuitry from potential harm.
Amidst the intricate web of electronic components, these light-linked entities serve as silent guardians, ensuring the integrity and safety of interconnected systems. Their significance transcends mere functionality, embodying a symbiotic relationship between the realms of light and electricity.
Exploring the inner workings of these light-mediated messengers unveils a realm of intricacy and precision engineering, where photons dance across miniature landscapes, carrying the whispers of data and commands. Such devices, although diminutive in size, wield immense power in facilitating communication and control within electronic circuits.
Join us on an illuminating journey as we delve into the depths of these light-bound enigmas, unraveling their mysteries and uncovering the indispensable role they play in the tapestry of modern electronics.
Understanding the PC817 Optocoupler: Essential Features and Applications
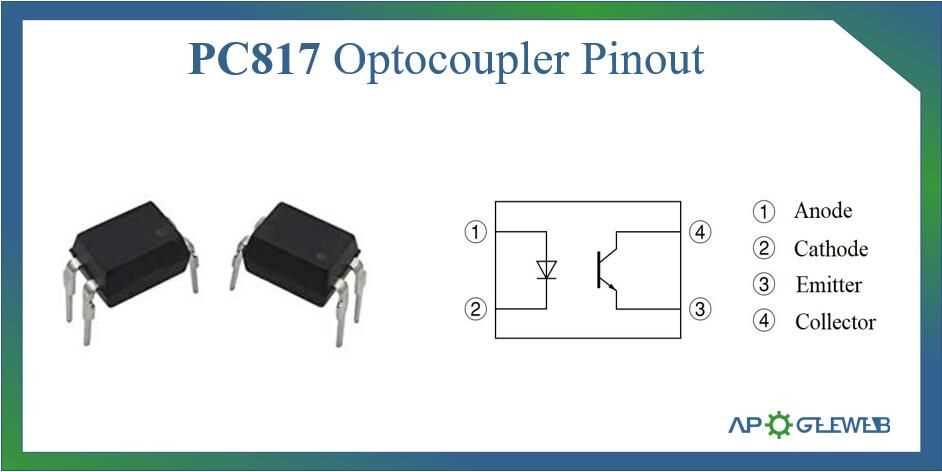
In this section, we delve into the core functionalities and potential applications of the PC817 optocoupler, shedding light on its pivotal role in electronic systems. Exploring its intrinsic characteristics and operational principles, we uncover how this component facilitates seamless signal transmission and isolation in various circuits.
Functionality Overview:
At its essence, the PC817 serves as a vital intermediary between input and output circuits, ensuring signal transfer while maintaining electrical isolation. By leveraging optical coupling, it effectively bridges the gap between disparate voltage levels or grounds, safeguarding sensitive components from potential damage.
Key Attributes:
With its compact footprint and robust design, the PC817 embodies reliability and efficiency. Equipped with an infrared emitter and phototransistor receiver, it enables high-speed data transmission and noise immunity, enhancing system performance even in demanding environments.
Applications:
The versatility of the PC817 extends across a myriad of applications, spanning from industrial automation to consumer electronics. Whether employed in power supplies, motor controls, or communication interfaces, this optocoupler excels in galvanic isolation, fostering reliable operation and mitigating interference.
Moreover, its integration in feedback loops and voltage regulators ensures precise control and stability, elevating the functionality of diverse electronic systems.
By harnessing the PC817’s capabilities, engineers can realize innovative solutions across an array of industries, bolstering performance and reliability in their designs.
Exploring the PC817 Datasheet: Pin Configuration and Electrical Characteristics

In this section, we delve into the intricacies of the PC817 optocoupler, examining its fundamental pin configuration and the essential electrical properties it entails. By understanding the layout of its pins and the electrical characteristics they represent, we gain insight into how this component operates within various electronic circuits.
Pin Configuration
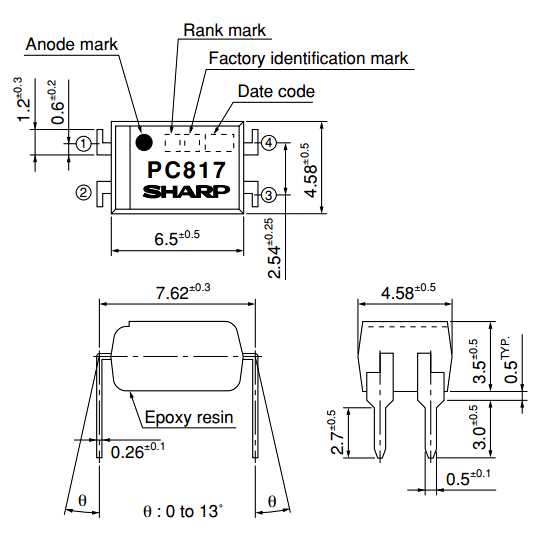
The PC817 optocoupler features a distinct pin arrangement that facilitates its function in isolation applications. Through a detailed analysis of its pin configuration, we uncover how signals are transmitted and received across its optically isolated barrier, enabling secure communication between different parts of a circuit.
Electrical Characteristics

Delving into the electrical characteristics of the PC817, we explore its key parameters such as forward current transfer ratio (CTR), isolation voltage, and input/output capacitance. By comprehending these electrical properties, engineers can effectively integrate the PC817 into their designs, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Utilizing PC817 Optocoupler: Circuit Design Tips and Best Practices
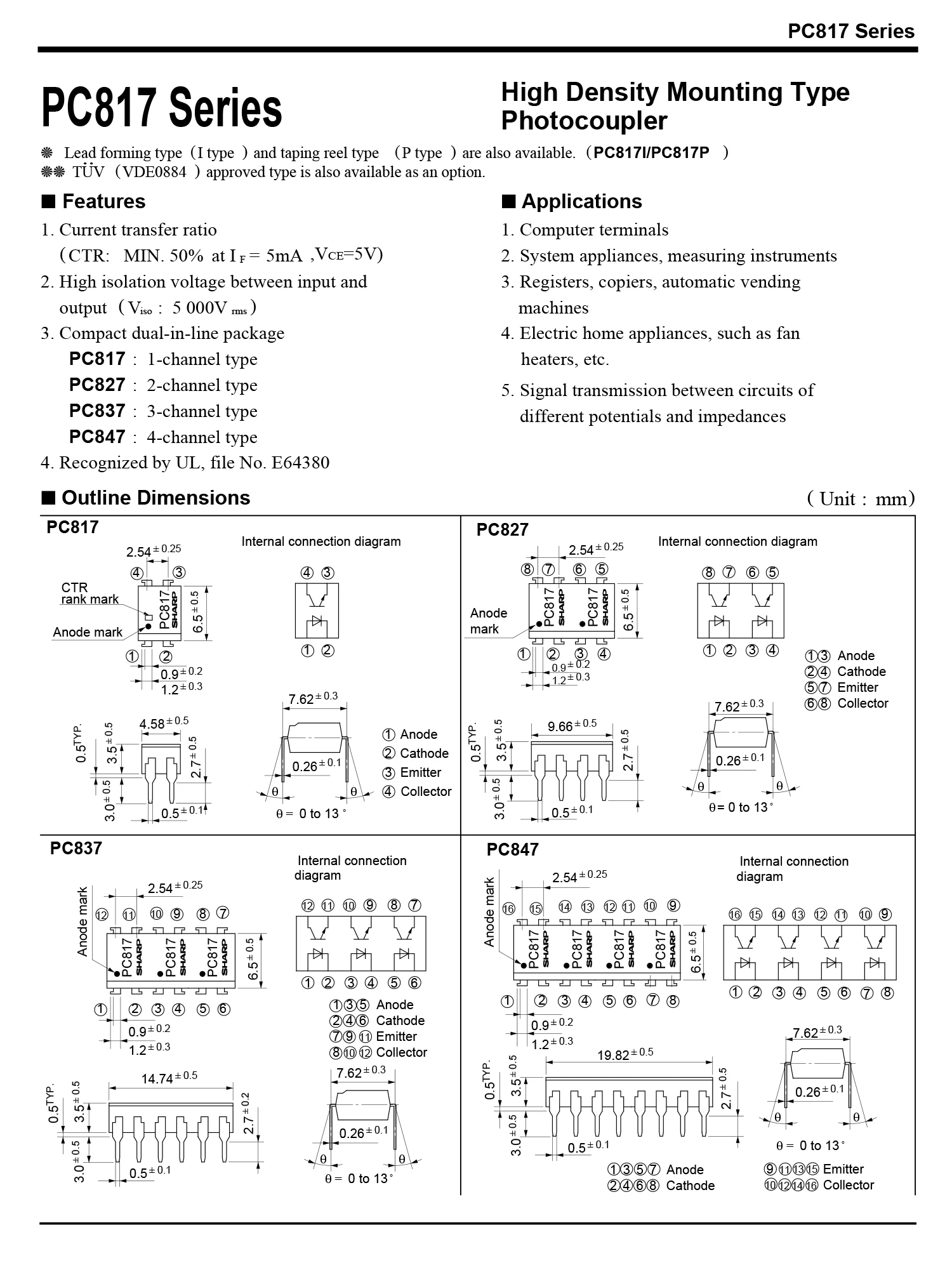
Exploring the potential of the PC817 optocoupler involves delving into efficient circuit design strategies and maximizing its functionality. This section elucidates essential considerations and effective approaches for integrating this component seamlessly within various electronic systems.
Understanding the intricacies of leveraging optocouplers like the PC817 entails grasping fundamental circuit design principles to ensure optimal performance and reliability. By implementing judicious design methodologies, engineers can enhance signal transmission, minimize noise interference, and bolster overall system stability.
Effective utilization of optocouplers necessitates meticulous attention to component selection, circuit layout, and signal conditioning techniques. By adhering to best practices in design, engineers can mitigate signal distortion, improve isolation performance, and mitigate potential issues arising from environmental factors.
Moreover, incorporating the PC817 optocoupler demands a comprehensive understanding of its specifications, functionality, and limitations. By leveraging this knowledge, engineers can tailor circuit designs to meet specific application requirements, optimize performance parameters, and ensure seamless integration within diverse electronic systems.
Furthermore, employing innovative circuit design techniques such as feedback control mechanisms, impedance matching, and noise suppression methodologies can augment the functionality and reliability of optocoupler-based circuits. By integrating these advanced strategies, engineers can overcome challenges associated with signal integrity, transient response, and electromagnetic compatibility.
In summary, mastering the utilization of the PC817 optocoupler entails a multifaceted approach encompassing thorough understanding of circuit design principles, diligent component selection, and adoption of innovative techniques. By adhering to best practices and leveraging advanced methodologies, engineers can unlock the full potential of this versatile component in diverse electronic applications.