
In the realm of advanced visual technology, a revolution has quietly taken place, spearheaded by a marvel known as Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED) displays. These futuristic marvels have incited the imagination of designers, providing a canvas for vibrant and immersive experiences. Deriving their brilliance from the properties of organic compounds, these state-of-the-art displays transcend the conventional boundaries of visual representation.
An intrinsic characteristic of OLED technology lies in its ability to self-illuminate, eliminating the need for a backlight and enabling unparalleled contrast and vividness. By intricately manipulating organic compounds, OLED displays achieve a new level of brilliance, faithfully reproducing colors and diving deep into the nuances of shades and tones. This technology unlocks a myriad of possibilities, breathing life into every pixel and captivating the human eye with its unequivocal brilliance.
Guided by the principles of innovation and sustainability, OLED displays epitomize the fusion of advanced engineering and ecological ethics. With their slim profiles and energy-efficient characteristics, these displays symbolize a breakthrough in the pursuit of environmentally conscious design. Keeping pace with the era of smart devices, OLED technology displays anchor the future of user interfaces, yielding impeccable touch responsiveness and finely tuned user experiences.
OLED Display Datasheet: Understanding the Key Specifications
In the world of cutting-edge technology, OLED displays have become increasingly popular due to their incredible visual quality and versatility in various electronic devices. To fully comprehend the potential of an OLED display, it is crucial to delve into the intricate details of its datasheet. This section aims to provide an insightful overview of the key specifications found in an OLED display datasheet, shedding light on the essential parameters that define its performance and functionality.
The Magic of Pixels: Resolution and Pixel Density
At the heart of an OLED display lies a mesmerizing array of pixels that work in unison to create stunning visual imagery. The resolution of an OLED display refers to the number of pixels it comprises horizontally and vertically, determining the level of detail and clarity in the displayed content. Additionally, pixel density, measured in pixels per inch (PPI), quantifies the level of sharpness, smoothness, and overall visual fidelity that the display can deliver. Understanding these specifications enables discerning users to determine the visual experience they can expect from the OLED display.
Beyond the Visible: Contrast Ratio and Color Gamut
The potential of an OLED display extends beyond its resolution and pixel density, encompassing the concepts of contrast ratio and color gamut. Contrast ratio measures the difference between the darkest black and the brightest white that the display can produce, contributing to the depth and richness of the displayed content. Meanwhile, color gamut refers to the range of colors that the display can accurately reproduce, providing vibrant and lifelike visuals. These specifications bring the visual representation of the OLED display to life, offering an immersive experience to the viewer.
Overall, comprehending the key specifications outlined in an OLED display datasheet empowers users to make informed decisions about their electronic device purchases. By understanding the significance of resolution, pixel density, contrast ratio, and color gamut, individuals can ensure that they invest in a display that aligns with their visual expectations and requirements. With OLED displays continuously pushing the boundaries of visual technology, delving into the finer details of their datasheets is an essential step towards unlocking their true potential.
Display Resolution and Size
In this section, we will explore the aspects of resolution and size when it comes to OLED displays. Understanding these factors is crucial in optimizing the visual experience and determining the overall quality of the display.
Resolution
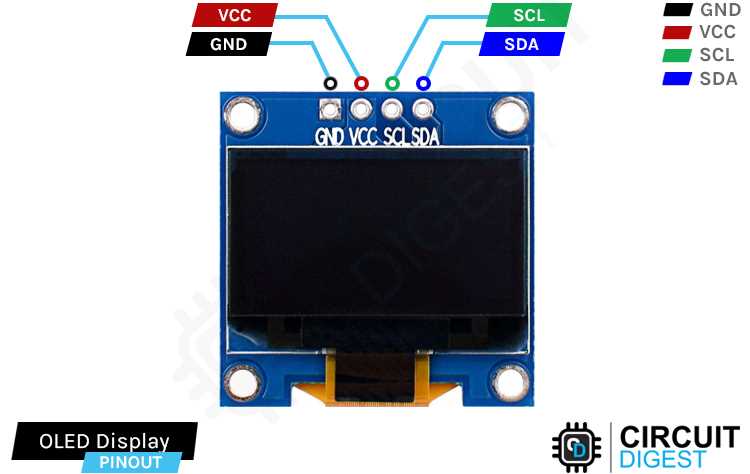
Resolution refers to the number of pixels contained in a display, and it directly affects the level of detail and clarity that can be rendered. A higher resolution results in sharper and more precise images, while a lower resolution may lead to pixelation and less defined visuals. The resolution is determined by the number of pixels both horizontally and vertically and is usually denoted as width x height (e.g., 1920×1080).
Size
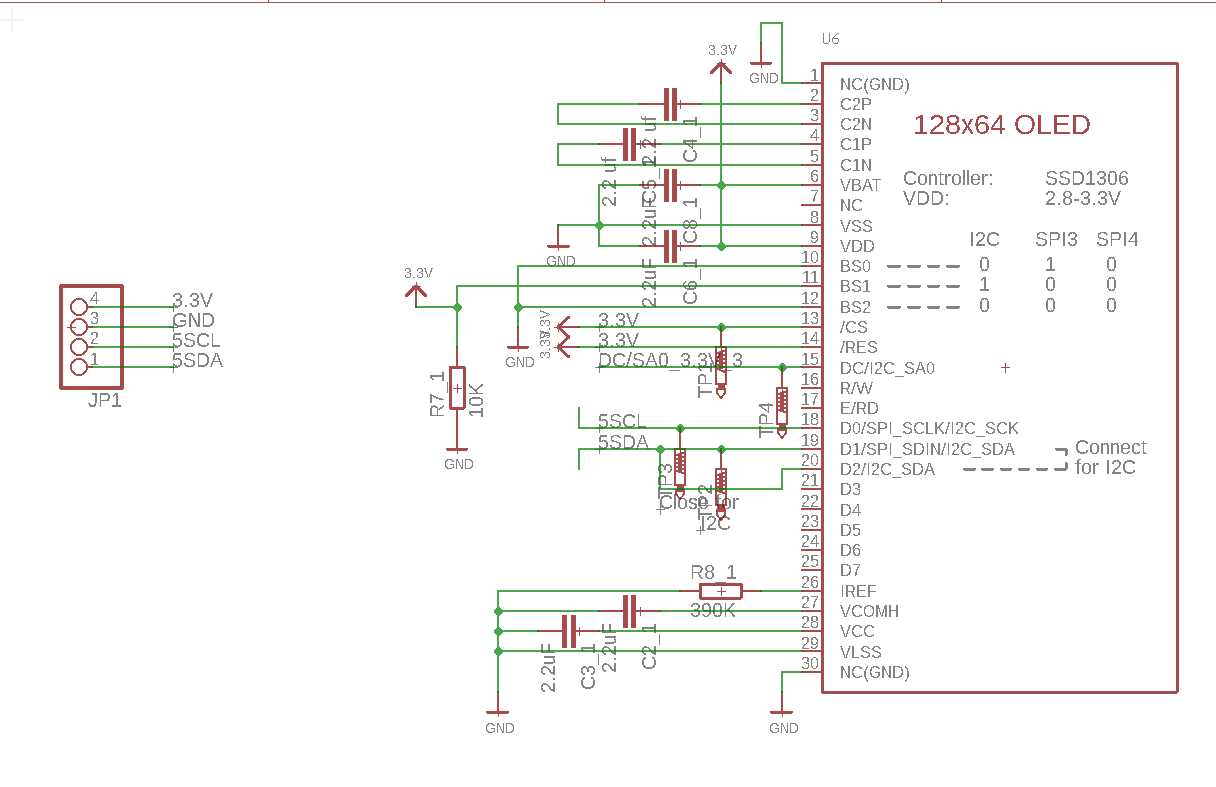
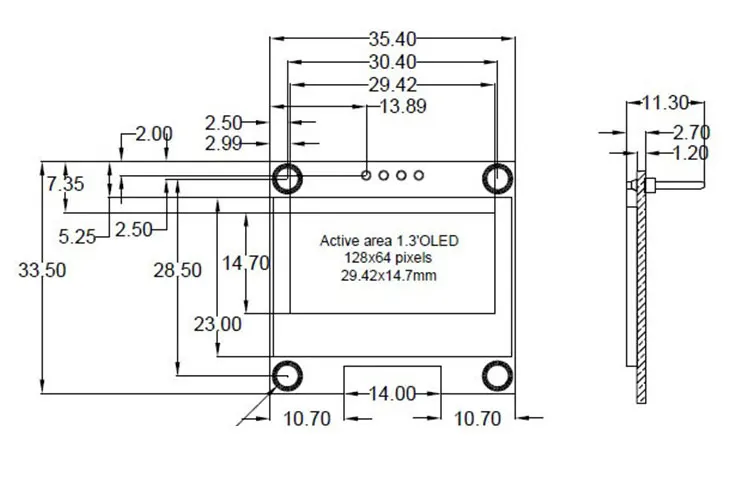
The size of an OLED display is another crucial factor to consider. It determines the physical dimensions of the screen and impacts the overall viewing experience. A larger display offers a more immersive and engaging visual experience, especially for multimedia content such as movies and games. However, it is essential to strike a balance between size and viewing distance to avoid eye strain and ensure comfortable usage.
When selecting an OLED display, it is important to consider both the resolution and size that best fit your specific requirements. Higher resolutions and larger sizes generally result in more visually appealing displays, but it is also essential to consider the application, viewing distance, and intended use of the display to make an informed decision.
- Resolution determines the level of detail and clarity of visuals.
- Size impacts the overall viewing experience.
- Consider both resolution and size when selecting an OLED display.
- Strike a balance between size and viewing distance for optimal usage.
By understanding the concepts of resolution and size in OLED displays, one can make informed decisions that result in the best visual experience for their intended application.
Refresh Rate and Response Time
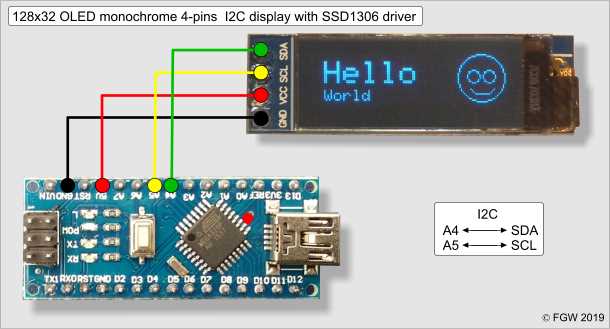
The performance of OLED displays goes beyond their vibrant colors and high resolution. Two key factors that determine the quality of an OLED display are the refresh rate and response time. These parameters play a crucial role in delivering smooth and responsive visuals.
Refresh Rate
Refresh rate refers to the number of times the display updates its image per second. It is measured in hertz (Hz). A higher refresh rate means that the display can update its image more frequently, resulting in smoother motion and reduced motion blur. This is particularly important for fast-paced content such as gaming and action movies.
Response Time
Response time measures the time it takes for a pixel to transition from one state to another. It is typically measured in milliseconds (ms). A lower response time indicates that the pixels can change their state quickly, resulting in sharper and more fluid transitions between frames. This is especially important for eliminating ghosting, where remnants of previous frames are visible on the screen.
The refresh rate and response time work together to provide a seamless viewing experience. For example, a high refresh rate combined with a low response time ensures that fast-moving objects are displayed smoothly without any motion blur or artifacts.
Manufacturers often specify the refresh rate and response time in the datasheet of an OLED display. Designers and consumers can use this information to make informed decisions about the suitability of the display for their specific needs.
| Refresh Rate | Response Time |
|---|---|
| 60Hz | 5ms |
| 120Hz | 2ms |
| 240Hz | 1ms |
It’s important to note that while a higher refresh rate and lower response time generally result in better display performance, they may also come at a higher cost. Designers and consumers should strike a balance between their budget and the desired visual experience.
Color Gamut and Contrast Ratio
The color gamut and contrast ratio are two important factors to consider when evaluating the visual performance of an OLED display. The color gamut refers to the range of colors that a display can reproduce, while the contrast ratio measures the difference between the darkest and brightest parts of an image. Understanding these specifications can provide insights into the display’s ability to accurately render colors and provide a vibrant viewing experience.
The color gamut of an OLED display determines the range of colors that can be displayed on the screen. It is typically represented as a percentage of the NTSC (National Television System Committee) color space, which is a widely accepted standard for color reproduction. A larger color gamut indicates a display’s ability to reproduce a wider range of colors, resulting in more vibrant and lifelike images. Manufacturers often provide color gamut values such as 100% sRGB or DCI-P3 to highlight the display’s color accuracy and fidelity.
On the other hand, the contrast ratio measures the difference between the darkest blacks and the brightest whites that a display can produce. A higher contrast ratio indicates a greater difference between the darkest and brightest parts of an image, resulting in improved depth and detail. It is a crucial factor for displaying content with high dynamic range, such as movies and games. The contrast ratio is typically represented as a numerical value, with higher values indicating better contrast performance.
| Color Gamut | Contrast Ratio |
|---|---|
| Wide color gamut for vibrant and lifelike colors | High contrast ratio for improved depth and detail |
| Accurate color reproduction | Enhanced visual experience |
| 100% sRGB or DCI-P3 | Numerical value representing the contrast ratio |
By considering the color gamut and contrast ratio specifications of an OLED display, users can make more informed decisions when selecting a display for their specific needs. Whether it’s for professional photo editing, gaming, or multimedia consumption, understanding these factors can ensure a rich and immersive visual experience.