Exploring the realm of embedded systems, one encounters a myriad of microcontroller modules that serve as the backbone for a wide array of projects and applications. Among these, a certain module stands out for its versatility and adaptability, offering a wealth of functionalities within a compact form factor. This component serves as a cornerstone for countless innovations across industries, enabling enthusiasts and professionals alike to bring their ideas to life with ease and efficiency.
Within the realm of electronics, this module has garnered attention for its seamless integration capabilities, enabling seamless communication with various peripherals and sensors. Its compact design belies its robust performance, making it a favorite among hobbyists and professionals seeking to push the boundaries of innovation. This module serves as a canvas upon which creators can paint their visions, offering a myriad of possibilities limited only by one’s imagination.
Join us on a journey, as we delve into the intricacies of this microcontroller module, uncovering its hidden potentials and unraveling the mysteries that lie within its specifications and functionalities. Through this exploration, we aim to equip enthusiasts and professionals alike with the knowledge and insights needed to harness the full capabilities of this versatile component, propelling their projects to new heights of creativity and functionality.
The Fundamentals of Nodemcu ESP 12E Specifications
In this section, we delve into the foundational aspects of the Nodemcu ESP 12E documentation, elucidating its core components and functionalities. Understanding these fundamental principles is paramount for comprehending the intricacies of this microcontroller module.
- Introduction to Device Overview
- Exploring Hardware Specifications
- Analyzing Pin Configuration
- Understanding Communication Protocols
- Examining Power Requirements
- Reviewing Environmental Operating Conditions
Each aspect contributes to the holistic understanding of the Nodemcu ESP 12E ecosystem, paving the way for proficient utilization and integration into various projects and applications.
Understanding Hardware Specifications
In this section, we delve into comprehending the intricacies of the hardware specifications of the device under scrutiny. It is imperative to grasp the fundamental aspects that delineate the capabilities and functionalities of the system. By gaining a profound understanding of the hardware specifications, users can effectively harness the potential of the device and tailor their projects accordingly.
Key Components Overview
Before delving into the technical nuances, let’s first outline the key components that constitute the device. By dissecting its foundational elements, we lay the groundwork for a more comprehensive exploration of its hardware specifications.
- Processor: The central processing unit of the device, responsible for executing instructions and performing computations.
- Memory: This encompasses both volatile (RAM) and non-volatile (ROM, Flash) memory components, crucial for storing and accessing data and program instructions.
- Communication Interfaces: These include various ports, connectors, and wireless modules facilitating interaction with external devices and networks.
- Power Management System: Vital for regulating power consumption and ensuring efficient operation of the device.
- Peripheral Devices: Additional hardware components such as sensors, actuators, and display modules that augment the device’s functionality.
Interpreting Specifications
Interpreting hardware specifications necessitates a nuanced approach, as it involves deciphering technical jargon and understanding the significance of each parameter in the context of device performance and functionality. By scrutinizing specifications such as clock speed, memory capacity, and connectivity options, users can gauge the device’s capabilities and ascertain its suitability for their intended applications.
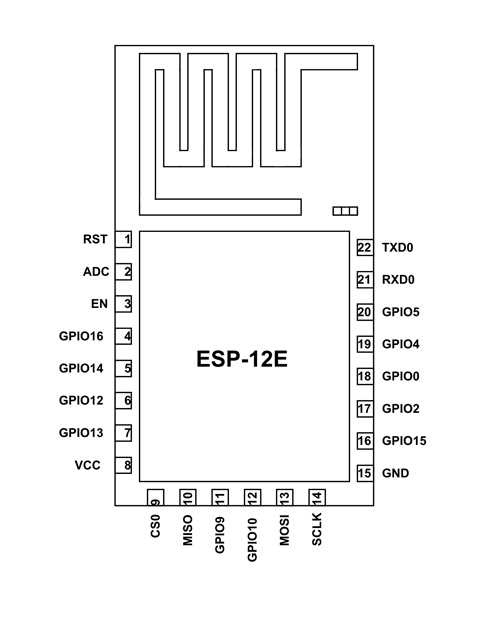
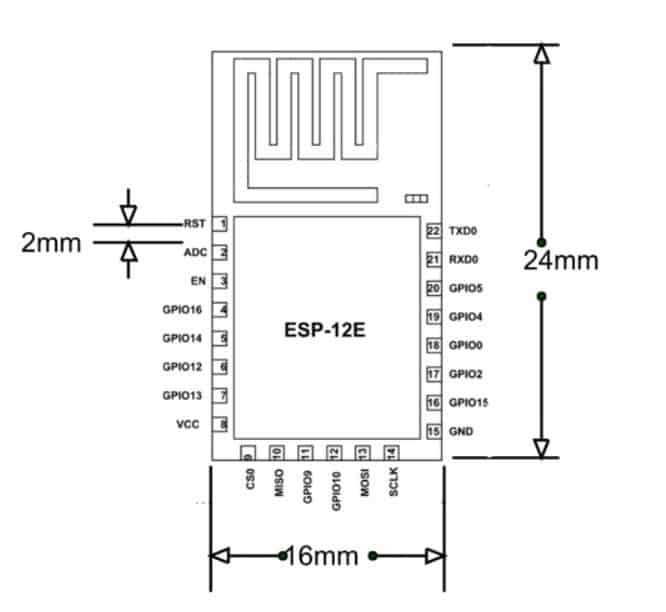
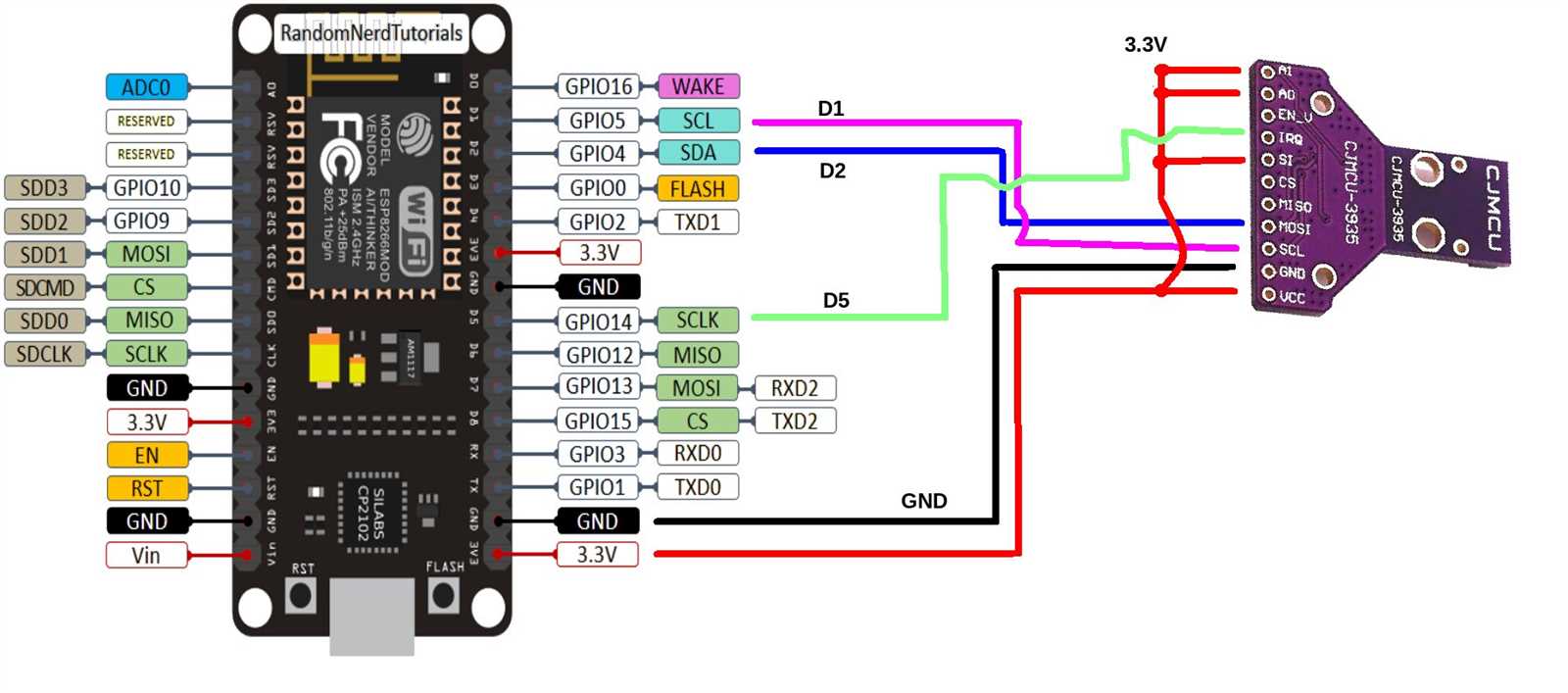
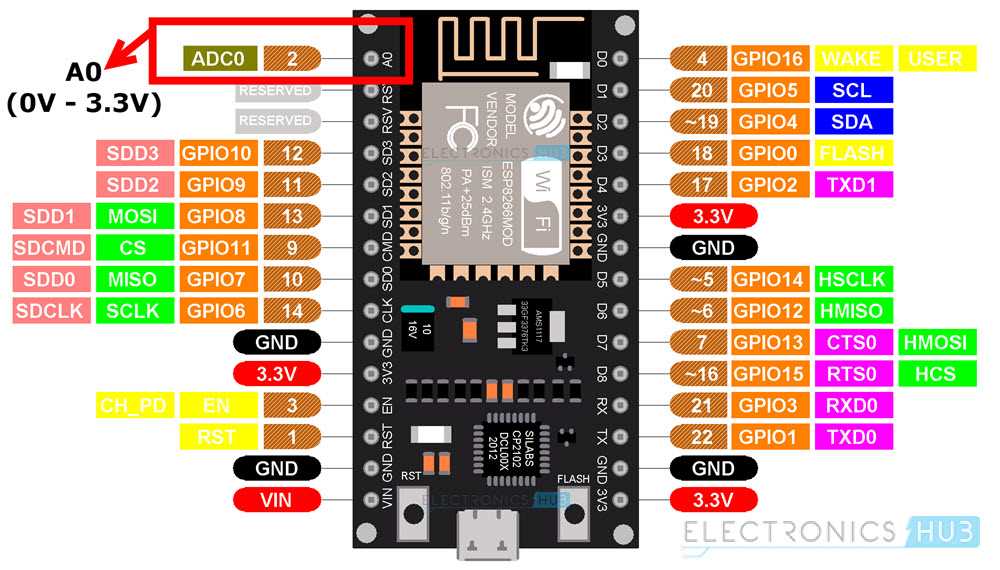
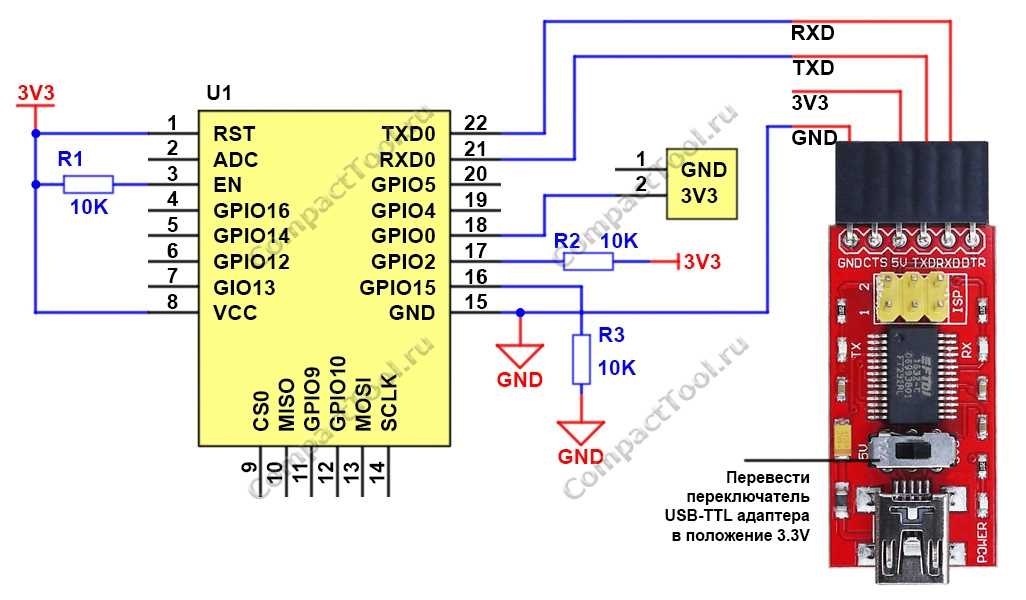
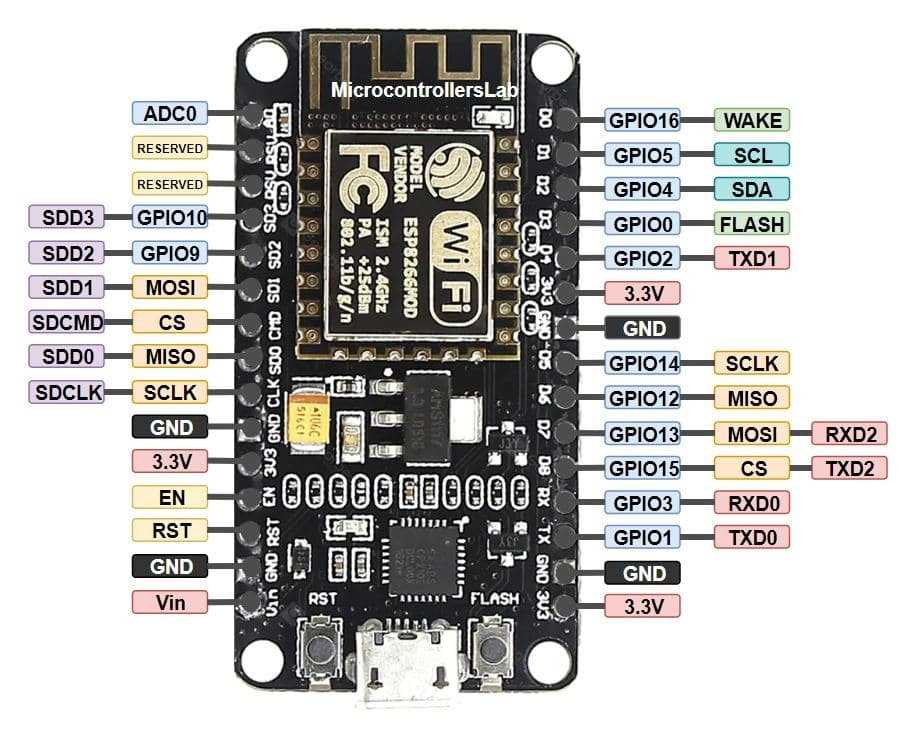
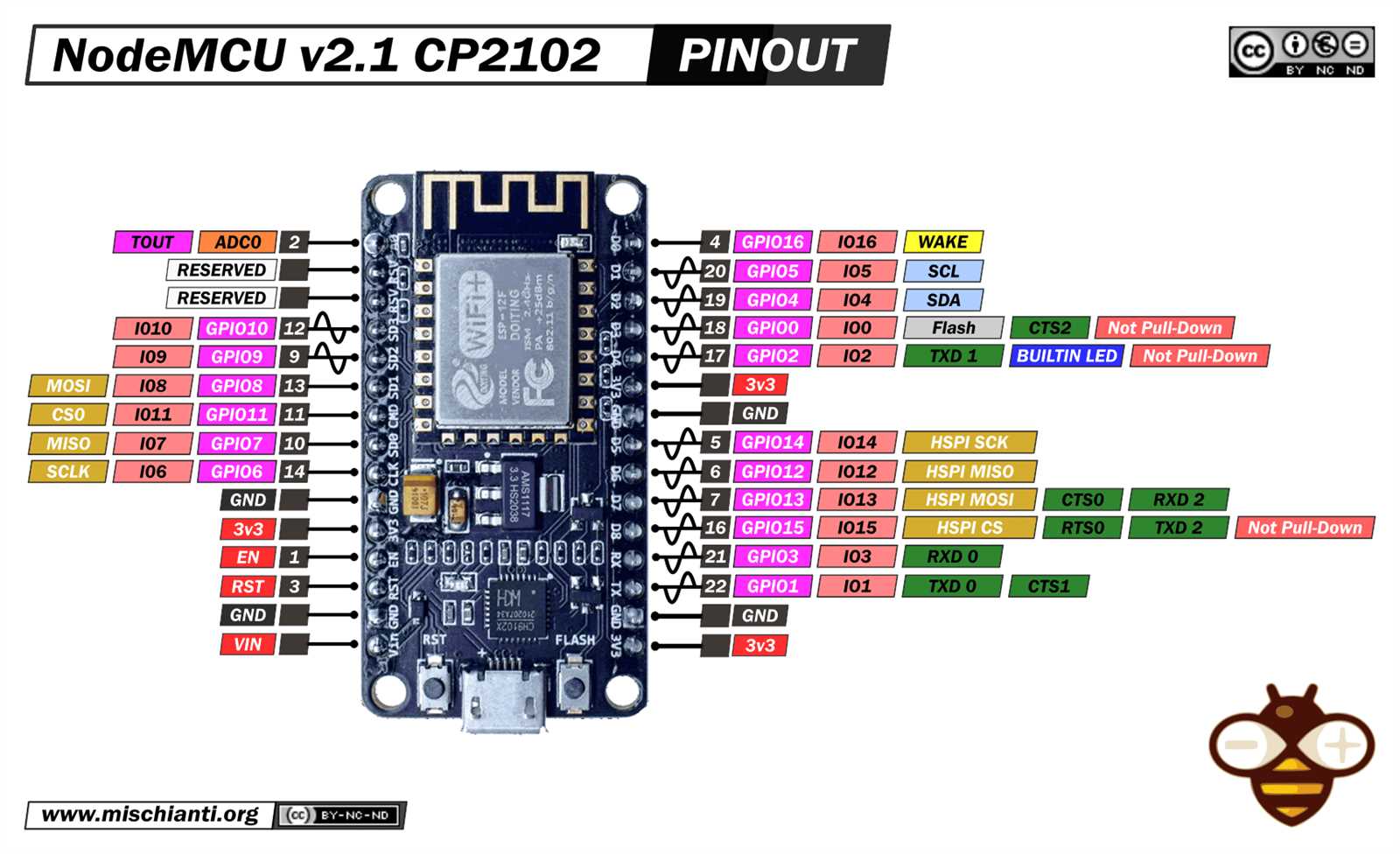
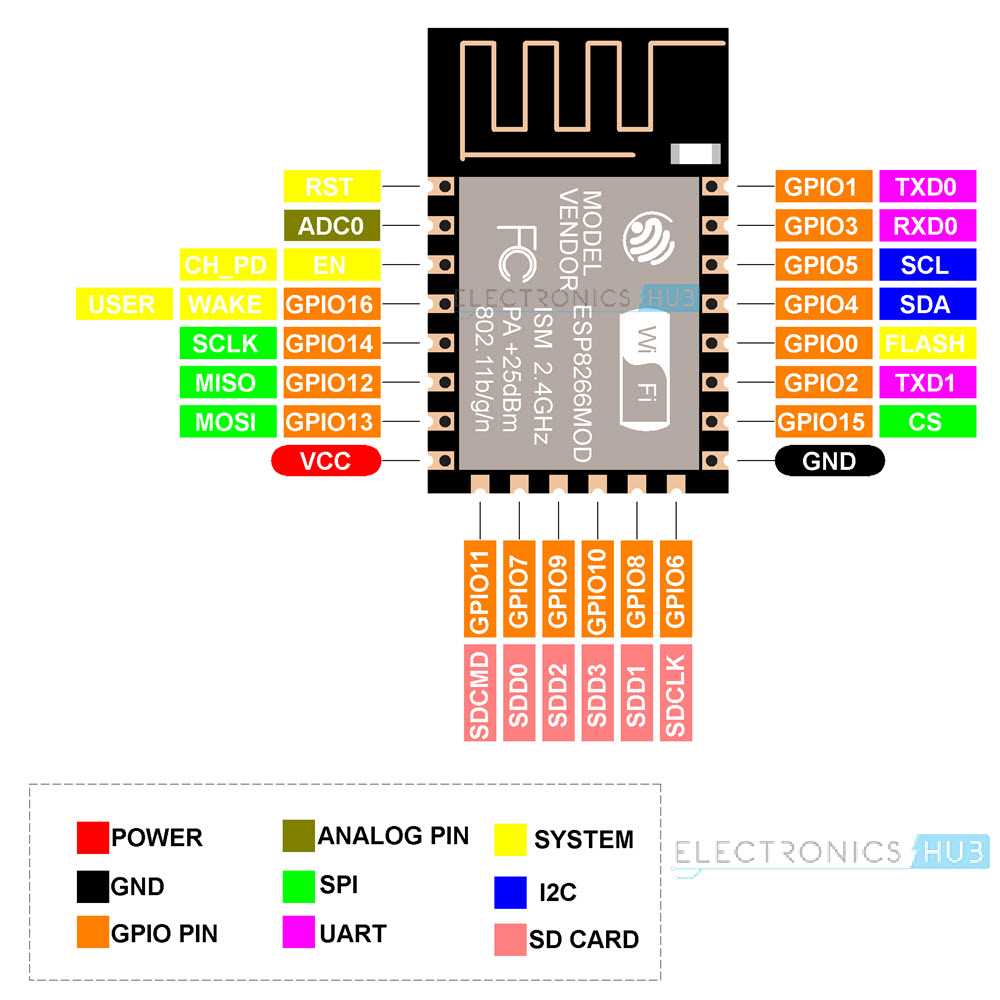
Exploring Pin Configuration and Functions
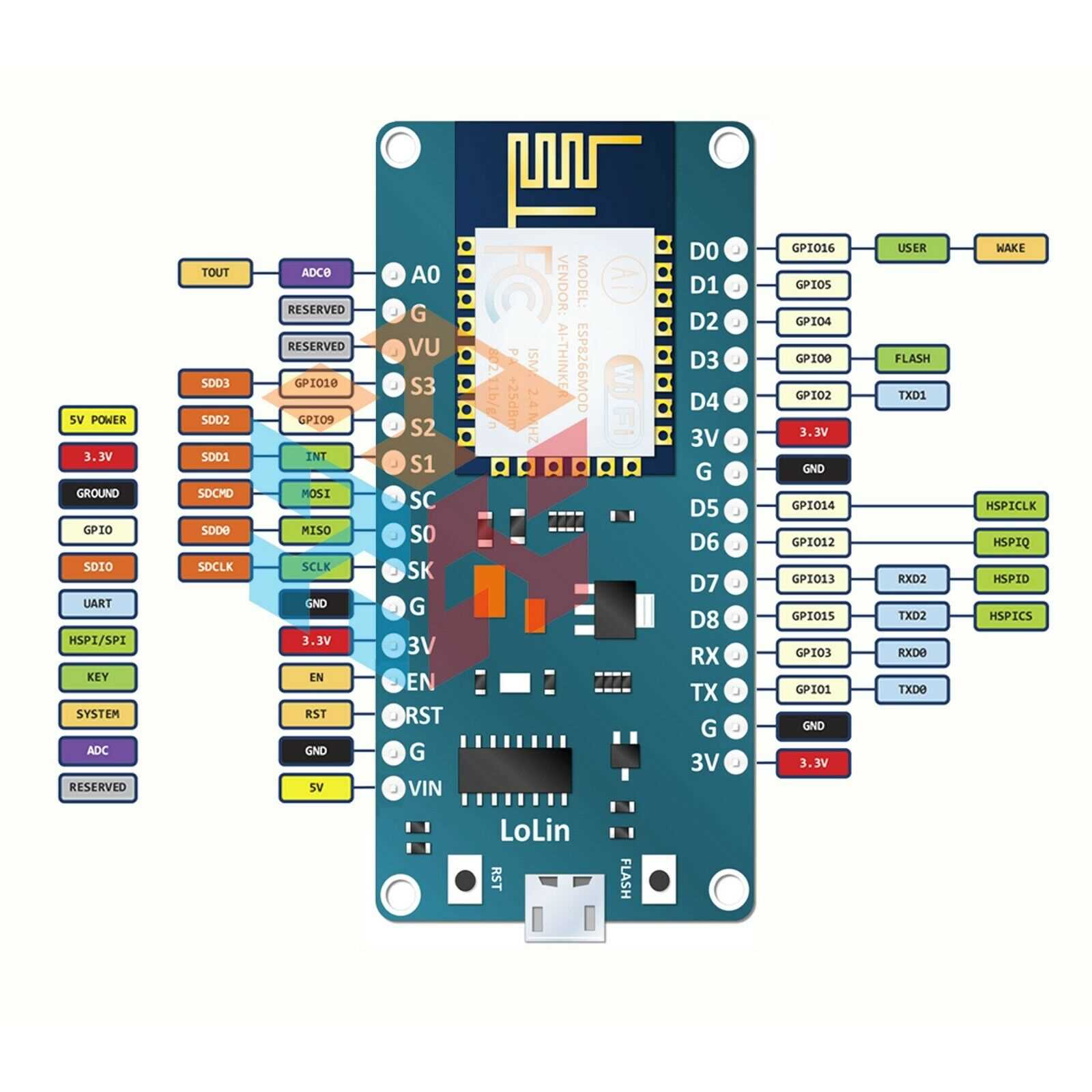
In this section, we delve into the intricacies of pin configurations and their associated functions within the framework of the device under discussion. Understanding the role of each pin and its capabilities is fundamental for effective utilization in various projects and applications.
Pin Layout Overview
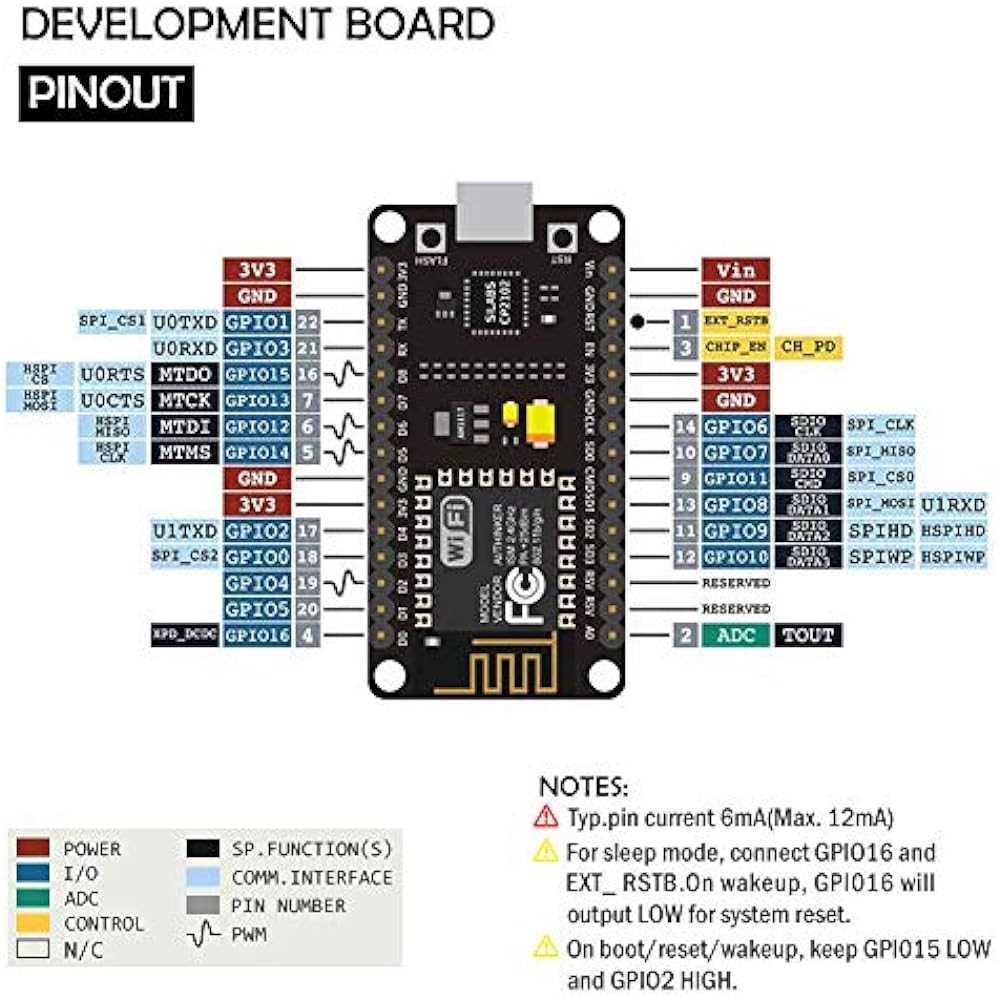
The pin layout of the device embodies a network of connections that facilitate input and output operations, serving as conduits for data transmission and control signals. Each pin exhibits unique characteristics, contributing to the versatility and adaptability of the system as a whole.
Functionality Analysis
Exploring the functionality of individual pins unveils a spectrum of capabilities ranging from digital input/output to analog signals and specialized functionalities such as pulse width modulation (PWM) and interrupt handling. Each pin plays a distinct role in enabling communication with external components and peripherals, amplifying the device’s potential for diverse applications.
Analyzing Electrical Characteristics
In this section, we delve into the intricate details of the electrical properties inherent in the device under scrutiny. Understanding these characteristics is paramount for comprehending the operational dynamics and ensuring optimal performance.
Voltage Parameters
The assessment of voltage parameters provides insights into the permissible operating ranges and the device’s resilience against fluctuations. By scrutinizing voltage thresholds, tolerance levels, and potential variations, one can gauge the device’s stability and suitability for diverse applications.
Current Specifications
Examining current specifications elucidates the device’s power consumption patterns, load handling capabilities, and overall efficiency. Analysis of input and output currents, along with their respective dependencies, enables a comprehensive evaluation of the device’s electrical behavior.
| Parameter | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Voltage Range | Permissible voltage range for normal device operation | 3.3V – 5.5V |
| Input Current | Current consumed by the device under normal operation | 10mA – 250mA |
| Output Current | Maximum current the device can source or sink | 12mA – 20mA |
Through meticulous examination and interpretation of these electrical characteristics, one can formulate informed decisions regarding the integration and utilization of the device in various electronic endeavors.