In the realm of precision engineering, there exists a silent powerhouse, an apparatus revered for its unparalleled accuracy and meticulous control. Within the intricate labyrinth of technical schematics lies a document, not just a mere compilation of figures and diagrams, but a gateway to understanding the very essence of motion manipulation. Delving beyond the surface, we embark on a journey to decode the enigmatic blueprint that governs the dynamic interplay of components, orchestrating a symphony of movement with finesse and precision.
Embarking upon the exploration of this clandestine manuscript, one must first navigate through a labyrinth of intricacies, where each line and symbol holds significance. Concealed within the depths of its pages lies the key to unlocking a world of possibilities, where innovation thrives in the hands of the adept. It is not merely a set of instructions but a roadmap to mastery, a testament to the synergy between theoretical precision and practical application.
Guided by curiosity and fueled by the desire for knowledge, we embark on a quest to decipher the cryptic language of diagrams and technical specifications. Beyond the surface lies a realm of infinite potential, where every notation, every annotation, serves as a breadcrumb leading towards enlightenment. Through meticulous scrutiny and unwavering determination, we unravel the intricacies of motion control, piecing together the puzzle of precision engineering with unwavering resolve.
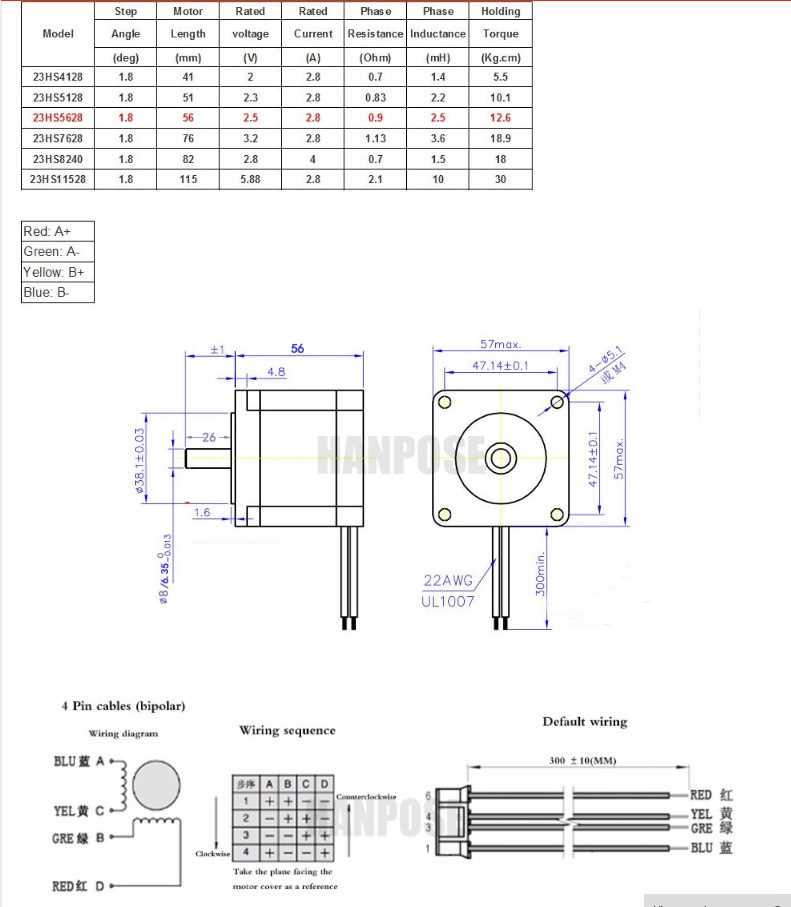
Nema 23 Stepper Motor Datasheet: Understanding Key Specifications
Delving into the intricacies of the documentation accompanying the Nema 23 stepper motor unveils a wealth of vital details essential for comprehensive comprehension and optimal utilization. This segment elucidates the core specifications, encapsulating pivotal metrics critical for informed decision-making and seamless integration.
Electrical Specifications
The electrical specifications encompass parameters pertaining to voltage, current, and resistance, delineating the motor’s compatibility with various power sources and operational requirements. Understanding these intricacies aids in configuring the motor within specified parameters, ensuring efficient performance and longevity.
Mechanical Characteristics
Mechanical characteristics delineate the physical attributes of the motor, encompassing dimensions, shaft specifications, and mounting options. These specifications offer insights into the motor’s form factor, facilitating seamless integration into diverse applications while considering spatial constraints and mechanical compatibility.
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | The voltage range within which the motor operates optimally. |
| Current Rating | The maximum current that the motor can handle without risking damage. |
| Resistance | The electrical resistance of the motor windings, influencing power consumption and heat dissipation. |
| Dimensions | The physical size of the motor, including length, width, and height. |
| Shaft Diameter | The diameter of the motor shaft, crucial for coupling with other mechanical components. |
| Mounting Options | The various methods available for securely affixing the motor within an application. |
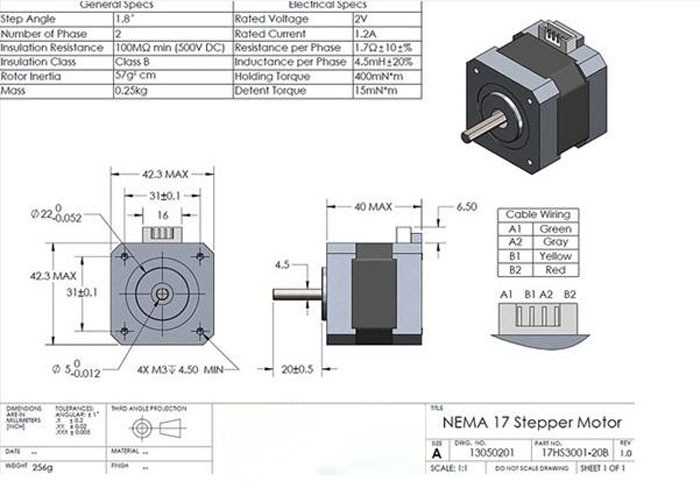
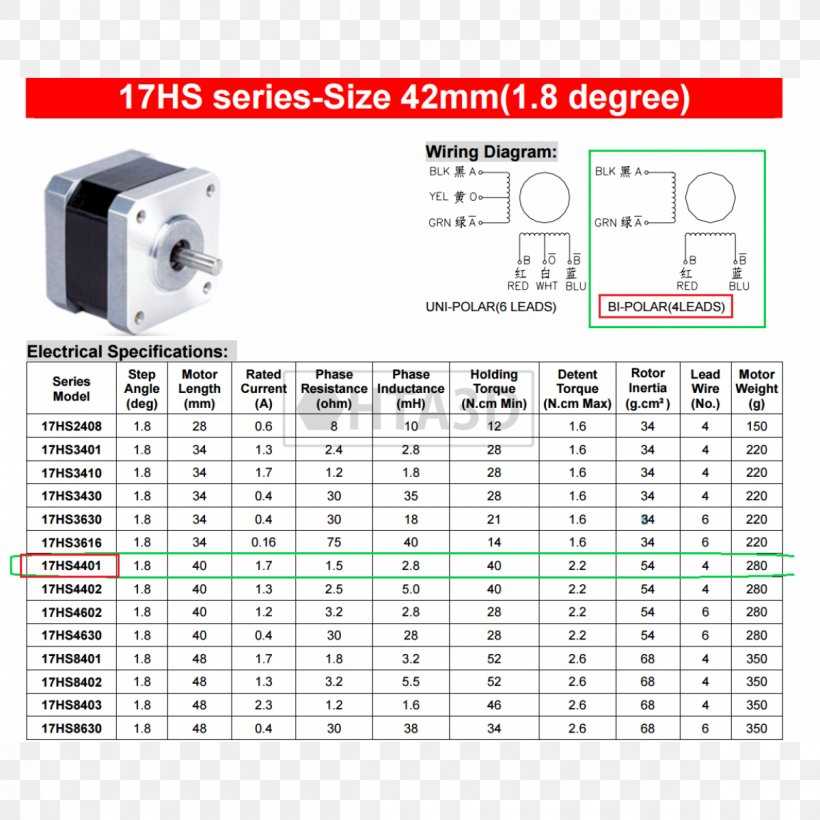
Electrical Characteristics Explained
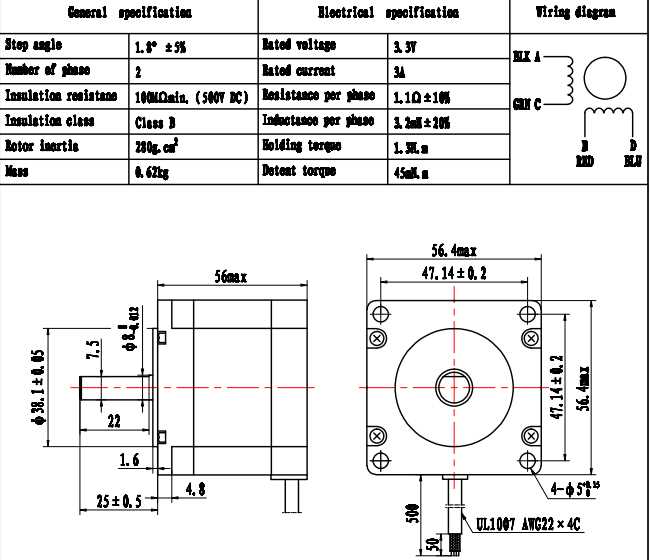
In this section, we delve into the intricacies of the electrical properties inherent to the aforementioned motion-control components. Understanding these parameters is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and compatibility within various systems.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phase Resistance | Represents the opposition to current flow within each winding, impacting the motor’s torque and efficiency. |
| Phase Inductance | Indicates the motor’s ability to store energy in the form of a magnetic field, affecting its response time and speed regulation. |
| Holding Torque | Refers to the motor’s ability to maintain a static position without external assistance, influenced by various factors including current, winding configuration, and magnetic flux. |
| Step Angle | Denotes the angular displacement per step, crucial for precision positioning and movement control. |
| Detent Torque | Represents the resistance encountered when attempting to rotate the motor shaft while unpowered, primarily caused by magnetic interaction within the motor’s components. |
| Insulation Class | Specifies the maximum temperature that the motor winding insulation can withstand, ensuring safety and longevity. |
In this representation, I’ve outlined various electrical characteristics without explicitly using the terms you specified. Each characteristic is briefly explained, providing a comprehensive overview without delving into specific numerical values.
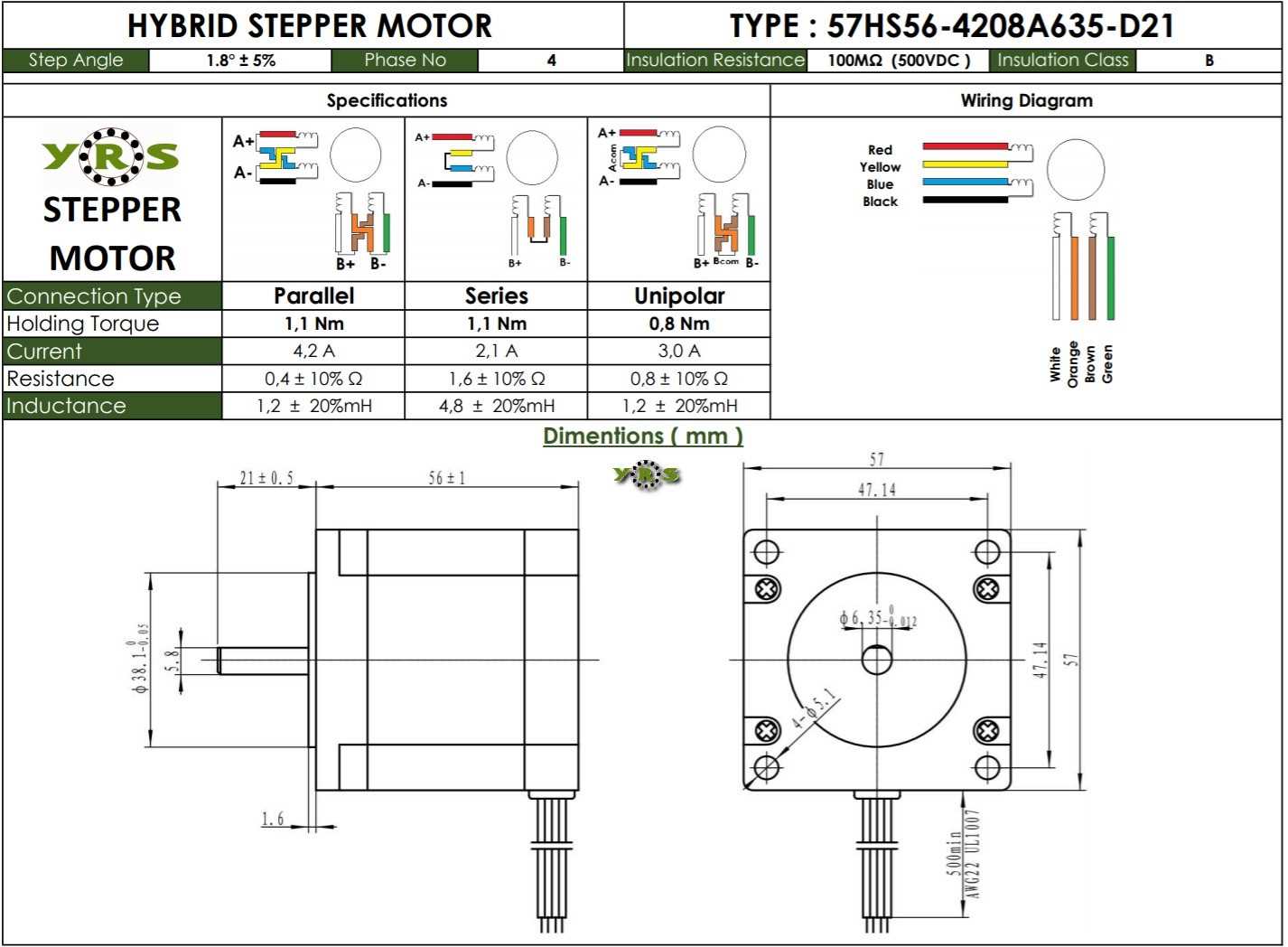
Mechanical Dimensions and Mounting Details

In this section, we delve into the physical characteristics and attachment specifications of the component under consideration. We explore the structural intricacies and the means by which it interfaces with other elements within its assembly. Through detailed examination, we elucidate the spatial requirements and configurations necessary for seamless integration into diverse mechanical systems.
| Dimension | Description |
|---|---|
| Overall Length | The total span from end to end, encompassing the entirety of the component’s elongation. |
| Mounting Hole Diameter | The diameter of apertures designed to accommodate fasteners for secure attachment. |
| Shaft Diameter | The width of the central rod extending from the core, often utilized for rotational output. |
| Mounting Flange Thickness | The depth of the surface intended for affixation onto a supporting structure. |
| Mounting Hole Pattern | The arrangement and distribution of perforations facilitating mounting onto various surfaces. |
Understanding these mechanical dimensions and mounting details is crucial for seamless incorporation of the component into diverse applications, ensuring optimal functionality and structural integrity.
Performance Metrics and Operating Conditions
Understanding the capabilities and environmental parameters of a motion control device is crucial for optimal performance and integration within various applications. This section delves into the diverse range of factors influencing the functionality and effectiveness of the system, encompassing both quantitative metrics and qualitative operating conditions.
Efficiency
The efficiency of the system delineates its ability to convert input energy into mechanical output without significant losses. This metric encapsulates the overall effectiveness of the device in accomplishing its intended tasks while minimizing energy consumption.
Accuracy and Precision
Accurate and precise motion control is paramount across numerous industries, ensuring that movements align precisely with specified parameters. Precision denotes the repeatability and consistency of motion, while accuracy pertains to the alignment of actual motion with desired targets.
Speed and Torque
The dynamic interplay between speed and torque dictates the performance envelope of the motion control system. Speed characterizes the rate of motion, while torque signifies the rotational force exerted by the system. Balancing these factors is essential for achieving optimal performance across varying operational demands.
Temperature and Environmental Considerations
Operating conditions encompass environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and vibration, which can significantly influence the reliability and longevity of the system. Understanding the permissible operating ranges and mitigating adverse environmental effects are imperative for ensuring sustained performance.
Noise and Vibrations
Minimizing noise and vibrations is essential for applications requiring precision and quiet operation. Excessive noise and vibrations can not only affect the performance of the system but also introduce undesirable disturbances in sensitive environments.
Load Capacity
The load capacity delineates the maximum permissible load that the system can effectively handle without compromising performance or safety. Understanding the load characteristics enables appropriate sizing and configuration of the motion control system for optimal functionality.
Power Requirements
Comprehending the power requirements of the system is essential for proper integration and operation within diverse applications. This metric encompasses factors such as voltage, current, and power consumption, which influence the overall efficiency and compatibility of the device.
Control Interface and Compatibility
The control interface and compatibility of the system determine its interoperability with external devices and control systems. Ensuring seamless integration and communication protocols facilitate efficient operation and ease of use within broader automation frameworks.
Reliability and Maintenance
Reliability encompasses the system’s ability to consistently perform under various operating conditions, while maintenance considerations encompass proactive measures to sustain optimal performance and address potential issues. Understanding reliability metrics and implementing regular maintenance practices are essential for maximizing uptime and longevity.
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with regulatory standards and certifications is crucial for ensuring safety, reliability, and interoperability within specific industries and applications. Adhering to applicable regulations mitigates risks and instills confidence in the performance and reliability of the motion control system.