
Delving into the intricacies of a pivotal component, this article embarks on a journey to dissect the specifications of a remarkable sensor. Embedded within its technical nuances lies a wealth of information crucial for understanding its functionality and applications. Through a meticulous exploration, we unravel the intricacies of this sensor, shedding light on its capabilities and potential.
Embarking on this voyage, we navigate through the labyrinth of specifications, deciphering the language of sensors and their inherent intricacies. Beyond mere numbers and figures, each specification holds a story, revealing the sensor’s prowess and versatility in various scenarios. By peering into its specifications, we gain insight into its performance, accuracy, and adaptability, empowering us to harness its capabilities to the fullest.
Join us as we embark on a quest, unraveling the enigma of this sensor’s specifications. Through this exploration, we aim to equip you with a deeper understanding of its functionality and unleash its potential across diverse fields and applications.
The Essentials of Understanding Mpx5010gp Documentation

When delving into the intricacies of electronic components, it’s essential to grasp the foundational aspects of their technical documentation. Within the realm of sensors and pressure measurement, comprehending the nuances of the Mpx5010gp datasheet is paramount for engineers and enthusiasts alike.
Deciphering Technical Specifications

Understanding the specifications entails more than just perusing a list of numerical values; it involves discerning the underlying functionality and performance parameters. These specifications serve as the blueprint for integrating the sensor into diverse applications, guiding users on its operational capabilities.
Navigating Application Notes and Usage Guidelines
Exploring application notes and usage guidelines provides invaluable insights into maximizing the potential of the sensor. These resources offer practical examples, tips, and considerations for optimizing performance while ensuring reliability and longevity in various scenarios.
Understanding the Specifications

In delving into the intricacies of this sensor’s documentation, we embark on a journey to decipher the nuanced language that delineates its capabilities and limitations. By comprehending the specifications provided, we gain insight into the sensor’s operational parameters, enabling informed decisions regarding its utilization.
Sensitivity: The sensitivity of the sensor elucidates its responsiveness to changes in the applied pressure, offering a measure of its ability to detect minute variations.
Operating Range: The operating range delineates the span within which the sensor can reliably measure pressure, encompassing both its lower and upper limits.
Accuracy: Accuracy denotes the degree of conformity between the sensor’s output and the true value of the measured pressure, portraying its precision and reliability.
Resolution: Resolution characterizes the smallest discernible change in pressure that the sensor can detect, providing insight into its granularity of measurement.
Response Time: The response time delineates the duration required for the sensor to register a change in pressure and produce a corresponding output signal, influencing its real-time responsiveness.
Temperature Sensitivity: Temperature sensitivity elucidates the sensor’s susceptibility to variations in ambient temperature, highlighting its thermal stability and compensatory mechanisms.
Output Type: The output type specifies the format of the signal produced by the sensor, whether analog or digital, shaping compatibility with interfacing circuits and systems.
Supply Voltage: Supply voltage denotes the range of voltages within which the sensor operates optimally, ensuring compatibility with power sources and facilitating integration into diverse applications.
By unraveling the intricacies of these specifications, one can navigate the realm of sensor applications with clarity and precision, harnessing its capabilities to fulfill a myriad of sensing requirements.
Application Circuit Design Tips

In this section, we’ll delve into essential guidelines for crafting effective application circuit designs utilizing the components outlined in the provided documentation. Understanding the intricacies of circuit design is pivotal for achieving optimal performance and reliability in diverse applications. By integrating prudent design practices and leveraging the inherent characteristics of the components, engineers can streamline functionality and enhance overall system efficiency.
1. Consideration of Component Interaction: When devising an application circuit, it’s imperative to analyze how various components interact within the system. Pay close attention to voltage levels, current requirements, and signal integrity to ensure seamless integration and compatibility.
2. Voltage Regulation and Signal Conditioning: Implement robust voltage regulation techniques to maintain stable operating conditions and mitigate fluctuations that could compromise performance. Additionally, incorporate effective signal conditioning mechanisms to enhance signal accuracy and integrity, thereby optimizing the overall functionality of the circuit.
3. Noise Reduction Strategies: Noise can significantly impact circuit performance, leading to erroneous readings or erratic behavior. Employ noise reduction strategies such as filtering and shielding to minimize external interference and maintain signal fidelity throughout the system.
4. Thermal Management: Efficient thermal management is crucial for preventing overheating and ensuring long-term reliability. Integrate heat sinks, thermal pads, or other cooling mechanisms as necessary to dissipate heat and maintain optimal operating temperatures for all components.
5. Layout Optimization: Carefully design the physical layout of the circuit to minimize signal distortion, reduce parasitic effects, and facilitate ease of assembly and maintenance. Strategic placement of components and thoughtful routing of traces can significantly enhance overall performance and longevity.
6. Robustness and Resilience: Anticipate potential failure points and implement redundancy or protective measures to enhance the robustness and resilience of the circuit. By incorporating fail-safe mechanisms and adhering to industry best practices, engineers can mitigate risks and improve overall system reliability.
7. Compliance and Standards: Ensure compliance with relevant industry standards and regulatory requirements to guarantee the safety, reliability, and interoperability of the final product. Thorough testing and validation procedures are essential to confirm adherence to specifications and identify any potential compliance issues.
By conscientiously applying these application circuit design tips, engineers can navigate the complexities of component integration and system optimization, ultimately delivering robust and reliable solutions tailored to specific application requirements.
Calibration and Compensation Techniques
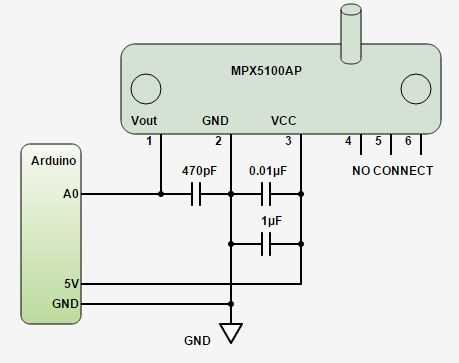
In the realm of sensor technology exploration, the pursuit of accuracy and reliability is paramount. This section delves into the intricate realm of calibration and compensation techniques, where the focus lies on refining and enhancing sensor performance without resorting to the rigidity of predetermined specifications. By employing innovative methods, this section elucidates strategies to mitigate inaccuracies and fluctuations inherent in sensor measurements.
Temperature Compensation

One fundamental aspect of sensor calibration involves temperature compensation. Temperature variations can significantly impact sensor readings, introducing errors that compromise data integrity. Through sophisticated algorithms and thermal management techniques, temperature-induced inaccuracies can be mitigated, ensuring consistent and reliable sensor output across diverse operating conditions.
Offset Nulling and Gain Adjustment

Another vital facet of sensor calibration encompasses offset nulling and gain adjustment. Imperfections within sensor circuitry can lead to offset errors and non-linear response characteristics. Through meticulous calibration procedures, these imperfections are rectified by nulling offsets and fine-tuning gain parameters. By optimizing sensor performance in this manner, enhanced accuracy and linearity are achieved, bolstering the sensor’s utility across a spectrum of applications.
| Technique | Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Compensation | Improved accuracy across varying thermal conditions | Complex algorithms and thermal management required |
| Offset Nulling and Gain Adjustment | Enhanced linearity and reduced offset errors | Requires meticulous calibration procedures |