Delving into the intricacies of a certain technological marvel, one finds a wealth of possibilities awaiting exploration. In the realm of electronic components, there exists a cornerstone, a silent hero that bridges the realms of digital communication with seamless efficacy. This enigmatic catalyst, with its myriad of applications and subtle nuances, serves as the linchpin for countless devices and systems.
Discovering the essence of this silent guardian, one unravels a tapestry of connectivity, where signals traverse vast distances with unparalleled reliability. Its role extends beyond mere functionality, permeating the very fabric of modern electronics, weaving a narrative of efficiency and resilience.
Embark on a journey to unearth the secrets concealed within its datasheets, where each specification, each parameter, hints at the immense potential lying dormant within. Through meticulous scrutiny and discerning analysis, one can unlock the gateway to innovation, ushering in a new era of technological prowess.
Understanding the Specifications and Key Attributes of the MAX3232CD

In delving into the intricacies of the MAX3232CD documentation, it’s imperative to navigate through its labyrinth of specifications and features with clarity and precision. This section aims to unravel the essential elements encapsulated within the datasheet, shedding light on the pivotal attributes that define its functionality and performance.
Key Features
The MAX3232CD epitomizes a myriad of functionalities, encompassing a spectrum of features designed to cater to diverse application needs. From robust voltage regulation to seamless interface compatibility, each attribute contributes to its versatility and reliability.
Specifications Overview
A meticulous examination of the MAX3232CD specifications unveils a comprehensive framework dictating its operational parameters and limits. Ranging from electrical characteristics to mechanical dimensions, these specifications serve as the cornerstone for seamless integration and optimal utilization within electronic systems.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | Defines the permissible voltage range for stable operation. |
| Data Rate | Specifies the maximum data transmission speed supported. |
| Operating Temperature | Indicates the temperature range within which the device operates efficiently. |
| Package Type | Describes the physical package configuration for mounting and integration. |
By dissecting these specifications and features, a holistic understanding of the MAX3232CD emerges, empowering engineers and enthusiasts alike to leverage its capabilities effectively.
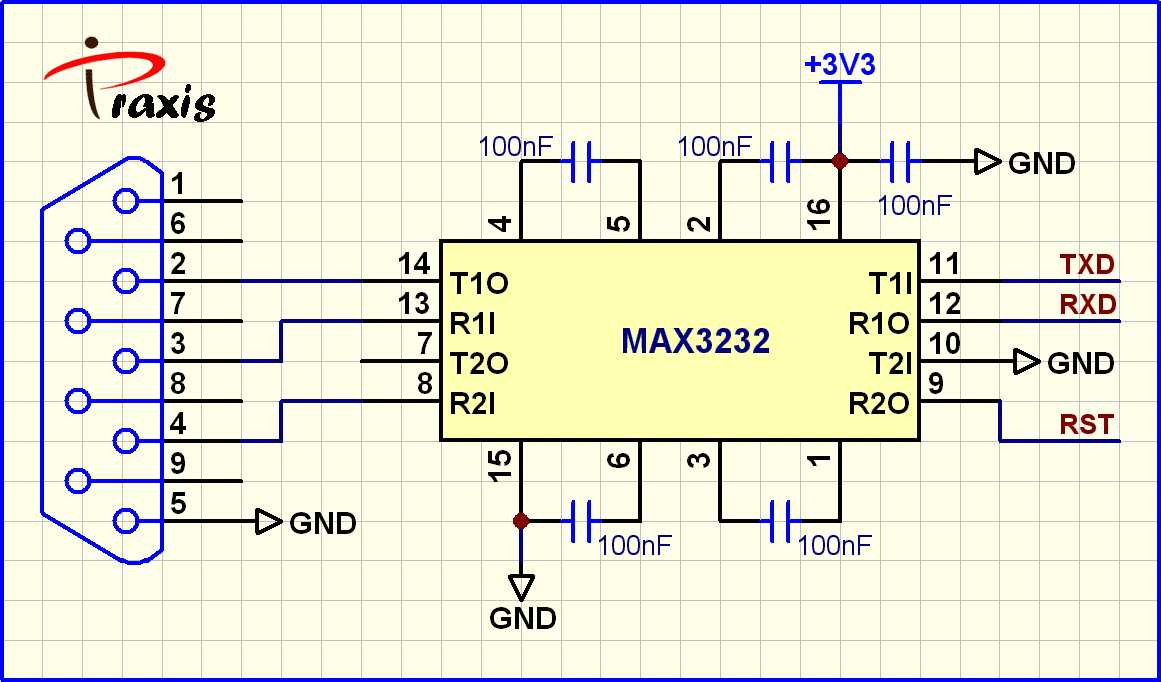
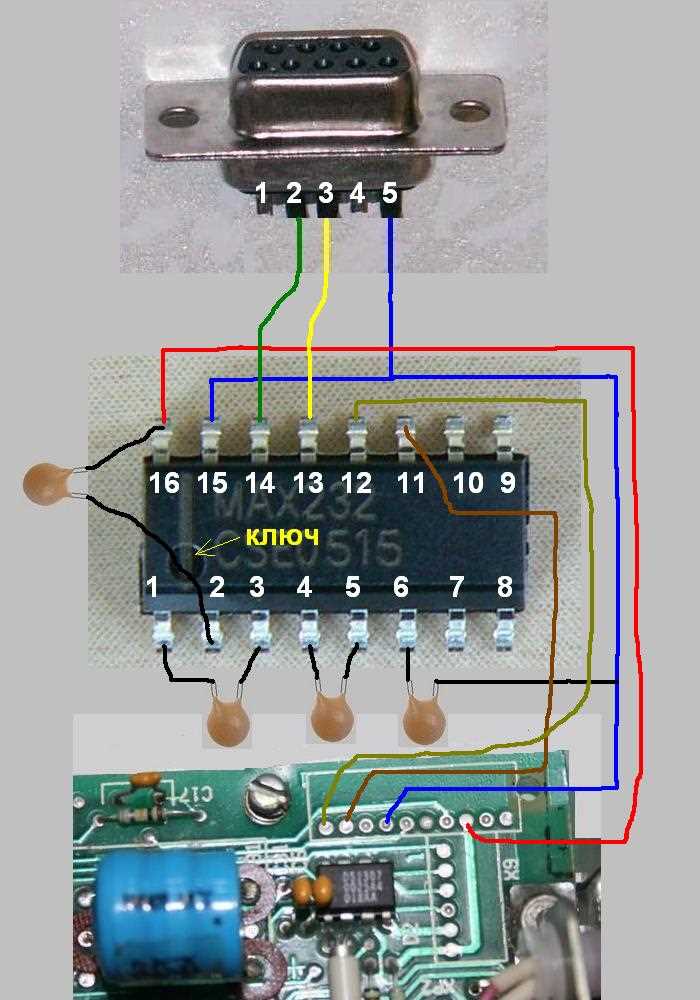
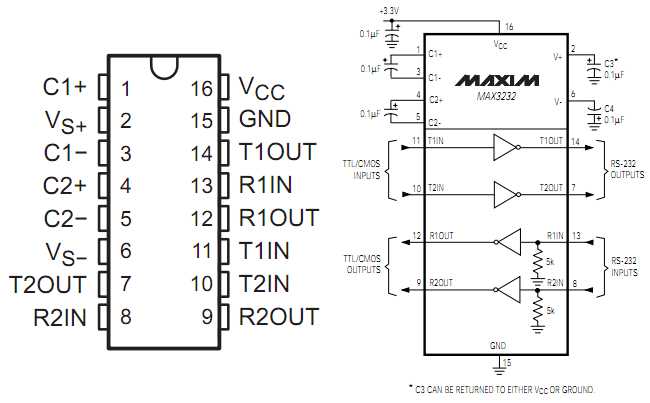
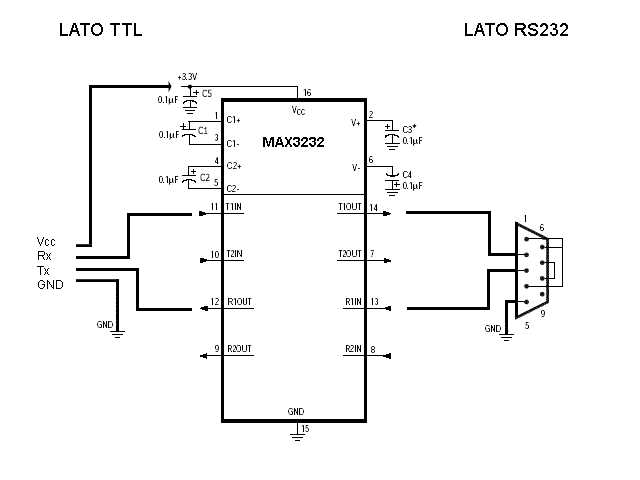
Exploring the Functional Overview and Pin Configuration
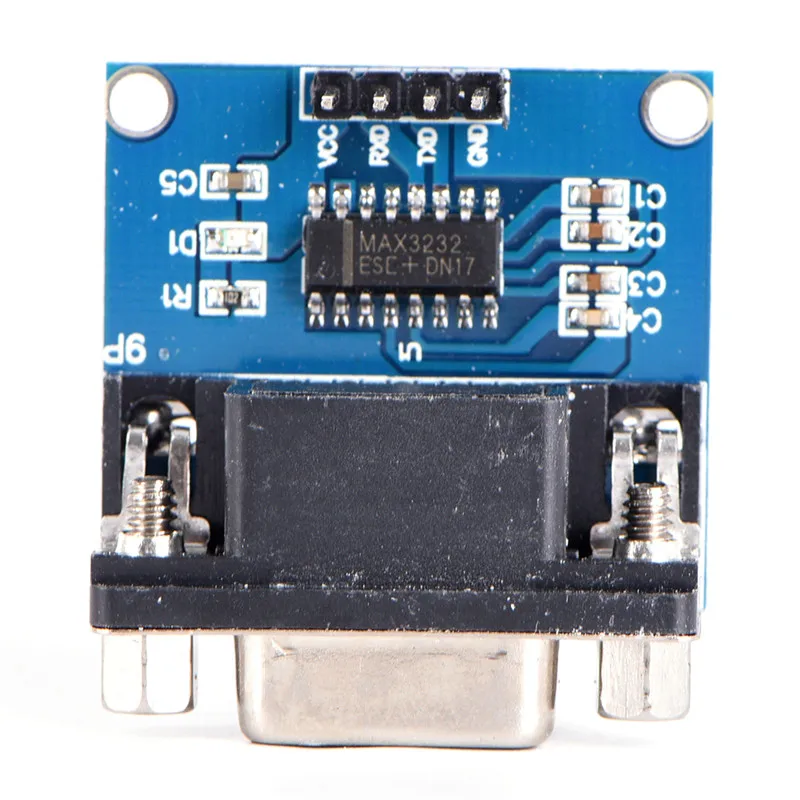

In this section, we delve into the operational principles and arrangement of connectors of a specific integrated circuit, providing a comprehensive understanding of its functionality and physical layout.
Understanding the Functional Overview: Before delving into the specifics of pin configuration, it’s crucial to grasp the overarching functions and operational principles of the integrated circuit. This entails comprehending its primary tasks, signal processing capabilities, and interaction with external components.
Exploring Pin Configuration: With a foundational understanding of its functionality, we proceed to dissect the pin configuration, elucidating the roles and connections of each pin. This entails identifying power supply pins, data input/output pins, ground connections, and any specialized pins for particular functions.
Analyzing Signal Flow: An integral aspect of understanding the pin configuration involves analyzing the flow of signals within the integrated circuit. This involves tracing the path of data, voltage, and other signals through the various pins and internal circuitry, elucidating how information is processed and transmitted.
Examining Pin Functions: Each pin serves a specific function within the integrated circuit ecosystem. By examining datasheets and technical documentation, we can discern the purpose of each pin, whether it’s facilitating data transmission, receiving control signals, or providing power.
Optimizing Connectivity: Understanding the pin configuration isn’t merely an exercise in comprehension but also an opportunity for optimization. By strategically connecting external components to the appropriate pins, engineers can maximize performance, mitigate interference, and ensure seamless integration within larger systems.
Conclusion: Through a detailed exploration of the functional overview and pin configuration, we equip ourselves with the knowledge necessary to leverage the capabilities of the integrated circuit effectively. This deeper understanding not only facilitates troubleshooting and debugging but also fosters innovation in circuit design and application.
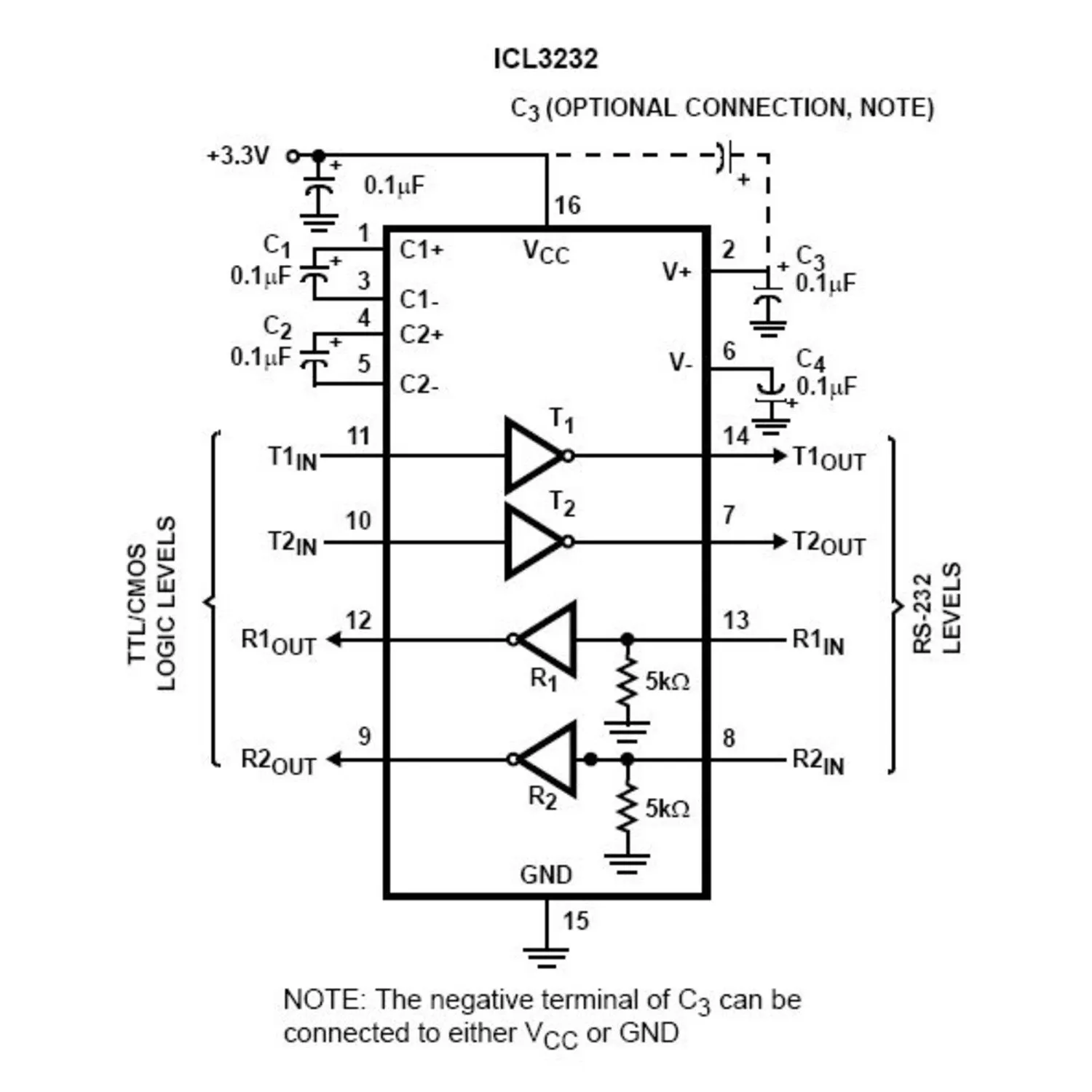
Interpreting Electrical Characteristics and Performance Ratings
Understanding the intricacies of electrical specifications and performance evaluations is crucial for effectively utilizing electronic components. In this section, we delve into the comprehensive analysis of the electrical characteristics and performance ratings of the component under scrutiny. By deciphering these specifications, engineers and enthusiasts can gain profound insights into its functionality, limitations, and compatibility within various circuits and systems.
Key Parameters
Before delving into the nuances of interpreting electrical characteristics, it’s imperative to grasp the significance of key parameters. These parameters encompass a spectrum of attributes, including voltage tolerance, current handling capacity, signal propagation delay, power consumption, and environmental operating conditions. Each parameter plays a pivotal role in defining the component’s behavior under diverse operating scenarios.
Evaluating Performance Ratings
Performance ratings encapsulate the component’s ability to meet specified criteria under predefined conditions. This entails scrutinizing parameters such as operating frequency range, signal integrity, noise immunity, and efficiency. By meticulously evaluating performance ratings, engineers can ascertain the component’s suitability for specific applications and ensure optimal performance within desired parameters.
- Voltage Tolerance: Refers to the maximum and minimum voltage levels the component can withstand without malfunctioning.
- Current Handling Capacity: Indicates the maximum current the component can safely conduct without exceeding its operational limits.
- Signal Propagation Delay: Measures the time taken for a signal to travel through the component, influencing system response times.
- Power Consumption: Reflects the amount of electrical power consumed by the component during operation, impacting overall energy efficiency.
By comprehensively analyzing these parameters and performance ratings, engineers can make informed decisions regarding component selection, circuit design, and system integration, thereby ensuring robust and reliable electronic systems.
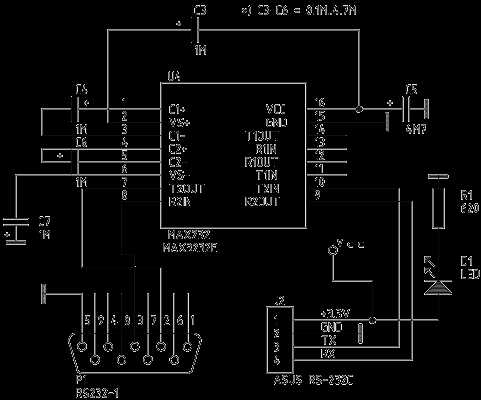
Application Circuit Design Insights and Troubleshooting Strategies
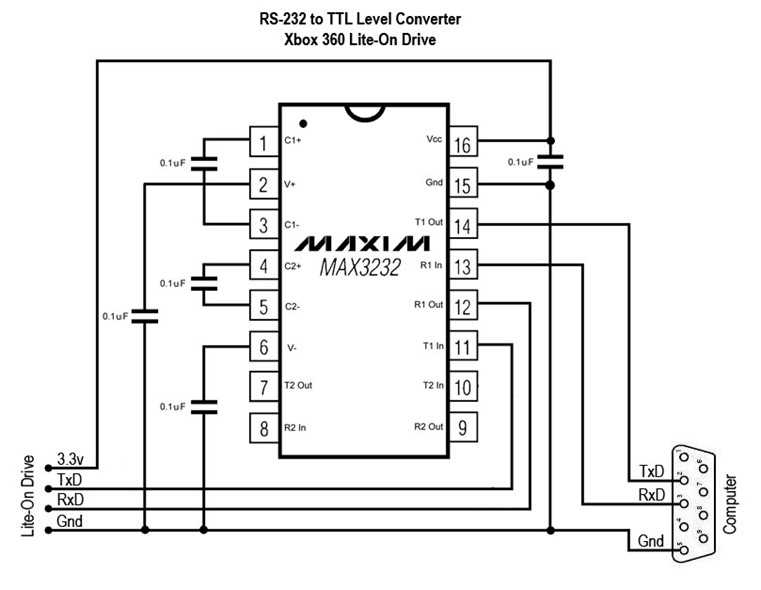
In this section, we delve into essential insights and strategies for crafting effective application circuit designs while addressing common troubleshooting scenarios. Understanding the intricate nuances of circuit design and troubleshooting is paramount for ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Understanding Circuit Dynamics
1. Component Selection: The selection of components plays a pivotal role in determining the overall performance of the circuit. Paying meticulous attention to parameters such as voltage ratings, current handling capabilities, and frequency response is imperative. Additionally, consider factors like temperature coefficients and tolerance levels to ensure compatibility and reliability.
2. Signal Integrity: Maintaining signal integrity throughout the circuit is crucial for preventing data corruption and signal degradation. Employing proper grounding techniques, minimizing parasitic capacitance and inductance, and optimizing signal routing are effective strategies for preserving signal integrity.
Troubleshooting Strategies
1. Systematic Analysis: When encountering circuit malfunctions, adopt a systematic approach to isolate and diagnose the root cause of the issue. Begin by examining power supply connections, checking for short circuits or open circuits, and verifying component values against specifications.
2. Signal Tracing: Utilize signal tracing techniques to pinpoint areas of potential signal degradation or loss. Employ oscilloscopes, signal analyzers, and probing tools to trace the signal path, identify anomalies, and assess signal quality at various points within the circuit.
By integrating these design insights and troubleshooting strategies, engineers can develop robust application circuits that exhibit superior performance and reliability across diverse operational environments.