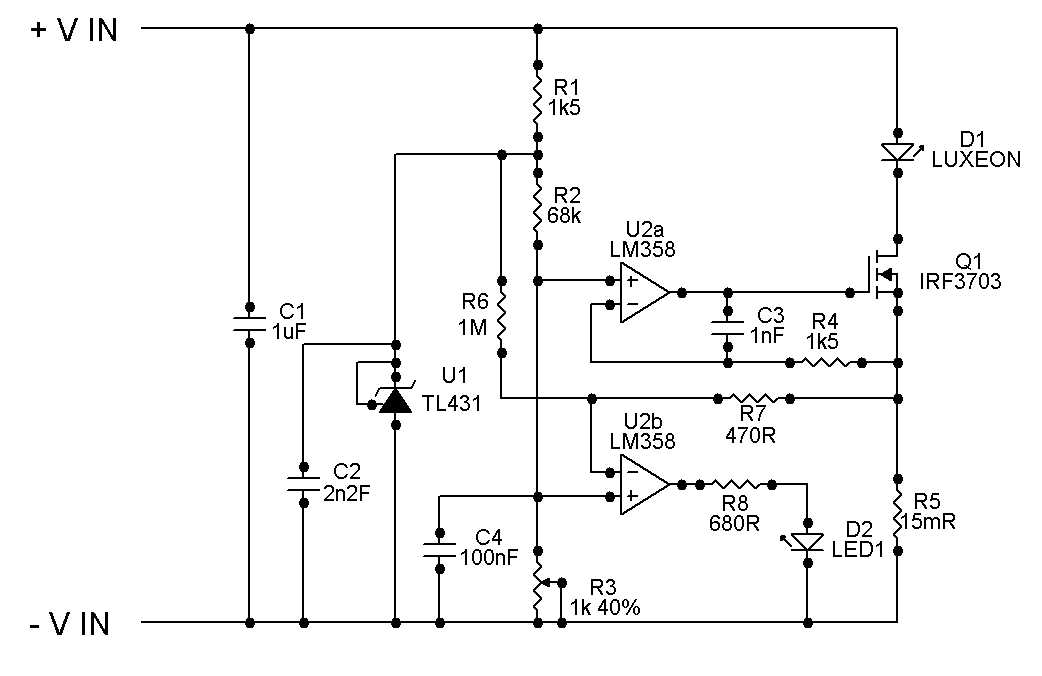
In the realm of electronic components, there exists a vast repository of technical documentation that serves as the guiding light for engineers and enthusiasts alike. These documents are more than mere compilations of specifications and diagrams; they encapsulate the essence of innovation and the promise of technological advancement. Within these pages, enthusiasts uncover the blueprints of creativity, while engineers find the building blocks of their next masterpiece.
Delving into the intricacies of these documents, one discovers a treasure trove of insights waiting to be unveiled. Each line of text, each diagram, and each specification holds the potential to spark ingenuity and fuel imagination. It’s a narrative of precision, where every detail matters, and every measurement carries significance. Beyond the technical jargon lies a story of possibilities, waiting to be deciphered by those with the curiosity to explore.
As we embark on a journey through the labyrinth of electronic documentation, we peel back the layers of complexity to reveal the core principles that underpin modern technology. It’s a voyage of discovery, where knowledge serves as the compass, and innovation as the destination. Join us as we navigate through the realms of electronic components, uncovering the secrets hidden within the pages of technical documentation.
Understanding the Specifications of the LM358DT Integrated Circuit

In dissecting the intricacies of the LM358DT integrated circuit, it becomes imperative to delve into its fundamental specifications. These delineate the performance parameters and operational characteristics essential for comprehending its functionality and application scope.
Operational Parameters:
The LM358DT embodies a set of pivotal operational parameters that define its behavior within diverse circuit configurations. These parameters encapsulate crucial aspects such as input offset voltage, input bias current, and slew rate, among others. Understanding these intricacies is fundamental for optimal integration and performance.
Performance Characteristics:
Examining the performance characteristics unveils the dynamic behavior of the LM358DT under varying operational conditions. Key metrics include gain bandwidth product, open-loop gain, and common-mode rejection ratio. Mastery of these metrics facilitates the design and optimization of circuits leveraging the LM358DT.
Electrical Specifications:
Exploring the electrical specifications elucidates the LM358DT’s response to electrical stimuli across its operational range. Parameters such as supply voltage range, output voltage swing, and power consumption delineate its electrical behavior, providing crucial insights for circuit design and integration.
Temperature Dependencies:
The LM358DT’s performance is intrinsically tied to temperature variations, necessitating a meticulous examination of its thermal characteristics. Parameters such as thermal resistance and operating temperature range delineate its thermal behavior, guiding thermal management strategies for reliable operation.
Application Considerations:
Translating the specifications into practical applications requires a nuanced understanding of the LM358DT’s capabilities and limitations. Considerations such as input and output configurations, as well as recommended operating conditions, empower designers to harness the full potential of the LM358DT in diverse applications.
Conclusion:
Comprehending the key specifications of the LM358DT integrated circuit is pivotal for its effective utilization in diverse electronic applications. By delving into its operational parameters, performance characteristics, electrical specifications, temperature dependencies, and application considerations, designers can unlock its full potential and realize innovative circuit solutions.
Exploring the Technical Specifications
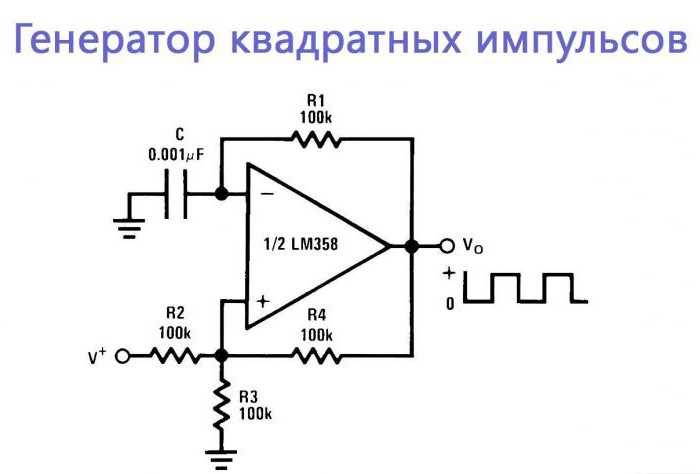
In this section, we delve into the intricate details and specifications that characterize the electronic component under scrutiny. By dissecting its operational parameters and performance metrics, we gain a comprehensive understanding of its functionality and potential applications.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Input Offset Voltage | Refers to the inherent voltage differential required between the input terminals for the device to function optimally. |
| Input Bias Current | Denotes the minimal current flowing into the input terminals necessary for proper operation. |
| Common Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR) | Expresses the capability of the component to reject signals that are common to both input terminals. |
| Gain Bandwidth Product | Represents the product of the device’s open-loop voltage gain and its bandwidth, indicative of its frequency response characteristics. |
| Slew Rate | Specifies the rate at which the output voltage of the component can change in response to a step input signal. |
| Supply Voltage Range | Defines the permissible range of voltage levels that can be applied to power the component. |
By meticulously examining these technical specifications, engineers can ascertain the suitability of the component for diverse electronic circuit designs and ensure optimal performance in various operating conditions.
Key Electrical Characteristics and Ratings
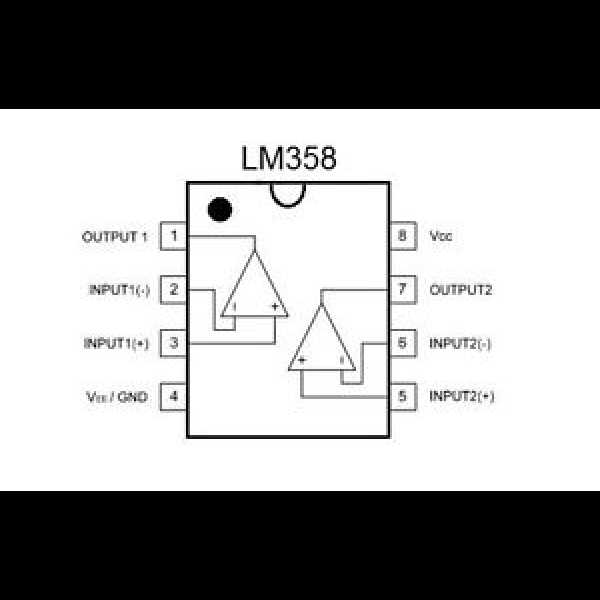
In this section, we delve into the fundamental electrical properties and performance parameters crucial for understanding the operational behavior and limitations of the LM358DT integrated circuit. These characteristics and ratings encapsulate the device’s capability to process electrical signals, maintain stability under varying conditions, and ensure reliable operation within specified limits.
| Parameter | Description | Symbol | Conditions | Typical Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply Voltage | The range of voltage levels required to power the device. | VCC | Operating | ± 1.5 to ± 18 | V |
| Input Offset Voltage | The voltage difference needed between the input terminals for the output to be zero. | VIO | Common Mode | 2 | mV |
| Input Bias Current | The average current drawn into the input terminals when no external input voltage is applied. | IB | VCM = 0V | 45 | nA |
| Common Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR) | The ability of the device to reject common-mode signals. | CMRR | 1 kHz | 70 | dB |
| Output Voltage Swing | The range of output voltage levels the device can produce. | VOUT | RL = 10kΩ | 0 to VCC-1.5 | V |
These parameters collectively define the operational boundaries and performance benchmarks for the device, influencing its suitability for various analog signal processing applications.
Applications of LM358DT: Practical Implementations

Exploring the versatile applications of this integrated circuit unveils a spectrum of practical implementations, demonstrating its adaptability across various domains. From signal processing to voltage regulation, the LM358DT facilitates seamless integration in diverse electronic systems, enhancing functionality and efficiency.
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Signal Conditioning | By fine-tuning input signals, the LM358DT aids in optimizing sensor data for accurate measurements in fields such as environmental monitoring and industrial automation. |
| Comparator Circuits | Utilizing its precision voltage comparators, the LM358DT enables the creation of robust comparator circuits for tasks like level detection and motor control, ensuring reliable operation in various systems. |
| Active Filters | With its operational amplifier functionality, the LM358DT facilitates the implementation of active filter designs, crucial for noise reduction and frequency shaping in audio and communication systems. |
| Feedback Control Systems | Integrated within feedback loops, this IC supports the stabilization and regulation of systems, enhancing performance in applications ranging from power supplies to temperature control. |
| Instrumentation Amplifiers | Through its differential input configuration, the LM358DT serves as a building block for instrumentation amplifiers, amplifying small signals while rejecting common-mode noise, essential in precise measurement devices. |
These are just a few examples illustrating the breadth of practical implementations achievable with the LM358DT, showcasing its pivotal role in modern electronic circuits.
Utilizing LM358DT in Signal Conditioning Circuits
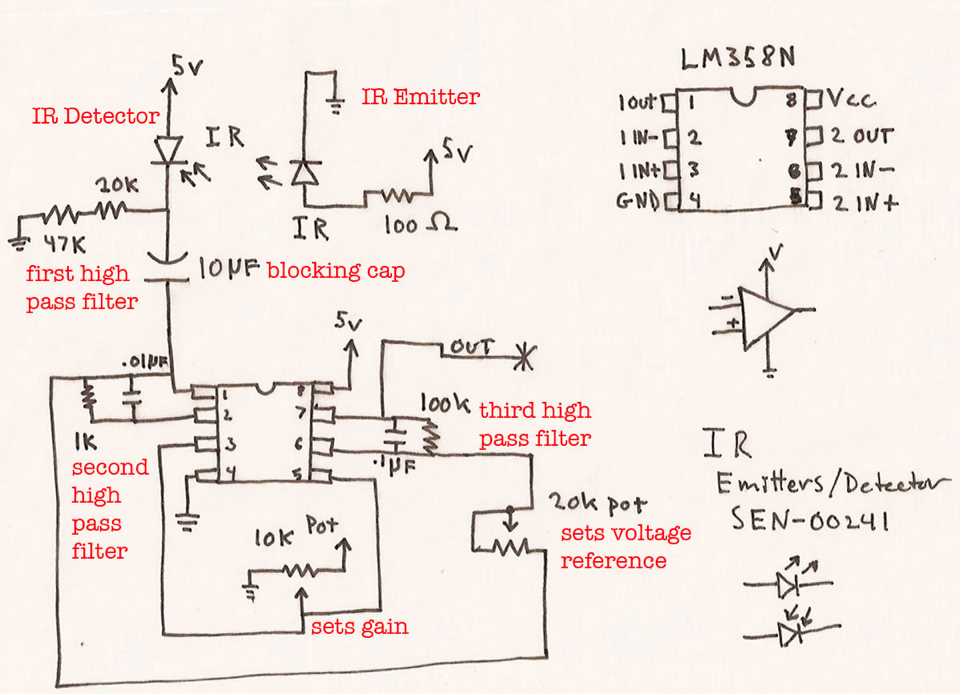
Signal conditioning circuits play a crucial role in optimizing the performance of electronic systems by modifying, filtering, or amplifying signals to meet specific requirements. In this section, we explore the application of a versatile operational amplifier – the LM358DT – in signal conditioning tasks. Operational amplifiers serve as fundamental building blocks in signal processing, offering precise control over signal characteristics without the need for complex circuitry.
Introduction to LM358DT
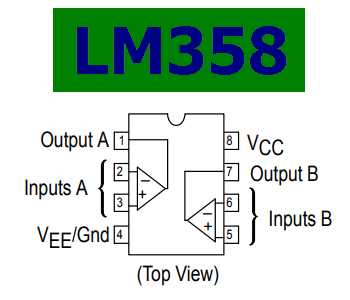
The LM358DT, a dual operational amplifier, facilitates signal conditioning through its ability to amplify weak signals, adjust signal levels, and filter unwanted noise. With its wide input voltage range and high slew rate, the LM358DT provides flexibility and efficiency in various signal processing applications.
In signal conditioning circuits, the LM358DT serves as a reliable component for tasks such as voltage amplification, current-to-voltage conversion, and active filtering. Its low input offset voltage and low quiescent current make it suitable for precision signal processing, ensuring minimal distortion and accurate signal representation.
Applications of LM358DT in Signal Conditioning
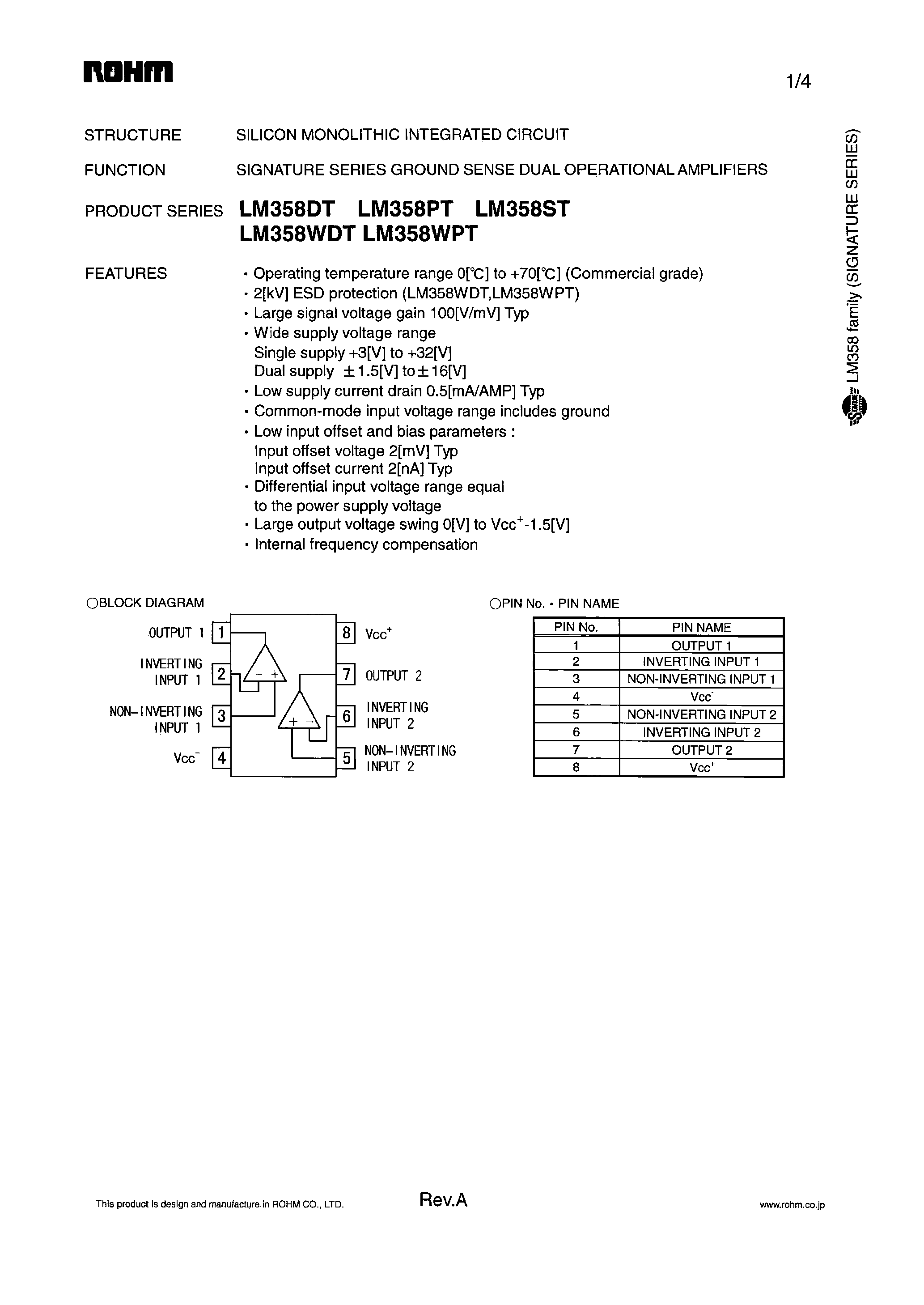
The LM358DT finds extensive use in signal conditioning circuits across diverse industries, including sensor interfacing, audio processing, and instrumentation. In sensor interfacing applications, it acts as a buffer amplifier, isolating the sensor output from the load while amplifying the signal to match the input range of subsequent stages.
Moreover, in audio processing systems, the LM358DT facilitates impedance matching, signal filtering, and volume control, enhancing audio fidelity and clarity. Its compatibility with various passive and active components enables the implementation of tailored signal conditioning solutions to meet specific audio requirements.
Furthermore, in instrumentation circuits, the LM358DT contributes to signal conditioning by providing gain control, offset adjustment, and signal isolation functionalities. Its robust design and low distortion characteristics make it ideal for precise measurement and analysis tasks, ensuring reliable data acquisition in demanding environments.
| Feature | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Wide input voltage range | Facilitates compatibility with diverse signal sources |
| Low input offset voltage | Ensures high accuracy in signal processing |
| High slew rate | Enables rapid response to dynamic signals |
| Low quiescent current | Minimizes power consumption in battery-powered applications |
In summary, the LM358DT serves as a versatile and efficient solution for signal conditioning tasks, offering precise control over signal characteristics and ensuring optimal performance in electronic systems.