Within the realm of electronic instrumentation lies a realm of paramount significance: the realm where minute fluctuations in ambient conditions are meticulously monitored, analyzed, and responded to. In this domain, the pursuit of accuracy is relentless, and the tools employed are as diverse as the phenomena they measure. Imagine a device so finely tuned, so intricately designed, that it serves as the silent sentinel, capturing the nuances of environmental warmth with unparalleled precision.
Delving into the intricacies of environmental monitoring unveils a world where subtlety reigns supreme. It is a landscape where the slightest variation in temperature holds the potential to alter outcomes, where the ability to discern minuscule shifts is paramount. This pursuit of subtlety births a class of devices that serve as the vanguards of precision measurement, each one a testament to human ingenuity in the face of natural variability.
At the heart of this pursuit lies a cornerstone technology, a marvel of engineering that stands as a testament to the relentless quest for accuracy. It is a device that transcends mere measurement, delving into the realm of inference and analysis. Within its compact form resides the ability to translate thermal fluctuations into tangible data, empowering systems to adapt, react, and evolve in response to their surroundings.
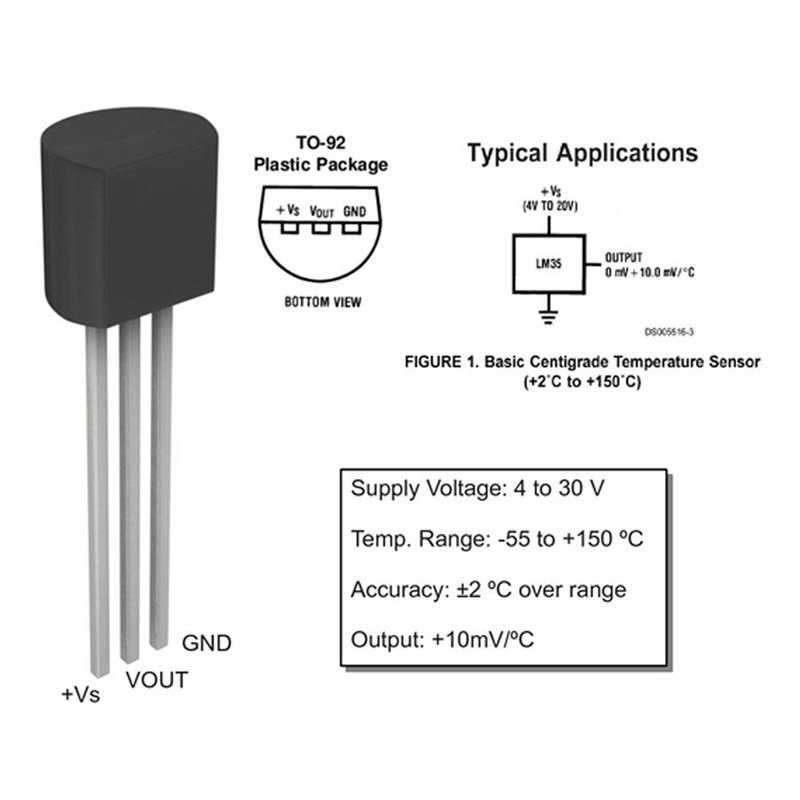
The Essentials of LM335 Temperature Sensor Documentation
In the realm of electronic components, there exists a small yet significant device that plays a crucial role in various applications requiring precise temperature measurement. This component, often delineated in technical documentation, serves as a cornerstone for engineers and enthusiasts alike, facilitating the accurate monitoring and control of temperature-sensitive systems.
Within the comprehensive documentation pertaining to this device, one encounters a wealth of information elucidating its functionality, specifications, and usage scenarios. Through a meticulous examination of this documentation, one can gain profound insights into the intricacies of integrating this component into diverse projects, thereby fostering innovation and efficiency.
Amidst the myriad of technical details contained within these documents, one discerns fundamental principles elucidating the underlying operation of this sensor. By grasping these foundational concepts, engineers can navigate through the intricacies of temperature sensing with acumen and precision, paving the way for the development of robust and reliable systems.
Furthermore, the documentation expounds upon the electrical characteristics and performance metrics inherent to this sensor, offering invaluable guidance to engineers seeking to optimize its utilization within their respective applications. Armed with this knowledge, practitioners can harness the full potential of this device, harnessing its capabilities to meet the exacting demands of their projects.
Moreover, beyond the realms of technical specifications, the documentation imparts practical wisdom garnered from extensive real-world applications, providing invaluable insights into best practices and potential pitfalls. By heeding these experiential insights, engineers can navigate through the complexities of implementation with finesse, mitigating challenges and achieving optimal outcomes.
Thus, delving into the intricacies of the LM335 temperature sensor documentation unveils a trove of knowledge essential for engineers and enthusiasts alike. Through a judicious exploration of its contents, practitioners can unlock new realms of possibility, leveraging this humble yet indispensable component to realize their innovative visions.
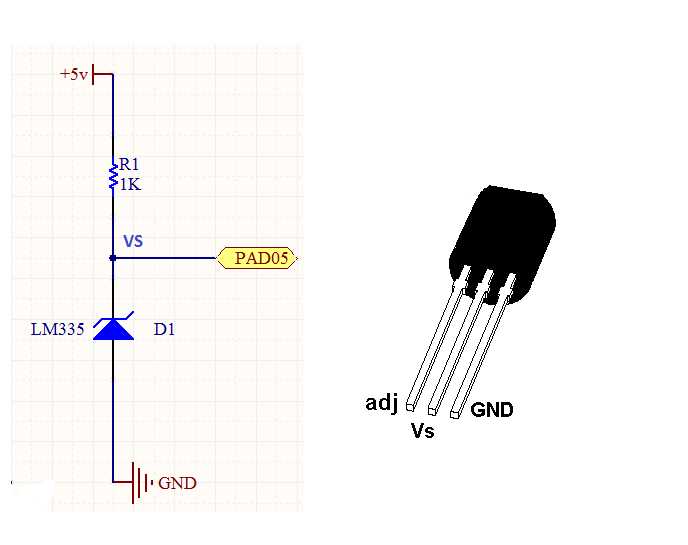
Understanding Specifications of the LM335 Thermal Sensing Device
In delving into the intricacies of the LM335 thermal sensing device, it becomes paramount to decipher its specifications comprehensively. This section aims to elucidate the nuanced details surrounding the operational characteristics and performance metrics of this electronic component.
1. Electrical Parameters

When exploring the operational realm of the LM335, it is imperative to scrutinize its electrical parameters. These encompass various facets such as voltage range, current requirements, and power dissipation, all of which delineate the device’s electrical behavior within a circuit.
- Voltage Range: Refers to the permissible span of voltages across which the LM335 operates effectively, dictating its compatibility with different power sources and circuit configurations.
- Current Requirements: Signifies the amount of current necessary for the LM335 to function optimally, crucial for designing circuits with appropriate power supplies.
- Power Dissipation: Reflects the amount of power dissipated by the device during operation, influencing considerations regarding heat management and overall system efficiency.
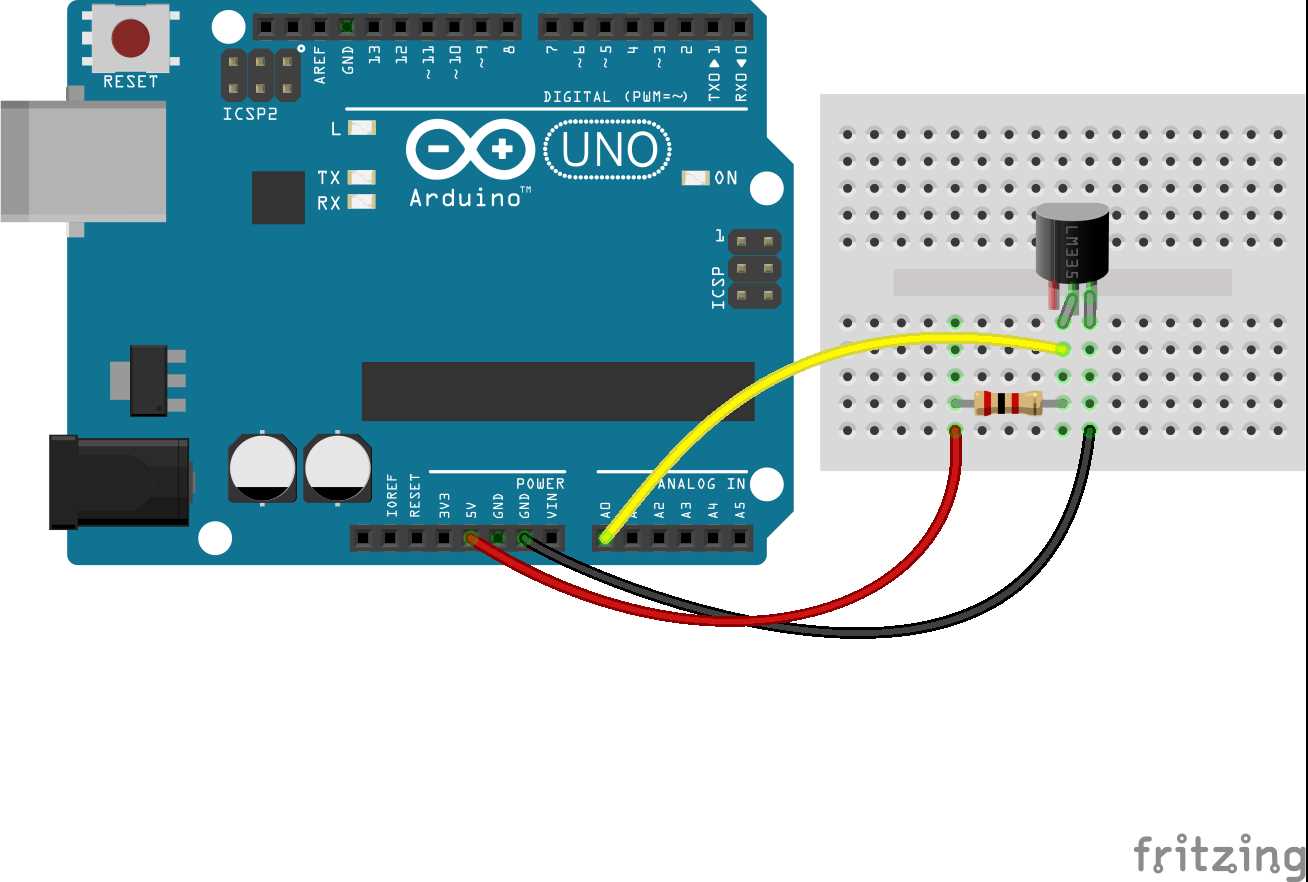
2. Thermal Characteristics
Another pivotal aspect pertains to the thermal characteristics exhibited by the LM335, which profoundly influence its performance in temperature sensing applications. Understanding these parameters is fundamental for accurate temperature measurement and calibration.
- Temperature Coefficient: Denotes the rate of change in output voltage per unit temperature variation, elucidating the sensitivity of the device to temperature fluctuations.
- Temperature Range: Encompasses the minimum and maximum temperatures over which the LM335 can reliably operate, delineating its applicability in diverse environmental conditions.
- Stability: Signifies the device’s ability to maintain consistent performance over time and under varying thermal conditions, a critical factor in ensuring measurement accuracy and reliability.
By delving into these specifications with precision, engineers and enthusiasts alike can gain a profound understanding of the LM335 thermal sensing device, empowering them to harness its capabilities effectively in temperature monitoring and control applications.
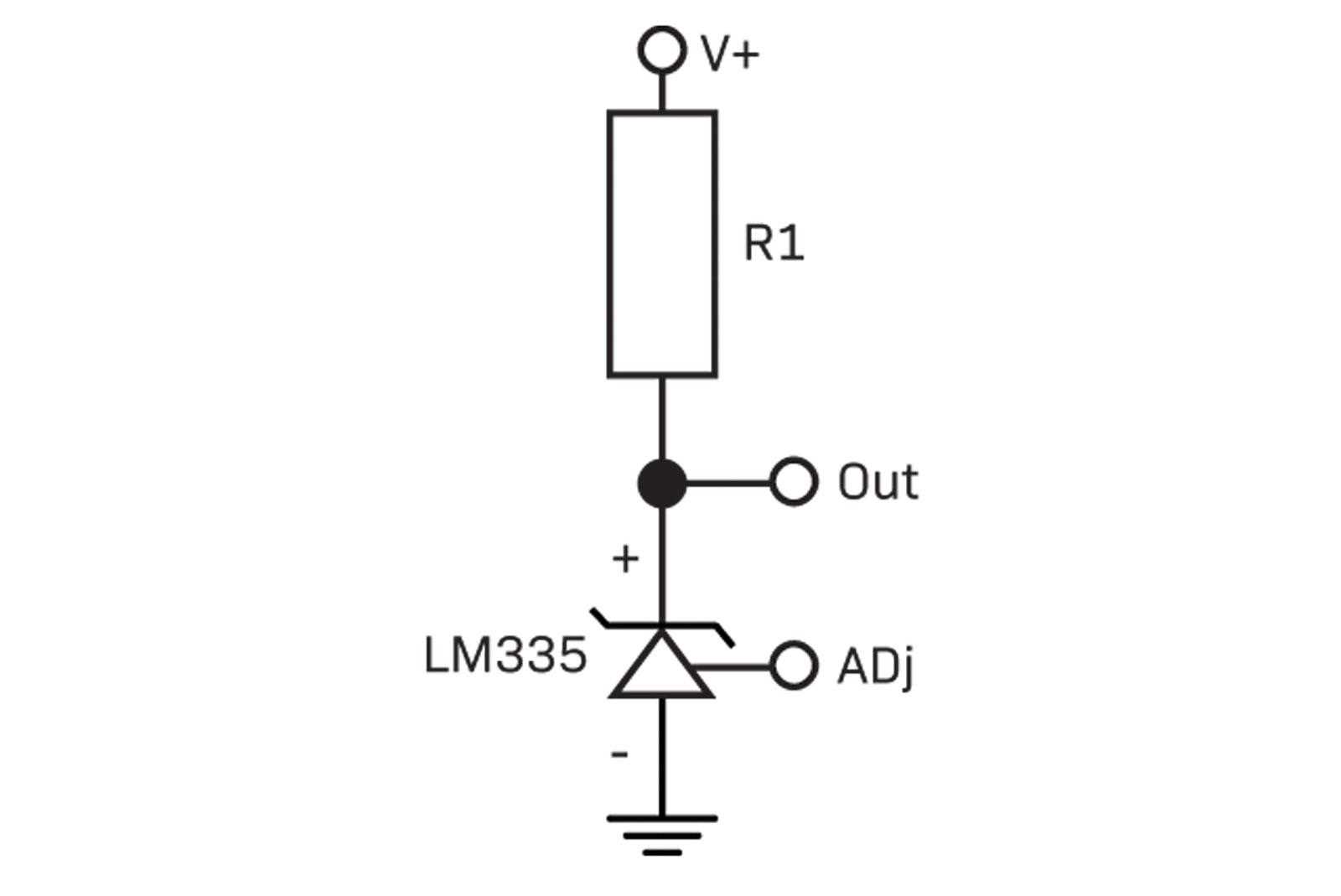
Interpreting LM335 Thermometric Component Electrical Characteristics
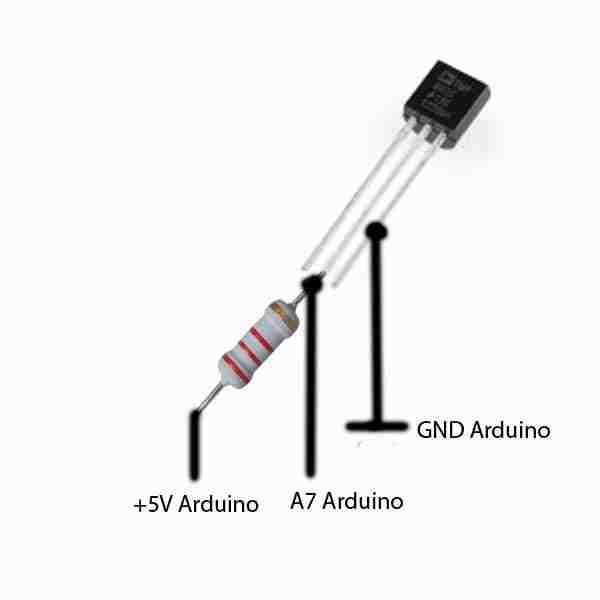

Understanding the intrinsic electrical properties of the LM335 thermometric device is paramount for accurate temperature measurement and efficient utilization. In this section, we delve into the nuanced nuances of its electrical characteristics, shedding light on its behavior under various conditions and providing insights into its operational intricacies.
1. Voltage Output: The LM335 thermometric component exhibits a voltage output that varies linearly with temperature changes, making it a reliable indicator of thermal fluctuations. Exploring the voltage-temperature relationship elucidates its sensitivity and responsiveness to environmental changes, facilitating precise temperature monitoring.
2. Sensitivity Analysis: Assessing the sensitivity of the LM335 reveals its ability to detect subtle temperature variations, crucial for applications requiring high precision. By scrutinizing its sensitivity profile across different temperature ranges, users can optimize performance and tailor its usage to specific requirements.
3. Linearity Examination: Ensuring the linearity of the LM335’s response is essential for accurate temperature measurement across its operational range. Analyzing its linearity characteristics elucidates deviations from ideal behavior and aids in calibration procedures to enhance measurement accuracy.
4. Thermal Hysteresis: Exploring the thermal hysteresis phenomena in the LM335 provides insights into its transient response to temperature changes. Understanding hysteresis effects empowers users to mitigate potential inaccuracies and enhance the stability of temperature measurements in dynamic environments.
5. Temperature Coefficient: Investigating the temperature coefficient of the LM335 elucidates its stability and reliability over a wide temperature range. Assessing how its electrical properties vary with temperature fluctuations aids in selecting appropriate operating conditions and optimizing performance under diverse thermal scenarios.
By comprehensively interpreting the electrical characteristics of the LM335 thermometric component, users can leverage its inherent properties to achieve precise temperature sensing in a myriad of applications, ranging from industrial process control to environmental monitoring.
Applications and Circuit Design Tips for LM335 Temperature Sensor

In this section, we delve into various practical uses and design considerations for the LM335 semiconductor device, renowned for its precise temperature measurement capabilities. Explore diverse applications and gain insights into optimizing circuit design to leverage the full potential of this versatile component.
- Temperature Control Systems: Discover how the LM335 can be integrated into temperature control systems for applications ranging from environmental monitoring to industrial process control.
- Thermal Management in Electronics: Explore strategies for utilizing the LM335 to monitor and regulate temperature within electronic devices, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
- Healthcare and Biomedical Applications: Learn about the integration of LM335 sensors in medical devices for monitoring body temperature with accuracy and consistency.
- Automotive Temperature Sensing: Gain insights into the role of LM335 sensors in automotive applications, such as engine temperature monitoring and climate control systems.
- Energy Efficiency Optimization: Understand how precise temperature sensing using the LM335 contributes to energy-efficient HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems and appliances.
Furthermore, explore essential circuit design tips to maximize the performance and reliability of LM335-based temperature sensing systems:
- Optimal Voltage Biasing: Ensure proper voltage biasing to the LM335 sensor for accurate temperature measurement, considering factors such as supply voltage stability and noise reduction.
- Noise Mitigation Techniques: Implement effective filtering and shielding techniques to minimize noise interference and enhance the signal-to-noise ratio of the temperature sensing circuit.
- Calibration and Compensation: Employ calibration methods and temperature compensation techniques to mitigate inaccuracies arising from component variations and environmental factors.
- Thermal Considerations: Address thermal management challenges by optimizing sensor placement, heat sinking, and insulation to minimize thermal gradients and ensure consistent temperature readings.
- Power Supply Decoupling: Utilize proper decoupling capacitors and power supply arrangements to maintain stable operating conditions and prevent voltage fluctuations that could affect sensor performance.
By exploring diverse applications and incorporating these circuit design tips, you can harness the full potential of the LM335 temperature sensor in your projects, achieving precise and reliable temperature measurement in various environments and applications.