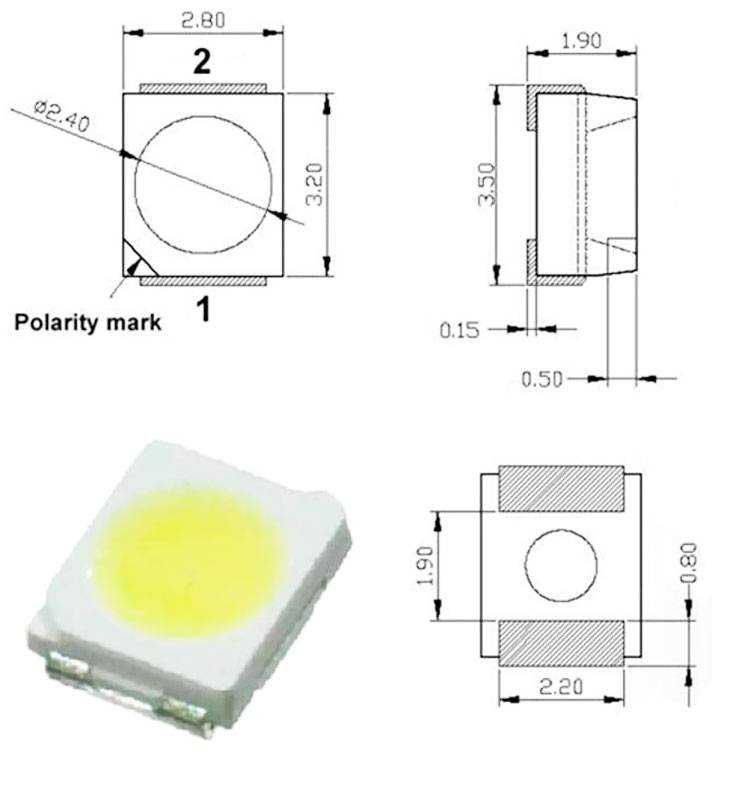
Illuminate your understanding of the intricacies within the realm of modern lighting technology. Venture into the radiant universe where small yet powerful components orchestrate mesmerizing displays of brilliance. Delve into the heart of innovation as we uncover the enigmatic details of these diminutive luminaries, unveiling their secrets layer by layer.
Embark on a journey through the luminous landscape, where each component serves as a pixel in the grand tapestry of illumination. Discover the unsung heroes behind the scenes, the silent conductors of light that shape our modern visual experiences.
Peer into the intricacies of these microscopic emissaries, exploring their capabilities beyond the surface gloss. Unravel the mysteries of their construction, composition, and functionality as we decipher the cryptic language of luminescence, translating it into tangible knowledge.
Understanding the Key Specifications of SMD 3528 LED Datasheets
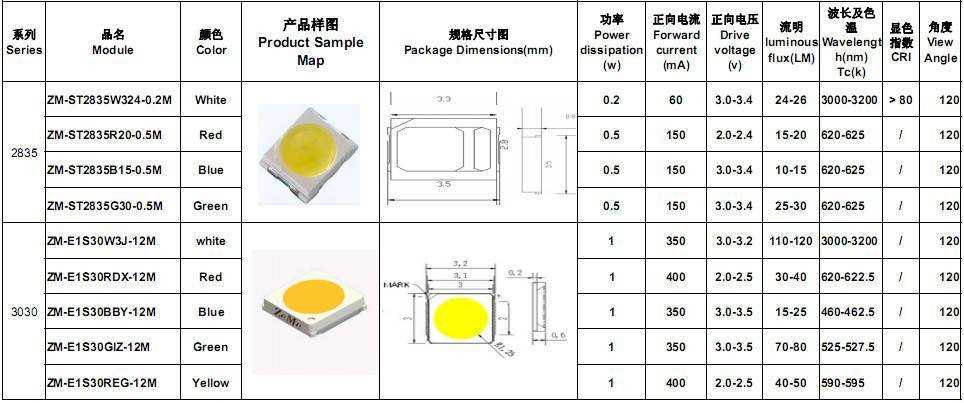
In the realm of electronic components, comprehending the intricacies of product specifications is paramount for informed decision-making and successful implementation. Delving into the details of SMD 3528 LED datasheets unveils crucial insights into the performance and capabilities of these miniature luminaires. This section elucidates the essential parameters encapsulated within these documents, facilitating a deeper grasp of their functionalities and potential applications.
Electrical Characteristics
One fundamental aspect elucidated in SMD 3528 LED datasheets encompasses their electrical characteristics, which delineate the behavior of these devices under various operating conditions. This segment encompasses parameters such as forward voltage, forward current, and reverse voltage, shedding light on the voltage requirements and operational limits of the LEDs. Understanding these specifications aids in configuring appropriate driving circuits and ensuring optimal performance.
Optical Performance

Beyond their electrical traits, the optical performance of SMD 3528 LEDs serves as a pivotal determinant of their suitability for diverse applications. Parameters like luminous intensity, viewing angle, and color temperature elucidate the luminous efficacy and visual properties of these LEDs. Grasping these specifications facilitates the selection of LEDs tailored to specific illumination requirements, ensuring desired brightness levels and light dispersion characteristics.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Forward Voltage | The voltage required for the LED to conduct current in the forward direction. |
| Forward Current | The maximum current that can safely pass through the LED in the forward direction. |
| Reverse Voltage | The voltage at which the LED starts to conduct in the reverse direction, potentially leading to damage. |
| Luminous Intensity | The measure of the visible light emitted by the LED, typically expressed in millicandelas (mcd) or lumens (lm). |
| Viewing Angle | The angle over which the emitted light is spread, influencing the LED’s coverage area and directionality. |
| Color Temperature | The perceived warmth or coolness of the light emitted by the LED, measured in Kelvin (K). |
Exploring Electrical Characteristics

Delving into the intricate details of the electrical properties unveils a profound understanding of the performance metrics inherent within this technology. By scrutinizing the fundamental attributes that govern its functionality, we embark on a journey to unveil the underlying principles shaping its operation.
The Essence of Electrical Specifications

At the core of this exploration lies the essence of electrical specifications, encapsulating a myriad of parameters essential for comprehending its behavior and capabilities. Through an in-depth analysis of voltage thresholds, current ratings, and power consumption metrics, we illuminate the intricate interplay between these variables, shedding light on the dynamic nature of its electrical profile.
Unraveling the Dynamics of Circuitry

Further delving into the realm of electrical characteristics unravels the intricate dynamics of circuitry, elucidating the voltage-current relationship and the nuances of resistance within the system. By dissecting the impedance characteristics and examining the transient response, we gain insight into the transient behavior and stability considerations crucial for optimal performance.
Interpreting Optical Parameters
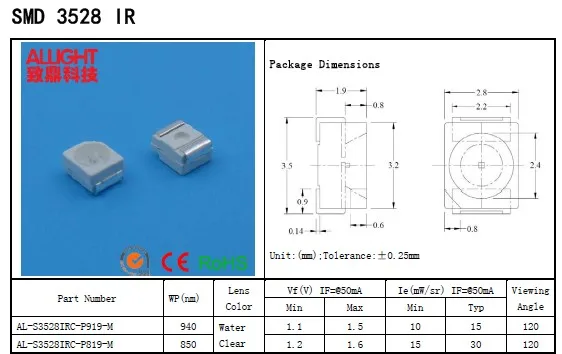
Understanding the intricacies of luminous characteristics is paramount in grasping the functionality and performance of light-emitting diodes (LEDs). Delving into the optical parameters of these components provides valuable insights into their light-emission capabilities, guiding the selection process for various applications.
Intensity and Brightness
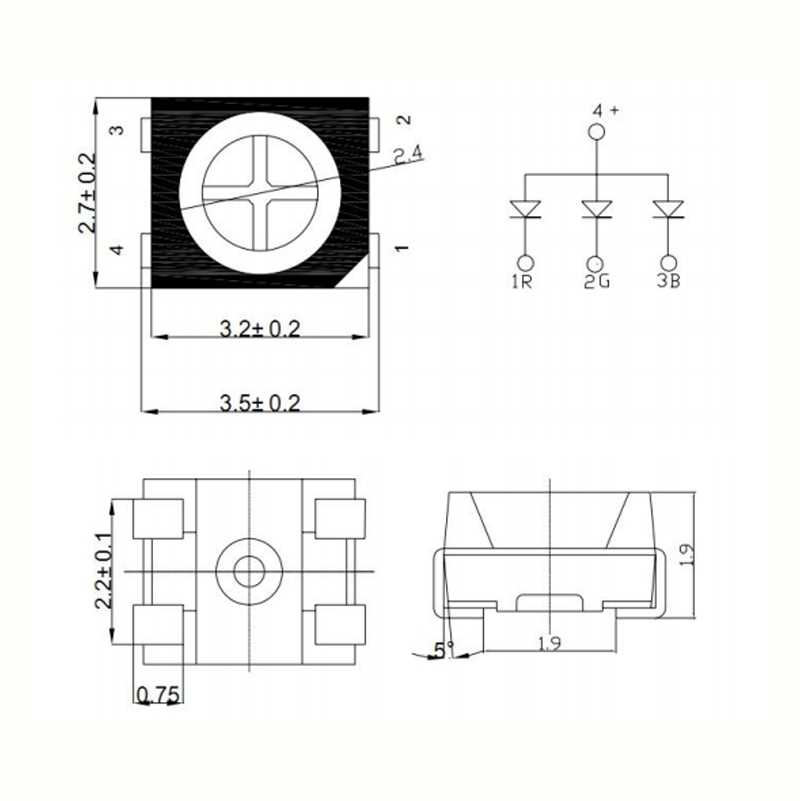
One fundamental aspect to consider is the luminous intensity and brightness of LEDs. These metrics delineate the magnitude of emitted light and its perceived luminance, respectively. Analyzing these parameters aids in gauging the visual impact and effectiveness of LED illumination in diverse settings.
Color Rendering and Temperature
Another crucial facet is color rendering and temperature, elucidating the LED’s ability to accurately reproduce colors and the perceived warmth or coolness of emitted light. These factors play a pivotal role in determining the ambiance and functionality of lighting installations, influencing aspects ranging from aesthetics to visual comfort.
Deciphering Thermal Management Details
In the realm of semiconductor component specifications, understanding the intricacies of thermal management is paramount. This section delves into the nuanced aspects of regulating temperature within electronic components, providing insights crucial for optimizing performance and longevity.
Understanding Heat Dissipation
At the core of effective thermal management lies the ability to dissipate heat efficiently. Exploring methods to enhance heat dissipation without compromising component integrity is imperative for maximizing operational efficiency.
Optimizing Thermal Pathways
Delving into the labyrinth of thermal pathways, this section illuminates strategies to streamline heat transfer mechanisms within electronic systems. From material selection to design considerations, every aspect plays a pivotal role in maintaining optimal operating temperatures.
- Exploring heat sink designs to augment thermal conductivity
- Implementing effective ventilation strategies to mitigate temperature buildup
- Utilizing thermal interface materials to enhance heat transfer efficiency