
Delve into the enigmatic world of tiny luminous emissaries, each bearing the promise of radiant brilliance.
In this voyage through the realm of electronic enlightenment, we embark on an odyssey beyond mere components.
Within the microcosm of circuitry, these diminutive heralds illuminate realms vast and minuscule.
Prepare to unravel the secrets veiled within the microscopic architecture, unveiling the essence of luminous potency.
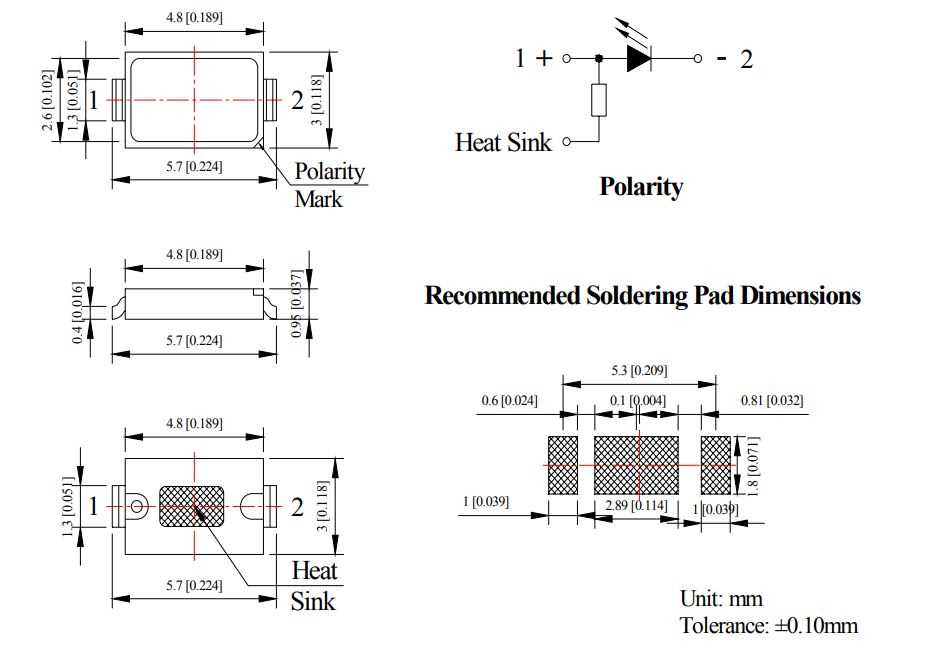
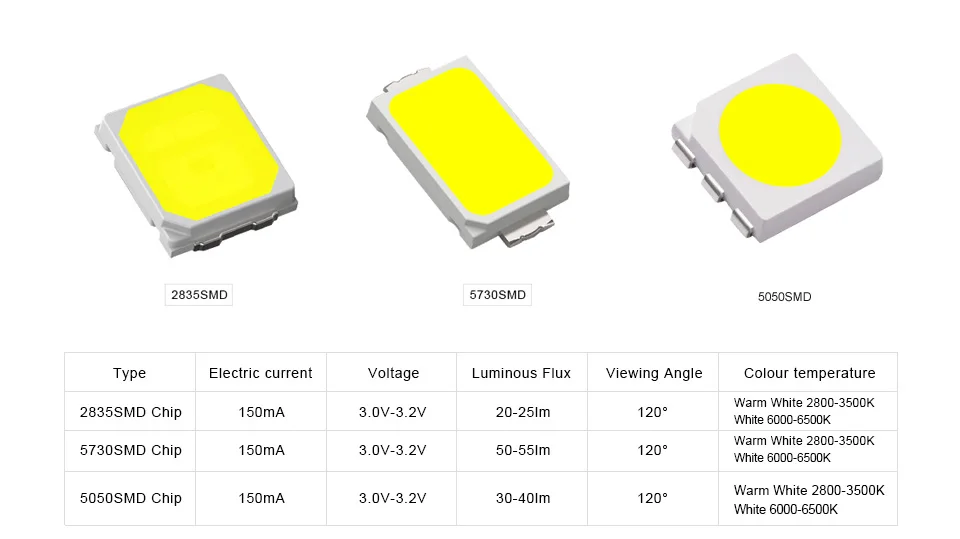
Understanding the SMD 5730 Light Emitting Diode Documentation

In the realm of electronic component comprehension, delving into the intricacies of the SMD 5730 LED documentation is pivotal. This segment navigates through the essential aspects of interpreting the comprehensive guide provided for this component.
Key Parameters Deciphered
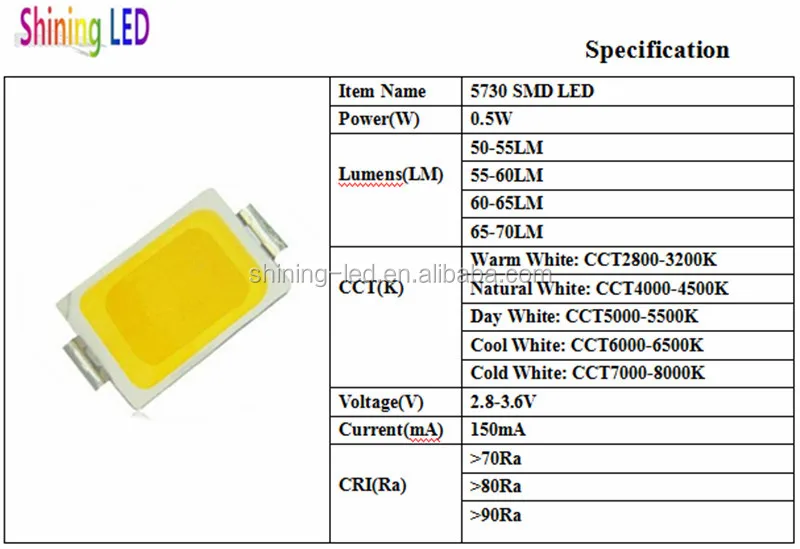
- Illuminate insights into pivotal metrics
- Uncover critical specifications
- Decipher vital characteristics
Interpreting Graphical Representations
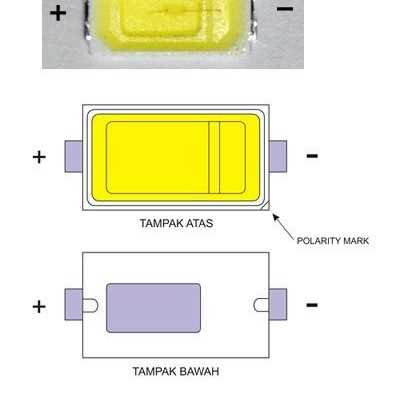
- Grasp graphical data with precision
- Decode visual depictions
- Comprehend schematic diagrams
By grasping the nuances of SMD 5730 LED documentation, engineers unlock the pathway to optimized integration and performance within their designs.
Exploring the Technical Specifications
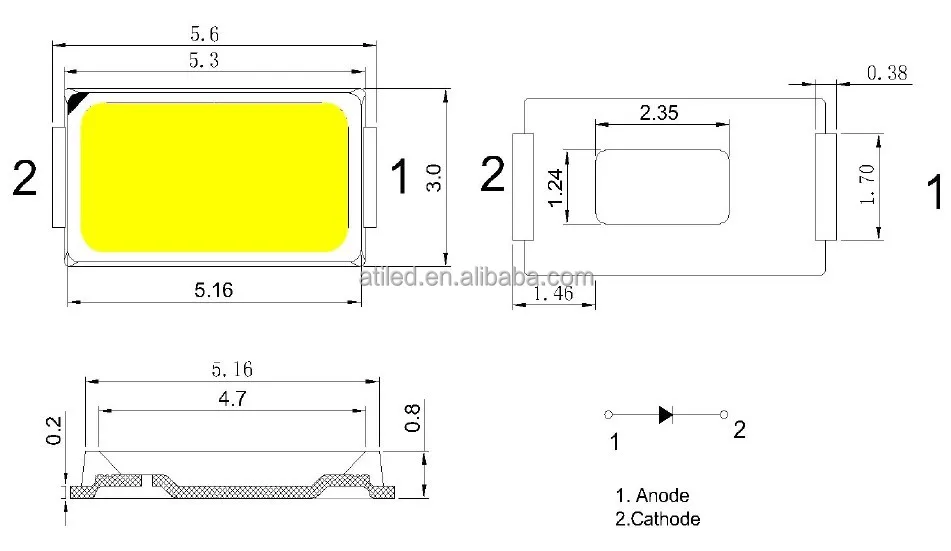
In this segment, we delve into the intricate details and performance metrics of cutting-edge surface-mount diodes (SMDs), shedding light on their capabilities and functionalities. Unveiling the intricacies of these components goes beyond mere enumeration of figures; it’s about deciphering their prowess in illuminating realms from efficiency to luminosity without overt dependence on conventional attributes.
Performance Metrics
Embarking on a journey through the performance metrics reveals a tapestry of characteristics that define the prowess of these components. From luminous efficacy to color rendering index (CRI), each metric paints a unique picture of the SMD’s capability, illuminating the pathway for nuanced applications across diverse sectors.
Technical Attributes
Scrutinizing the technical attributes provides a panoramic view of the SMD’s inner workings. From forward voltage and current rating to thermal resistance, each specification intricately weaves into the fabric of its performance profile, offering insights into its operational dynamics and compatibility with varying circuit configurations.
| Performance Metric | Definition |
|---|---|
| Luminous Efficacy | The measure of how efficiently the SMD converts electrical power into visible light, typically expressed in lumens per watt (lm/W). |
| Color Rendering Index (CRI) | An indicator of the SMD’s ability to accurately render colors compared to natural light, measured on a scale from 0 to 100. |
| Forward Voltage | The voltage drop across the SMD when current flows through it in the forward direction, a critical parameter for determining operational voltage requirements. |
| Current Rating | The maximum current that the SMD can withstand without compromising its performance or longevity, often specified in milliamps (mA). |
| Thermal Resistance | The measure of the SMD’s ability to dissipate heat generated during operation, influencing its operational reliability and lifespan. |
Interpreting Electrical Characteristics
In the realm of semiconductor components, comprehending the intricacies of their electrical properties is paramount for effective utilization. This section delves into the analysis and comprehension of pertinent electrical attributes, shedding light on their significance in assessing the performance and applicability of these components.
Understanding Parameter Specifications

Electrical characteristics of electronic components encapsulate a spectrum of parameters, delineating their behavior under various operating conditions. These specifications serve as fundamental indicators, guiding engineers and enthusiasts in selecting components tailored to their specific requirements. Interpretation of these parameters involves deciphering their implications on performance, efficiency, and compatibility within a given circuit.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Forward Voltage | Signifies the voltage required to initiate conduction in the forward direction, elucidating the energy threshold for light emission. |
| Reverse Current | Reflects the leakage current when the LED is subjected to reverse bias, delineating its susceptibility to undesired conduction. |
| Luminous Intensity | Quantifies the brightness emitted per unit solid angle, offering insights into the LED’s luminous efficacy. |
| Forward Current | Specifies the maximum current that can be safely passed through the LED, crucial for preventing thermal degradation and ensuring longevity. |
| Temperature Coefficient | Illustrates the sensitivity of electrical parameters to variations in temperature, facilitating thermal management strategies for optimal performance. |
Interpreting Performance Curves
Beyond discrete parameters, performance curves provide a graphical representation of an LED’s behavior across a range of operating conditions. These curves delineate relationships between voltage, current, and luminous output, offering a comprehensive view of the component’s dynamic characteristics. Analyzing these curves aids in optimizing circuit designs, maximizing efficiency, and mitigating potential pitfalls such as thermal runaway.
Optimizing Performance and Efficiency
In the pursuit of enhancing the functionality and efficacy of modern electronic components, it becomes imperative to delve into strategies that amplify their operational capabilities while concurrently maximizing resource utilization. This section navigates through methodologies aimed at refining the performance and energy efficiency of these components, fostering advancements in technological landscapes.
Efficient Utilization of Resources
One pivotal aspect of augmenting the operational prowess of electronic components involves the judicious allocation and utilization of available resources. By implementing streamlined processes that harness resources effectively, manufacturers can enhance the overall efficiency of their products without compromising on performance.
Performance Optimization Techniques
Exploring innovative approaches to enhance performance entails a multifaceted endeavor encompassing various optimization techniques. From refining circuit designs to fine-tuning operational parameters, each facet contributes synergistically towards elevating the performance metrics of electronic components.
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Dynamic Voltage Scaling | Adjusting voltage levels dynamically based on workload demands to optimize power consumption without sacrificing performance. |
| Thermal Management | Implementing efficient heat dissipation mechanisms to mitigate thermal constraints and ensure sustained performance levels. |
| Algorithmic Enhancements | Refining algorithms to minimize computational overhead and expedite processing tasks, thereby enhancing overall system performance. |