
Unleash the full potential of electronic systems with the remarkable Irfp140. This exceptional component paves the way for improved power delivery, enhanced efficiency, and increased reliability across a wide range of applications. With its cutting-edge technology, the Irfp140 reigns supreme as a go-to solution for today’s demanding circuit designs and power management needs.
Delve into the captivating world of the Irfp140 and unlock a whole new level of possibilities. This datasheet provides you with a comprehensive overview of the key features and specifications that make the Irfp140 a game-changer in the realm of power electronics. By harnessing the power of advanced materials and innovative design, this component opens doors to unprecedented performance and unrivaled capability.
Immerse yourself in the impeccable technical details and explore the true potential of the Irfp140. Discover its remarkable ability to facilitate high voltage operation, low on-resistance, and efficient power dissipation. With its robust construction and exceptional thermal capabilities, the Irfp140 empowers your circuit designs to tackle the most demanding challenges with ease.
Witness a new era in power electronics as the Irfp140 revolutionizes your applications. Whether you’re designing industrial control systems, audio amplifiers, or motor control circuits, the Irfp140’s versatility and reliability ensure exceptional performance in every endeavor. Experience a paradigm shift in electronic design and optimize your systems with the unparalleled power of the Irfp140.
The Main Specifications of the IRFP140 Transistor
In this section, we will explore the key specifications of the advanced power MOSFET known as the IRFP140 transistor. Understanding these specifications is crucial for determining the transistor’s performance and compatibility with various electronic applications.
1. Power Dissipation: Power dissipation refers to the maximum amount of power that the transistor can handle without exceeding its temperature limits. It is an essential specification to consider as exceeding the recommended power dissipation level can damage or even destroy the transistor.
2. Drain-Source Voltage: The drain-source voltage (Vds) is the maximum voltage that can be applied across the drain and source terminals of the transistor. Exceeding this voltage can lead to breakdown and irreversible damage to the device.
3. Continuous Drain Current: Continuous drain current (Id) indicates the maximum current that the transistor can handle continuously without overloading. Operating the transistor beyond its rated continuous drain current may cause adverse effects on its performance.
4. Gate-Source Voltage: The gate-source voltage (Vgs) represents the voltage that needs to be applied between the gate and source terminals to activate or control the transistor. Different applications may require different gate-source voltage levels to achieve optimal results.
5. Input Capacitance: Input capacitance (Ciss) defines the amount of capacitance between the gate and source terminals. It influences the transistor’s responsiveness and stability in high-frequency applications. Lower input capacitance makes the transistor suitable for high-speed switching applications.
6. Output Capacitance: Output capacitance (Coss) is the measure of capacitance between the drain and source terminals. It affects the transistor’s efficiency and performance in switching operations. A lower output capacitance allows for faster switching times and reduces power dissipation.
7. Total Gate Charge: Total gate charge (Qg) specifies the amount of charge required to switch the transistor between on and off states. It directly affects switching speed and efficiency. Lower gate charge results in faster switching times and reduced power losses.
8. Drain-Source On-State Resistance: Drain-source on-state resistance (Rds(on)) represents the resistance between the drain and source terminals when the transistor is fully turned on. Lower Rds(on) values indicate higher conductivity and lower power losses.
By considering these main specifications of the IRFP140 transistor, engineers and designers can make informed decisions regarding its suitability for various electronic circuits and applications.
An Overview of the IRFP140 Transistor

In this section, we will provide an introduction and overview of the IRFP140 transistor, a power MOSFET device widely used in various electronic applications. The IRFP140 transistor offers high voltage capabilities and low on-resistance, making it suitable for applications where high power switching is required. This overview will provide a general understanding of the transistor’s features and performance characteristics, without delving into specific technical details.
To start, it is important to note that the IRFP140 is part of the power MOSFET family of transistors, designed to handle high power and voltages. Its high voltage rating ensures that it can operate safely in systems that require high voltage switching, such as in power supplies, motor control circuits, and audio amplifiers. The low on-resistance of the transistor allows for efficient power transfer and reduced power losses.
One of the key features of the IRFP140 transistor is its ruggedness and reliability. It is built using advanced semiconductor technology, making it capable of withstanding a range of environmental conditions and ensuring its long-term performance. This reliability is crucial in applications where the transistor may be subjected to high temperatures, humidity, or other challenging operating conditions.
The IRFP140 transistor also offers high switching speeds, allowing for fast and efficient switching operations. This characteristic makes it suitable for applications that require rapid switching, such as in power converters, motor control, and switching power supplies. Additionally, the transistor’s low gate charge and input capacitance enable easy driveability and reduce the power needed to control the device.
Furthermore, the IRFP140 transistor features a compact and industry-standard TO-247 package, enabling easy integration into various electronic systems. With its standardized package, the transistor can be easily mounted on a heat sink to ensure proper thermal management, especially in high-power applications where excessive heat generation can degrade device performance.
Overall, the IRFP140 transistor represents a versatile power MOSFET device, offering high voltage capabilities, low on-resistance, ruggedness, reliability, and fast switching speeds. Its wide range of applications and performance characteristics make it an attractive choice for designers and engineers working on power electronics projects.
| Features: | Applications: |
|---|---|
| High voltage capabilities | Power supplies |
| Low on-resistance | Motor control circuits |
| Ruggedness and reliability | Audio amplifiers |
| High switching speeds | Power converters |
| Compact TO-247 package | Switching power supplies |
The Electrical Characteristics of the IRFP140
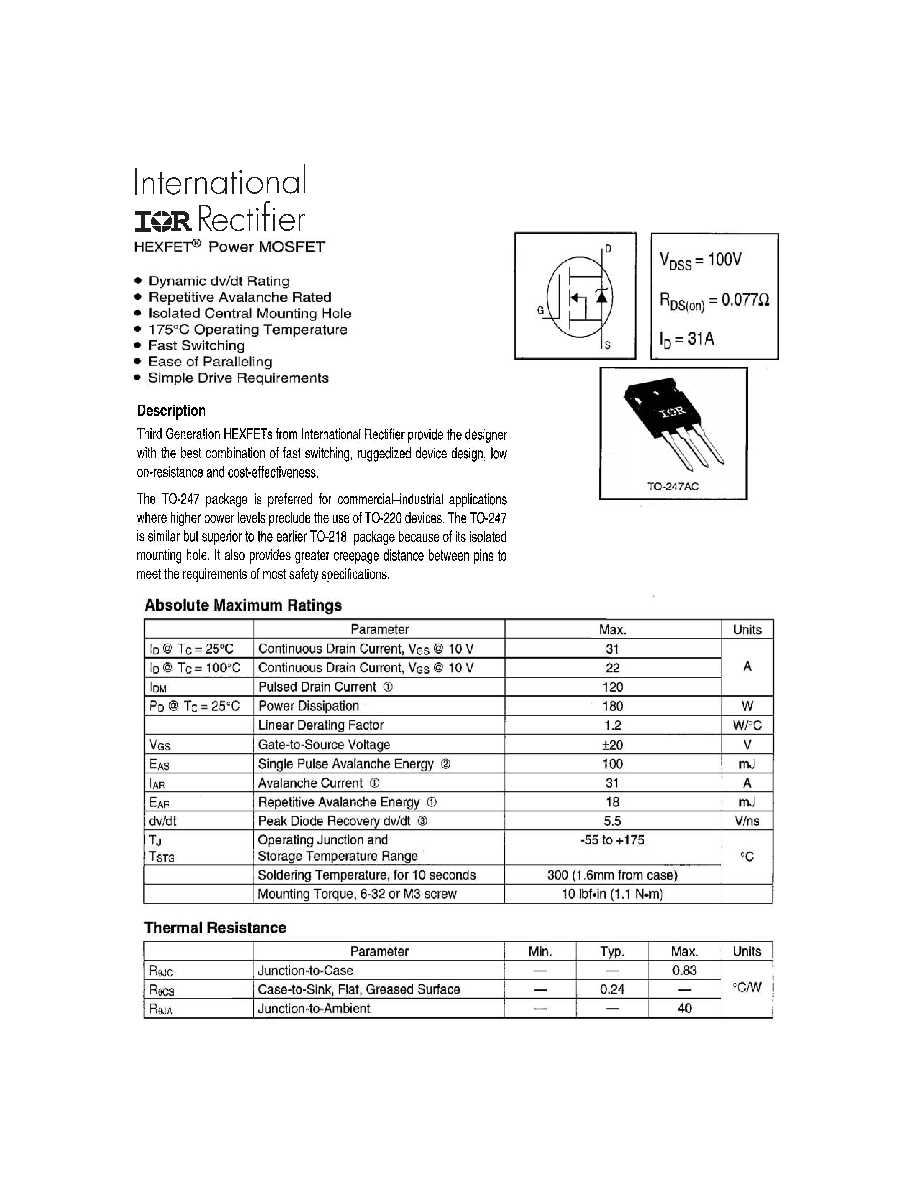
In this section, we will explore the various electrical characteristics of the high power MOSFET known by its part number IRFP140. Understanding these characteristics is essential for engineers and enthusiasts who wish to utilize this component in their electronic designs.
One of the key features of the IRFP140 is its high voltage capability. It can withstand and handle significant voltage levels, making it suitable for applications requiring high power output. This attribute is particularly relevant when designing power supplies, motor control circuits, or audio amplifiers.
Another important characteristic is the low on-state resistance of the IRFP140. This indicates that when the MOSFET is fully conducting, it offers minimal resistance to the flow of current. The lower the on-state resistance, the more efficient the component is in terms of power dissipation. Therefore, the IRFP140 can effectively handle high current loads without significant losses.
Furthermore, the IRFP140 exhibits excellent thermal performance. This means that it can operate at high temperatures without suffering from overheating issues. Such capability is crucial in applications where the MOSFET is subjected to high power dissipation or ambient temperature variations.
Additionally, the IRFP140 offers fast switching speeds, enabling rapid transitions between the on and off states. This characteristic is advantageous in applications such as motor control or switching power supplies, where quick response times are required for efficient operation.
Lastly, it is worth mentioning the durable construction of the IRFP140, which ensures reliability and longevity. The robust design allows the MOSFET to withstand various environmental conditions, ensuring consistent performance over an extended operational lifespan.
In conclusion, the IRFP140 showcases several unique electrical characteristics that make it a desirable component for high power applications. Its high voltage capability, low on-state resistance, excellent thermal performance, fast switching speeds, and durable construction all contribute to its effectiveness in electronic designs.
Important Considerations for Using the IRFP140 Transistor
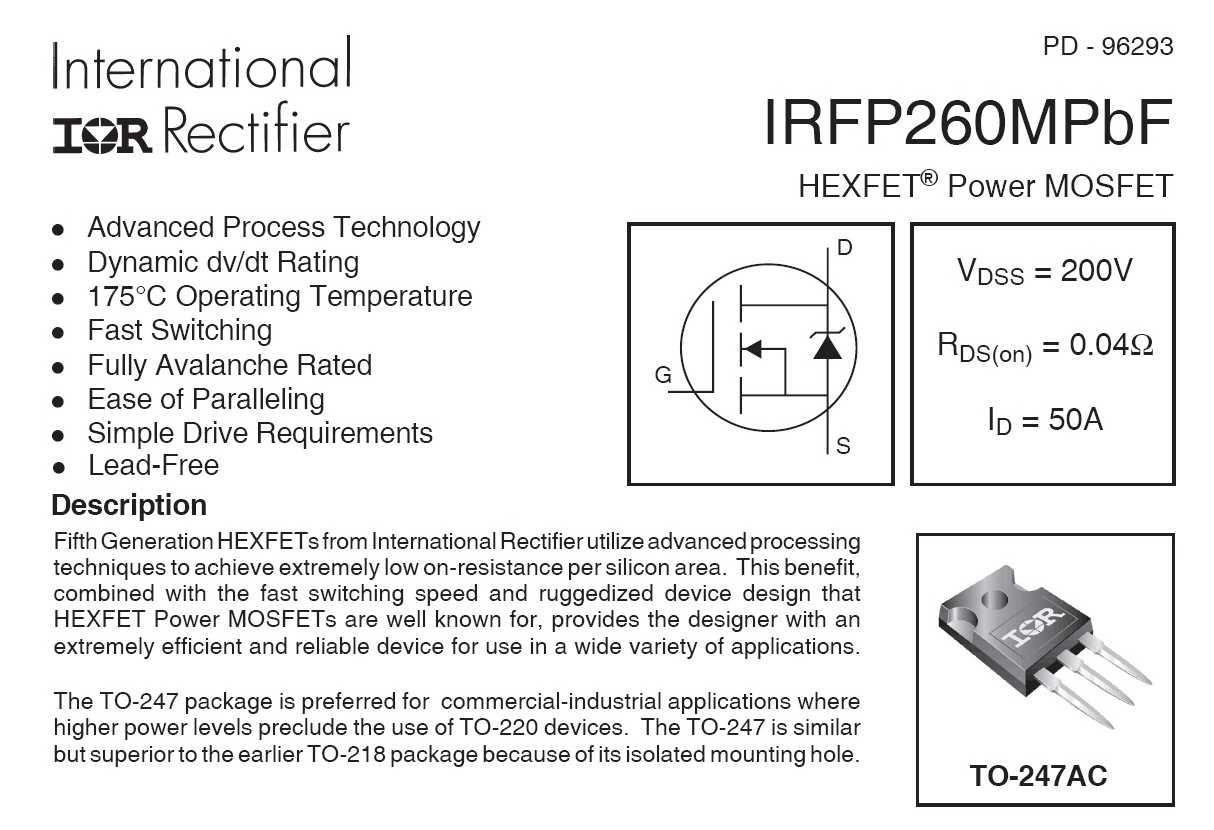
When utilizing the IRFP140 transistor for various applications, it is crucial to take into account several significant factors that can affect its performance and reliability. Understanding these considerations will enable you to optimize the operation of the transistor and ensure its proper functioning in your electronic circuitry.
1. Voltage and Current Ratings
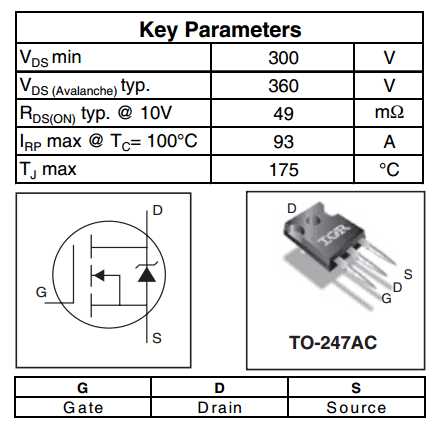
The IRFP140 transistor has specific voltage and current ratings that must be adhered to in order to prevent potential damage or failure. Carefully review the datasheet for the recommended maximum voltage and current ratings for both the collector and emitter terminals. Operating the transistor beyond these specified limits can result in instability, overheating, or even permanent damage.
2. Heat Dissipation

Given its power handling capabilities, the IRFP140 transistor generates heat during operation. Adequate heat dissipation measures are essential to prevent overheating, which can lead to reduced performance and premature transistor failure. Ensure proper heat sinking by using a suitable heatsink and applying thermal compound between the transistor case and the heatsink surface. Additionally, ensure proper airflow within the electronic system to avoid heat buildup.
3. Safe Operating Area (SOA)
The IRFP140 transistor has a Safe Operating Area (SOA) that defines the maximum voltage and current conditions under which it can operate without exceeding its thermal or breakdown limits. Operating the transistor outside of the SOA can result in catastrophic failure. Carefully analyze the SOA graph provided in the datasheet to ensure the operating conditions for your specific application fall within this defined region.
4. Gate Voltage Control

Proper control and management of the gate voltage is crucial for optimal performance of the IRFP140 transistor. The gate voltage directly affects the conduction of the transistor and its switching characteristics. Ensure that the gate voltage is within the recommended range specified in the datasheet. Implement appropriate impedance matching and drive circuitry to ensure reliable and efficient switching.
5. Power Supply Considerations
Consider the stability and quality of the power supply used with the IRFP140 transistor. Any fluctuations or disturbances in the power supply voltage can affect the transistor’s performance. Ensure that the power supply is well regulated and provides a stable voltage within the specified range for proper operation.
| Consideration | Summary |
|---|---|
| Voltage and Current Ratings | Adhere to specified voltage and current limits to prevent damage or failure. |
| Heat Dissipation | Proper heat sinking and airflow to prevent overheating. |
| Safe Operating Area (SOA) | Ensure operating conditions fall within the defined Safe Operating Area. |
| Gate Voltage Control | Properly control gate voltage for optimal conduction and switching. |
| Power Supply Considerations | Stable and well-regulated power supply for reliable transistor performance. |