Unlocking the potential of cutting-edge electronic components demands a nuanced comprehension of their technical documentation. These cryptic scrolls, often revered as blueprints of innovation, encapsulate the essence of modern electronic engineering. Within their labyrinthine passages lie the keys to harnessing power, optimizing efficiency, and transcending the limitations of conventional circuitry.
Embarking on a quest to decipher these arcane texts unveils a realm where electrons dance to the rhythm of voltage gradients, and conductivity reigns supreme. Amidst this tapestry of symbols and specifications, the seeker encounters a trove of insights into the behavior of silicon titans that shape the landscape of power electronics.
Delve deep, and one may unravel the mysteries of amplification, conductivity thresholds, and thermal resilience, woven intricately within the fabric of these enigmatic manuscripts. Yet, beware the pitfalls of presumption, for amidst the allure of raw technical data lies the potential for misinterpretation, leading the unwary astray in the labyrinth of electronic design.
Deciphering Key Parameters

In dissecting the fundamental characteristics of the semiconductor component under scrutiny, it becomes imperative to delve into the intricate details that underpin its operational prowess. This segment embarks on an exploration of pivotal metrics pivotal to comprehending the functionality and performance nuances of the device.
Threshold Voltage
Embedded within the core functionality of this electronic element lies a pivotal metric known as the threshold voltage. This parameter delineates the minimum voltage requisite to initiate significant conduction through the semiconductor material, thus delineating the onset of its operational regime.
On-State Drain Current
Central to the efficacy of the component is the on-state drain current, a pivotal determinant of its operational capacity. This metric elucidates the magnitude of current flow permitted through the device when it operates within its designated operational parameters, thereby dictating its capacity to facilitate electronic processes.
- Gate-Source Voltage (VGS): The voltage differential applied between the gate and source terminals assumes a critical role in modulating the conductivity of the semiconductor material, thereby exerting profound influence over its operational behavior.
- Drain-Source Voltage (VDS): This metric delineates the voltage differential sustained across the drain and source terminals during operational cycles, thereby offering insights into the voltage handling capabilities of the device.
- Input Capacitance (Ciss): The input capacitance signifies the intrinsic capacitance associated with the device, influencing its responsiveness to alterations in the applied voltage, and consequently, its operational dynamics.
By meticulously deciphering these key parameters, stakeholders can gain profound insights into the operational characteristics and performance envelope of the semiconductor component, thereby facilitating informed decision-making and optimizing its utilization within diverse electronic applications.
Interpreting Performance Characteristics
Understanding the operational behaviors of electronic components goes beyond mere technical specifications. It delves into the intricate nuances of their performance under various conditions, offering insights into their functionality and potential applications.
When delving into the intricacies of these devices, it’s crucial to analyze their behavior under load, response to voltage fluctuations, and thermal management capabilities. These factors not only dictate their performance but also determine their suitability for specific tasks.
Drawing correlations between different parameters reveals a deeper understanding of how these components interact within a circuit. By examining trends across various operational conditions, engineers can anticipate their behavior and optimize circuit designs accordingly.
Moreover, evaluating the transient response of these components provides invaluable insights into their dynamic performance. Understanding how they react to rapid changes in input signals is crucial for applications requiring precise control and stability.
In essence, interpreting the performance characteristics of electronic components involves more than just analyzing numbers on a datasheet. It requires a holistic approach, integrating theoretical knowledge with practical insights to unlock the full potential of these fundamental building blocks of modern electronics.
Unlocking Potential: Exploring Applications of High-Power Enhancement Mode Field-Effect Transistors
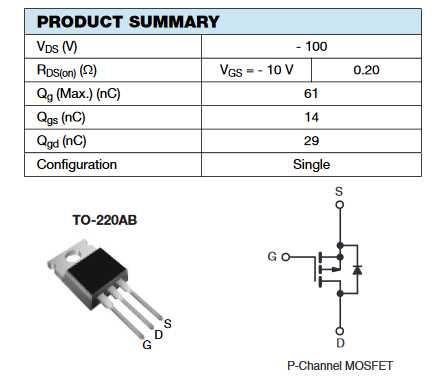
In this section, we delve into the myriad of innovative applications where cutting-edge high-power enhancement mode field-effect transistors (HEM-FETs) like the Irf9540 can truly shine. These versatile semiconductor devices offer unparalleled potential across various industries, enabling efficient power management and enhancing system performance.
1. Power Electronics
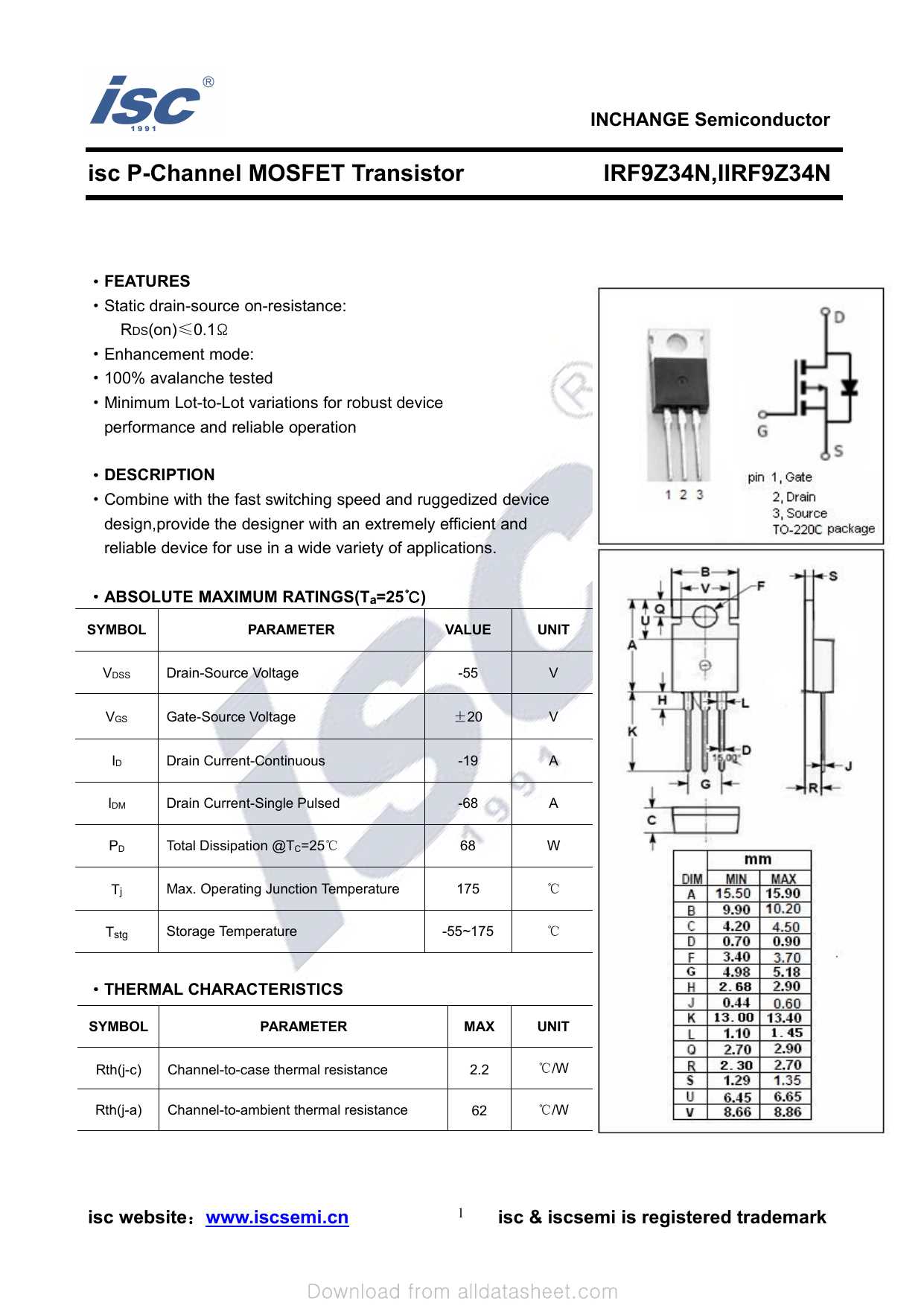
One of the primary domains harnessing the prowess of HEM-FETs is power electronics. These components serve as pivotal building blocks in diverse circuits ranging from voltage regulators and power inverters to motor control systems. With their ability to handle high currents and voltages, HEM-FETs facilitate precise control and conversion of electrical energy, thereby optimizing efficiency and reliability.
2. Renewable Energy Systems
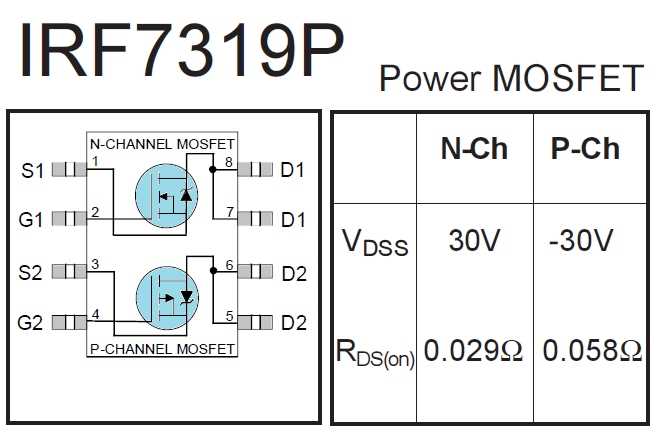
In the realm of renewable energy, HEM-FETs play a crucial role in the development of photovoltaic inverters, wind turbine converters, and energy storage systems. By seamlessly integrating these transistors into power conversion units, renewable energy installations can efficiently harvest and distribute clean electricity. The robustness and performance capabilities of HEM-FETs ensure seamless operation and maximum energy yield, contributing to a sustainable future.
- Grid-Tied Solar Inverters
- Wind Turbine Converters
- Battery Management Systems
Unlocking the full potential of HEM-FETs like the Irf9540 opens avenues for innovation in various sectors, driving advancements in energy efficiency, automation, and beyond. As technology continues to evolve, these high-performance transistors will continue to underpin transformative solutions, empowering industries and shaping the future of power electronics.
Power Electronics in Modern Systems

In the realm of contemporary engineering, the realm of power electronics stands as a pivotal domain, orchestrating the symphony of energy conversion and control within diverse systems. It serves as the silent conductor, seamlessly converting electrical energy to power the myriad devices that define our technological landscape.
The Evolution of Energy Management
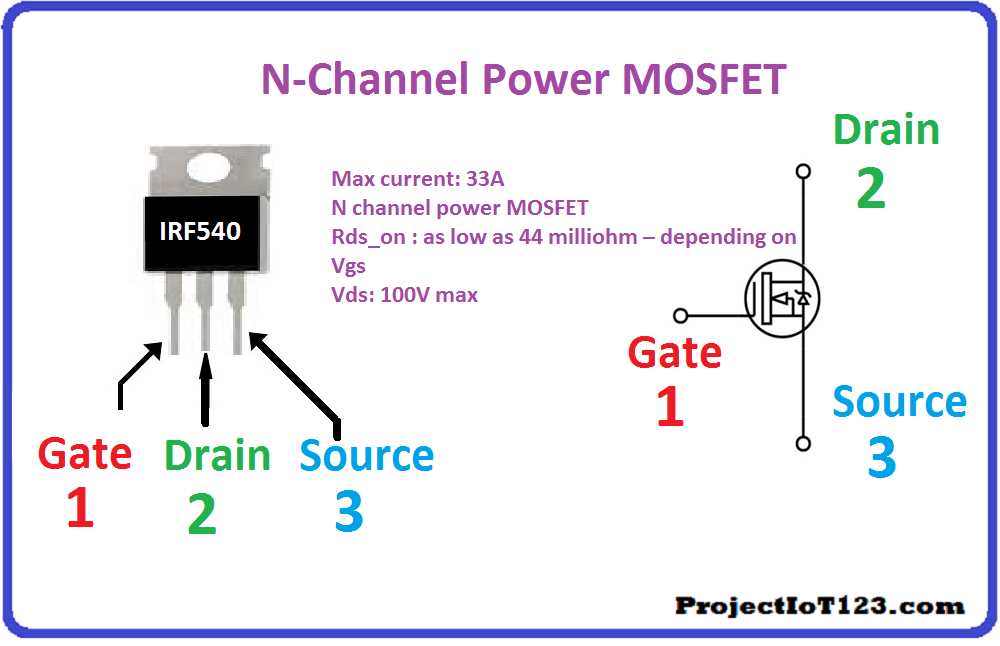
Within the intricate tapestry of modern systems, power electronics emerges as the linchpin, fostering efficiency, reliability, and versatility. Through the adept manipulation of voltage, current, and frequency, it engenders the seamless integration of renewable energy sources, the propulsion of electric vehicles, and the efficient operation of industrial machinery.
Advancing Technological Frontiers
Power electronics not only fuels our present technological prowess but also propels us towards new frontiers. From grid-scale energy storage to microelectronics, its innovations underpin the foundation of future technologies, promising a world where energy is harnessed with unprecedented precision and sustainability.
Industrial and Automotive Implementations
In the realm of industrial and automotive applications, the utilization of cutting-edge electronic components is paramount for achieving optimal performance, reliability, and efficiency. This section delves into the diverse array of scenarios where advanced semiconductor technologies, like those encapsulated in the Irf9540 MOSFET, find indispensable utility.
Industrial Applications
Within industrial settings, the demand for robust electronic components capable of enduring harsh environmental conditions while maintaining consistent functionality is incessant. From motor control systems to power management units, the deployment of high-performance MOSFETs facilitates seamless operation and ensures the longevity of critical machinery. These components serve as the backbone of modern industrial automation, enabling precise control, rapid switching, and minimal power loss.
Automotive Implementations
Similarly, in the automotive domain, where reliability and efficiency are paramount, MOSFETs play a pivotal role in powering various subsystems ranging from engine control modules to advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). The stringent requirements of automotive applications necessitate components capable of enduring extreme temperatures, voltage fluctuations, and mechanical stressors. MOSFETs, with their inherent ruggedness and high switching speeds, contribute to the seamless operation of vehicle electronics, enhancing both performance and safety.
| Application | Functionality | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Motor Control Systems | Precise speed and torque control | Enhanced efficiency and productivity |
| Power Management Units | Regulation and distribution of electrical power | Optimized energy utilization |
| Engine Control Modules | Management of engine parameters | Improved fuel efficiency and emissions control |
| Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) | Collision avoidance and autonomous driving features | Enhanced vehicle safety |