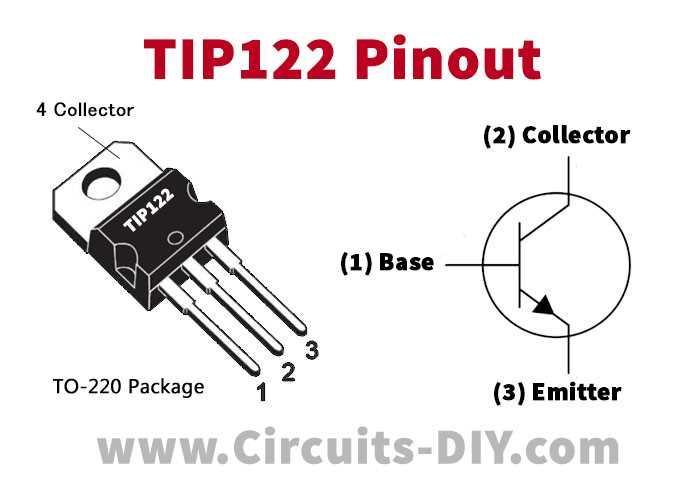
Understanding the intricacies of electronic components involves delving into the details beyond mere specifications. These vital elements of circuitry serve as the building blocks for a myriad of devices, from consumer electronics to industrial machinery. In the realm of semiconductor components, each product boasts a dossier of information crucial for engineers and enthusiasts alike. Today, we embark on a journey through the documentation of a particular semiconductor component, delving into its properties, characteristics, and applications.
Embarking on an exploration of electronic components leads us to the realm of datasheets, comprehensive documents offering insights into a component’s behavior under various conditions. These documents encapsulate the essence of a component’s functionality, providing engineers with essential information for design and implementation. In this journey, we shine a light on one such semiconductor component, unraveling its intricacies and uncovering the wealth of knowledge hidden within its datasheet.
Join us as we dissect the specifications of a semiconductor component, peering into the realm of electrical parameters, thermal characteristics, and mechanical dimensions. Through meticulous analysis and interpretation, we aim to demystify the technical jargon and empower enthusiasts and professionals alike with a deeper understanding of these fundamental building blocks of modern technology.
The Essentials of Understanding Component Specifications
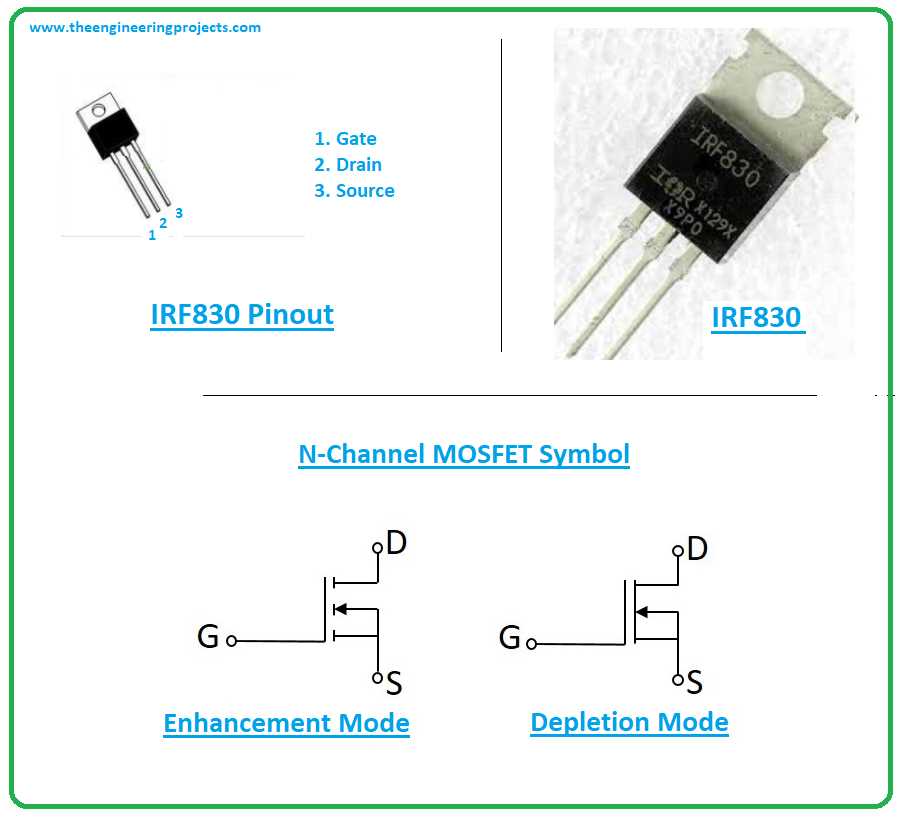
In exploring the fundamental aspects of comprehending technical documents, it is imperative to grasp the foundational concepts underlying the information provided. These documents serve as pivotal resources, offering insights into the characteristics, functionalities, and operational parameters of electronic components.
Interpreting Performance Metrics
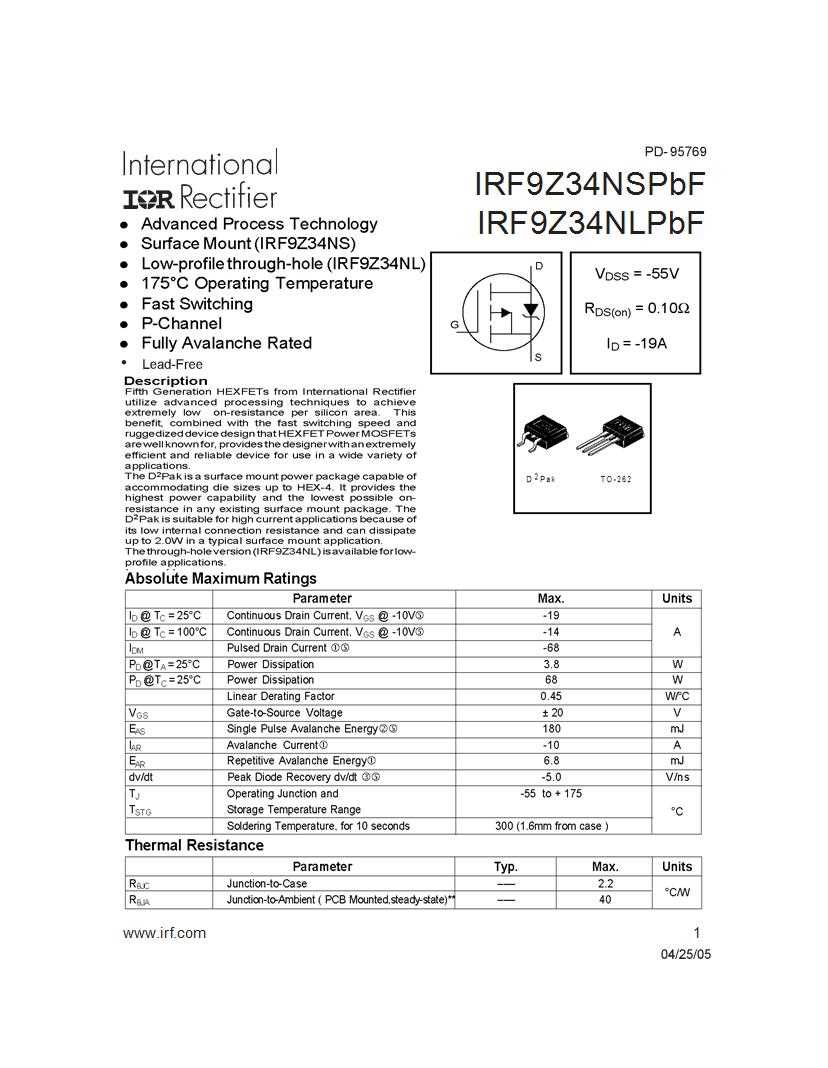
Within the realm of component documentation, pertinent details regarding performance metrics play a crucial role. These metrics encompass a spectrum of attributes such as electrical characteristics, thermal properties, and operational specifications. Understanding the implications of these metrics facilitates informed decision-making in component selection and application.
Deciphering Electrical Characteristics
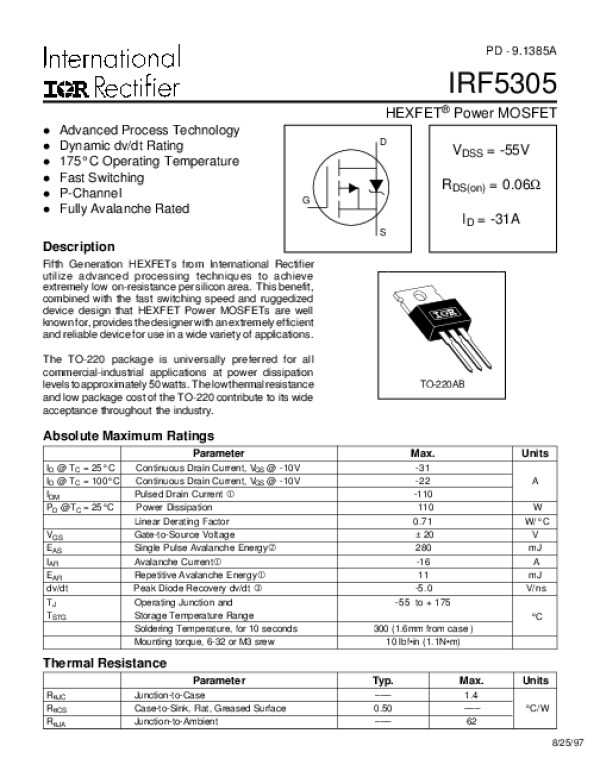
Electrical characteristics delineate the behavior of components under varying operating conditions, encompassing parameters like voltage ratings, current ratings, and impedance profiles. Mastery of these characteristics enables engineers to ascertain the compatibility of components within a given circuit configuration, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Voltage Ratings | Specifies the maximum allowable voltage across the component. |
| Current Ratings | Indicates the maximum current that the component can handle without exceeding its specified limits. |
| Impedance Profiles | Describes the component’s resistance to the flow of alternating current, providing insights into its behavior within different frequency ranges. |
By delving into these fundamental aspects, engineers can navigate technical documentation with proficiency, leveraging the insights gleaned to optimize design processes and enhance overall system performance.
Understanding Key Specifications and Features
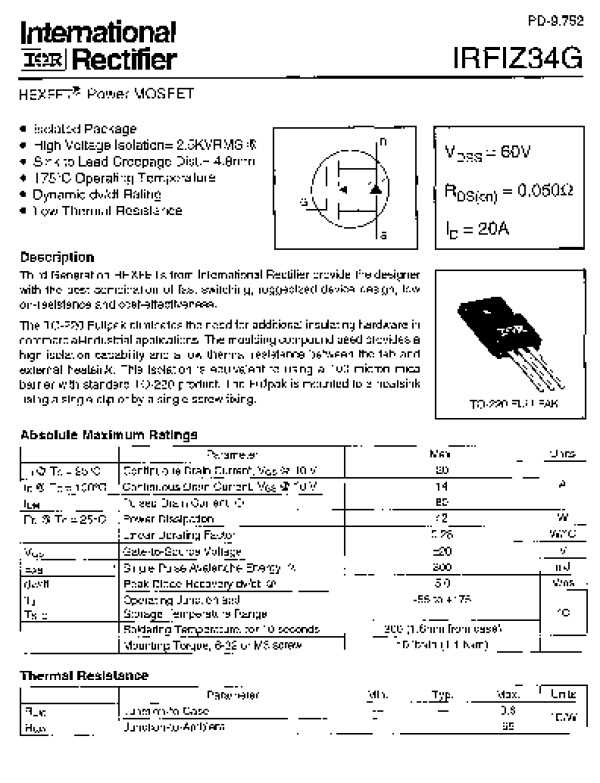
In this section, we delve into the fundamental aspects and characteristics crucial for comprehending the intricacies of the device in focus. Exploring the core specifications and features enables a comprehensive understanding of its operational nuances and potential applications.
Electrical Performance: Delving into the electrical performance provides insights into how the device behaves under various operating conditions. This encompasses parameters such as voltage ratings, current handling capabilities, and power dissipation, which collectively dictate its suitability for specific applications.
Thermal Characteristics: Understanding the thermal behavior of the device is paramount for ensuring reliable operation and longevity. Factors like junction-to-ambient thermal resistance and maximum operating temperature shed light on its thermal management requirements and constraints.
Switching Characteristics: The switching characteristics delineate how swiftly the device can transition between different states, impacting its efficiency and response time. Parameters such as turn-on and turn-off times, gate charge, and capacitances elucidate the device’s switching prowess and dynamic performance.
Protection Features: An examination of the protection features elucidates the safeguards incorporated to shield the device from potentially damaging conditions. Overcurrent protection, overvoltage protection, and thermal shutdown mechanisms augment the device’s reliability and safeguard it against detrimental operating scenarios.
Application Considerations: Understanding the application considerations entails evaluating how the device integrates into diverse circuit topologies and systems. This involves assessing compatibility with voltage levels, load characteristics, and environmental conditions to ascertain its suitability for intended applications.
Reliability Metrics: Reliability metrics provide insights into the device’s longevity and robustness, crucial for mission-critical applications. Mean time between failures (MTBF), failure rate, and operating lifetime statistics offer valuable information regarding the device’s reliability profile and anticipated lifespan.
By dissecting these key specifications and features, one can gain a holistic understanding of the device’s capabilities, limitations, and potential deployment scenarios, facilitating informed decision-making and optimized utilization.
Application Insights for Irf9520n Datasheet
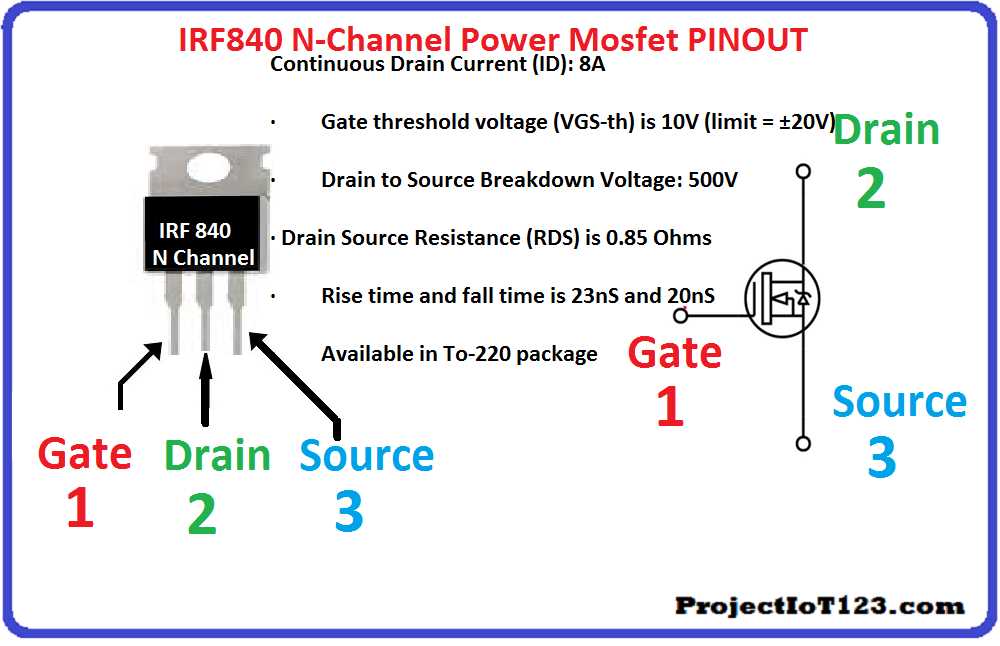
In this section, we delve into the practical uses and real-world scenarios where understanding the intricacies of the component can lead to optimized performance and enhanced functionality. By exploring application insights, we uncover the diverse contexts where the component’s specifications and features prove invaluable, offering solutions to a myriad of engineering challenges.
| Application Scenario | Insights |
|---|---|
| Power Management Systems | Examining how the component contributes to efficient power regulation and distribution, ensuring stable operation within various power management systems. |
| Audio Amplification | Understanding the role of the component in amplifying audio signals with precision and clarity, optimizing sound reproduction in audio equipment. |
| Motor Control | Exploring how the component facilitates precise control and modulation of motor functions, enabling smooth operation and precise motion control in robotics and automation. |
| Signal Processing | Investigating the component’s contribution to signal processing tasks, including filtering, amplification, and modulation, enhancing signal integrity in communication systems and instrumentation. |
| Switching Applications | Analyzing the component’s suitability for various switching applications, such as power switching and voltage regulation, ensuring efficient energy management and protection. |
By examining these application insights, engineers can gain a comprehensive understanding of how to leverage the capabilities of the component effectively, paving the way for innovative solutions across a spectrum of industries and technological domains.
Optimizing Circuit Design and Performance
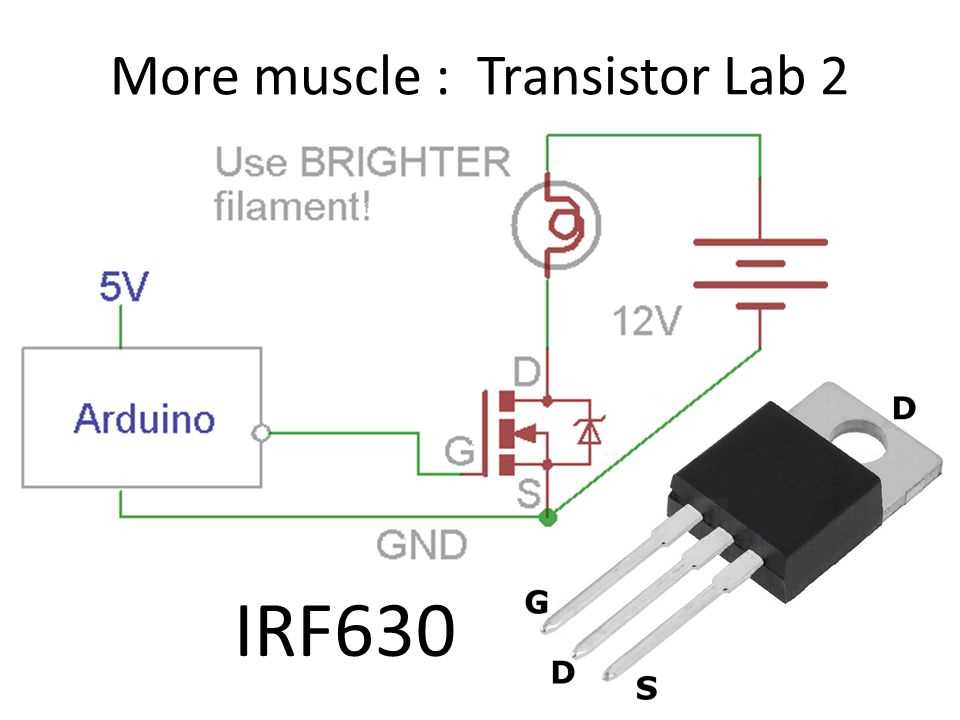
In the realm of electronic engineering, achieving optimal circuit design and performance is akin to orchestrating a symphony of components harmoniously interacting to produce desired outcomes. This section delves into strategic methodologies and considerations to enhance circuit efficiency, reliability, and functionality, thereby transcending mere functionality to achieve excellence in design.
Component Selection and Integration

The foundation of any circuit lies in the careful selection and integration of components, each playing a unique role in shaping its behavior. By meticulously analyzing specifications, characteristics, and operational parameters of diverse components, engineers can tailor a circuit to meet specific requirements. Moreover, judicious integration of components fosters synergy, minimizing inefficiencies and maximizing overall performance.
Signal Integrity and Noise Mitigation

Signal integrity is paramount in ensuring robust circuit performance amidst the cacophony of electromagnetic interference and noise. Employing techniques such as impedance matching, shielding, and proper grounding mitigates signal degradation and enhances fidelity. Furthermore, advanced signal processing algorithms and noise filtering mechanisms bolster circuit resilience, ensuring reliable operation in diverse environmental conditions.
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Efficient Power Management | Implementing power-efficient architectures and voltage regulation mechanisms to minimize energy consumption and enhance battery life. |
| Thermal Management | Employing thermal dissipation techniques such as heat sinks and thermal pads to prevent overheating and ensure long-term reliability. |
| Advanced Simulation and Modeling | Utilizing simulation tools and computational models to predict circuit behavior, optimize design parameters, and expedite development cycles. |
By embracing these strategies and methodologies, engineers can transcend conventional limitations, unlocking the full potential of circuit design and performance.
Advanced Tips and Troubleshooting
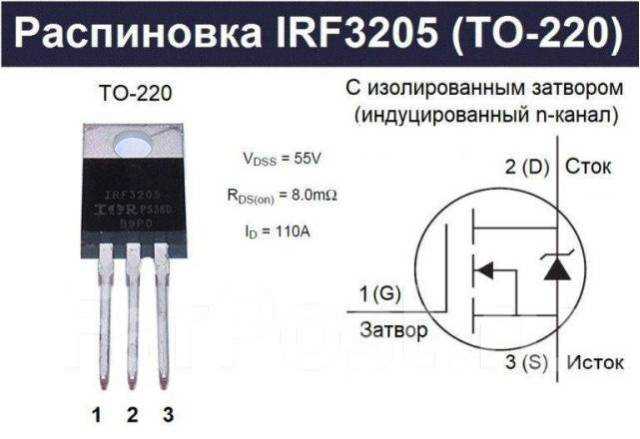
In this section, we delve into advanced strategies and solutions for optimizing performance and resolving issues encountered while working with electronic components. Whether you’re navigating intricate circuitry or troubleshooting elusive glitches, these insights will empower you to overcome challenges with finesse.
1. Fine-tuning Circuit Design: Explore methods to refine your circuit designs for enhanced efficiency and functionality. Consider adjusting component values, optimizing signal paths, and implementing advanced techniques such as feedback mechanisms to achieve desired performance levels.
2. Debugging Strategies: Uncover effective approaches for identifying and rectifying faults within electronic systems. From systematic fault isolation to utilizing diagnostic tools such as oscilloscopes and logic analyzers, learn how to efficiently troubleshoot issues and streamline the debugging process.
3. Thermal Management: Mitigate thermal challenges to ensure the reliability and longevity of electronic components. Discover techniques for effective heat dissipation, including proper component placement, thermal interface materials, and active cooling solutions, to prevent overheating and maintain optimal operating conditions.
4. Signal Integrity Optimization: Address signal integrity issues to preserve the integrity and accuracy of data transmission within electronic circuits. Explore strategies such as impedance matching, signal conditioning, and noise suppression to minimize signal degradation and maximize system performance.
5. Component Selection Considerations: Navigate the vast landscape of electronic components with confidence by understanding key factors influencing component selection. Evaluate criteria such as operating parameters, reliability metrics, and compatibility with existing systems to make informed decisions that align with project requirements and objectives.
6. EMI/EMC Compliance: Ensure compliance with electromagnetic interference (EMI) and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards to mitigate interference issues and maintain regulatory compliance. Learn about shielding techniques, filtering methods, and layout optimization strategies to minimize electromagnetic emissions and susceptibility, fostering robust and interference-resistant designs.
7. Advanced Simulation and Modeling: Harness the power of simulation tools and modeling software to simulate, analyze, and optimize complex electronic systems before physical implementation. From circuit simulation to electromagnetic field analysis, leverage virtual prototyping to anticipate performance characteristics, verify design feasibility, and accelerate development cycles.
By incorporating these advanced tips and troubleshooting strategies into your electronic design endeavors, you can overcome challenges with confidence and unlock the full potential of your projects.