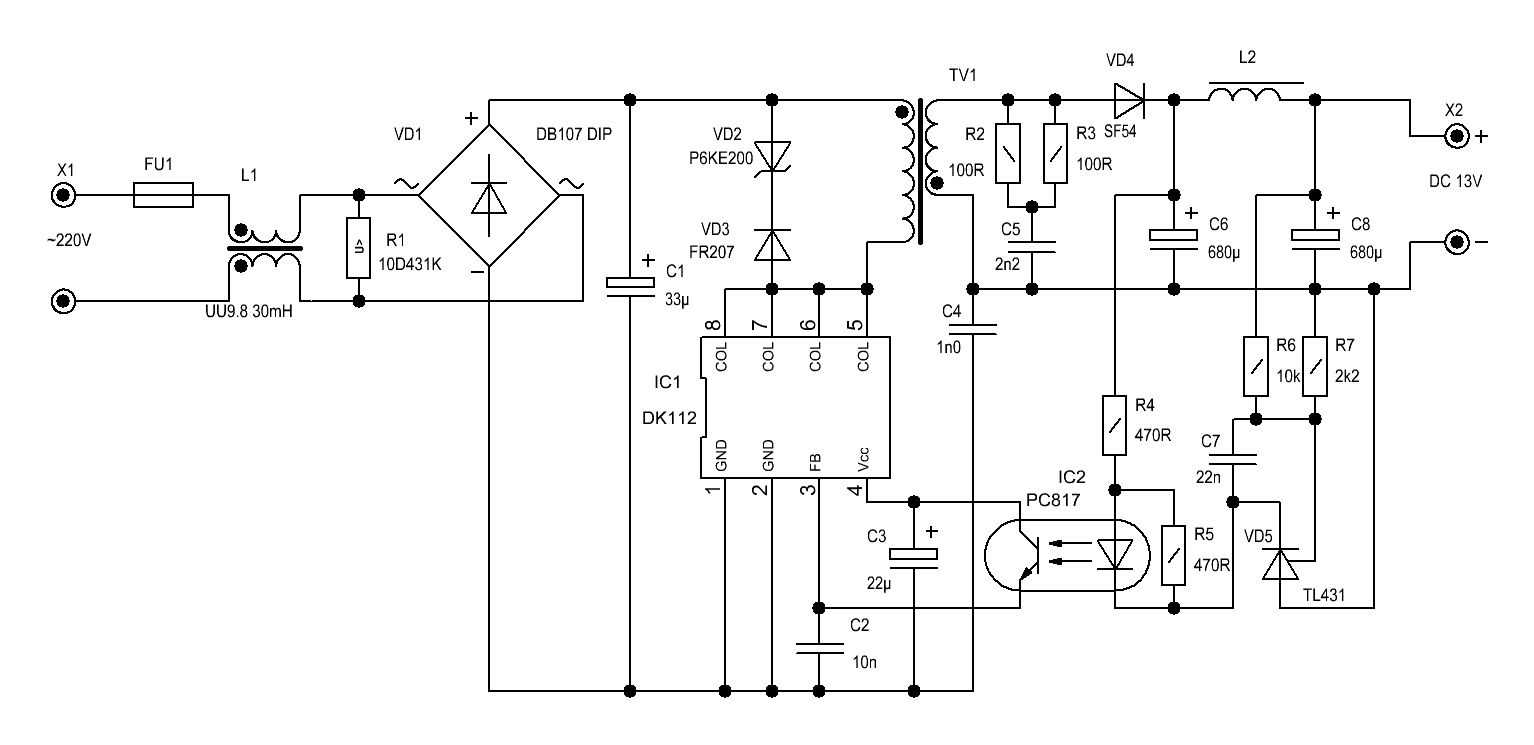
Step into the realm of luminosity, where brilliance meets innovation in the compact form of 3-watt light-emitting diodes (LEDs). Embark on a journey through the radiant possibilities of these miniature powerhouses as we delve into their technical specifications and performance characteristics.
Uncover the secrets behind the illumination revolution as we dissect the anatomy of these diminutive yet mighty sources of light. From their efficient energy utilization to their remarkable lifespan, each facet of these LEDs holds a promise of enlightenment for your projects.
Experience the sheer intensity of illumination as we explore the nuanced intricacies of 3-watt LEDs, unveiling the ways in which they redefine the boundaries of luminous potential. Prepare to be captivated by the sheer brilliance these devices offer, igniting a spark of creativity in every application they illuminate.
Understanding Specifications for Powerful LED Components
In the realm of lighting technology, deciphering the intricate details within component documentation holds paramount importance for engineers and enthusiasts alike. Within the realm of illuminative technology, these documents serve as invaluable resources, offering insights into the capabilities and characteristics of state-of-the-art luminous devices. Exploring the intricate specifics of these documents unveils a world of possibilities, allowing for informed decision-making and optimized integration of these components into various applications.
Deciphering Luminescent Component Documentation:
Delving into the wealth of information provided within the documentation of high-intensity luminous elements requires a keen eye for detail and a solid understanding of pertinent technical jargon. These documents, akin to detailed maps of functionality, elucidate critical aspects such as luminous flux, forward voltage, and thermal resistance, among others. Through a nuanced comprehension of these specifications, enthusiasts and professionals can effectively gauge the performance and compatibility of these components within diverse lighting scenarios.
Unraveling the Mysteries of Performance Metrics:
Within the labyrinthine corridors of LED documentation, performance metrics serve as guiding beacons, shedding light on the efficacy and limitations of these potent luminous devices. Parameters such as luminous efficacy, color rendering index (CRI), and forward current facilitate a comprehensive understanding of luminous performance under varying operational conditions. Mastery of these metrics empowers individuals to navigate the complex landscape of LED integration with precision and confidence, ensuring optimal outcomes in diverse lighting endeavors.
Interpreting Thermal Characteristics:
Beneath the surface of luminous prowess lies the intricate realm of thermal management, a facet of LED operation crucial for sustained performance and longevity. Thermal resistance, thermal pad resistance, and junction temperature specifications provide invaluable insights into the thermal behavior of LED components under different operating conditions. Mastery of these thermal characteristics enables practitioners to implement effective heat dissipation strategies, mitigating the risk of performance degradation and ensuring the longevity of luminous installations.
Conclusion:
Understanding the nuances encapsulated within the documentation of high-intensity luminous elements is paramount for enthusiasts and professionals alike. By deciphering the intricacies of performance metrics and thermal characteristics, individuals can harness the full potential of LED technology, unlocking a realm of illuminative possibilities.
Key Components and Specifications
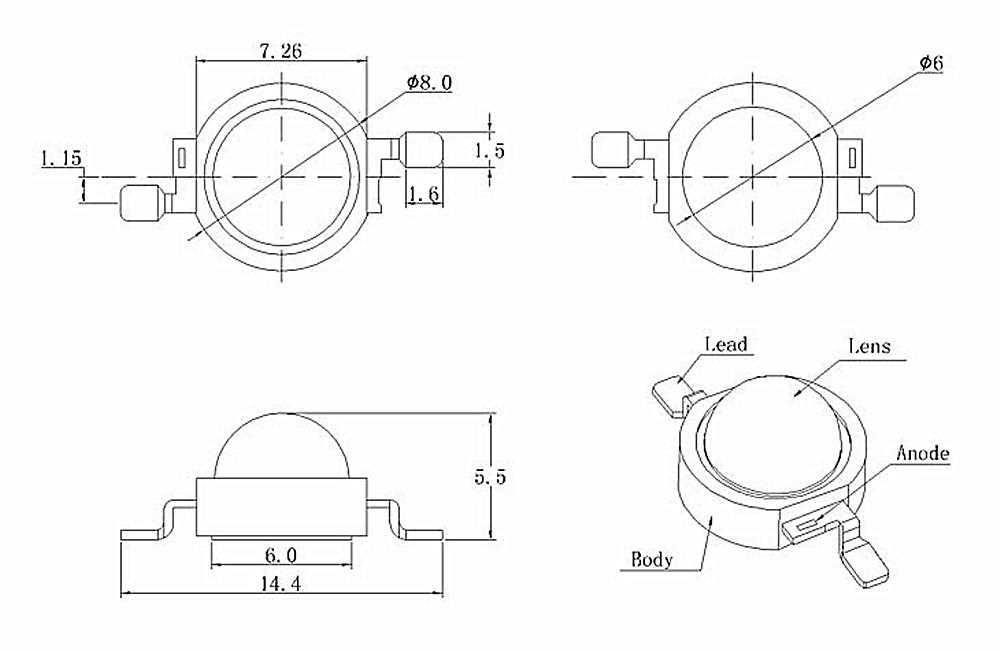
In exploring the intricacies of this technology, it’s imperative to delve into the foundational elements and intricate details that define its performance and functionality. Within this section, we navigate through the essential constituents and intricacies that underpin the operational dynamics of this innovative lighting solution.
Core Elements:
At the heart of this luminary innovation lie critical components meticulously designed to ensure optimal performance and longevity. These fundamental constituents, meticulously engineered and seamlessly integrated, form the backbone of the system, facilitating efficient light emission and power management.
Technical Specifications:
Complementing the core elements are meticulously calibrated technical specifications, meticulously tailored to meet diverse application requirements. These specifications encapsulate crucial parameters such as luminous efficacy, color rendering index, and thermal management capabilities, ensuring precision in output performance and operational reliability.
Functional Attributes:
Embedded within the intricate architecture of this lighting solution are functional attributes that elevate its utility and versatility. From adaptable dimming capabilities to robust heat dissipation mechanisms, each attribute enhances user experience and augments the applicability of the technology across various domains.
Performance Metrics:
Quantifying the prowess of this cutting-edge technology are performance metrics meticulously evaluated through rigorous testing protocols. These metrics, ranging from luminous flux output to forward voltage characteristics, provide insights into the efficiency and efficacy of the system, guiding informed decision-making processes.
Environmental Considerations:
Amidst the pursuit of technological advancement, due consideration is accorded to environmental implications, with eco-conscious design features embedded within the system. From energy-efficient operation to recyclable materials utilization, sustainability remains integral to the ethos driving the evolution of this innovative lighting solution.
Future Prospects:
Anticipating the evolving landscape of illumination technology, this section explores future prospects and potential avenues for enhancement. Leveraging ongoing research and development endeavors, the technology continually evolves to meet emerging challenges and seize new opportunities, ensuring its relevance and resilience in an ever-changing world.
Understanding the Performance of 3-Watt Light-Emitting Diodes
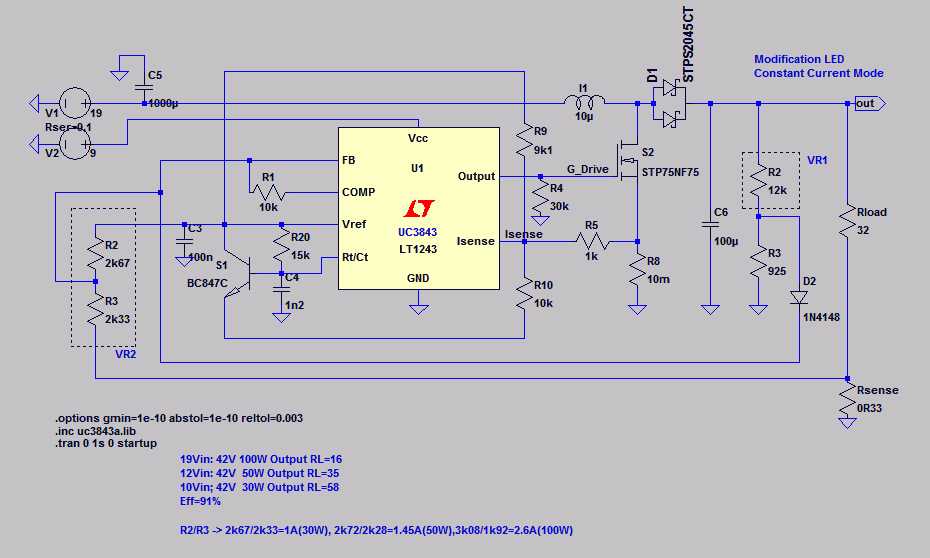
In this section, we delve into the intricacies of evaluating the effectiveness and capabilities of 3W LEDs. By dissecting various performance metrics, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of how these light-emitting diodes function and perform in diverse applications.
Efficiency: One of the key indicators of LED performance is its efficiency in converting electrical power into light output. This metric is crucial for assessing the overall energy consumption and cost-effectiveness of the lighting solution.
Luminous Flux: Luminous flux measures the total amount of visible light emitted by the LED, expressed in lumens. Understanding luminous flux is essential for determining the brightness of the LED and its suitability for different lighting tasks.
Color Rendering Index (CRI): CRI quantifies the LED’s ability to render colors accurately compared to natural light. A high CRI indicates better color rendition, making the LED suitable for applications where color fidelity is critical.
Forward Voltage: The forward voltage denotes the voltage required to operate the LED at its specified current. Understanding this parameter is vital for proper integration of the LED into the electrical circuit.
Thermal Resistance: Thermal resistance characterizes the LED’s ability to dissipate heat generated during operation. Efficient thermal management is essential for maintaining the LED’s performance and longevity.
Viewing Angle: The viewing angle defines the angular spread of light emitted by the LED. This metric influences the LED’s coverage area and its suitability for specific lighting applications.
Reliability Metrics: Reliability metrics such as Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) provide insights into the LED’s expected lifespan and long-term performance stability.
By comprehending these performance metrics and their implications, users can make informed decisions regarding the selection and utilization of 3W LEDs in various lighting scenarios.
Efficiency, Luminous Flux, and Color Rendering

In the realm of illuminative technology, the efficacy of lighting systems encompasses various facets, including their luminous efficiency, flux output, and ability to render colors accurately. These attributes are pivotal in determining the overall performance and quality of illumination sources.
- Luminous Efficiency: This aspect pertains to the effectiveness with which a lighting system converts electrical power into visible light. It signifies the ratio of emitted luminous flux to the power consumed by the system.
- Flux Output: Often referred to as luminous flux, this metric quantifies the total amount of visible light emitted by a lighting source. It is measured in lumens and signifies the brightness perceived by the human eye.
- Color Rendering: An essential characteristic, color rendering denotes the ability of a lighting source to accurately reproduce the colors of objects in comparison to a natural light source. It plays a crucial role in various applications, such as photography, retail displays, and architectural lighting.
Understanding these parameters aids in evaluating the performance and suitability of lighting solutions for diverse environments and applications. High efficacy, ample luminous flux, and superior color rendering are indicative of a lighting system’s capability to deliver optimal visual experiences.
Application Considerations for 3W LEDs
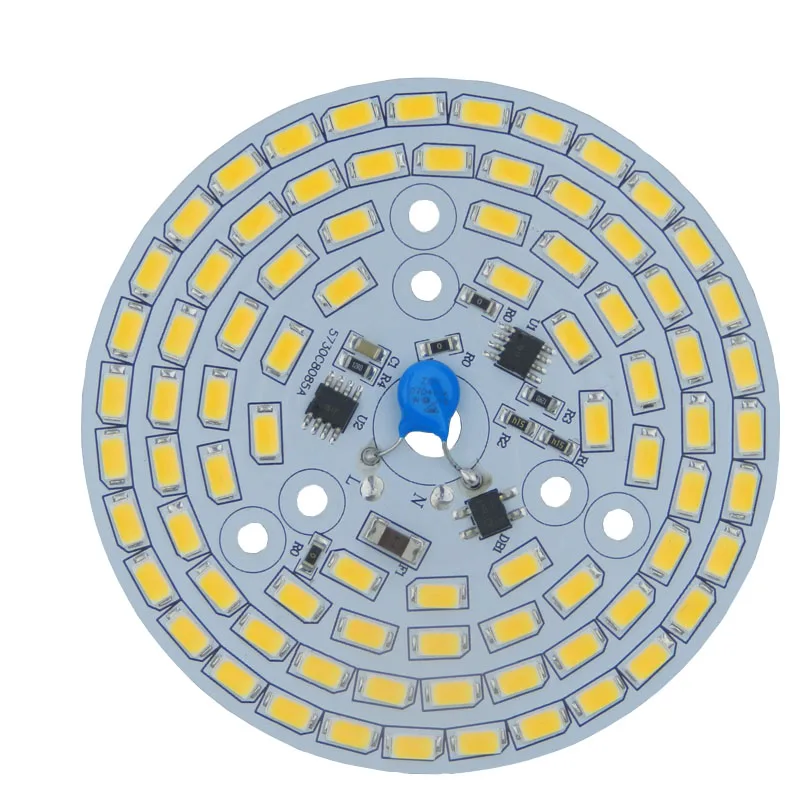
Exploring the practical aspects of integrating three-watt light-emitting diodes (LEDs) into various systems demands a nuanced understanding of their operational intricacies. Harnessing their luminosity requires careful attention to several critical factors, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
When incorporating these high-intensity illumination components, it’s imperative to evaluate factors beyond mere wattage. Factors such as thermal management, voltage compatibility, and circuit design intricacies profoundly influence the efficacy and reliability of the LED system. Consequently, a comprehensive comprehension of these considerations is paramount for seamless integration and sustained functionality.
| Consideration | Key Points |
| Thermal Management | Efficient heat dissipation mechanisms are essential to mitigate the adverse effects of thermal stress, safeguarding the LED’s luminous efficacy and prolonging its operational lifespan. |
| Voltage Compatibility | Ensuring alignment between the LED’s operating voltage and the power supply’s output voltage is critical to prevent voltage fluctuations that could compromise performance or lead to premature failure. |
| Circuit Design | Thoughtful circuitry design, including appropriate current regulation and protective measures against voltage spikes, is indispensable for stable LED operation and safeguarding against electrical anomalies. |
| Optical Considerations | Understanding the LED’s optical characteristics, such as beam angle and color rendering properties, facilitates optimal placement and configuration to achieve desired lighting outcomes. |
| Environmental Factors | Assessing environmental conditions, including temperature variations and humidity levels, enables the implementation of measures to fortify the LED system against adverse effects, ensuring consistent performance in diverse settings. |
In summation, successful integration of three-watt LEDs necessitates a holistic approach encompassing thermal management, voltage compatibility, circuit design, optical considerations, and environmental factors. By addressing these considerations conscientiously, practitioners can unlock the full potential of these luminous components, delivering enduring illumination solutions across a spectrum of applications.