
Unlocking the potential of light-dependent devices involves delving into a realm where ambient light dictates functionality. These components, imbued with the ability to respond to varying luminance levels, form the backbone of numerous applications across industries.
In this segment, we embark on a journey to comprehend the intricate workings of elements that react to light stimuli, illuminating pathways to innovation and advancement.
Discover the underlying mechanisms behind these light-sensitive entities, unraveling their significance in modern technology landscapes. Through insightful exploration, gain a deeper understanding of their behavior and applications, paving the way for transformative breakthroughs.
Understanding the GL5539 Light-Sensitive Resistor: Essential Features and Practical Implementations
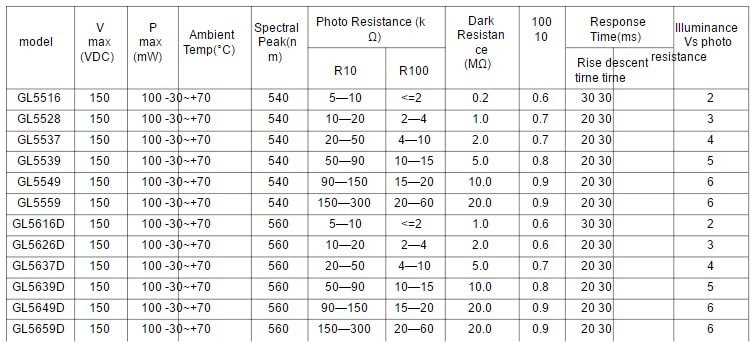
Exploring the realm of light-sensitive resistors opens pathways to innovative applications in various industries. This section delves into the intricate workings and versatile applications of the GL5539, a prominent component in light detection technology.
At its core, the GL5539 functions as a reactive component to light stimuli, offering a dynamic response to varying light levels. Its design facilitates modulation of electrical resistance in correspondence to incident light intensity, enabling nuanced control in diverse environments.
- Sensitivity: The GL5539 boasts remarkable sensitivity, adept at discerning subtle changes in light levels. This heightened sensitivity equips it for applications demanding precise light detection, such as ambient light sensing in electronic devices and automated lighting systems.
- Response Time: With swift response times, the GL5539 swiftly adapts to fluctuating light conditions, ensuring real-time adjustments in connected systems. This rapid responsiveness is pivotal in applications requiring immediate feedback, including camera exposure control and light-responsive switches.
- Wide Operating Range: Operating across a broad spectrum of light wavelengths, the GL5539 offers versatility in its applications. From ultraviolet to infrared, its adaptability spans various lighting scenarios, making it indispensable in fields like photography, industrial automation, and security systems.
- Reliability: Engineered for durability and stability, the GL5539 upholds reliability even in challenging environmental conditions. Its robust construction ensures consistent performance over extended periods, making it a preferred choice in mission-critical applications like solar tracking systems and weather monitoring devices.
Embracing the GL5539 opens avenues for innovation across industries, from enhancing energy efficiency to augmenting sensory capabilities in smart technologies. By harnessing its sensitivity and versatility, engineers and developers can craft solutions that harmonize with the dynamic interplay of light in the modern landscape.
The Science Behind GL5539: Understanding the Functionality of a Light Dependent Resistor

Light Dependent Resistors (LDRs), like the GL5539, operate on the principle of light sensitivity, making them vital components in various electronic systems. These devices exhibit a fascinating property wherein their resistance alters in response to incident light intensity. This section delves into the intricate mechanisms underlying the functionality of these sensors, shedding light on their pivotal role in modern technology.
At the core of an LDR’s operation lies its ability to modulate electrical resistance according to the intensity of light it encounters. This dynamic behavior stems from the unique semiconductor material composition within the resistor. When exposed to light, the semiconductor material undergoes subtle changes at the atomic level, influencing the flow of electrical current through the device. As a result, the resistance of the LDR fluctuates, directly correlating with the ambient light levels.
- Photon Absorption and Electron Excitation: When photons, the fundamental particles of light, strike the surface of the LDR, they impart energy to the semiconductor atoms. This energy absorption prompts electrons within the material to transition to higher energy states, creating electron-hole pairs.
- Conduction Band Excursion: The energized electrons migrate from the valence band to the conduction band, leaving behind positively charged holes in the valence band. This movement of charge carriers alters the conductivity of the semiconductor, affecting its overall resistance.
- Intensity-Dependent Conductivity: The extent of electron excitation and subsequent conductivity changes in the semiconductor material depends on the intensity of incident light. Higher light levels result in more significant electron excitation, leading to a decrease in resistance, while lower light levels correspond to increased resistance.
Understanding the intricate interplay between incident light, semiconductor properties, and electrical conductivity unveils the underlying principles driving the operation of light-dependent resistors like the GL5539. This nuanced relationship forms the basis of their functionality across diverse applications, from light-sensing circuits in automated lighting systems to exposure control mechanisms in photography equipment.
Practical Implementations: Leveraging the GL5539 in Diverse Electronic Applications

In the realm of electronic engineering, the integration of light-sensitive resistors, such as the GL5539, has become paramount for a multitude of innovative applications. This section explores the practical utilization of a light-dependent resistor (LDR) within various electronic systems, showcasing its versatility and adaptability across different domains.
One of the primary domains benefiting from the incorporation of light-sensitive resistors is ambient light sensing. By harnessing the unique properties of the GL5539, electronic systems can dynamically adjust display brightness levels, providing optimal viewing experiences in diverse lighting conditions. Additionally, these resistors find extensive use in the realm of security systems, where they serve as critical components for detecting unauthorized entry by monitoring changes in ambient light levels.
Furthermore, the application of light-dependent resistors extends into the realm of environmental monitoring. Within this domain, these components facilitate the development of sophisticated systems capable of measuring light intensity variations in outdoor environments. Such systems play a pivotal role in weather forecasting, agriculture, and urban planning by providing valuable data on sunlight exposure and environmental changes.
| Electronic System | Application |
|---|---|
| Display Systems | Automatic brightness adjustment based on ambient light levels |
| Security Systems | Detection of unauthorized entry through monitoring ambient light changes |
| Environmental Monitoring | Measurement of light intensity for weather forecasting and environmental analysis |
Moreover, the GL5539 facilitates the development of innovative solutions in the domain of automation. By integrating these resistors into electronic circuits, automated systems can respond intelligently to changes in light conditions, optimizing energy consumption and enhancing overall efficiency.
In conclusion, the practical applications of the GL5539 extend far beyond conventional light sensing, encompassing a diverse array of electronic systems. From enhancing display technologies to advancing environmental monitoring capabilities, the integration of light-dependent resistors continues to drive innovation across various domains, underscoring their indispensable role in modern electronic engineering.
Optimizing Performance: Tips for Enhancing Usage and Calibration of Light-Sensitive Sensor
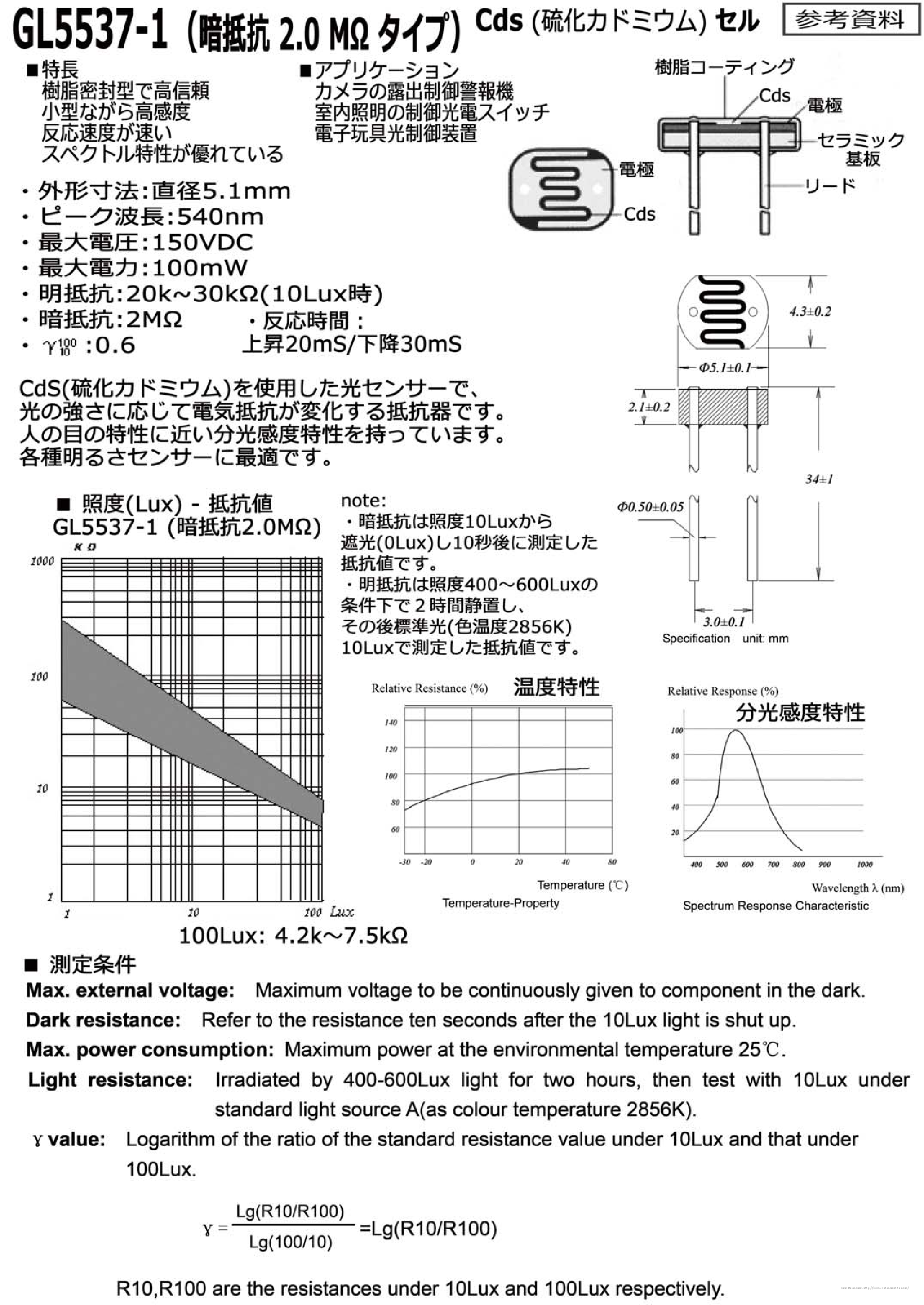
Exploring the intricacies of maximizing the efficiency and accuracy of a certain light-sensitive sensor involves a comprehensive approach that encompasses both meticulous usage and precise calibration. In this section, we delve into the nuanced strategies and techniques aimed at refining the performance of this sensor, ensuring optimal functionality and reliability in varied applications.
Understanding Environmental Influences
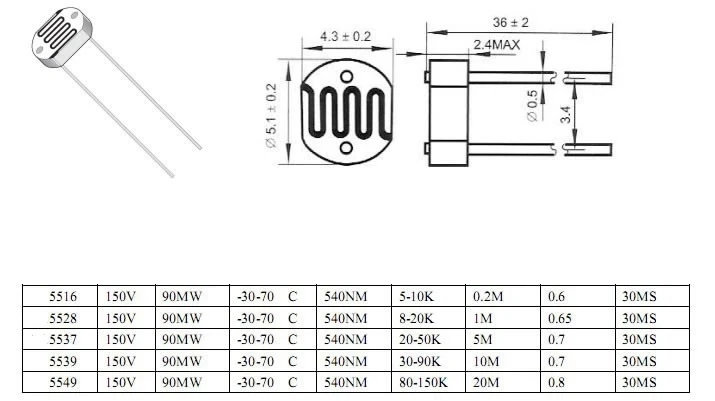
One pivotal aspect in harnessing the full potential of this sensor lies in comprehending the multifaceted influences exerted by the surrounding environment. From ambient light fluctuations to temperature variations, each factor plays a significant role in shaping the sensor’s responsiveness and accuracy. By acknowledging and proactively mitigating these environmental nuances, users can enhance the sensor’s performance and maintain consistent results across diverse conditions.
Fine-Tuning Calibration Parameters

Calibration stands as a cornerstone in the quest for precision and reliability in sensor applications. Through meticulous adjustment of calibration parameters, users can align the sensor’s output with desired specifications, minimizing discrepancies and optimizing performance. This section delves into the intricacies of fine-tuning calibration settings, offering insights into the process of achieving optimal sensor response and accuracy through precise adjustments.