
When it comes to achieving a reliable and effective seal between two or more parts, one component plays a crucial role – the gasket. However, understanding the intricacies and specifications of gaskets can be a perplexing task. In this article, we delve into the world of gasket data, exploring the various elements that contribute to the seamless functionality of these essential components.
The Key to Success: Gasket Specifications
An assembly line or a mechanical system is like a well-oiled machine, where each part has a designated purpose. In this intricate setup, gaskets act as the unsung heroes, ensuring a secure connection and preventing leakage or contamination. But what makes a gasket successful? It all boils down to precise specifications.
From material selection to surface finish requirements, gasket datasheets contain a wealth of information that can make or break an application. By thoroughly examining these specifications, engineers can make informed decisions about the correct gasket to use, maximizing efficiency and performance.
Decoding the Secrets: Material Characteristics
When it comes to gaskets, one size certainly does not fit all. In fact, gaskets come in a wide range of materials, each possessing unique characteristics tailored to specific applications. From rubber and silicone to metal and fiber materials, gasket datasheets outline the ideal properties required for compatibility, temperature resistance, and chemical resistance.
By understanding the material properties and their relevance to the application at hand, engineers can select the most suitable material for their gasket, ensuring a perfect seal that withstands the test of time.
A Closer Look: Technical Data and Performance
Behind every successful gasket lies a treasure trove of technical data and performance metrics. Gasket datasheets provide comprehensive information about compression levels, maximum and minimum operating temperatures, pressure ratings, and more, enabling engineers to fine-tune their designs for optimal performance.
With these vital statistics at their disposal, engineers can ensure that the gasket not only meets the demands of the application but also extends the lifespan of the overall system, saving time and resources in the long run.
Unlocking the secrets of gasket datasheets equips engineers with the knowledge needed to select, design, and implement gaskets with precision, ensuring a reliable and efficient seal in any given application. So, whether it’s in the automotive industry, machinery, or plumbing systems, a thorough understanding of gasket data is crucial for success.
Understanding Gasket Specifications and Terminology

In this section, we will delve into the key specifications and terminology used in the field of gaskets. By understanding these terms and their significance, you will be able to make informed decisions when selecting the appropriate gasket for your specific application.
Types of Gaskets
Before delving into the specifications, it is crucial to have a basic understanding of the different types of gaskets available. Gaskets are commonly classified into three main categories: sheet gaskets, spiral wound gaskets, and ring gaskets. Each type has its distinct characteristics and recommended applications, ensuring optimal performance for different sealing needs.
Common Gasket Specifications

When it comes to selecting the right gasket for your application, several specifications need to be taken into consideration. These specifications include dimensions, material composition, temperature range, pressure rating, and chemical compatibility. Each of these factors plays a crucial role in ensuring a proper seal and preventing leakage in various operating conditions.
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | Refers to the size and shape of the gasket, including inner and outer diameter, thickness, and tolerances. |
| Material Composition | Indicates the materials used in constructing the gasket, such as rubber, metal, or a combination, and their respective properties. |
| Temperature Range | Specifies the minimum and maximum temperatures the gasket can withstand without compromising its sealing capabilities. |
| Pressure Rating | Refers to the maximum pressure the gasket can handle without extrusion or failure, typically measured in pounds per square inch (psi) or bars. |
| Chemical Compatibility | Indicates the gasket’s resistance to various chemicals, solvents, and fluids, ensuring it will not degrade or react adversely when exposed to specific substances. |
By familiarizing yourself with these specifications and understanding their significance, you will be able to choose the right gasket that meets your operational requirements and ensures a reliable and long-lasting seal.
Selecting the Right Gasket Material for Various Applications
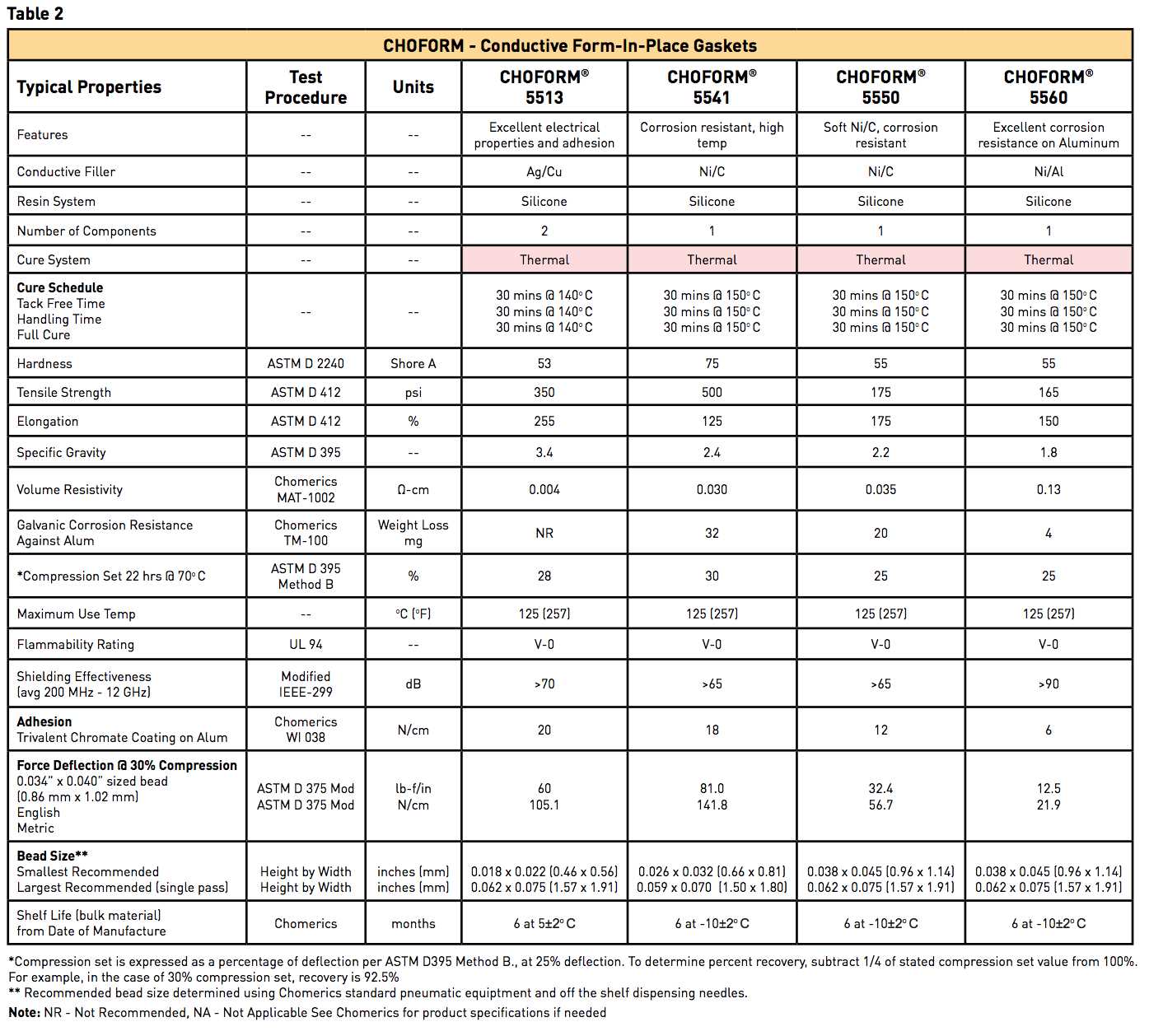
In the field of industrial sealing, it is crucial to carefully choose the appropriate gasket material for different applications. A gasket acts as a barrier between two surfaces, preventing leakage or the ingress of contaminants. The selection of the right gasket material depends on several factors, including the operating conditions, the type of fluid or gas being sealed, and the physical properties required for the specific application.
Factors to Consider

When selecting a gasket material, it is important to take into account the temperature range that it will be exposed to. Different materials have varying thermal capabilities, and choosing a gasket material with the appropriate temperature resistance is essential to ensure the seal remains intact under extreme conditions.
Additionally, the compatibility of the gasket material with the fluid or gas it will be sealing is critical. Certain chemicals can cause degradation or swelling of certain gasket materials, leading to ineffective seals and potential hazards. Therefore, understanding the chemical compatibility between the gasket material and the fluid or gas is crucial in selecting the right material.
Gasket Material Options
There are several types of gasket materials available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. One common option is rubber gaskets, which are versatile and used in various applications. Rubber gaskets offer good temperature resistance, chemical compatibility, and flexibility.
Metallic gaskets, on the other hand, offer superior temperature and pressure resistance. They are often used in high-pressure applications and where extreme temperatures are involved. Metallic gaskets are known for their durability and ability to maintain a tight seal even under harsh conditions.
Another option is fiber gaskets, which are made from materials such as paper, aramid, or cellulose. These gaskets offer excellent resistance to chemicals and can be used in applications where flange surfaces are not perfectly flat. However, they are less suitable for high-temperature applications.
- Consider the operating temperature range when selecting a gasket material.
- Ensure the compatibility of the gasket material with the fluid or gas being sealed.
- Evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of different gasket materials like rubber, metallic, and fiber gaskets.
By carefully considering the factors mentioned above and evaluating the specific requirements of each application, it is possible to select the right gasket material that will provide an effective seal and ensure the proper functioning of the equipment or system.
Installation and Maintenance Tips for Long-lasting Gasket Performance

When it comes to ensuring the longevity and optimal functioning of your sealing component, there are certain key factors to consider during the installation and maintenance process. By following these best practices, you can enhance the performance and longevity of your gasket without compromising its integrity.
- Thoroughly inspect the sealing surface before installing the gasket. Visually examine the area for any signs of debris, corrosion, or damage that could hinder proper sealing. Address any issues before proceeding, as a clean and smooth surface is essential for achieving an effective seal.
- Ensure the gasket is positioned correctly. Align it precisely in the designated area, taking into account any specific markings or instructions provided by the manufacturer. Proper alignment will help to evenly distribute stress and prevent potential leaks.
- Apply the appropriate torque during installation. Over-tightening can cause damage to the gasket, while under-tightening may lead to insufficient compression and leakage. Refer to the manufacturer’s specifications or guidelines to determine the correct torque value to ensure a secure but not excessive fit.
- Regularly monitor the gasket for any signs of wear or deterioration. Inspect it visually and check for any abnormalities such as cracks, tears, or loss of elasticity. Address any issues promptly to prevent potential performance issues or leakage.
- Consider using a gasket lubricant or sealant when appropriate. This can help facilitate easier installation, reduce friction, and enhance the sealing capabilities of the gasket.
- Implement a regular maintenance schedule to prolong the lifespan of your gasket. Follow the recommended maintenance intervals provided by the manufacturer or establish a schedule based on the specific operating conditions of your application. This will help identify any potential issues early on and allow for timely repairs or replacements.
- Take into account the specific operating conditions and requirements of your application when selecting a gasket material. Different materials possess varying resistance to temperature, pressure, chemicals, and other factors. Choosing the right material for your specific needs will optimize performance and ensure longer-lasting sealing capabilities.
By adhering to these installation and maintenance tips, you can ensure the long-lasting performance and reliability of your gaskets. Remember, while gaskets may vary in design and material, proper installation and regular maintenance are universal principles that promote optimal sealing functionality in any application.