In today’s digital landscape, navigating through the intricacies of electronic components is akin to deciphering a complex puzzle. Every electronic device, from the simplest gadgets to the most sophisticated machinery, relies on a myriad of components to function seamlessly. Within this intricate ecosystem, one crucial aspect lies in understanding the specifications and functionalities of these components. Technical documents serve as the guiding light, offering a comprehensive roadmap to engineers and enthusiasts alike.
Within the realm of electronic engineering, these documents, akin to blueprints, unveil the inner workings of components with precision and clarity. Among these documents lies a particular treasure trove, often sought after by enthusiasts and professionals alike. Delving into the specifications, capabilities, and intricacies of electronic components, these documents offer insights that transcend mere descriptions, providing a gateway to innovation and exploration.
Embarking on a journey through these documents unveils a world of possibilities, where each specification carries significance and every detail holds potential. As we embark on an exploration of one such document, we delve into the depths of innovation and ingenuity, where every line of text whispers secrets waiting to be uncovered. Join us as we navigate through the labyrinth of technical documentation, uncovering the nuances and intricacies that shape the world of electronic engineering.
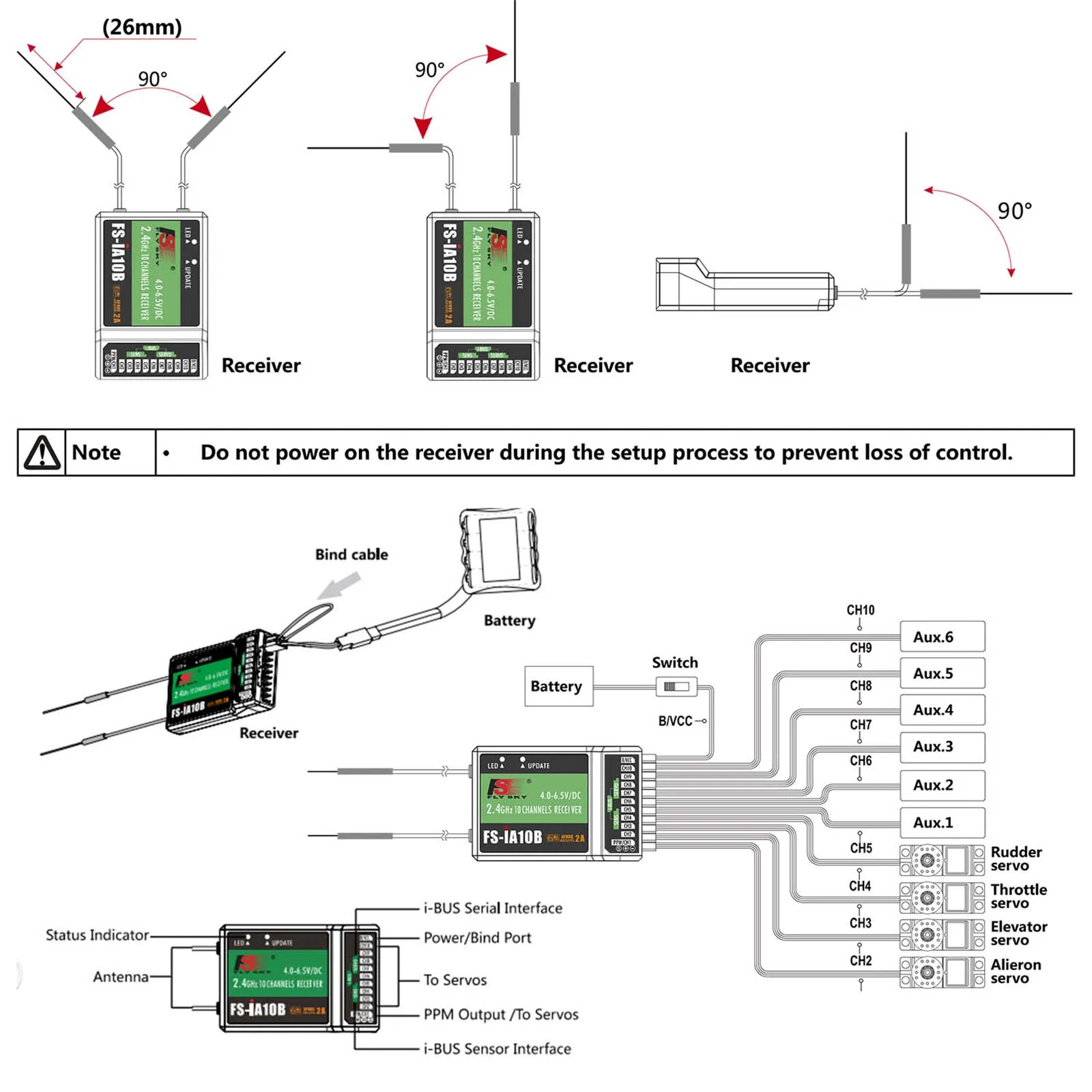
Fs-ia10b Datasheet Overview

Within this section, we delve into an expansive exploration of the essential components and functionalities encapsulated within the intricate framework of the Fs-ia10b documentation. This elucidation aims to furnish a comprehensive understanding of the manifold features and operational modalities integral to the aforementioned entity, thereby facilitating an informed comprehension for stakeholders and enthusiasts alike.
Functional Insights

Embarking upon a journey through the intricacies of the Fs-ia10b apparatus, one encounters a panorama of functionalities meticulously engineered to cater to a diverse array of operational requisites. These functionalities, woven intricately into the fabric of the device, serve as the cornerstone for its efficacy and versatility, enabling seamless integration within myriad contexts and applications.
Technical Specifications

Delving deeper into the realm of technical specifications, one unearths a trove of quantitative data elucidating the nuanced intricacies of the Fs-ia10b’s architecture. From transmission frequencies to signal processing capabilities, each specification delineates a facet of the device’s prowess, underpinning its capacity to transcend conventional boundaries and redefine operational paradigms.
Understanding the Key Features
In this section, we delve into the essential aspects that define the functionality and capabilities of the device under scrutiny. Through a comprehensive examination of its primary attributes, we aim to provide a clear understanding of its operational scope and potential utility.
1. Core Functionality
The fundamental operations and functionalities encapsulated within the device constitute the cornerstone of its efficacy. From its core functionalities stem a myriad of capabilities, each contributing to its overall performance and versatility. Understanding these core features lays the groundwork for leveraging the device to its fullest potential.
2. Innovative Characteristics
Beyond its basic functionalities lie a host of innovative characteristics that set the device apart in its niche. These distinctive traits encompass advanced technologies, novel methodologies, and unique approaches to problem-solving. By comprehending these innovative features, users can harness the full spectrum of the device’s capabilities for various applications.
| Key Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Integration | The seamless integration of diverse components enhances interoperability and ease of use. |
| Robustness | The device’s robust design ensures resilience and reliability even in demanding environments. |
| Scalability | Scalable architecture enables the device to adapt to evolving requirements and scale effortlessly. |
| Customizability | Flexible configurations allow for customization tailored to specific user needs and preferences. |
Exploring Technical Specifications
Delving into the intricacies of electronic components entails a comprehensive examination of their technical specifications. These specifications serve as the blueprint, outlining the functional capabilities, performance metrics, and operational parameters of the device. In this section, we embark on a journey to dissect and elucidate the multifaceted aspects of the component’s technical attributes, unraveling its intricacies and shedding light on its potential applications.
Functional Capabilities
Understanding the functional capabilities of a component involves deciphering its intended purpose and the range of tasks it can perform within a given system. This encompasses an analysis of its operational modes, input-output interfaces, signal processing capabilities, and compatibility with other system components. By scrutinizing these aspects, one gains insight into the component’s versatility and its ability to fulfill specific requirements within diverse applications.
Performance Metrics
Performance metrics serve as quantitative measures of a component’s efficiency, reliability, and effectiveness in carrying out its designated functions. These metrics encompass parameters such as data transfer rates, latency, power consumption, signal-to-noise ratio, and operating temperature range. Through a meticulous examination of these metrics, one can assess the component’s overall performance under various operating conditions and ascertain its suitability for specific tasks.
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Transfer Rate | The rate at which data is transmitted between the component and other devices, typically measured in bits per second (bps) or bytes per second (Bps). |
| Latency | The delay incurred in processing and transmitting data, often measured in milliseconds (ms) or microseconds (μs). |
| Power Consumption | The amount of electrical power consumed by the component during operation, expressed in watts (W) or milliwatts (mW). |
| Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) | The ratio of the amplitude of the signal to the amplitude of noise present in the system, typically measured in decibels (dB). |
| Operating Temperature Range | The range of temperatures within which the component can safely operate without experiencing degradation or failure, specified in degrees Celsius (°C) or Fahrenheit (°F). |
By meticulously examining these technical specifications, engineers and designers can make informed decisions regarding the integration of the component into their systems, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Optimizing Performance with the Cutting-Edge Technology
To unlock the full potential of this advanced hardware, it’s crucial to delve into the intricacies of fine-tuning and maximizing efficiency. This section explores strategies for elevating performance metrics and achieving optimal outcomes with state-of-the-art technology.
Streamlining Operations: Enhancing operational fluidity entails a comprehensive evaluation of system dynamics, identifying bottlenecks, and implementing streamlined processes. By fine-tuning operational procedures, users can harness the full power of their hardware investment.
Maximizing Efficiency: Efficiency optimization revolves around leveraging resources judiciously and minimizing wastage. Through meticulous calibration and resource allocation, users can achieve peak performance without overburdening the system.
Enhancing Throughput: Elevating throughput requires a multifaceted approach involving software optimization, hardware configuration, and algorithmic enhancements. By prioritizing throughput enhancement strategies, users can elevate productivity and accelerate task completion.
Improving Latency: Latency reduction is paramount for real-time applications, necessitating latency-aware design considerations and latency optimization techniques. By mitigating latency hurdles, users can enhance responsiveness and ensure seamless user experiences.
Optimizing Power Consumption: Power optimization strategies focus on striking a balance between performance requirements and energy efficiency. Through voltage regulation, power gating, and low-power modes utilization, users can minimize power consumption without compromising performance.
Fine-tuning Parameters: Fine-tuning involves meticulous adjustment of parameters to align system behavior with performance objectives. By optimizing configurations and parameter settings, users can tailor the system to specific workload requirements and achieve optimal performance.
Implementing Best Practices: Best practices encompass a spectrum of proven methodologies for maximizing performance, encompassing code optimization, task parallelization, and utilization of hardware acceleration features. By adhering to best practices, users can unlock the full potential of their hardware investment and achieve exceptional performance outcomes.
Tips for Streamlined Integration
Efficiently incorporating advanced electronic components into your projects requires careful planning and execution. Here are some strategies to optimize your implementation:
1. Prioritize Component Compatibility
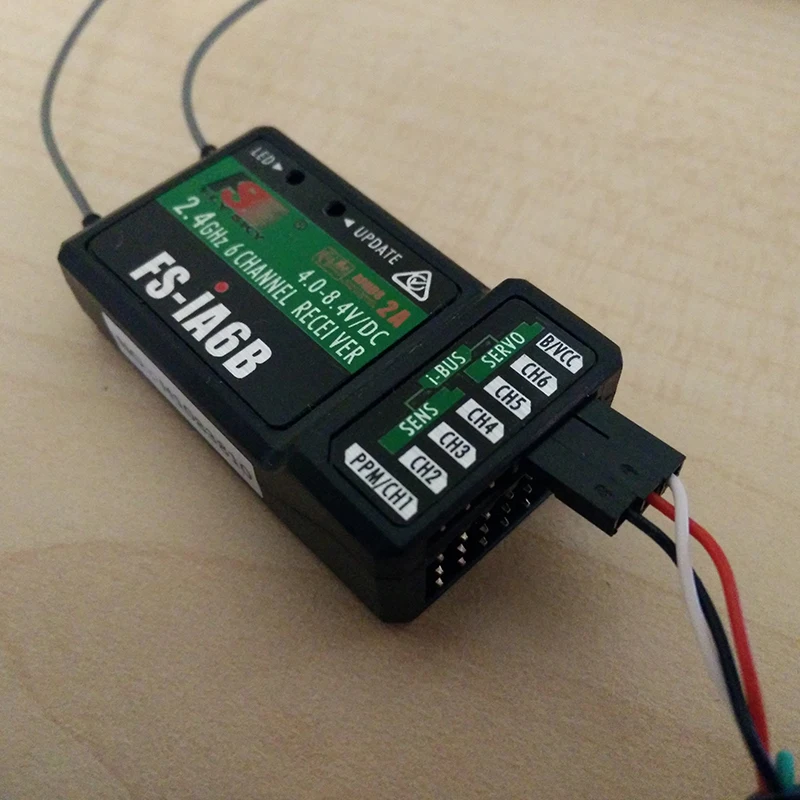
Ensure that the components you select are compatible with your project’s requirements and existing infrastructure. Compatibility issues can lead to delays and additional expenses during integration.
2. Optimize Power Management
Efficient power management is crucial for maximizing the performance and longevity of your system. Implementing intelligent power-saving techniques and selecting energy-efficient components can significantly enhance overall efficiency.
- Utilize low-power modes whenever possible to minimize energy consumption during idle periods.
- Consider implementing dynamic voltage scaling to adapt power supply levels based on workload demands.
- Explore alternative power sources such as renewable energy options to reduce reliance on traditional power grids.
3. Employ Effective Signal Routing
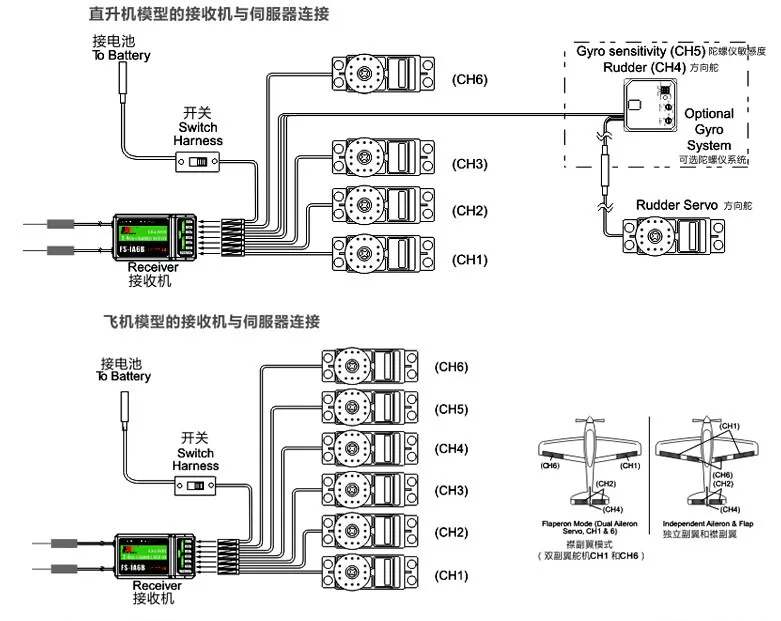
Proper signal routing is essential for maintaining signal integrity and minimizing electromagnetic interference (EMI). Follow best practices to ensure optimal signal paths and reduce the risk of signal degradation:
- Keep signal traces short and direct to minimize signal loss and interference.
- Implement ground planes and shielding techniques to mitigate EMI and reduce noise.
- Use high-quality connectors and cables to maintain signal integrity over long distances.
By prioritizing compatibility, optimizing power management, and employing effective signal routing techniques, you can streamline the integration process and maximize the performance of your electronic projects.