
Discovering the intricacies of an electronic component’s technical documentation entails delving into a realm where every specification holds significance, where seemingly mundane details can unlock profound insights into its functionality and application. Within the realm of electrical engineering, these documents serve as portals to understanding the capabilities and limitations of components, offering engineers a roadmap to harness their potential.
Within these comprehensive guides lie a wealth of knowledge waiting to be unearthed, offering a narrative of performance metrics, operational parameters, and design considerations. Through meticulous analysis and interpretation, engineers decode the language of specifications, transforming abstract numbers into actionable intelligence.
As engineers navigate through the labyrinth of technical jargon and performance graphs, they unearth critical nuances that shape their design decisions and define the success of their projects. Each data point, each curve, serves as a beacon guiding engineers towards optimal solutions, steering them away from pitfalls and towards innovation.
Understanding Specifications of Ferrite Bead Components
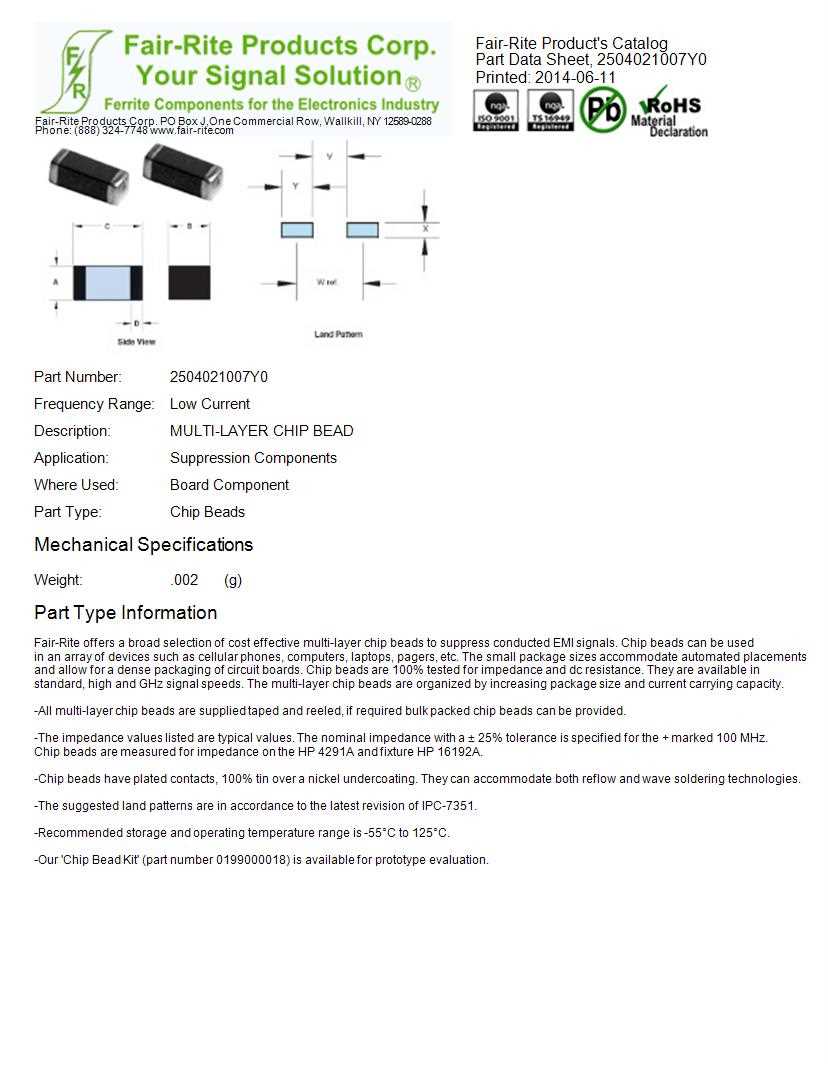
In this section, we delve into the intricacies of the technical specifications pertaining to the compact magnetic components commonly found in electronic circuits. By unraveling the nuances of these specifications, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of how these components contribute to circuit functionality.
Core Characteristics: The fundamental properties of these magnetic elements play a pivotal role in shaping their performance within electronic circuits. Exploring the core characteristics sheds light on their magnetic permeability, saturation flux density, and frequency response, all of which influence their effectiveness in suppressing electromagnetic interference.
Impedance Profile: Understanding the impedance profile unveils the behavior of ferrite beads across different frequencies, elucidating their ability to attenuate unwanted noise while preserving signal integrity. Analysis of impedance characteristics aids in selecting the most suitable component for specific applications, ensuring optimal performance.
DC Bias Performance: Evaluating the DC bias performance provides insights into the behavior of ferrite beads under varying levels of direct current. This parameter elucidates how the component’s impedance alters in response to DC bias, offering crucial information for designing circuits that operate within specified voltage ranges.
Temperature Stability: The temperature stability of ferrite beads delineates their resilience to fluctuations in operating conditions. Examining temperature coefficients and thermal resistance enables engineers to anticipate performance variations across different environmental scenarios, ensuring reliability in diverse applications.
Manufacturing Tolerances: Delving into manufacturing tolerances elucidates the degree of variation permissible in key parameters such as inductance and impedance. Understanding these tolerances aids in mitigating uncertainties during component selection and facilitates adherence to desired circuit specifications.
Application Considerations: Integrating the understanding of specifications with practical application scenarios enables engineers to make informed decisions regarding ferrite bead utilization. By aligning component characteristics with specific circuit requirements, designers can optimize performance and enhance overall system robustness.
By comprehensively grasping the nuances of ferrite bead specifications, engineers can leverage these compact yet essential components to mitigate electromagnetic interference effectively, bolstering the reliability and performance of electronic systems.
Deciphering Electrical Parameters

In the realm of electronic component specifications, understanding the intricacies of electrical parameters is paramount. These specifications serve as the cornerstone for evaluating the performance and compatibility of the component within a given circuit. Within the confines of a comprehensive datasheet, a wealth of electrical parameters are meticulously outlined, each carrying its significance in influencing the behavior and functionality of the component in operation.
Impedance Characteristics
One of the pivotal electrical parameters to scrutinize is the impedance profile, which delineates the component’s response to alternating current (AC) signals across a range of frequencies. This profile encapsulates the intricate interplay between the component and the electrical environment it is embedded within, providing insights into its efficacy in mitigating unwanted noise and interference.
Frequency Response

Another critical aspect to unravel is the frequency response, elucidating how the component’s impedance varies with respect to the frequency of the input signal. This elucidation is pivotal in discerning the component’s efficacy across different operational frequencies, thereby facilitating informed design decisions.
| Electrical Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Impedance Profile | Defines the component’s response to AC signals across various frequencies, crucial for noise suppression. |
| Frequency Response | Illustrates how the component’s impedance varies with the frequency of the input signal, aiding in frequency-dependent applications. |
Interpreting Performance Graphs

Understanding the graphical representations provided in the documentation is crucial for effectively utilizing the properties of the component. These visual aids offer insights into the behavior and functionality of the item under various conditions. By deciphering the patterns and trends depicted in these graphs, users can optimize their application’s performance and ensure seamless integration.
Key Parameters
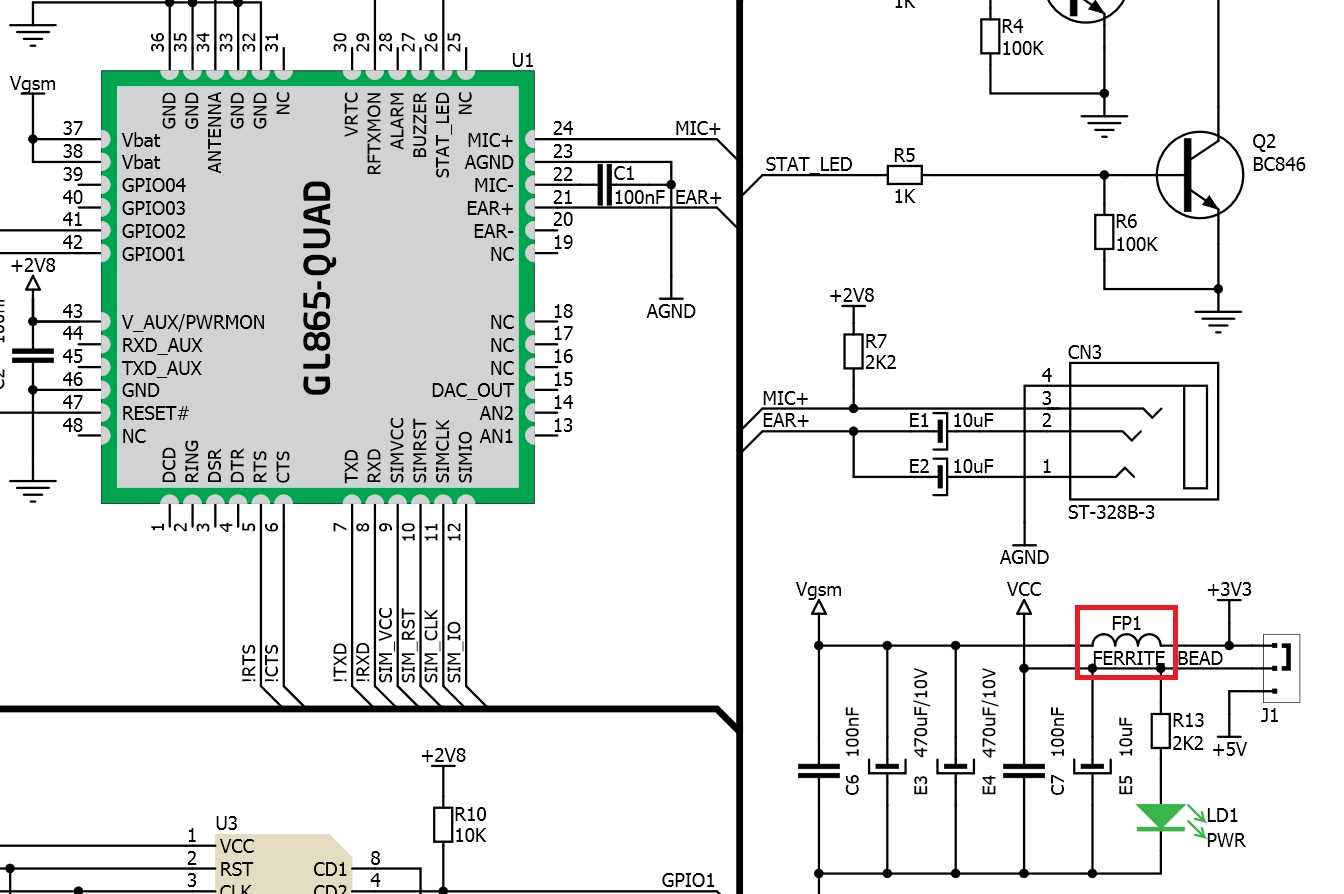
Before delving into the specifics of the graphs, it’s essential to grasp the key parameters they represent. These parameters encapsulate the essential characteristics of the component’s performance, such as its impedance, frequency response, and attenuation capabilities. Familiarizing oneself with these parameters is fundamental to interpreting the graphs accurately.
- Impedance: The opposition to the flow of alternating current, measured in ohms, defines how a component interacts with an electrical signal.
- Frequency Response: The variation in the component’s behavior concerning different frequencies of the input signal, often depicted in terms of gain or attenuation.
- Attenuation: The reduction in signal strength as it passes through the component, typically expressed in decibels (dB).
Graphical Analysis
Interpreting the graphs involves a systematic approach to analyze the relationships between the parameters across varying conditions. Paying close attention to the axes, scales, and annotations is paramount for accurate interpretation. Here are some fundamental aspects to consider:
- Trend Identification: Look for recurring patterns or trends across different graphs, indicating consistent behavior under specific conditions.
- Boundary Conditions: Identify the limits within which the component operates optimally, ensuring that the application adheres to these boundaries for optimal performance.
- Comparative Analysis: Compare multiple graphs to discern how different parameters interact with each other and how they influence the overall performance of the component.
By mastering the interpretation of performance graphs, users can harness the full potential of the component and make informed decisions regarding its integration into their designs.
Unlocking Application Insights in Component Documentation
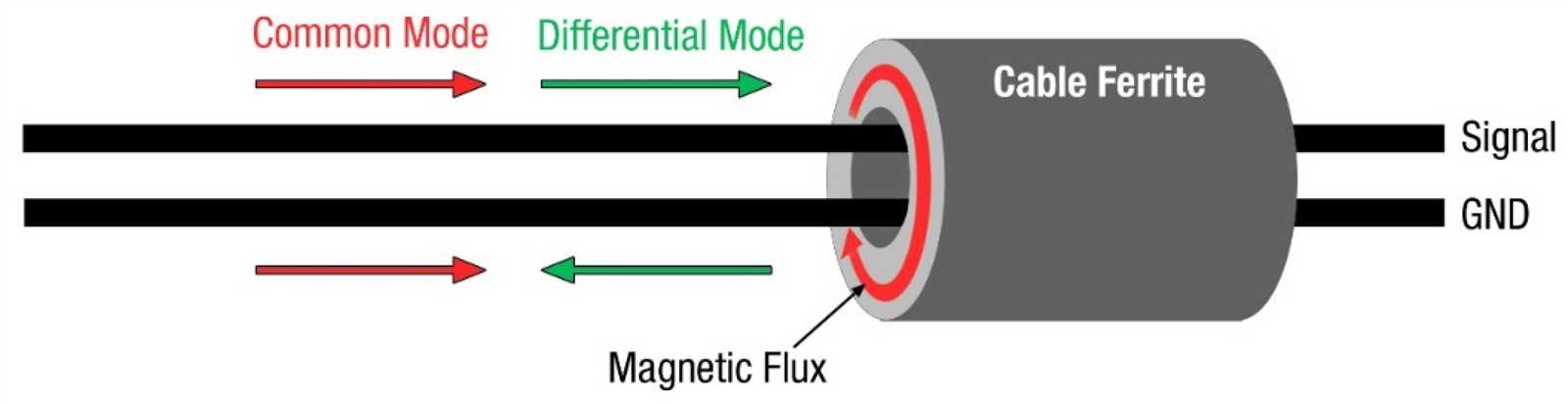
Delving into the intricacies of component documentation reveals a treasure trove of application insights waiting to be unearthed. Understanding how these components interact within various circuitry setups provides invaluable knowledge for engineers and designers alike.
Deciphering Performance Characteristics
Within the confines of technical documentation lies a wealth of information regarding the operational behavior of these vital components. By dissecting the performance characteristics outlined within these documents, engineers can gain crucial insights into how the component responds to different electrical stimuli.
Optimizing Integration Strategies

Furthermore, exploring the integration guidelines outlined in these materials unveils best practices for incorporating the component seamlessly into circuit designs. By discerning the recommended placement, connections, and environmental considerations, engineers can optimize the performance and reliability of their systems.
Unlocking these application insights empowers engineers to harness the full potential of these components, ultimately leading to more robust and efficient electronic designs.
Optimal Circuit Integration

In this section, we delve into the seamless integration of essential components to enhance the overall performance and efficiency of electronic circuits. Emphasizing the synergy between various elements, we explore strategies for maximizing circuit efficacy while minimizing potential drawbacks.
| Component Selection | Choosing the appropriate components plays a pivotal role in circuit optimization. By meticulously evaluating the specifications and characteristics of each element, engineers can ensure harmonious interaction within the circuit architecture. |
| Topology Consideration | Examining circuit topology offers insights into the arrangement and connectivity of components. Employing suitable topological configurations fosters efficient signal propagation and mitigates undesirable effects such as noise and interference. |
| Parameter Tuning | Fine-tuning circuit parameters allows for precise control over performance metrics. Adjusting parameters such as impedance, frequency response, and bandwidth optimizes circuit behavior to meet specific operational requirements. |
| Integration Techniques | Implementing advanced integration techniques facilitates seamless incorporation of components into the circuit framework. Strategies such as impedance matching, decoupling, and signal conditioning enhance compatibility and functionality. |
| Simulation and Testing | Simulation and rigorous testing serve as indispensable tools for evaluating circuit performance. Through simulation models and experimental validation, engineers can iteratively refine circuit design, ensuring optimal functionality under diverse operating conditions. |
By embracing a holistic approach to circuit integration, engineers can unleash the full potential of electronic systems, achieving superior performance, reliability, and functionality.