Exploring the intricacies of modern electronic equipment often leads us down the path of discovering the unsung heroes of innovation, the silent powerhouses that make our devices tick with precision and efficiency. Within this realm lies a particular component, discreet yet indispensable, embodying the essence of technological advancement without clamor or fanfare.
In our journey through the labyrinth of electronics, we encounter a vital entity that orchestrates the seamless conversion of energy, silently propelling our gadgets into action. This unsung hero, clad in magnetic attire, transcends the mundane to channel power with finesse and efficacy, shaping the very essence of our technological landscape.
Embark with us as we delve into the essence of this magnetic marvel, unraveling its intricacies and deciphering the language of efficiency and reliability it speaks through its silent yet profound presence. Join us in deciphering the blueprint of innovation, where every coil and core whispers tales of ingenuity and possibility.
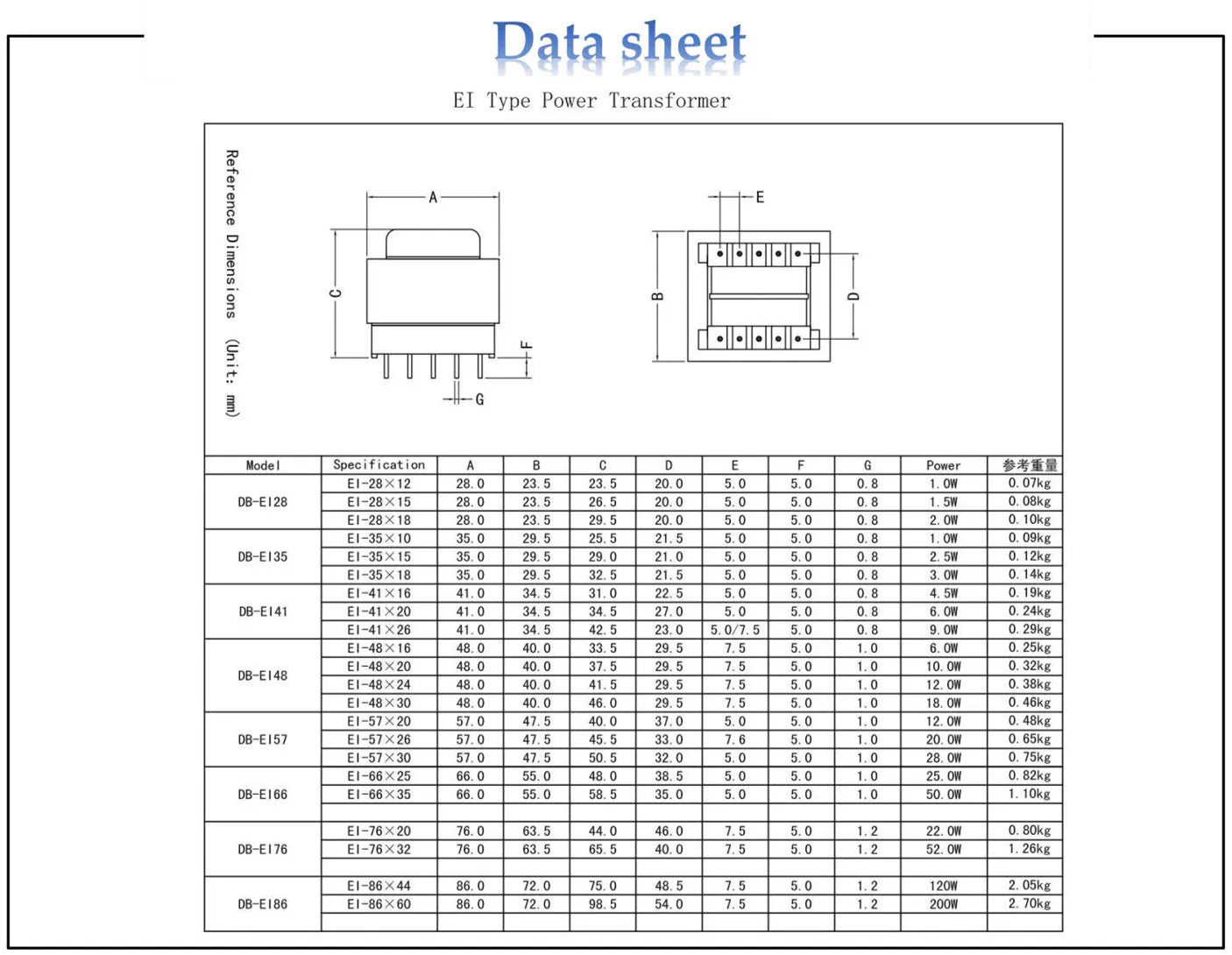
Deciphering Vital Specifications of the Ei33 Transformer

In this segment, we delve into the fundamental metrics and indicators that define the operational prowess of the Ei33 transformer. Understanding these key specifications is paramount for engineers and enthusiasts alike, as they provide crucial insights into the performance and compatibility of this essential component.
1. Power Rating: At the heart of the Ei33 transformer lies its power rating, a measure of its ability to handle electrical load without compromise. This parameter delineates the maximum power that can flow through the transformer under optimal conditions, influencing its suitability for diverse applications.
2. Frequency Range: Another pivotal aspect is the frequency range within which the transformer operates efficiently. This range encompasses the frequencies at which the transformer can transmit electrical energy with minimal loss, ensuring seamless integration into various systems.
3. Primary and Secondary Voltage Ratings: The primary and secondary voltage ratings elucidate the voltage levels at which the transformer functions optimally. Understanding these values is imperative for configuring circuits and ensuring compatibility with input and output devices.
4. Impedance: Impedance characterizes the opposition to the flow of alternating current within the transformer. It not only influences the efficiency of power transfer but also affects the stability and performance of connected components.
5. Insulation Class: The insulation class denotes the thermal endurance and insulation capabilities of the transformer, safeguarding against overheating and electrical breakdown. This specification is pivotal for determining the operational reliability and longevity of the transformer.
6. Temperature Rise: Temperature rise delineates the extent to which the transformer’s temperature increases during operation. It is a critical parameter for assessing thermal management requirements and ensuring the longevity and reliability of the transformer in demanding environments.
7. Efficiency: Efficiency signifies the ratio of output power to input power, reflecting the transformer’s ability to minimize energy losses and maximize performance. This metric is instrumental in evaluating the overall effectiveness and economic viability of the transformer.
8. Dimensional Specifications: Beyond electrical parameters, dimensional specifications encompass the physical dimensions and form factor of the transformer. These specifications are pivotal for mechanical integration and spatial constraints within diverse applications.
By comprehensively understanding these key specifications, engineers and enthusiasts can effectively harness the capabilities of the Ei33 transformer, unlocking its full potential across a myriad of applications.
Deciphering Electrical Ratings and Performance Metrics
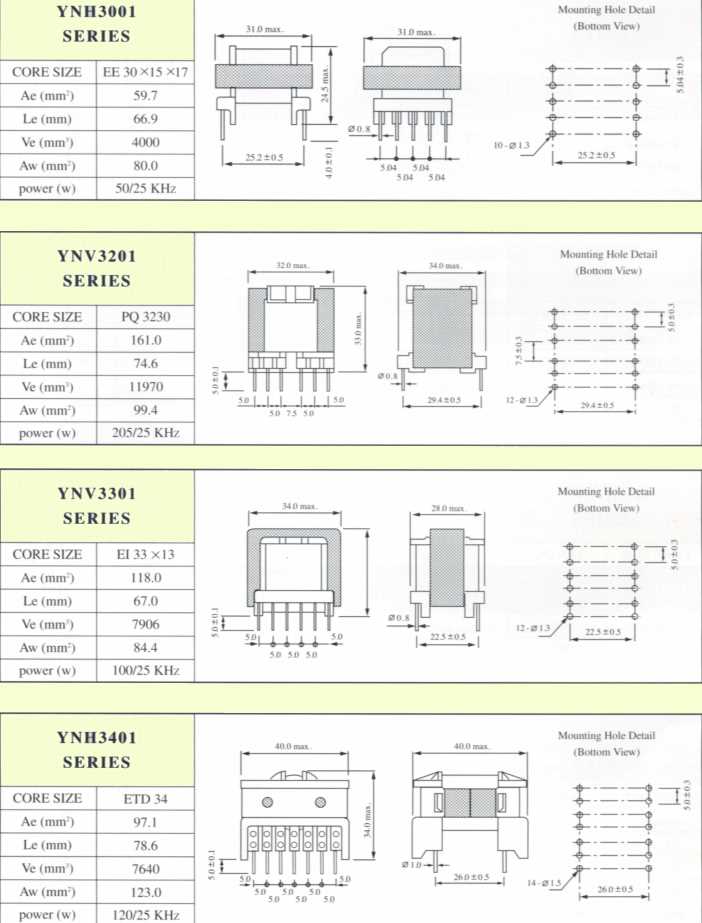
In the realm of electrical components, understanding the intricacies of technical specifications and performance indicators is paramount for optimal utilization. This section delves into the nuances of deciphering electrical ratings and performance metrics, shedding light on crucial parameters that define the functionality and efficiency of these vital components.
Core Parameters:
At the core of comprehending the capabilities of electrical components lie a series of fundamental parameters. These metrics serve as the foundation upon which the performance and suitability of a component for a given application are evaluated. Exploring parameters such as efficiency, impedance, and power handling capacity provides invaluable insights into the operational characteristics of the component.
Efficiency, often expressed as a percentage, signifies the ability of the component to convert input electrical energy into useful output with minimal losses. Understanding efficiency ratings aids in selecting components that minimize energy wastage and optimize overall system performance.
Impedance, denoted in ohms, delineates the opposition offered by the component to the flow of alternating current. This parameter plays a pivotal role in determining the compatibility of the component within a circuit and influences factors like voltage regulation and signal integrity.
Power handling capacity encompasses the maximum amount of electrical power that a component can effectively manage without exceeding specified limits. This metric is crucial for ensuring the longevity and reliability of the component under varying load conditions.
Performance Characteristics:
Beyond the basic parameters lie a spectrum of performance characteristics that provide deeper insights into the operational behavior of electrical components.
Frequency Response delineates the component’s ability to respond to varying frequencies within a specified range. Understanding frequency response aids in predicting the component’s behavior across different operating conditions and frequency regimes.
Temperature Stability refers to the component’s ability to maintain consistent performance across a range of operating temperatures. This characteristic is particularly pertinent in applications where environmental conditions fluctuate significantly.
Linearity describes the degree to which the component’s output faithfully replicates its input over a specified range. Components exhibiting high linearity ensure accurate signal processing and fidelity, crucial in applications requiring precise control and measurement.
By delving into these electrical ratings and performance metrics, engineers and designers can make informed decisions regarding component selection, ensuring optimal functionality and reliability in their applications.
Exploring Physical Dimensions and Mounting Options
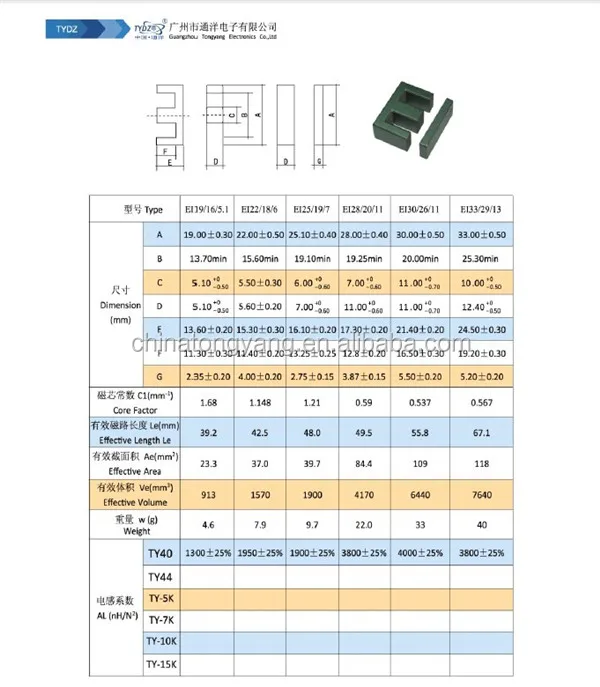
In this section, we delve into the various aspects of the physical attributes and installation possibilities of the component under scrutiny. Understanding the dimensions and mounting options plays a pivotal role in integrating the device effectively within diverse electronic systems.
Physical Dimensions
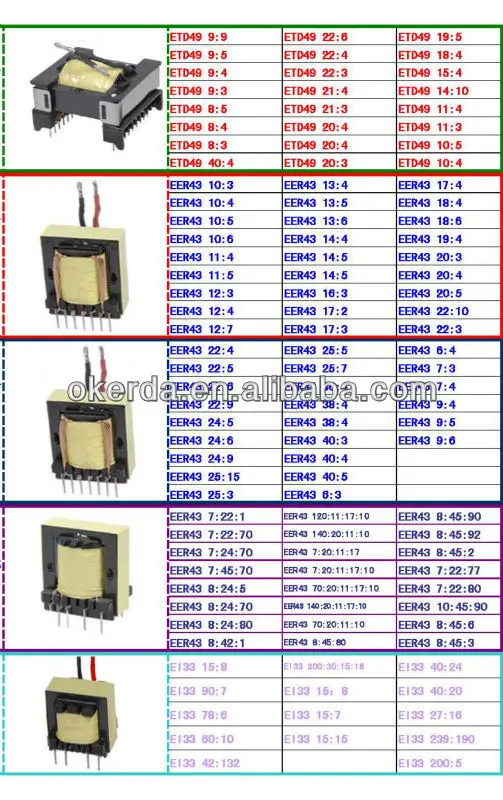
The physical dimensions of the component encompass its size, shape, and overall form factor. These aspects dictate how the component fits within the layout of a circuit or a larger electronic assembly. Moreover, they influence factors such as space utilization, heat dissipation, and mechanical compatibility with other components.
Mounting Options

Mounting options refer to the methods by which the component can be securely attached or affixed to a substrate or mounting surface. These options may include through-hole mounting, surface mount technology (SMT), or specialized mounting techniques tailored for specific applications. The choice of mounting method depends on factors such as assembly requirements, mechanical stability, and ease of manufacturing.
| Mounting Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Through-Hole Mounting | High mechanical strength, ease of manual soldering | Requires drilled holes in the PCB, may restrict routing flexibility |
| Surface Mount Technology (SMT) | Compact size, suitable for automated assembly | Less mechanical robustness compared to through-hole mounting |
| Specialized Mounting Techniques | Customized solutions for specific applications, enhanced thermal performance | Higher manufacturing complexity, may require specialized equipment |
By exploring the physical dimensions and mounting options of the component, engineers can make informed decisions regarding its integration into electronic designs, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Analyzing Thermal Characteristics and Efficiency Ratings

Exploring the thermal behavior and effectiveness metrics of electrical components forms a crucial aspect of engineering scrutiny. This section delves into the intricate nuances of heat management and operational proficiency, shedding light on the thermal dynamics and efficacy benchmarks.
Understanding how these components respond to thermal stress and evaluating their efficiency under varied conditions is paramount for optimal performance assessment. By dissecting the thermal attributes and efficiency parameters, we gain insights into the operational reliability and energy utilization of these vital components.
Through meticulous analysis of thermal signatures and efficiency ratings, engineers can ascertain the efficacy of these components in real-world applications. This scrutiny aids in devising strategies for heat dissipation and enhancing overall system performance, ensuring robustness and longevity.