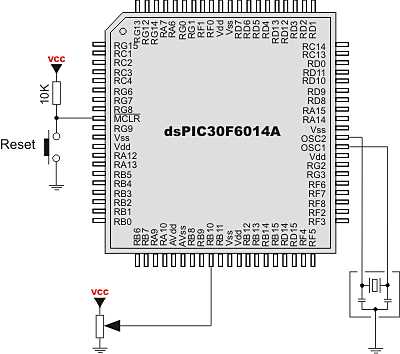
In today’s digital era, where technology reigns supreme, the need for robust and efficient microcontrollers has become increasingly important. These small yet mighty devices serve as the backbone of countless electronic systems, enabling them to perform intricate tasks with precision. In this article, we delve into the fascinating realm of microcontrollers, focusing specifically on the incredible capabilities of the dspic series.
The dspic series stands out as a game-changer in the field of microcontrollers, elevating the standard for performance and versatility. Designed to tackle the most demanding applications, these microcontrollers boast a wide range of features that enable engineers and developers to push the boundaries of what is possible. Whether it’s controlling complex systems, processing real-time data, or executing sophisticated algorithms, the dspic series excels in delivering unparalleled performance.
At the heart of the dspic series lies a powerful processing core that combines the best of both worlds: digital signal processing and microcontroller functionality. This fusion allows for seamless integration of digital systems and ensures optimal performance in diverse applications. The microcontrollers in the dspic series are armed with abundant memory resources, high-resolution analog-to-digital converters, and advanced communication peripherals, enabling them to handle intricate tasks with ease.
With the dspic series, engineers and developers have access to a treasure trove of possibilities. From designing cutting-edge industrial automation systems to creating innovative medical devices, these microcontrollers have the potential to revolutionize various industries. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a curious enthusiast, join us on a journey into the world of dspic microcontrollers, where groundbreaking ideas become reality.
Dspic Family Overview
The purpose of this section is to provide an overview of the Dspic family of microcontrollers, highlighting their key features and applications. This family of microcontrollers offers a wide range of options for engineers and developers looking for powerful and efficient solutions for their projects.
- The Dspic family is known for its high-performance digital signal processing capabilities, making it suitable for a variety of applications where complex computations and real-time processing are required.
- These microcontrollers offer advanced features such as high-speed pipelined architecture, multiple PWM modules, and integrated peripherals, which enable designers to implement various functions without the need for external components.
- With different variants available in terms of memory, clock speed, and pin count, the Dspic family caters to a diverse range of project requirements, from low-power applications to high-performance embedded systems.
- In addition to their powerful processing capabilities, these microcontrollers also provide flexible communication options, including UART, SPI, I2C, and USB, enabling seamless connectivity with other devices and systems.
- The Dspic family is widely used in various industries, including automotive, industrial automation, consumer electronics, and medical devices, due to its reliability, performance, and versatility.
- Furthermore, the availability of development tools, software libraries, and comprehensive documentation allows engineers to quickly start developing applications and leveraging the features of the Dspic microcontrollers.
In summary, the Dspic family of microcontrollers offers a versatile and powerful solution for a wide range of applications. With their advanced processing capabilities, integrated peripherals, and flexible communication options, these microcontrollers empower engineers and developers to design innovative and efficient systems in various industries.
Dspic Architecture and Features
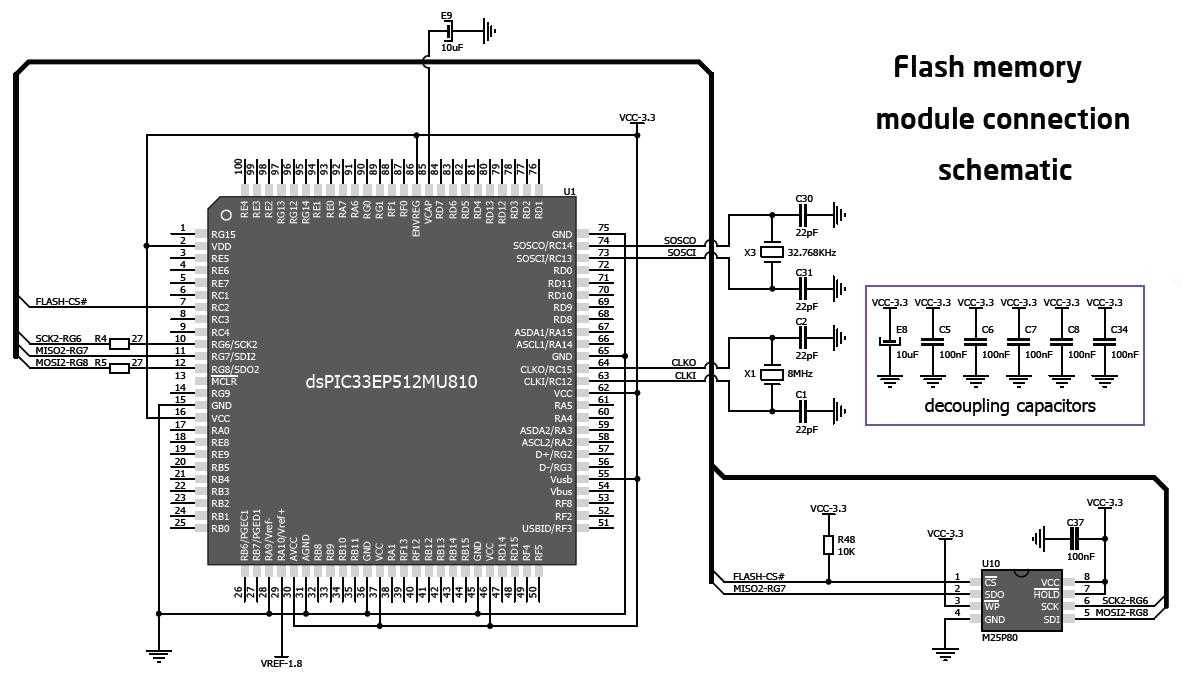
The section on Dspic Architecture and Features provides an in-depth understanding of the underlying structure and capabilities of the Dspic microcontroller. This analysis aims to showcase the intricate design and functionalities of this powerful device, offering insights into its core components, overall system architecture, and the myriad features that make it a versatile solution for a wide range of applications.
Throughout this section, the emphasis is placed on describing the various building blocks that constitute the Dspic microcontroller, including its central processing unit (CPU), memory organization, and input/output (I/O) capabilities. Moreover, key features such as the advanced analog-to-digital converter (ADC), motor control peripherals, and communication interfaces are highlighted to showcase the adaptability and flexibility of the Dspic microcontroller.
Furthermore, this section explores the unique advantages offered by the Dspic architecture, such as the presence of Digital Signal Processing (DSP) capabilities, which enable efficient and optimized processing of digital signals. The incorporation of a high-performance RISC-like CPU, along with enhanced instruction sets and pipeline architecture, ensures rapid execution of instructions, making the Dspic microcontroller ideal for time-critical applications.
In addition to its robust architecture, the Dspic microcontroller boasts a comprehensive set of features designed to simplify development and enhance system capabilities. The presence of multiple timers and capture/compare/PWM modules allows for precise event timing and control applications, while the integrated hardware multiplier accelerates mathematical computations, facilitating complex algorithm implementation.
Overall, the Dspic Architecture and Features section serves as an essential resource for engineers and enthusiasts seeking to gain a comprehensive understanding of the intricacies and functionalities of the Dspic microcontroller. By exploring its architecture and features, readers can uncover the immense potential of this versatile device and harness its capabilities to realize innovative and efficient embedded systems.
Programming Guidelines for Dspic Microcontrollers
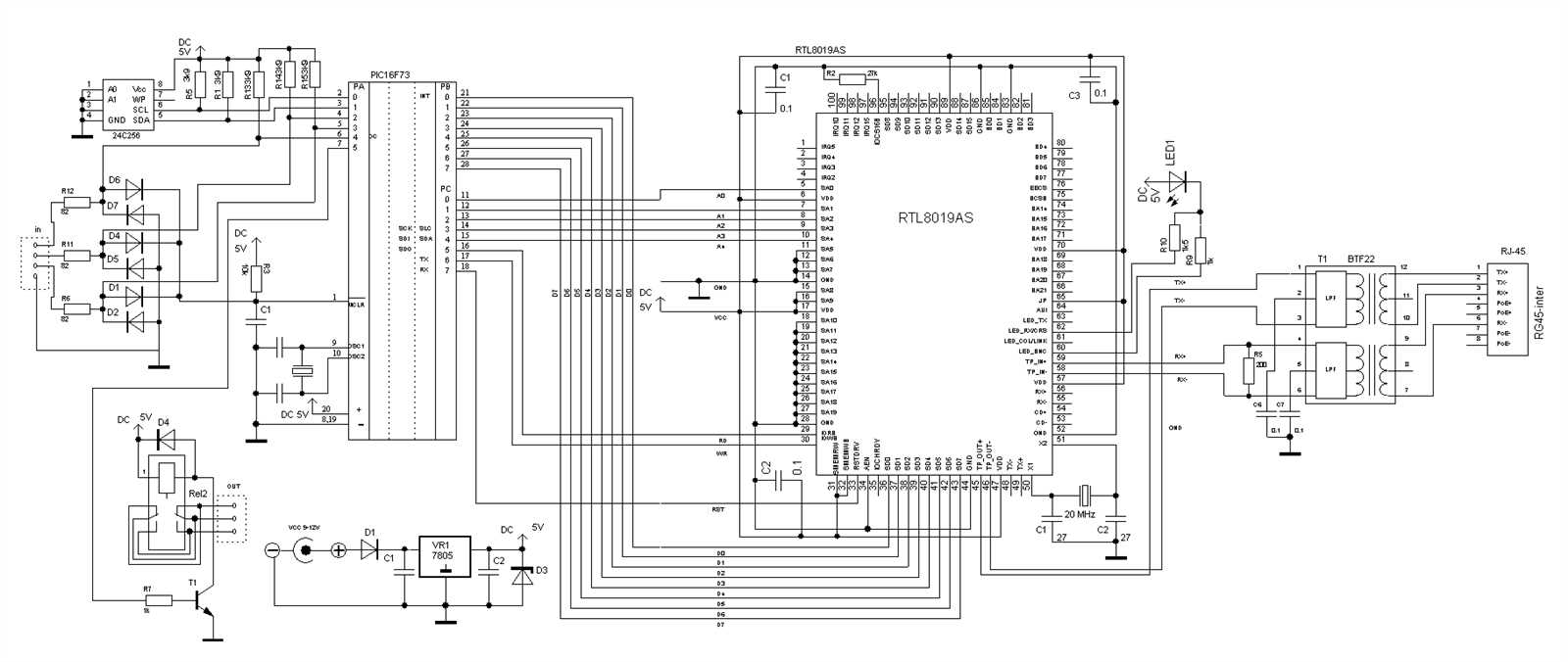
When working with these powerful microcontrollers, it is important to follow certain programming guidelines to ensure optimal performance and functionality. This section provides key recommendations and best practices for programming Dspic microcontrollers, enabling developers to unlock the full potential of these advanced devices without compromising on efficiency or reliability.
1. Understand the Architecture:
- Gain a deep understanding of the architecture and features of Dspic microcontrollers, such as their high-performance CPU cores, integrated peripherals, and advanced instruction sets.
- Explore the various memory types available, including program memory, data memory, and specialized memory sections for specific tasks.
- Familiarize yourself with the register map and the purpose of each register, as this will play a crucial role in efficient programming.
2. Use Efficient Code Techniques:
- Employ efficient coding techniques such as using optimized algorithms, minimizing resource utilization, and optimizing loops to maximize performance and minimize memory usage.
- Avoid unnecessary branching or nested loops to prevent code slowdown.
- Utilize compiler optimizations and explore available libraries to leverage existing optimized code.
3. Handle Interrupts Properly:
- Understand the interrupt handling mechanism and set up priorities for different interrupts to efficiently handle them when they occur.
- Minimize the processing time within an interrupt service routine to prevent delays in the main program execution.
- Ensure proper synchronization and data integrity when accessing shared resources within both interrupt and main code sections.
4. Utilize Power Management Features:
- Take advantage of power-saving modes and features offered by Dspic microcontrollers to optimize power consumption in low-power applications.
- Implement efficient power management strategies, such as dynamically adjusting clock frequencies and disabling unnecessary peripherals, to extend battery life and reduce energy consumption.
5. Debug and Test Thoroughly:
- Utilize in-circuit debuggers and programming tools to debug and test the code for errors, anomalies, and unexpected behavior.
- Use debugging features like breakpoints, watchpoints, and variable tracing to identify and resolve issues efficiently.
- Perform thorough testing of the software in different scenarios and edge cases to ensure overall system stability and reliability.
By following these programming guidelines, developers can harness the full capabilities of Dspic microcontrollers, achieving optimal performance, efficiency, and reliability in their embedded applications.
Best Practices for Efficient Code Execution
In the realm of microcontrollers, optimizing code execution is crucial for achieving high performance and maximizing resource utilization. This article explores a set of best practices that can significantly enhance the efficiency of code execution, resulting in improved overall system performance and reduced power consumption.
- Utilize efficient algorithms and data structures: Choosing the most appropriate algorithms and data structures for a given task can have a profound impact on code efficiency. Well-designed algorithms help minimize the number of instructions executed, reduce memory usage, and enhance data access efficiency.
- Optimize code for speed: Writing code with speed in mind involves employing techniques such as loop unrolling, inline assembly, and code profiling. These practices help eliminate unnecessary operations, reduce branching, and streamline functionality to maximize execution speed.
- Minimize memory usage: Careful memory management can significantly contribute to efficient code execution. This includes minimizing the use of global variables, allocating memory dynamically when necessary, and freeing up memory once it is no longer required.
- Utilize hardware acceleration: Many microcontrollers offer specialized hardware features that can accelerate specific operations, such as multiply-accumulate (MAC) units or dedicated DMA controllers. Leveraging these hardware accelerators can greatly enhance code execution speed and reduce CPU workload.
- Optimize code size: For embedded systems with limited storage capacity, keeping code size as small as possible is essential. Techniques such as function and variable optimization, effective use of preprocessor directives, and removing unnecessary code can help minimize the footprint of the compiled code.
- Profile and benchmark: Profiling and benchmarking are essential tools for identifying performance bottlenecks and areas that require optimization. By measuring code execution time and resource usage, developers can identify areas for improvement and prioritize their optimization efforts.
- Minimize interrupt service routine (ISR) execution time: Efficient execution of interrupt service routines is crucial for real-time systems. Minimizing the duration of ISRs ensures timely response and reduces the risk of missing critical events.
- Optimize power consumption: Efficient code execution is not just about performance; it also plays a vital role in power optimization. Techniques such as power gating, clock gating, and optimizing idle waiting loops can help minimize power consumption, extending battery life in portable devices.
Implementing these best practices requires a deep understanding of the microcontroller architecture, as well as thorough testing and profiling. By employing these techniques, developers can achieve optimal code execution efficiency, resulting in improved system performance, reduced power consumption, and better resource utilization.
Debugging and Troubleshooting Tips
When working with the technical documentation of a microcontroller, such as the dspic datasheet, it is important to have a good understanding of how to debug and troubleshoot any issues that may arise during the development process. This section presents useful tips and strategies for identifying and resolving common problems without explicitly referring to the specific microcontroller or datasheet.
One key aspect of effective debugging is to thoroughly analyze the symptoms of the issue. By carefully examining the behavior of the system or the specific component in question, you can gain valuable insights into the root cause of the problem. It is essential to accurately describe and document these symptoms to facilitate the troubleshooting process.
Another crucial tip is to divide and conquer. Rather than attempting to solve the entire problem at once, break it down into smaller, more manageable parts. By isolating specific sections or functionalities, you can systematically test and eliminate potential causes, making it easier to pinpoint the specific area where the issue lies.
Furthermore, utilizing systematic and logical reasoning is highly beneficial when troubleshooting. By asking targeted questions and following a structured approach, you can uncover potential sources of error more effectively. This involves checking for common mistakes, reviewing relevant documentation or specifications, and conducting thorough tests.
It is also essential to utilize available resources and tools. The internet, forums, and online communities can provide valuable insights and solutions to commonly encountered problems. Leveraging these resources can save time and effort when troubleshooting, as others may have already encountered and resolved similar issues.
Lastly, documenting the entire debugging and troubleshooting process is highly recommended. Keeping a record of all steps taken, observations made, and solutions attempted can be immensely helpful in both solving the current issue and providing future reference for similar problems. Well-documented troubleshooting efforts also improve collaboration among team members and aid in knowledge sharing.