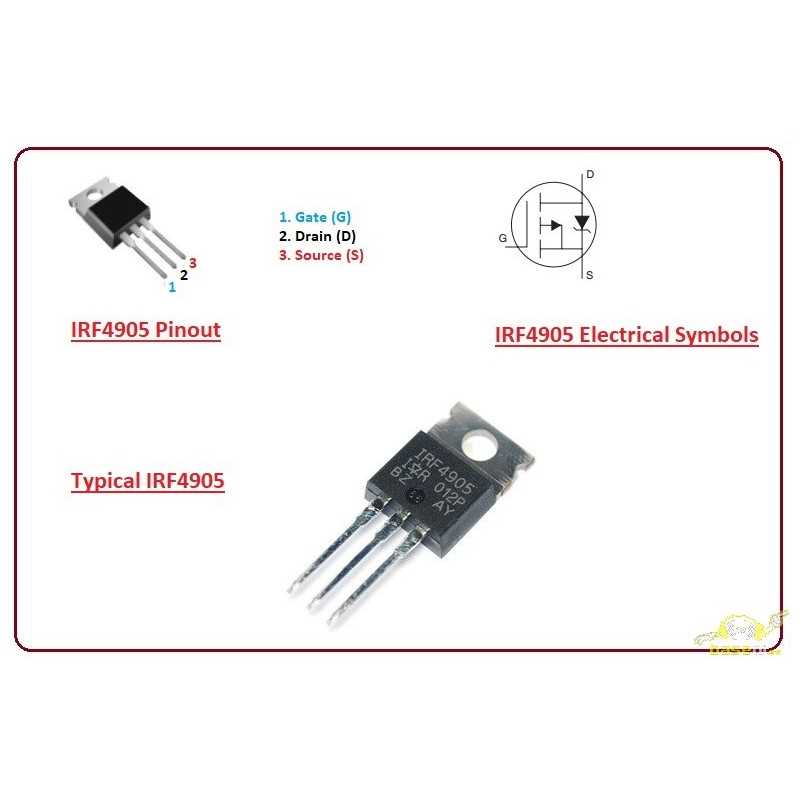
Unlocking the potential of cutting-edge electronics, delving into the intricate realm of semiconductor technology, we embark on a journey to unravel the secrets concealed within the heart of contemporary circuitry. Within this labyrinth lies a crucial element, shrouded in technical complexity yet pivotal in its functionality, driving the dynamics of modern electronic systems.
Behold the cornerstone of power management and amplification, a silent yet omnipotent guardian orchestrating the flow of electrical currents with precision and finesse. Within the vast landscape of semiconductor devices, this enigmatic component stands as a beacon of efficiency, promising transformative capabilities in the realm of electrical engineering and beyond.
Prepare to venture into the realm of technological prowess, where the boundaries of innovation are pushed ever further by the relentless pursuit of efficiency and performance. Through meticulous exploration and analysis, we shall uncover the essence of this integral component, shedding light on its functionalities, applications, and the intricate mechanisms that render it indispensable in the modern age.
Understanding the IRF5305 Specifications
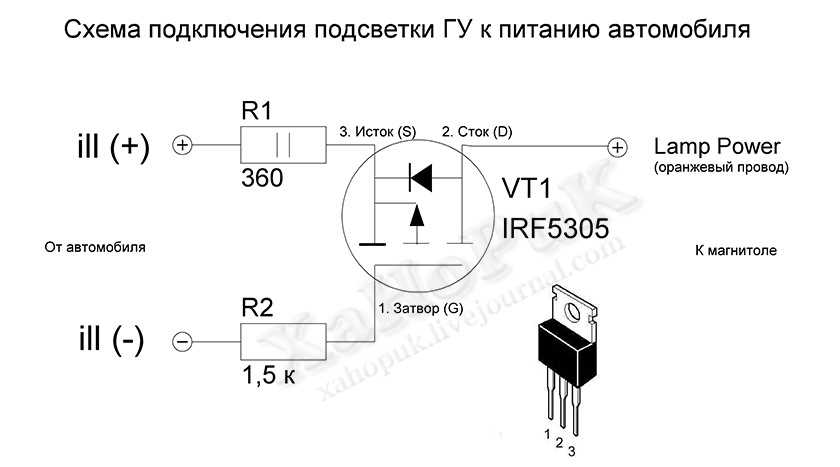
When delving into the intricacies of electronic components, a crucial document serves as the compass guiding engineers and enthusiasts alike: the comprehensive specifications for the IRF5305 MOSFET. This vital resource is more than a mere collection of figures and graphs; it is a roadmap to understanding the capabilities and limitations of this power transistor.
At its core, the IRF5305 datasheet offers a detailed insight into the performance characteristics and operational parameters of this semiconductor device. Through meticulous analysis, one can unravel the nuances of its electrical behavior, thermal management, and mechanical dimensions, thus unlocking its full potential in various applications.
- Electrical Characteristics: Within these pages lie a treasure trove of information regarding voltage ratings, current capabilities, and switching characteristics. By deciphering these metrics, one gains a profound understanding of how the IRF5305 interacts with external circuits and influences overall system performance.
- Thermal Considerations: Temperature plays a pivotal role in the reliability and longevity of electronic components. The datasheet sheds light on thermal resistance, junction-to-case, and junction-to-ambient values, guiding engineers in designing effective cooling solutions to prevent overheating and ensure optimal operation.
- Mechanical Dimensions: Beyond its electrical prowess, the physical dimensions of the IRF5305 are equally crucial. From package outlines to lead assignments, every detail is meticulously documented to facilitate seamless integration into diverse PCB layouts and mechanical assemblies.
Moreover, the datasheet serves as a beacon of clarity amidst the complexities of semiconductor specifications, offering invaluable insights into performance under varying conditions and environments. Armed with this knowledge, engineers can make informed decisions, troubleshoot issues, and unleash the true potential of the IRF5305 in their designs.
Unraveling the Technical Specifications
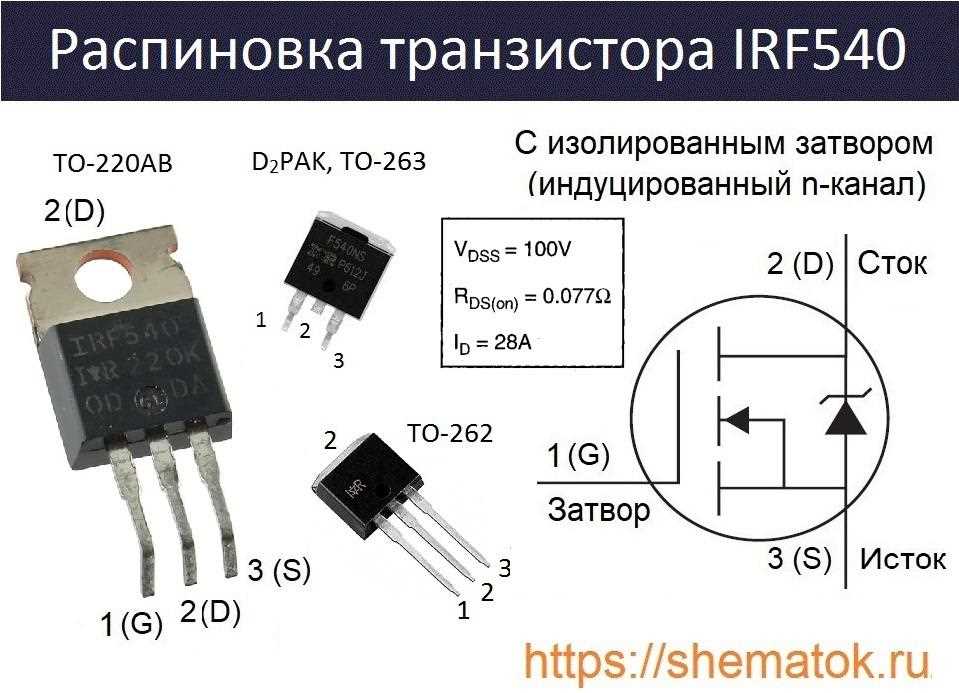
In this segment, we delve into the intricate details and technical intricacies that define the performance parameters of a certain electronic component. Through careful analysis and interpretation, we aim to elucidate the specifications, shedding light on its capabilities and potential applications without explicitly naming the component in question. Let’s embark on a journey through the realm of technical intricacies, deciphering the language of specifications to uncover the true essence of its functionality.
Understanding Performance Metrics

Within the realm of electronic components, a myriad of performance metrics governs their functionality. These metrics encompass various aspects such as electrical characteristics, operational limits, and efficiency parameters. By comprehensively understanding these metrics, engineers can discern the suitability of a component for diverse applications, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Analyzing Operational Parameters
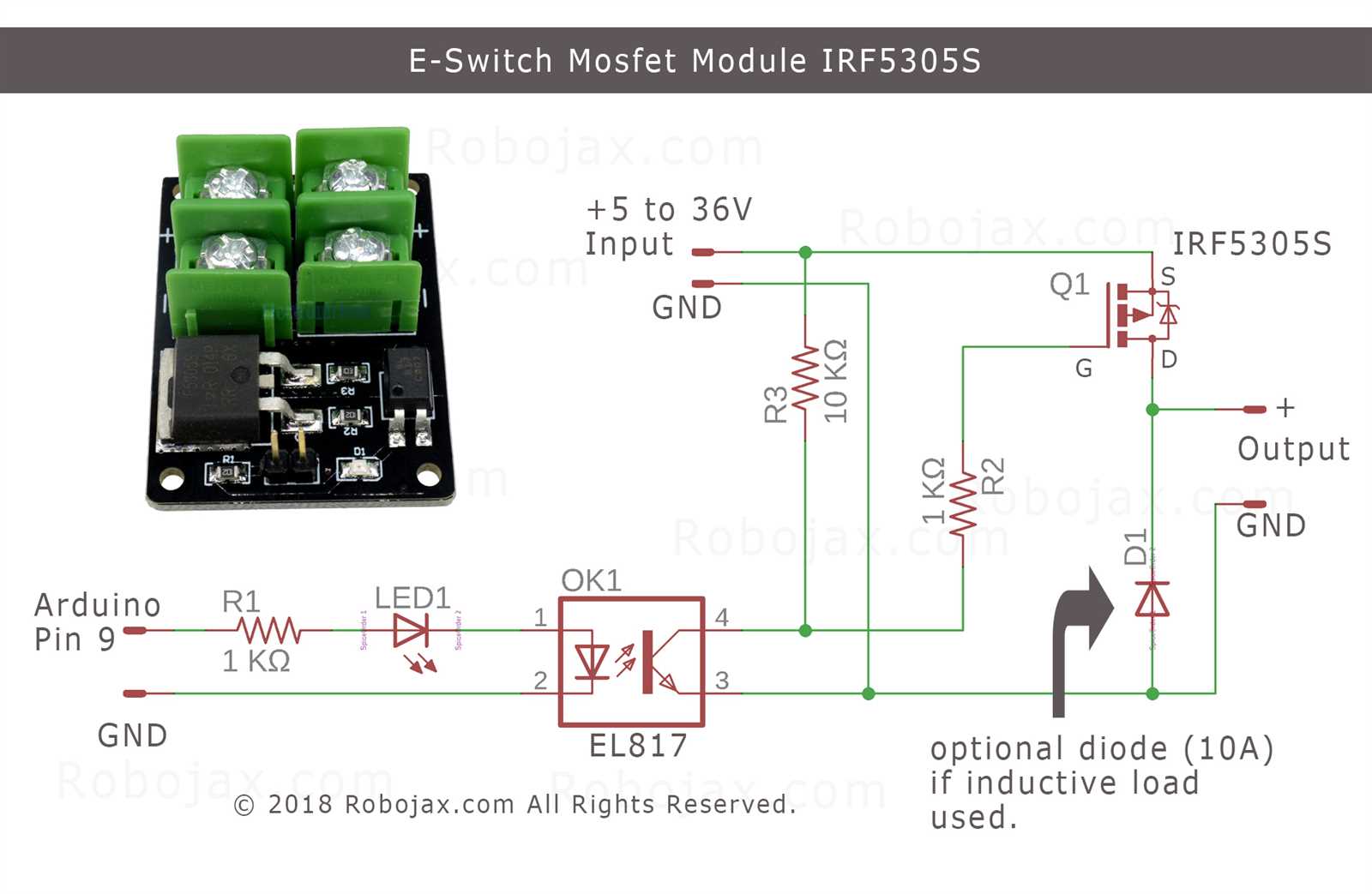
Delving deeper, we scrutinize the operational parameters that delineate the behavior of the component in different scenarios. From voltage and current ratings to thermal characteristics and switching speeds, each parameter plays a pivotal role in defining the component’s operational envelope. Through meticulous analysis and interpretation, engineers can ascertain the component’s behavior under varying conditions, enabling precise integration into diverse electronic circuits.
Exploring Application Guidelines

In this section, we delve into the practical aspects of utilizing electronic components to achieve optimal performance in diverse applications. By understanding the fundamental principles governing the utilization of semiconductor devices like the one in question, we can effectively harness their capabilities in various circuits and systems.
Understanding Operational Parameters

Before delving into specific application scenarios, it’s imperative to grasp the crucial operational parameters that dictate the behavior of the semiconductor component under consideration. These parameters encompass a spectrum of characteristics, ranging from electrical and thermal properties to reliability metrics.
- Electrical Characteristics: Explore the electrical properties such as voltage ratings, current handling capabilities, and impedance characteristics to ensure compatibility with the intended application requirements.
- Thermal Considerations: Assess the thermal limitations and thermal resistance of the component to prevent overheating and ensure reliable operation under various operating conditions.
- Reliability Metrics: Evaluate reliability metrics such as mean time between failures (MTBF) and failure modes to anticipate potential issues and design robust systems.
Optimizing Circuit Design
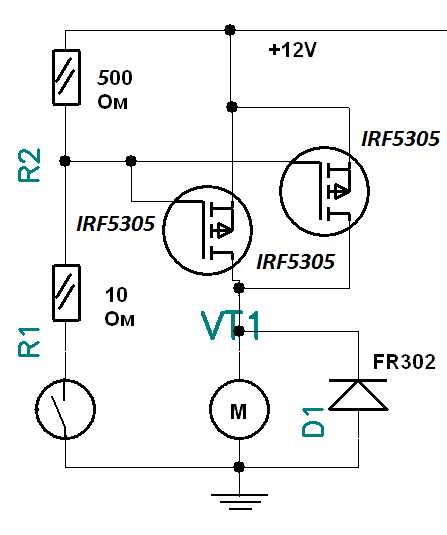
Efficient circuit design plays a pivotal role in maximizing the performance and longevity of electronic systems. By adhering to best practices and guidelines, designers can mitigate potential issues and achieve desired outcomes.
- Layout Considerations: Pay meticulous attention to the layout design to minimize parasitic elements, optimize signal integrity, and mitigate electromagnetic interference (EMI).
- Drive and Control Circuitry: Implement appropriate drive and control circuitry to ensure proper operation and protection of the semiconductor device, thereby enhancing system reliability.
- Application-Specific Optimization: Tailor the circuit configuration and component selection to suit the specific requirements of the intended application, considering factors such as load characteristics and environmental conditions.
By integrating these application guidelines into the design process, engineers can leverage the full potential of semiconductor components like the one under scrutiny, fostering innovation and efficiency in electronic systems.
Interpreting Performance Graphs and Charts
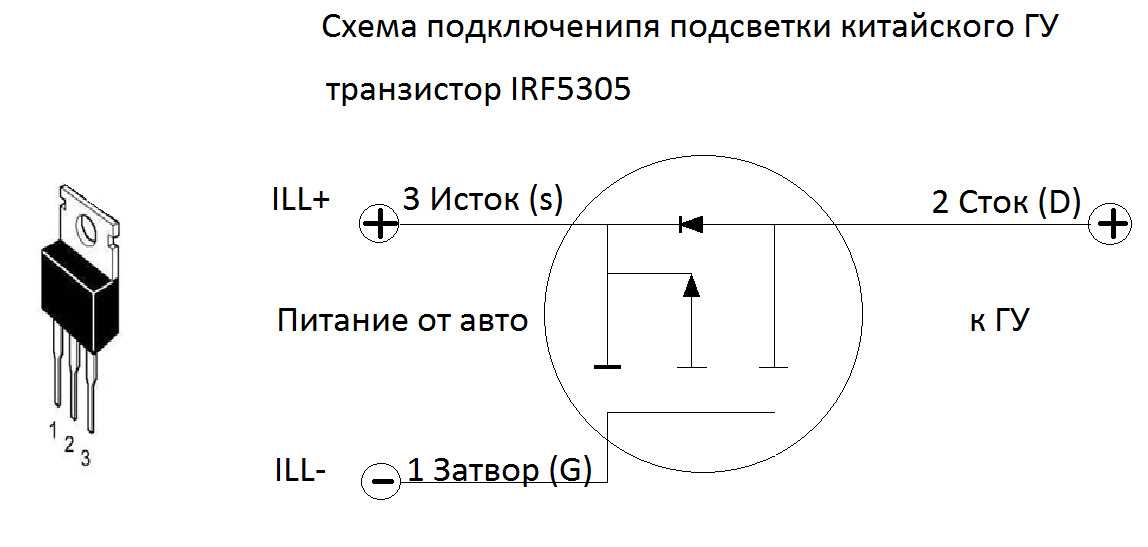
Understanding the visual representations of component specifications is essential for grasping their operational characteristics and capabilities. Performance graphs and charts serve as invaluable tools in this regard, offering insights into the behavior and efficiency of electronic components without delving into technical minutiae.
Graphical Data Representation: Performance graphs depict various parameters such as voltage, current, and frequency in a visually intuitive manner. By analyzing these graphs, engineers can discern trends, relationships, and limitations of a component’s functionality.
Key Metrics Identification: Charts often highlight key performance metrics such as maximum ratings, efficiency curves, and temperature dependencies. Identifying these metrics aids in determining the operational boundaries and optimal conditions for the component.
Comparative Analysis: Graphs allow for direct comparison between different components or variants. By overlaying multiple graphs, engineers can assess trade-offs and make informed decisions based on specific project requirements.
Behavioral Patterns: Patterns within the graphs reveal crucial insights into the transient response, switching characteristics, and stability of the component under varying operating conditions. Understanding these patterns aids in designing reliable and efficient circuits.
Application Considerations: Interpreting performance graphs is not merely about understanding technical specifications but also about applying this knowledge to real-world scenarios. Engineers must consider factors such as thermal management, voltage regulation, and load conditions when interpreting and utilizing these graphs effectively.
Conclusion: Performance graphs and charts are indispensable aids in comprehending the operational behavior and capabilities of electronic components. By mastering the art of interpreting these visual representations, engineers can optimize designs, troubleshoot issues, and unleash the full potential of their projects.