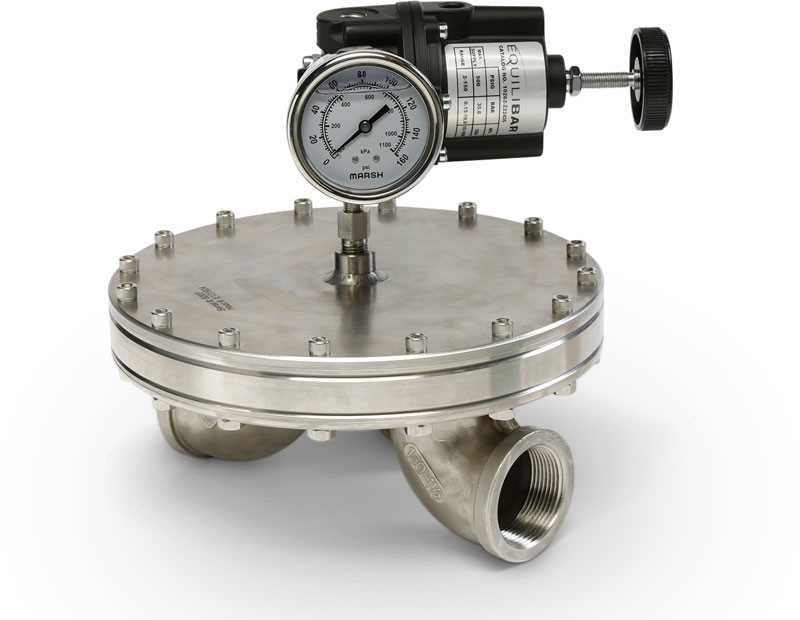

Efficient and reliable flow control is paramount in a wide range of industries, from manufacturing and oil refining to chemical processing and pharmaceutical production. To optimize fluid systems and ensure peak performance, engineers turn to state-of-the-art devices that employ innovative pressure modulation mechanisms. These advanced solutions, commonly referred to as back pressure regulators, offer precise adjustment capabilities to maintain optimal pressure levels throughout the entire system.
By utilizing cutting-edge technology and sophisticated design, back pressure regulators empower engineers to regulate fluid flow and pressure with exceptional accuracy and efficiency. These highly responsive devices are engineered to withstand extreme conditions and deliver unparalleled performance in challenging environments. With their ability to handle a wide range of fluids and gases, back pressure regulators provide unmatched flexibility to cater to diverse applications.
One crucial element that sets these advanced devices apart is their comprehensive and reliable datasheets. A datasheet serves as a comprehensive guide, offering engineers essential information about the performance, dimensions, and operating parameters of back pressure regulators. This invaluable resource allows engineers to make informed decisions when selecting the ideal regulator for their specific applications.
Understanding the Importance of Back Pressure Regulation
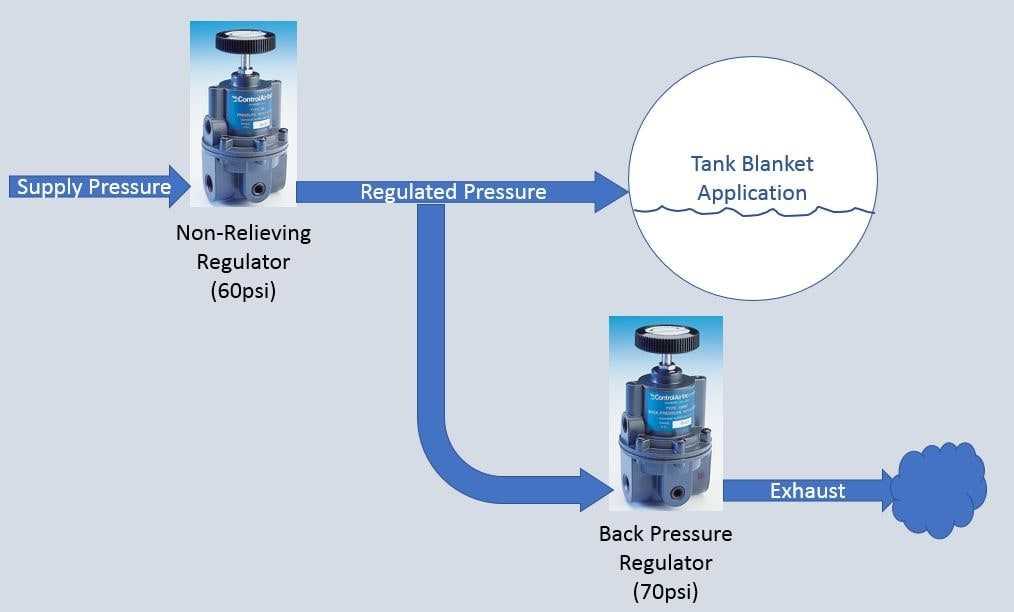
In the world of fluid dynamics, the control and management of flow is of paramount importance. One crucial aspect of fluid flow is back pressure, which refers to the resistance encountered by a fluid as it moves through a system. Effective management of back pressure is essential to ensure optimal functioning and performance of various industrial processes that rely on fluid flow.
Back pressure regulation plays a vital role in achieving a balance between system performance and efficiency. It involves the use of specialized devices that control the pressure of a fluid flowing through a system, thereby maintaining uniform flow rates and preventing any potential disruptions or limitations. By carefully regulating back pressure, operators can ensure that the system operates within desired parameters, minimizing the risk of damage or inefficiency.
One of the key benefits of back pressure regulation is the ability to enhance the reliability and stability of a system. By controlling the pressure exerted on the fluid, excessive force or stress can be avoided, leading to reduced wear and tear on system components. This not only extends the lifespan of the equipment but also helps maintain consistent performance over time, ultimately improving overall productivity.
Furthermore, back pressure regulation can also aid in optimizing the efficiency of a system. By ensuring a steady and controlled flow of fluid, operators can eliminate potential fluctuations or disturbances that may hinder the performance of downstream equipment. This, in turn, leads to improved energy efficiency and reduced operational costs, making back pressure regulation a valuable tool for industries seeking to enhance their bottom line.
Back pressure regulation is particularly important in applications where precise flow control is critical, such as chemical manufacturing, pharmaceutical production, and oil and gas processing. In these industries, even minor variations in back pressure can have significant consequences, ranging from reduced product quality to safety hazards. Therefore, implementing robust back pressure regulation mechanisms is essential for maintaining process reliability and integrity.
| Advantages of Back Pressure Regulation: |
|---|
| • Improved system reliability and stability |
| • Enhanced equipment lifespan |
| • Consistent performance and productivity |
| • Optimal energy efficiency and cost savings |
Overview of Back Pressure Regulator Datasheets
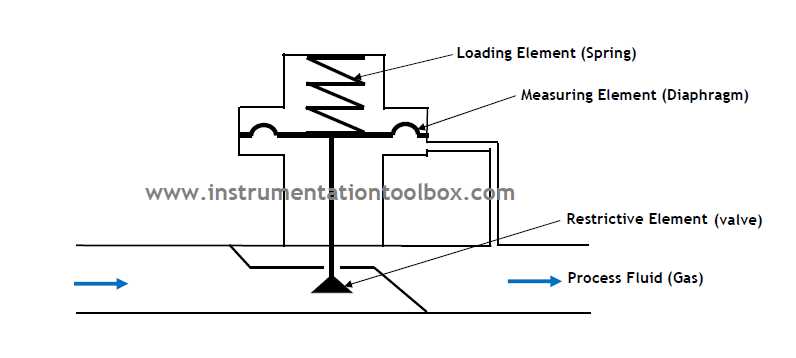
In this section, we will provide a comprehensive summary of the informational documents that describe the specifications and features of devices designed to regulate the flow of fluid within a system, focusing on devices utilized for counteracting the force of fluid moving in the opposite direction.
As we explore the content of these data sheets, we will delve into the intricacies and essential details of these devices, without explicitly referring to them by their common names, ensuring that key information and characteristics are conveyed effectively.
Through these documents, one can gain valuable insights into the performance parameters, operating principles, and potential applications of these fluid control components. The datasheets provide an in-depth understanding of the factors that influence their functionality and how they can be integrated into various industrial processes.
The content includes specifications such as the range of flow rates they can handle, the stability they offer under varying conditions, and the precision with which they can maintain desired levels. Furthermore, the datasheets elucidate the different materials of construction, allowing users to select the appropriate regulator for their specific needs based on compatibility and resistance to various fluids and environments.
Moreover, these documents outline the various control options available for these devices, such as manual adjustment or automated electronic control. They also highlight features like response time, accuracy, and repeatability, aiding users in determining the suitability of a back pressure regulator in their system.
By examining different back pressure regulator datasheets, users can familiarize themselves with the terminology and technical details associated with these devices. This knowledge empowers individuals to make informed decisions when selecting and incorporating back pressure regulators into their fluid control systems, optimizing efficiency and ensuring reliable and consistent performance.
Key Components and Specifications in Back Pressure Regulator Datasheets
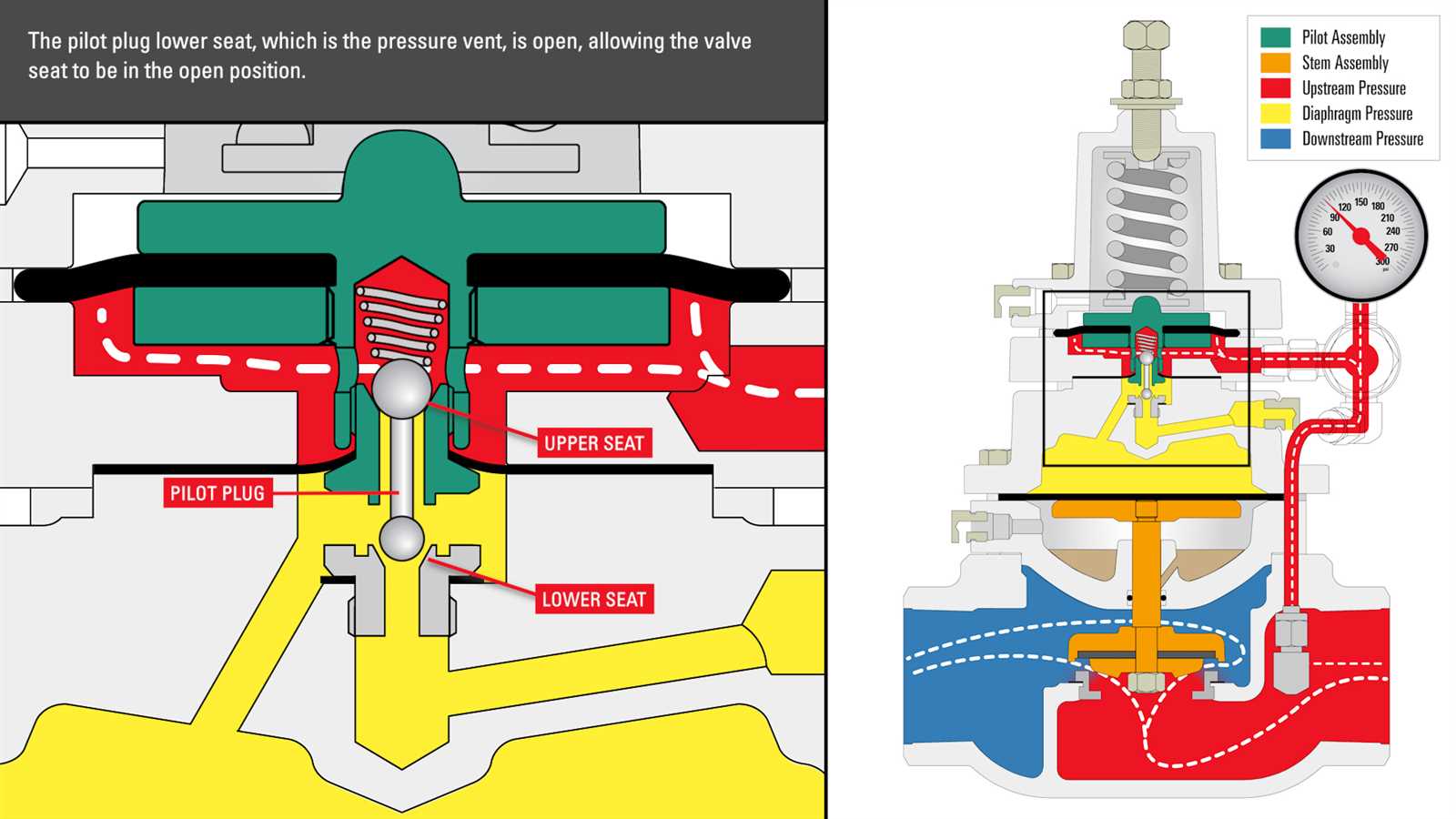
In this section, we will explore the essential elements and important specifications found in datasheets for devices that regulate the flow of fluids or gases. These documents, which provide detailed information about the product’s features and capabilities, are an invaluable resource for engineers and technicians seeking to select the right back pressure regulator for their application.
One of the critical components highlighted in these datasheets is the sensing element or diaphragm. This thin membrane, often made of a flexible material such as stainless steel or elastomer, plays a crucial role in detecting and responding to changes in pressure. By monitoring the pressure differential across the diaphragm, the regulator can adjust the flow to maintain a desired back pressure.
Another essential component to consider is the control mechanism. Datasheets often describe the type of control used in the back pressure regulator, such as a spring-loaded mechanism or a pilot-controlled design. These control mechanisms dictate how the regulator adjusts the opening of the valve to maintain the desired pressure conditions. Understanding the control mechanism is crucial in ensuring the regulator’s compatibility with the specific application requirements.
The flow capacity or Cv value is a vital specification provided in back pressure regulator datasheets. It represents the volume of fluid or gas that can pass through the regulator under specified pressure conditions. The Cv value is important for determining the appropriate size and capacity of the regulator for a given application. It is essential to match the flow capacity of the regulator with the expected flow rate in the system to ensure optimal performance.
Furthermore, datasheets often include details about the pressure range in which the back pressure regulator can operate effectively. This specification indicates the minimum and maximum pressure levels that the device can handle while maintaining accurate pressure control. It is crucial to select a regulator that can handle the anticipated pressure range in the system to prevent damage or inaccurate pressure regulation.
Finally, back pressure regulator datasheets may provide information about additional features and accessories that enhance the functionality and versatility of the device. These could include options for built-in pressure relief valves, different connection types, or specialized coatings for compatibility with corrosive or high-temperature environments. Examining these additional features can help engineers and technicians choose a regulator that meets their specific application needs.
| Component/Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Sensing Element | The component responsible for detecting and responding to changes in pressure. |
| Control Mechanism | The mechanism that adjusts the valve opening to maintain the desired pressure conditions. |
| Flow Capacity (Cv Value) | The volume of fluid or gas that can pass through the regulator under specified pressure conditions. |
| Pressure Range | The minimum and maximum pressure levels that the regulator can handle while maintaining accurate pressure control. |
Exploring the Different Types of Back Pressure Regulators

In this section, we will delve into the various categories and classifications of devices that control the flow within a system, specifically focusing on mechanisms that relieve or regulate pressure in the opposite direction. By analyzing the diverse selection of back pressure regulators available, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of their functionalities and applications in different industries.
Category 1: Flow-Driven Back Pressure Regulators

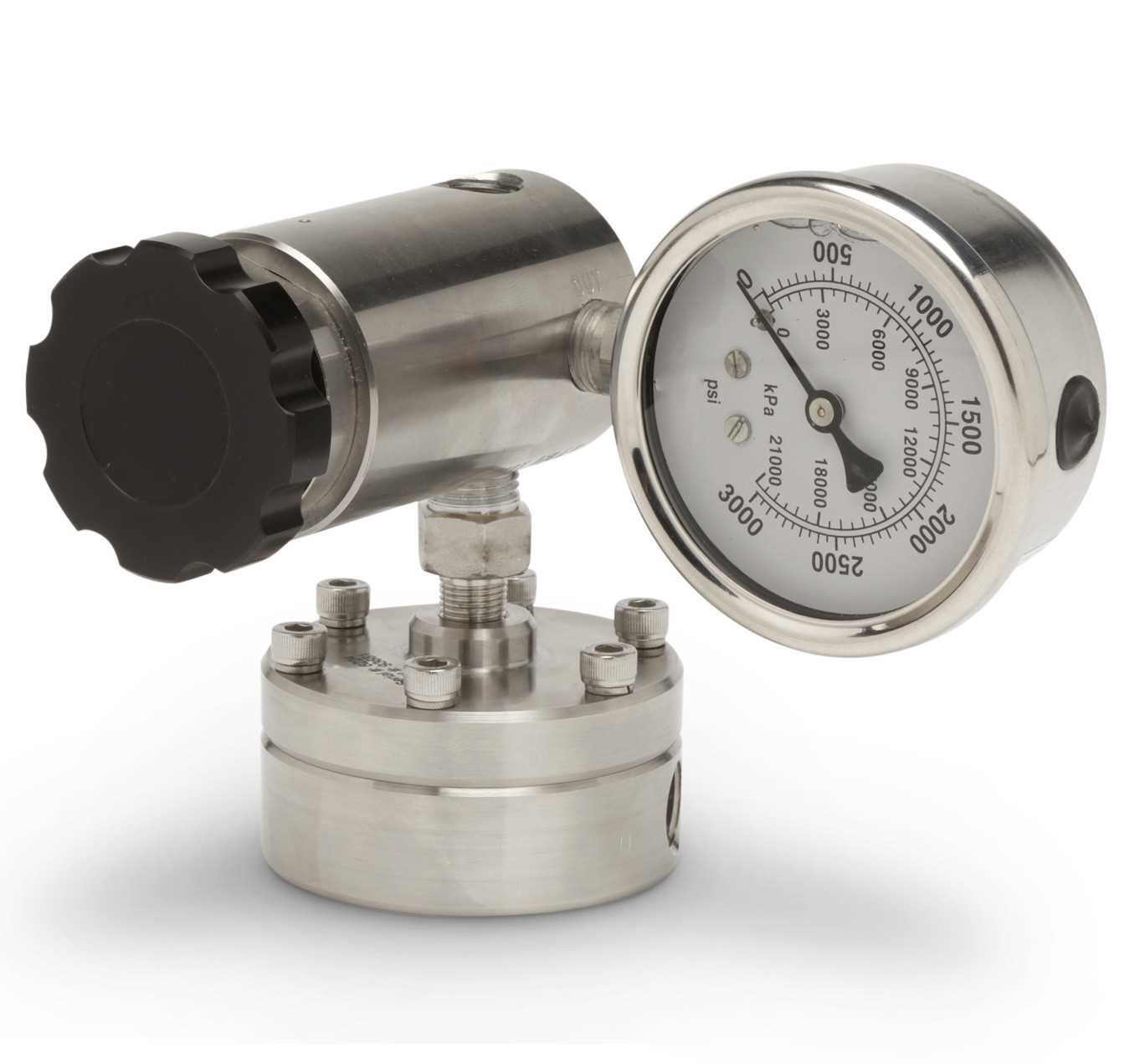
One category of back pressure regulators operates based on the principles of flow control. These devices are designed to maintain a certain pressure level by adjusting the flow rate within a system. By intelligently manipulating the flow, they ensure a consistent pressure gradient, safeguarding against potential disruptions caused by variations in pressure.
These flow-driven back pressure regulators are commonly utilized in applications where precision and stability of pressure control are paramount. Industries such as pharmaceuticals, chemical processing, and food production extensively rely on these regulators to guarantee a steady flow while preventing detrimental backflows or pressure surges that may compromise the efficiency or safety of their operations.
Category 2: Load-Driven Back Pressure Regulators
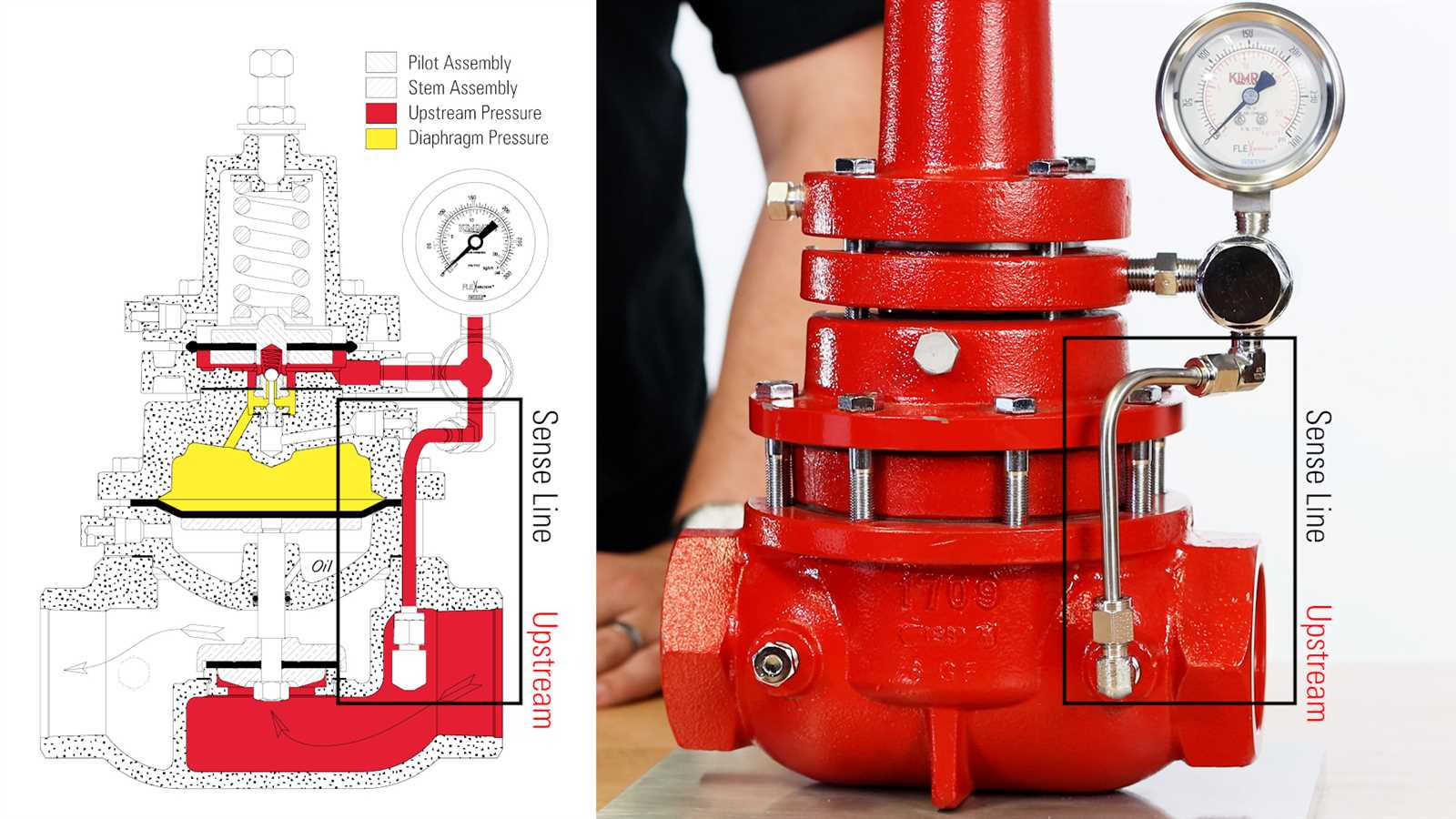
Another category of back pressure regulators functions based on load control. These devices maintain a stable pressure level by adjusting the system’s load, commonly accomplished by regulating the resistance or bypass in the path of the fluid. This dynamic ensures a consistent pressure throughout the system by modulating the load and mitigating any potential pressure imbalances.
The load-driven back pressure regulators find applications in a wide range of industries, including oil and gas, power generation, and water treatment. By effectively managing the load, these regulators enable a reliable and balanced flow of fluid, ensuring optimal performance, efficiency, and safety in diverse industrial settings.
In conclusion, the exploration of different types of back pressure regulators has shed light on the versatile and vital role they play in managing pressure within various systems. Flow-driven regulators and load-driven regulators each offer distinct advantages and applications depending on the specific requirements of different industries. Understanding the functionality and characteristics of these regulators is crucial for selecting the most suitable option to optimize performance and ensure reliable pressure control in any given system.
Essential Parameters and Performance Specifications to Consider

When evaluating a data sheet for a back pressure regulator, it is important to focus on several key parameters and performance specifications. These factors provide crucial insights into the regulator’s capabilities and help determine its suitability for a specific application.
1. Flow Capacity
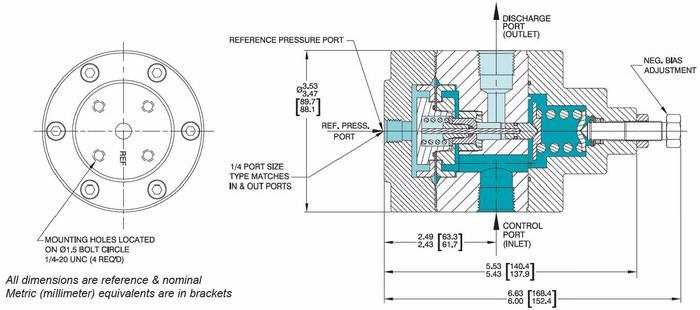
The flow capacity of a back pressure regulator refers to its ability to handle and control the flow of fluid or gas. It is paramount to consider the maximum and minimum flow rates that the regulator can accommodate, as well as its ability to maintain a stable flow across varying inlet pressures. Understanding the flow capacity ensures that the chosen regulator can handle the specific flow requirements of the system.
2. Pressure Range

The pressure range determines the minimum and maximum pressures that the back pressure regulator can operate within. It is crucial to assess whether the regulator can handle the expected system pressure and maintain consistent performance throughout the desired range. This ensures that the regulator will effectively control the pressure under various operating conditions.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Flow Capacity | The ability of the regulator to handle and control fluid or gas flow, considering maximum and minimum flow rates. |
| Pressure Range | The minimum and maximum pressures that the regulator can maintain effective performance within. |
By carefully evaluating these essential parameters and performance specifications, engineers and system designers can make informed decisions when selecting a back pressure regulator. Considering flow capacity and pressure range ensures compatibility with the application’s requirements, leading to optimal performance and efficient operation.