In the world of advanced electronic devices, there lies an innovative tool that revolutionizes the way we perceive and interact with our surroundings. This powerful and versatile creation ensures accuracy, efficiency, and endless possibilities in numerous applications. Today, we explore the technical specifications of an exceptional and intelligent electronic device that encompasses the ability to comprehend its environment and communicate its findings seamlessly. Let us dive deep into the intricacies and unique features of this groundbreaking invention!
Discover the immense potential afforded by this cutting-edge electronic mechanism – an instrument designed to facilitate precise measurements, obstacle detection, and object localization with remarkable precision. Embedded within this state-of-the-art technology lies a brilliant amalgamation of advanced sensors and intricate circuitry. This multifunctional marvel perceives its surroundings utilizing high-frequency sound waves, deciphering the echoes that rebound, offering an unprecedented insight into the world around us.
Prepare to be astonished as this exceptional electronic innovation intricately pairs acoustic waves and intelligent algorithms to create a device capable of calculating distances with incredible accuracy. These sophisticated capabilities empower this electronic masterpiece to adapt to diverse environments seamlessly. It seamlessly detects objects, determines their proximities, and provides a wealth of invaluable data for a wide range of applications, all while functioning with an efficiency that surpasses previous limitations in technological advancements.
Understanding the Basics of Ultrasonic Sensors
In this section, we will explore the fundamental principles behind the functionality of ultrasonic sensors. By delving into the core concepts, we can gain a better understanding of how these sensors operate and their potential applications in various fields.
Working Principle of Ultrasonic Sensors
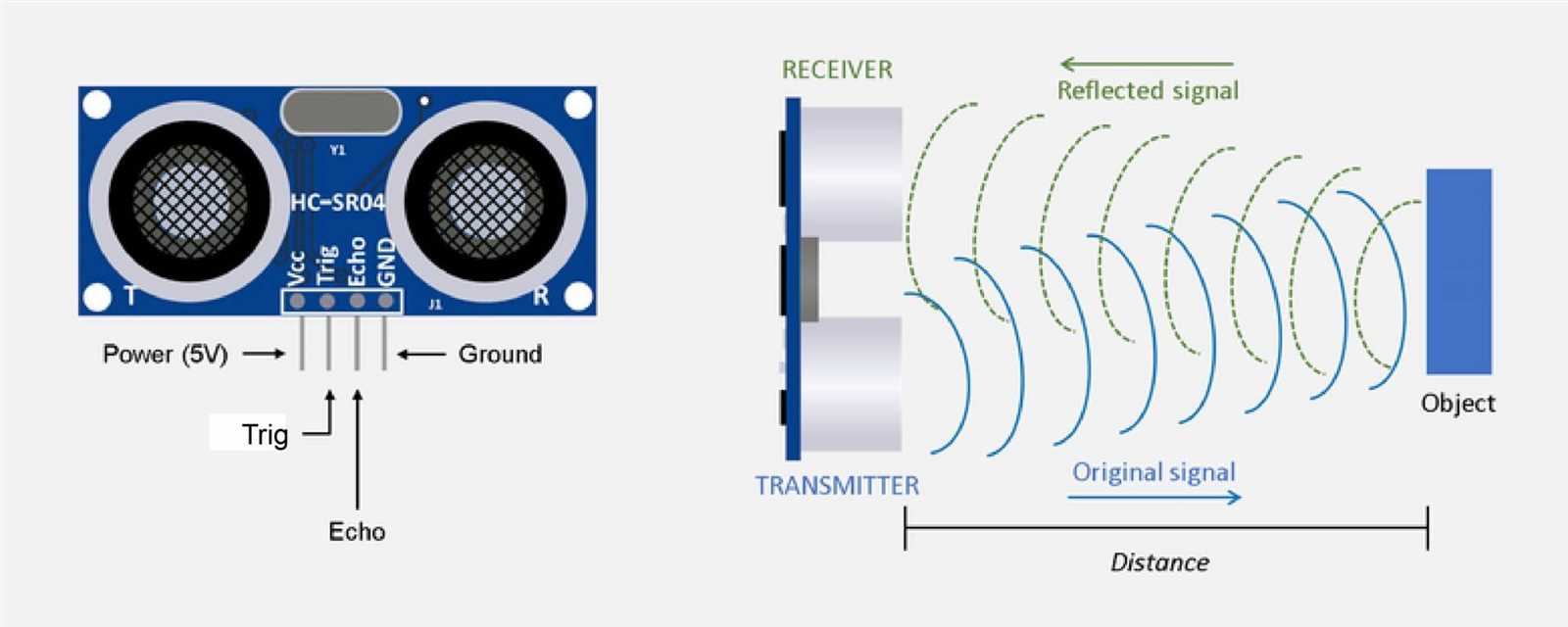
Ultrasonic sensors rely on the transmission and reception of high-frequency sound waves to detect objects or measure distances. These sensors emit ultrasonic waves and then measure the time it takes for the waves to bounce back after hitting an object. By analyzing the time delay, the sensor can determine the distance between itself and the object.
One of the key advantages of ultrasonic sensors is their ability to operate in a non-contact manner. This means that they do not need to physically touch the object they are detecting, making them suitable for applications where contact may not be desirable or practical. Additionally, ultrasonic sensors can provide accurate measurements even in challenging environments with dust, smoke, or other interferences.
Components of Ultrasonic Sensors
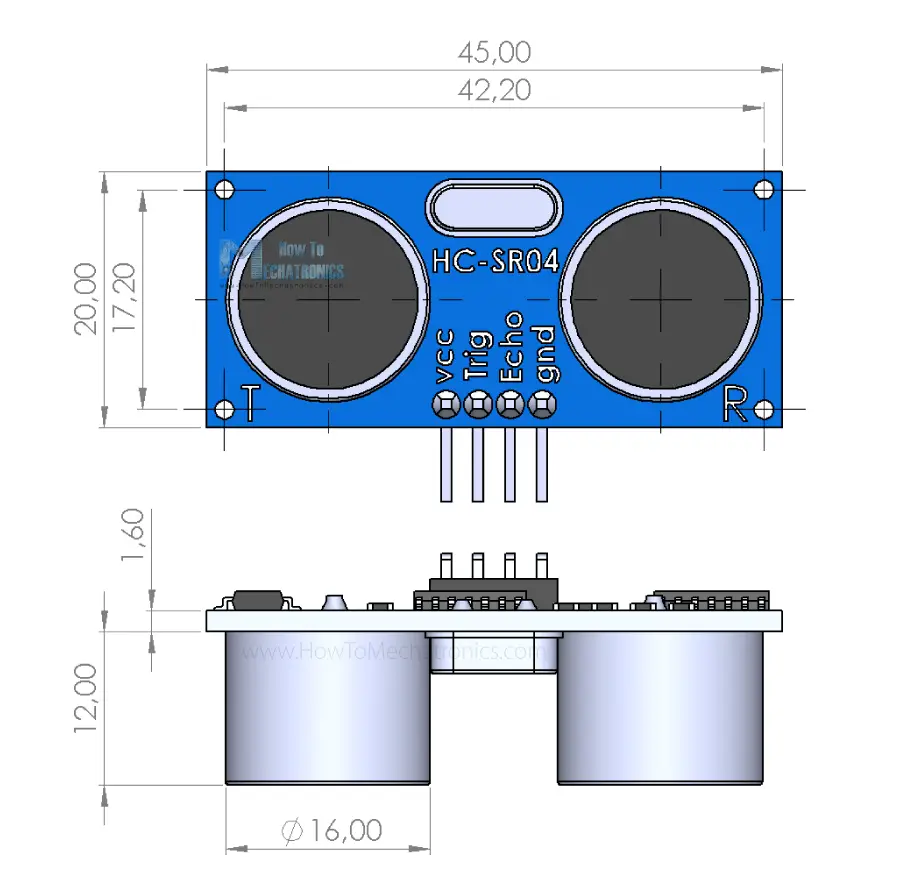
To understand the inner workings of ultrasonic sensors, it is important to be familiar with their main components. These typically include a transducer, which acts as both a transmitter and receiver of ultrasonic waves, and a signal processing unit, which converts the received signals into measurable data.
The transducer is responsible for generating high-frequency sound waves and converting them into electrical signals. It consists of a piezoelectric crystal that vibrates when an electrical voltage is applied to it, producing the ultrasonic waves. When these waves encounter an object, they are reflected back to the transducer.
The signal processing unit receives the reflected waves and converts them into electrical signals that can be processed further. It measures the time delay between the transmitted and received signals and calculates the distance based on the speed of sound in the medium of propagation.
Table: The table below summarizes the main components of ultrasonic sensors and their functions:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Transducer | Generates and receives ultrasonic waves |
| Signal Processing Unit | Converts received signals into measurable data |
By understanding the basics of ultrasonic sensors, we can explore their capabilities in various applications such as distance measurement, obstacle detection, and level sensing. This knowledge forms the foundation for designing and utilizing these sensors effectively in projects and systems.
Exploring the Specifications of the Arduino Ultrasonic Distance Measuring Module
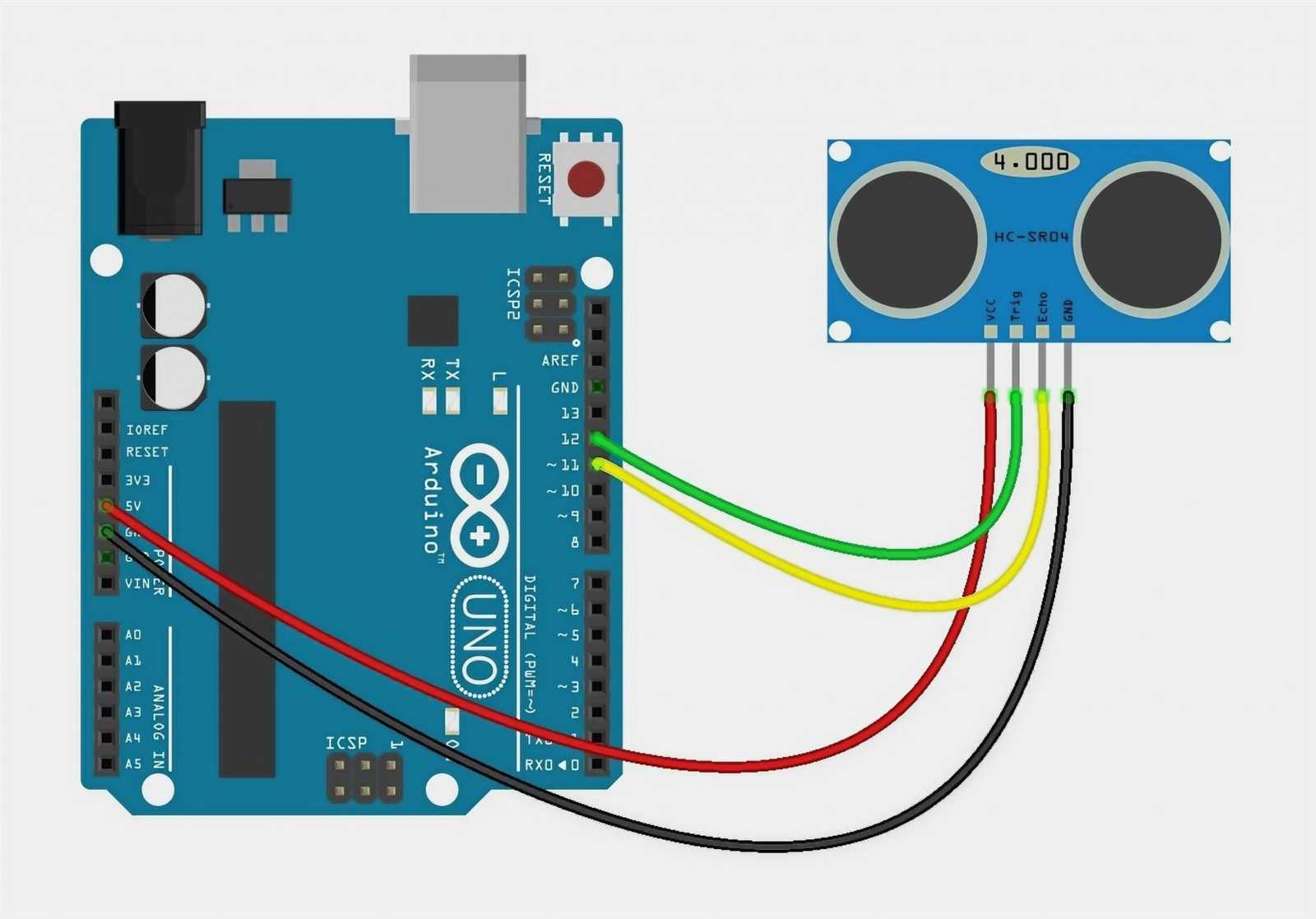
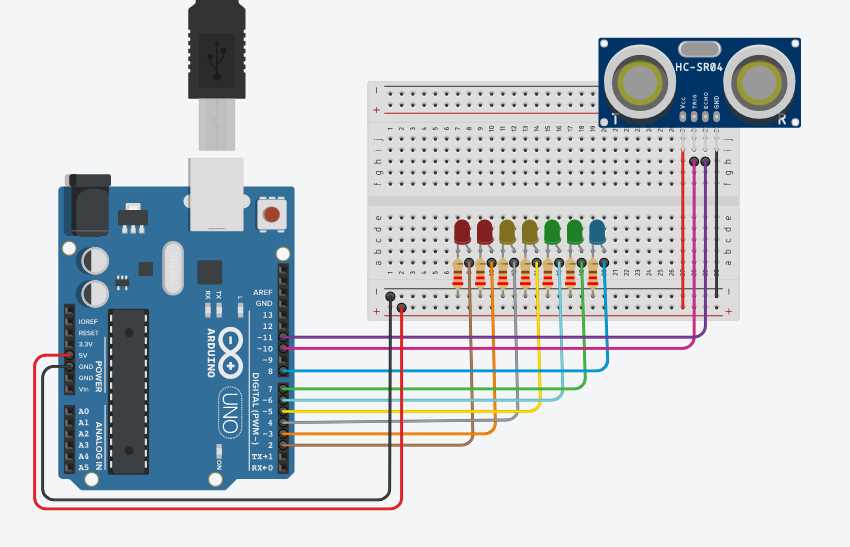
In this section, we will delve into the details of the technical specifications and capabilities of the distance measuring module found in the Arduino toolkit. By understanding the key parameters and features outlined in the datasheet, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of the module’s functionality and potential applications.
Operating Principle
To comprehend the inner workings of the distance measuring module, it is essential to first grasp its underlying operating principle. By utilizing sound waves, this module detects objects in its vicinity and measures the time it takes for the sound waves to bounce back. This enables the determination of the distance between the module and the detected object.
Key Technical Specifications
Below, we outline the critical technical specifications that play a vital role in the performance of the ultrasonic distance measuring module:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Measurement Range | The maximum distance that the module can accurately measure. |
| Resolution | The smallest measurable increment in distance. |
| Operating Voltage | The range of voltage within which the module can function correctly. |
| Output Interface | The method by which the module communicates the distance measurement data. |
| Operating Temperature | The range of temperatures within which the module can operate reliably. |
| Power Consumption | The amount of power required for the module to function properly. |
By carefully examining these technical specifications, we can effectively evaluate whether the ultrasonic distance measuring module is suitable for a specific project or application.
Applications and Benefits of Arduino Ultrasonic Sensors
Ultrasonic sensors offer a wide range of applications in various industries and fields. These sensors, based on the principles of sound waves and echolocation, provide a reliable and accurate way to measure distances and detect object presence. Their versatility and ease of use make them valuable tools in many projects.
1. Distance Measurement

One of the primary applications of Arduino ultrasonic sensors is distance measurement. These sensors emit high-frequency sound waves and measure how long it takes for the wave to bounce back after hitting an object. By calculating the time difference and using the speed of sound, the distance between the sensor and the object can be accurately determined. This capability is useful for robotics projects, automated systems, level monitoring, and navigation purposes.
2. Object Detection and Security Systems

Arduino ultrasonic sensors are commonly used in object detection systems to identify the presence or absence of an object within a specific range. These sensors can detect even non-metallic objects, making them suitable for a variety of applications. They are particularly useful in security systems, where they can trigger alarms or activate cameras when unauthorized individuals or objects are detected.
| Applications | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Smart parking systems | Efficient use of parking spaces |
| Proximity sensors | Prevent collisions and accidents |
| Tank level monitoring | Optimized resource management |
| Obstacle avoidance in robotics | Safe navigation and operation |
Other notable applications of Arduino ultrasonic sensors include smart parking systems, proximity sensors for collision prevention, tank level monitoring for optimized resource management, and obstacle avoidance in robotics. These sensors provide accurate and real-time data, enabling efficient and safe operations.
In conclusion, the wide range of applications and the various benefits offered by Arduino ultrasonic sensors make them indispensable tools in many projects. Whether it is for distance measurement, object detection, or security systems, the reliability and accuracy of these sensors play a critical role in ensuring successful implementation.