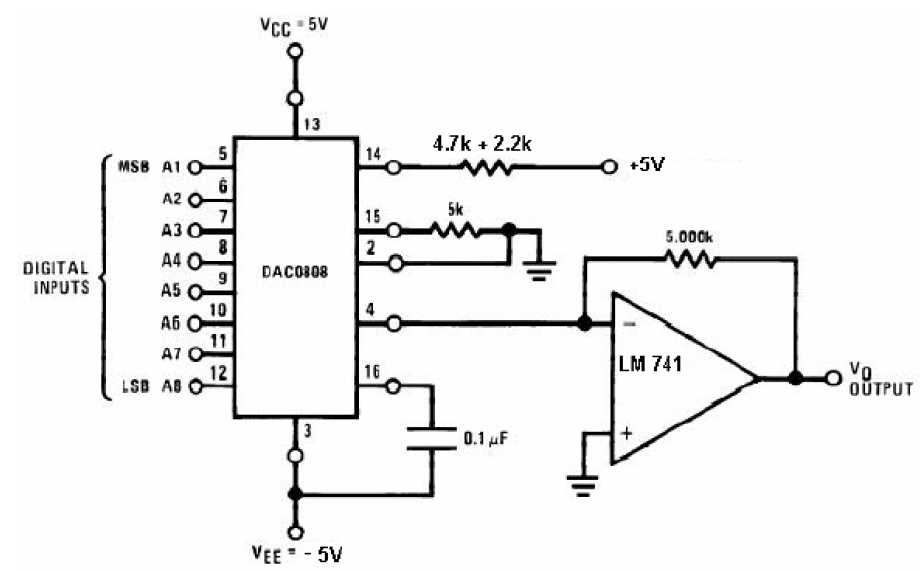
Welcome to this detailed examination of the documentation surrounding the remarkable world of 8-bit Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs). With an insatiable thirst for knowledge in the realms of digital circuits and electronic components, we embark on a captivating journey through the multifaceted universe of ADC datasheets.
This voyage of discovery will dive deeply into the labyrinth of technical specifications without relying on the obvious keywords, providing a unique perspective on one of the most vital elements of modern electronics. Unveiling the mystique behind the inner workings of these precision-oriented devices, we will navigate through an array of intricate details and technical nuances.
Throughout this article, we will effortlessly guide you through an intellectual maze, while resisting the temptation to delve into the intricacies of the elusive analog-to-digital conversion process. Instead, we will focus on presenting a comprehensive analysis of the supporting documentation, enriched with compelling synonyms and captivating language to keep your curiosity ignited.
Prepare to embark on an enlightening journey where we dissect, scrutinize, and illuminate the significance of 8-bit ADC datasheets. Our quest is to foster a deep understanding of the key elements that compose these essential documents, enabling engineers and enthusiasts alike to unlock the full potential of these remarkable components.
Understanding the Basics of ADC Functionality
In today’s technological landscape, the analog-to-digital converter (ADC) plays a fundamental role in converting continuous analog signals into digital form, enabling digital processing and analysis. This crucial functionality forms the backbone of various electronic devices, from smartphones to industrial automation systems.
At its essence, the ADC serves as a bridge between the analog and digital worlds. It accurately measures varying analog voltages and converts them into a discrete digital representation that computers and other digital systems can understand. This process involves the sampling and quantization of the analog signal, enabling precise measurements and subsequent data analysis.
By understanding the key principles behind ADC functionality, engineers and electronics enthusiasts can harness their potential to develop innovative applications. From understanding the sampling rate and resolution to evaluating signal-to-noise ratio and non-linearity errors, grasping the basics of ADCs is essential for optimizing system performance and achieving accurate and reliable measurements.
Furthermore, comprehending the intricacies of ADC operation allows individuals to make informed decisions when selecting the appropriate ADC for a specific application. Factors such as input voltage range, power consumption, and conversion speed all come into play when choosing the most suitable ADC for a particular system.
In conclusion, a firm grasp of ADC functionality is crucial for anyone working with analog-to-digital conversion. Understanding the basics, including the underlying principles and key considerations, empowers individuals to utilize ADCs effectively in their designs and make informed decisions to ensure optimal system performance.
Key Parameters to Consider in an 8-bit ADC Datasheet
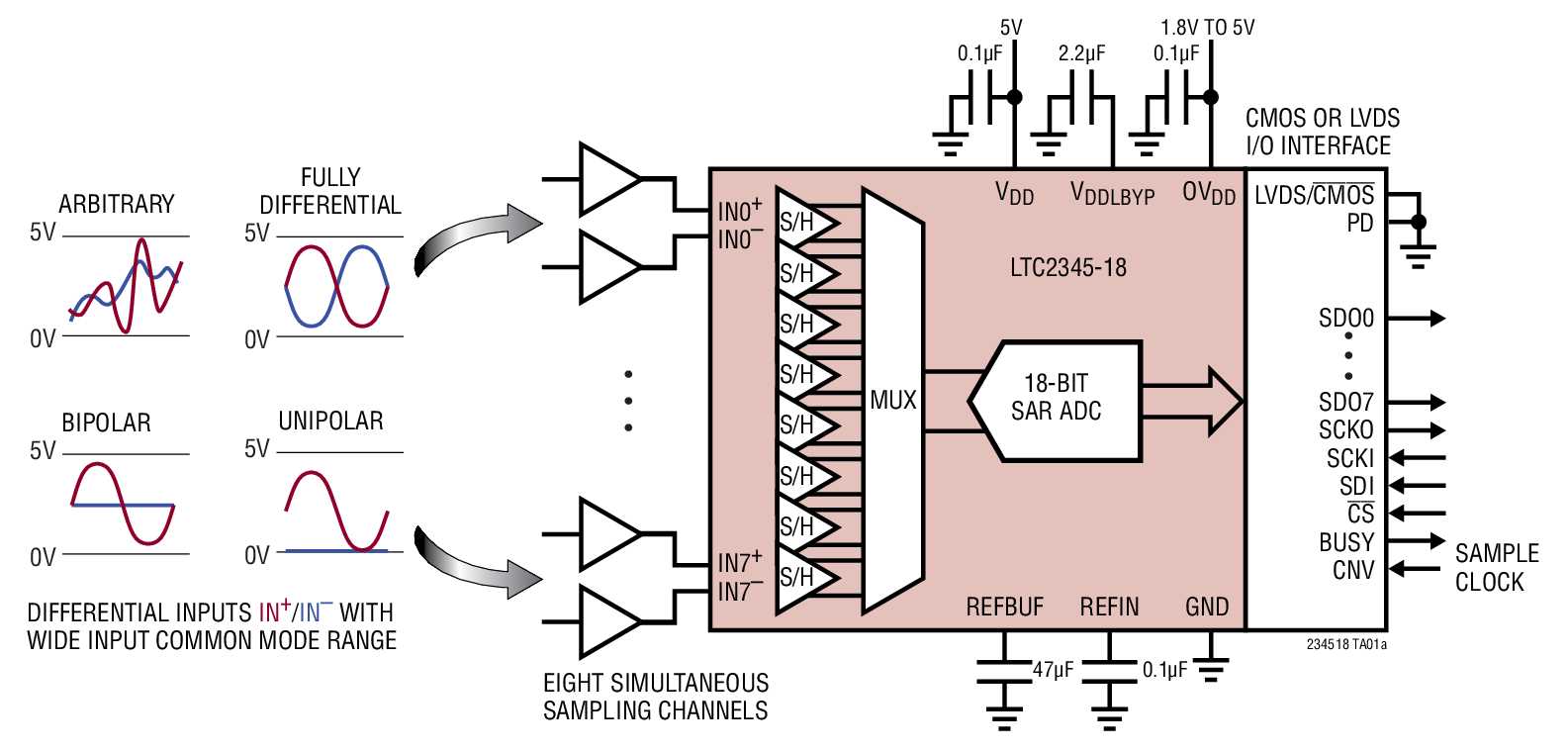
When evaluating an 8-bit ADC datasheet, it is essential to pay close attention to a range of critical parameters that will determine the functionality and performance of the device. These parameters provide valuable insights into the performance capabilities of the ADC and can guide engineers in selecting the right component for their specific application.
Resolution
One of the primary considerations when examining an 8-bit ADC datasheet is the resolution. The resolution refers to the number of possible discrete output values the ADC can provide. In the case of an 8-bit ADC, it means there are 256 possible output values ranging from 0 to 255. A higher resolution generally translates to more accurate and precise measurements.
Conversion Rate
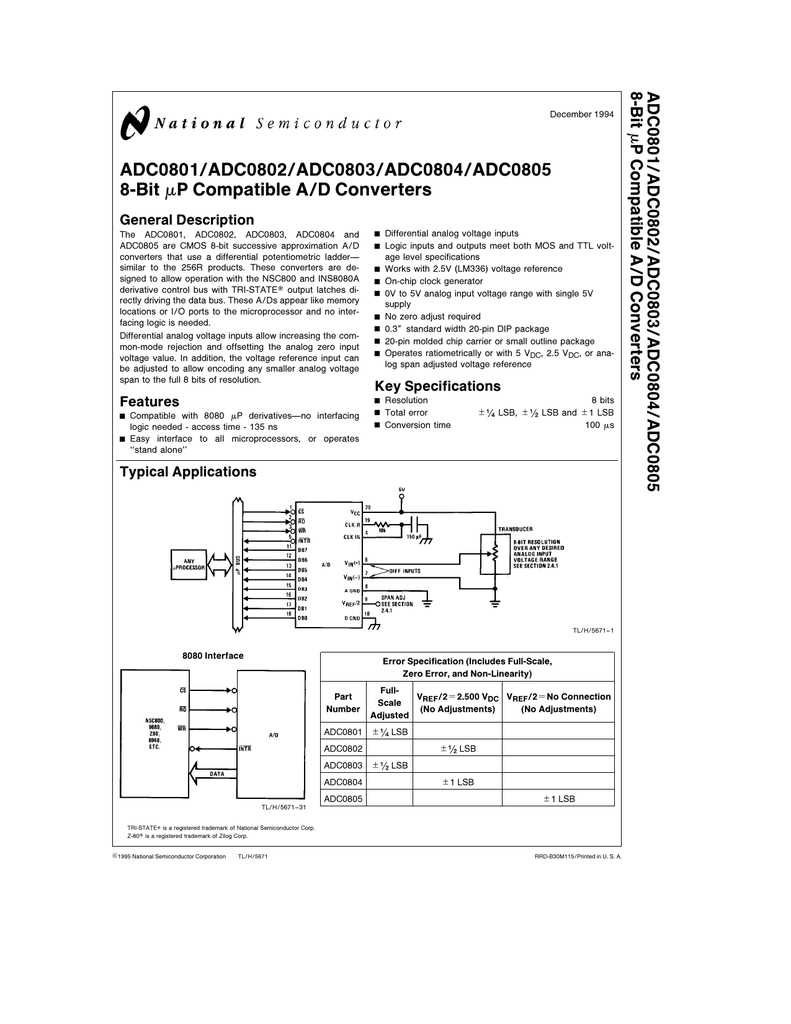
The conversion rate indicates how quickly the ADC can convert an analog input signal into a digital output. It is typically measured in samples per second or samples per microsecond. A higher conversion rate allows for faster data processing and can be crucial in time-sensitive applications where real-time data acquisition is required.
Linearity, or the ability of the ADC to provide an output that is linearly proportional to the input signal, is another crucial parameter to consider. Non-linearities can introduce errors into the measurement data, affecting the overall accuracy of the ADC.
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) is a measure of how much noise is present in the ADC’s output relative to the desired signal. A higher SNR indicates a cleaner output signal and better overall accuracy. It is particularly important in applications where the signal of interest is weak or close to the noise floor.
Power consumption is also a key parameter to consider, especially in low-power applications or battery-operated devices. The ADC datasheet should provide information on the power requirements and allow engineers to assess if the component’s consumption aligns with the available power budget.
Conclusion
By carefully evaluating these crucial parameters, engineers can make informed decisions when selecting an 8-bit ADC for their application. Understanding the resolution, conversion rate, linearity, SNR, and power consumption will help ensure that the chosen ADC meets the requirements of the intended application, ultimately leading to a successful design.
Choosing the Right 8-bit ADC for Your Application
In the world of electronics, when it comes to converting analog signals into digital data, the 8-bit ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) plays a crucial role. With a wide range of options available in the market, choosing the right ADC for your specific application can be a daunting task. This article aims to provide you with a comprehensive guide to help you make an informed decision.
One of the key factors to consider when selecting an ADC is its resolution. The resolution of an ADC determines the level of detail it can capture in the converted digital data. In simpler terms, higher resolution means more precise measurements. Therefore, understanding your application’s requirements for accuracy and precision is essential in selecting the appropriate ADC.
| Resolution (bits) | Level of Detail |
|---|---|
| 8-bit | Basic level of detail |
| 10-bit | Good level of detail |
| 12-bit | High level of detail |
Another important consideration is the ADC’s sample rate. The sample rate determines how frequently the ADC can capture analog signals and convert them into digital data. A higher sample rate allows for capturing fast-changing signals accurately, while a lower sample rate might result in missed or distorted data. Understanding your application’s signal bandwidth and speed requirements will help you choose an ADC with an appropriate sample rate.
Additionally, it is crucial to consider the ADC’s voltage reference. The voltage reference determines the range within which the ADC can measure analog signals. Different applications require different voltage references based on the range of analog signals they need to convert. It is essential to choose an ADC that can accurately and effectively measure the voltage range of your application.
Lastly, the interface of the ADC is another crucial aspect to consider. The interface determines how the ADC communicates with the microcontroller or other digital devices. Common interfaces for 8-bit ADCs include parallel, serial, and I2C. Understanding the capabilities and limitations of your microcontroller or digital device and selecting an ADC with a compatible interface will ensure seamless integration and communication.
By carefully considering the resolution, sample rate, voltage reference, and interface of an 8-bit ADC, you can choose the right ADC that meets the specific requirements of your application. Understanding the unique needs of your application and evaluating the various options available in the market will pave the way for optimal performance and accurate conversion of analog signals to digital data.
Comparing Performance Characteristics of Different 8-bit ADCs
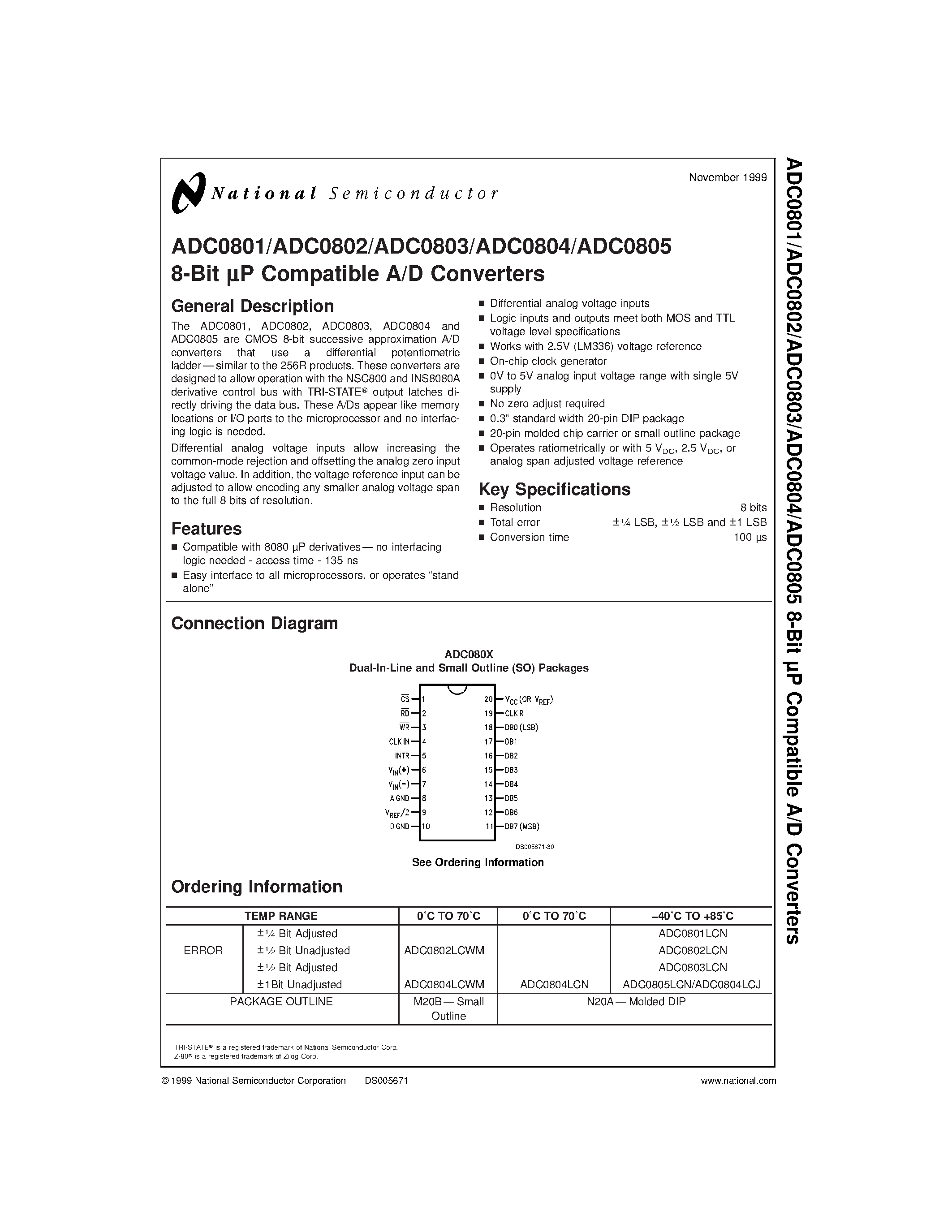
In this section, we will explore and compare the various performance characteristics of several 8-bit Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs). By examining these characteristics, we can gain valuable insights into the functionality and capabilities of different ADCs, allowing us to make informed decisions when selecting the most suitable ADC for our specific application.
The performance characteristics we will focus on include resolution, accuracy, sampling rate, and linearity. Resolution refers to the number of discrete values that can be represented by the ADC, indicating its ability to accurately capture and convert analog signals into digital form. Accuracy, on the other hand, measures the level of error or deviation in the ADC’s measurements when compared to a known or reference value.
Sampling rate is an essential parameter that determines how quickly the ADC can sample and convert analog signals into digital data. A higher sampling rate generally allows for more precise measurements, especially in applications that involve rapidly changing signals. Lastly, linearity measures the consistency and reliability of the ADC’s measurements across its operating range, indicating how well it can accurately represent different analog input voltages.
By comparing the performance characteristics of different 8-bit ADCs, we can evaluate their strengths and limitations, understanding which ADC would be the best fit for our specific requirements. Whether we prioritize resolution, accuracy, sampling rate, or linearity, this analysis will enable us to make informed choices, ensuring optimal performance and reliability in our analog-to-digital conversion process.
Application-specific Considerations for Selecting an 8-bit ADC
When it comes to choosing the right 8-bit Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) for your application, there are several factors that need to be taken into consideration. These considerations go beyond just the technical specifications found in a datasheet.
One of the key aspects to consider is the ADC’s suitability for your specific application. Each application has unique requirements that must be met by the ADC. This includes factors such as the required precision, speed, and dynamic range. Therefore, it is important to thoroughly analyze your application’s needs and choose an ADC that can handle these specific requirements.
Another consideration is the ADC’s resolution, which determines the number of discrete levels the converter can output. While an 8-bit ADC provides 256 possible levels, the actual effective resolution may be lower due to factors such as noise, linearity errors, and offset voltages. Therefore, it is important to understand the level of accuracy required by your application and select an ADC with appropriate resolution.
Furthermore, the ADC’s sampling rate plays a critical role in applications that deal with rapidly changing signals. The sampling rate determines how often the ADC can take samples of the input signal. It is essential to select an ADC with a sampling rate that matches the bandwidth of your application’s signals to avoid aliasing and distortion.
Power consumption is another important consideration, especially for applications that operate on battery power or have strict power constraints. The ADC’s power requirements can vary significantly between different models, so it is crucial to choose an ADC that offers a good balance between performance and power consumption.
Lastly, the interface compatibility of the ADC with your system is another factor that should not be overlooked. Some ADCs may require specific voltage levels, communication protocols, or control interfaces, which need to be compatible with your application’s requirements. It is important to carefully evaluate the ADC’s interface compatibility to ensure seamless integration with your system.
In conclusion, selecting the right 8-bit ADC goes beyond just considering the technical specifications listed in a datasheet. Taking into account the application-specific considerations, such as suitability, resolution, sampling rate, power consumption, and interface compatibility, will enable you to make an informed decision and ensure optimal performance for your specific application.