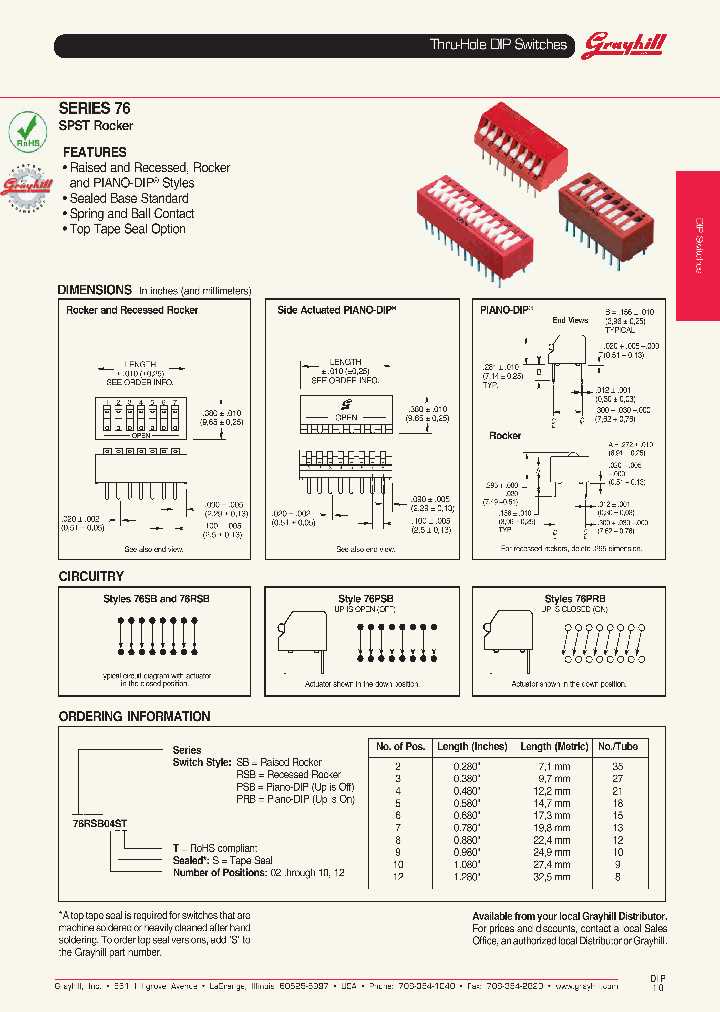
As technology continues to evolve at an unprecedented rate, the demand for efficient and reliable control switching devices has reached an all-time high. These devices play a crucial role in various industries, providing the ability to enable or disable specific functionalities of electrical circuits or systems.
In this article, we embark on a journey to uncover the intricacies of a fundamental control switching component, commonly known as a “DIP switch.” A DIP switch, also referred to as a control selector, provides an intuitive and accessible way to alter the behavior of electronic devices or systems.
Within the realm of electronic engineering, the DIP switch serves as a key element in circuit design and implementation. Its purpose is to enable customizable configurations, allowing engineers to fine-tune the functionality of their creations without the need for complex coding or programming.
Throughout this exploration, we delve deep into the world of DIP switch datasheets, essential resources that provide comprehensive information on the specifications and capabilities of these control switching devices. By examining these datasheets, engineers and enthusiasts gain valuable insights into the technical details, such as pin assignments, voltage ratings, contact ratings, and other critical parameters that ensure optimal performance and compatibility.
So join us as we navigate the intricate details of DIP switch datasheets, uncovering the integral information necessary for informed decision-making and successful integration of control switching devices into various applications. Through this exploration, we aim to empower individuals to make confident choices when selecting the ideal DIP switch for their projects, ultimately driving advancements in electronics and technology as a whole.
The Basics of Dip Switches
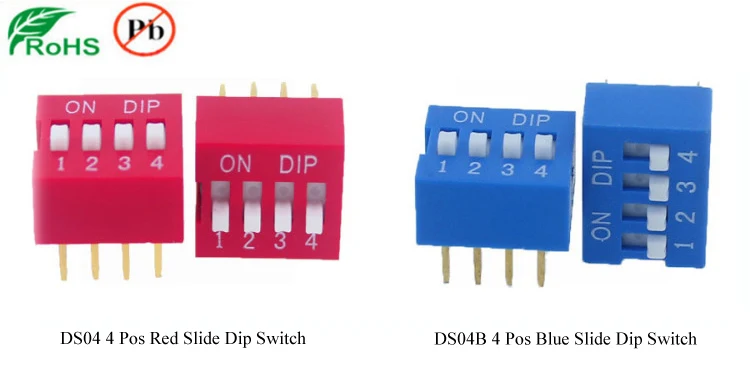
When it comes to electronic devices, the ability to customize settings and configurations is essential. One way this can be achieved is through the use of dip switches. These small, manually operated switches offer a simple and reliable solution for setting different options or modes in a variety of electronic applications.
Unlike traditional switches that rely on mechanical levers or buttons, dip switches utilize a series of tiny switches lined up on a small circuit board, resembling the shape of an integrated circuit. Each individual switch, which can be turned on or off independently, represents a specific configuration that the user can select.
The versatility of dip switches lies in their binary nature. Each switch can be thought of as a 1 or a 0, corresponding to the on or off positions respectively. By combining these individual positions, various combinations can be created, resulting in a wide range of possible settings. This binary system allows for a flexible and efficient way to control the functionality of a device.
One of the advantages of dip switches is their simplicity. They require no additional programming or software to operate, making them easy to understand and use. With just a quick glance at the switch positions, users can determine the current configuration or make adjustments as needed.
Dip switches are commonly used in applications such as computer motherboards, industrial control systems, and electronic toys. They offer a cost-effective solution for manufacturers to provide customizable options without the need for complex interfaces or programming.
- Provide a straightforward and reliable method for customization
- Utilize binary on/off positions for flexible settings
- Require no additional programming or software
- Used in various electronic applications
- Cost-effective solution for manufacturers
Overall, dip switches provide a fundamental means to adjust and personalize the settings of electronic devices. Their simplicity, versatility, and cost-effectiveness make them a valuable component in the world of electronics.
Understanding Dip Switch Functionality and Applications
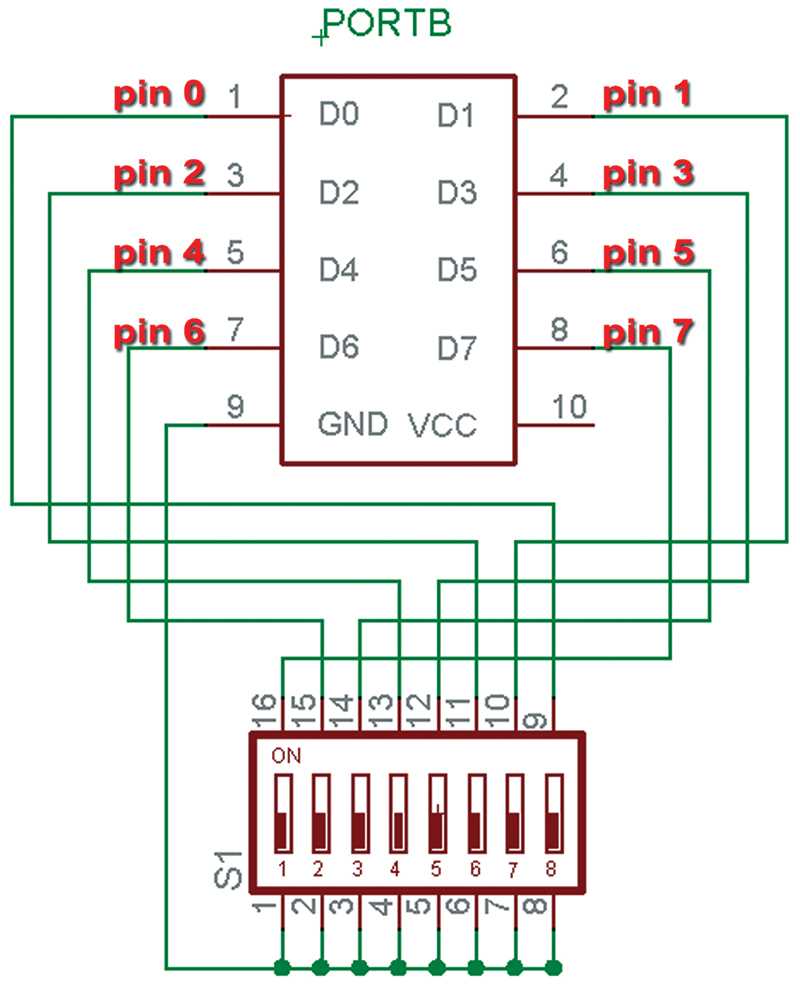
Exploring the Mechanics and Practical Applications of Dual In-line Package (DIP) Switches
Introduction
In the world of electronic components, few devices offer the versatility and simplicity of Dual In-line Package (DIP) switches. These small yet powerful tools enable users to easily configure and customize electronic circuits and systems. This section aims to provide a comprehensive overview of DIP switch functionality, discussing their mechanics, operation, and various applications.
Mechanism and Operation

DIP switches consist of multiple individual switches organized in a standard dual in-line package format. Each switch is designed with a sliding lever that can be set to either an ON or OFF position, effectively creating a binary state. These switches are commonly used to control the behavior of electronic devices, such as selecting different modes, setting addresses, or enabling specific functionalities.
The sliding lever mechanism of DIP switches allows for easy manual configuration, making them suitable for applications where frequent changes to system settings are required. This simplicity also ensures reliability, as the position of each switch can be easily visually inspected, reducing the risk of accidental misconfiguration.
Applications

DIP switches find widespread use in various electronic systems, especially those with limited or no software interfaces. Their versatility allows for numerous applications across different industries:
| Industry | Applications |
|---|---|
| Industrial Automation | Setting device parameters, configuring control systems |
| Telecommunications | Addressing, network configuration |
| Consumer Electronics | Mode selection, device customization |
| Automotive | Setting vehicle preferences, device calibration |
| Robotics | Configuring robot behavior, control options |
These examples demonstrate the broad range of applications where DIP switches provide an efficient and cost-effective solution for system configuration and customization. By providing a physical interface for user-defined settings, DIP switches offer flexibility and adaptability in various electronic devices and circuits.
How to Understand a Technical Document for Proper Setting Adjustment
When working with electronic components, it is important to be able to read and interpret the information provided in technical documents. This is especially crucial when configuring the settings of a device using a set of small switches, commonly known as a dip switch. In this section, we will discuss how to effectively interpret a dip switch datasheet in order to achieve the desired configuration.
Understanding the Terminology
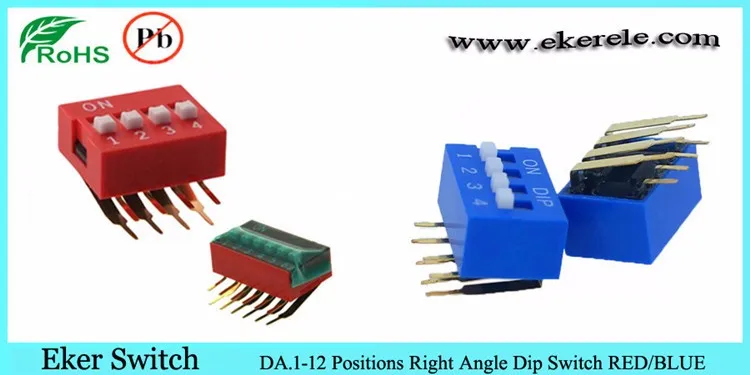
Before diving into the datasheet, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the technical terms commonly used in the document. Some terms you may encounter include:
| Parameter | The specific setting or characteristic being described. |
| Position | The possible states that a switch can be set to, often represented by numbers or letters. |
| Function | The purpose or effect of a specific switch setting. |
| Default | The initial or recommended setting for a switch. |
| Montage | The physical layout of the dip switch, specifying the number of switches, their positions, and other relevant details. |
Deciphering the Tables
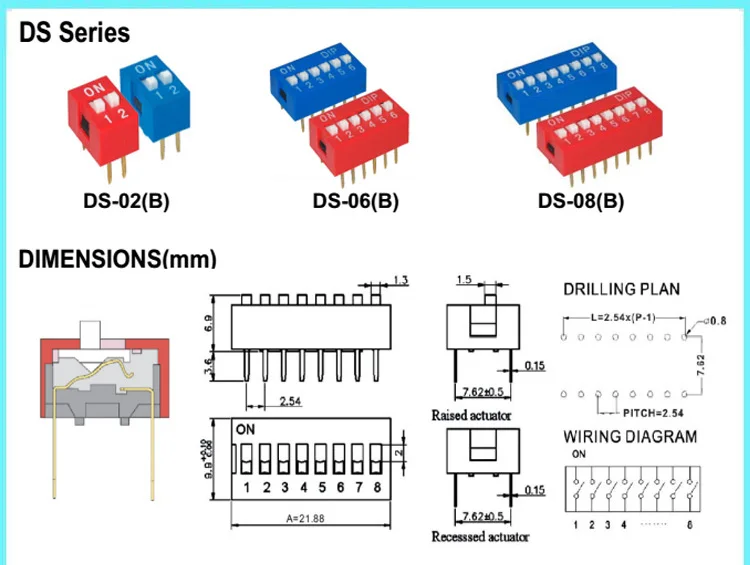
The main component of a dip switch datasheet is the table that outlines the various switch settings and their corresponding functions. Here’s how to make sense of the information presented:
1. Determine the Switch Positions: Look for a row or column that displays the possible switch positions. This will typically be indicated by numbers or letters. Identify the switches needed for your desired configuration.
2. Understand the Functions: Each switch position will have a corresponding function listed. This information describes what the setting does or how it alters the behavior of the device. Take note of the functions relevant to your requirements.
3. Consider the Default Settings: The datasheet may indicate a recommended or default setting for specific scenarios. These settings are often marked to guide users in achieving the commonly used configurations.
4. Visualize the Montage: The datasheet may include a diagram or visually represent the physical layout of the dip switch. This can be helpful in identifying the positions of each switch and understanding their arrangement on the device.
By carefully reading and understanding the dip switch datasheet, you will be able to configure the switches correctly and achieve the desired settings for your electronic device.
Choosing the Right Dip Switch for Your Electronic Device

In the realm of electronic devices, the proper selection of a small yet crucial component can greatly impact the functionality and performance of your device. When it comes to controlling settings, the dip switch is an important element to consider. During the decision-making process, it is imperative to evaluate various factors to ensure the dip switch chosen suits the specific requirements of your electronic device.
One key aspect to consider is the size of the dip switch. Depending on the available space within your device’s design, you need to choose a switch that fits perfectly without causing any obstructions or compromises. The ideal dip switch should blend seamlessly and not interfere with the overall form factor or aesthetics of the device.
Another important consideration is the number of positions or states required for your device. The dip switch must accommodate the required number of positions, allowing you to control and adjust the settings as needed. It is necessary to assess the functionality of your device and determine the range of options that should be available through the dip switch.
Reliability is a crucial factor when selecting a dip switch. The switch should be durable enough to withstand the demands of your device’s operating environment, ensuring smooth and consistent operation over an extended period. Additionally, it is important to select a dip switch that can handle the electrical current and voltage requirements of your electronic device.
Furthermore, the actuation force and actuation method of the dip switch are factors to consider. The actuation force refers to the level of pressure required to toggle the switch positions, and it is essential to choose a force that aligns with the intended user experience. Additionally, the actuation method, whether it be slide, rocker, or rotary, should be selected based on the device’s design and the ease of use desired.
Lastly, it is advisable to consider the available options for customization. Depending on specific preferences or branding requirements, the dip switch may need to be customizable in terms of color, labeling, or even additional features like illumination. Taking these customization options into account can enhance the overall appearance and user interface of your electronic device.
To summarize, selecting the right dip switch involves evaluating factors such as size, number of positions, reliability, actuation force and method, and customization options. By carefully considering these factors, you can ensure that the dip switch chosen for your electronic device is a perfect fit that enhances both the functionality and user experience.