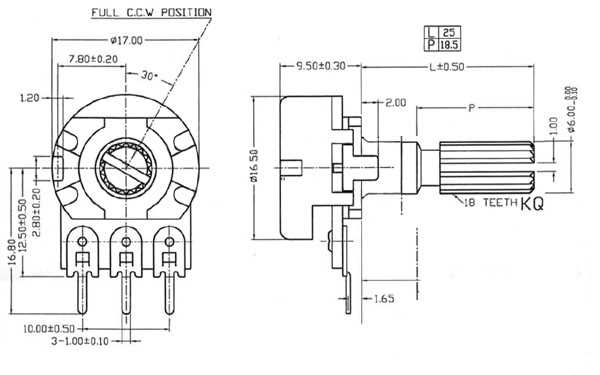
As technology continues to advance at an unprecedented pace, the demand for precision control and measurement in electronic devices has become more critical than ever. Variable resistors, also known as potentiometers, play a vital role in achieving this level of accuracy. In this section, we will delve into the intricacies of a key component datasheet, shedding light on the essential specifications that define its performance and versatility.
Like master puzzle pieces in an intricate design, variable resistors enable engineers and electronic enthusiasts to fine-tune the behavior of their circuits. These miniature marvels offer a wide range of resistive values, allowing for precise adjustments in voltage, current, and signal levels. To fully comprehend the power and potential of a variable resistor datasheet, it is essential to understand the meaning behind each specification, exploring the intricate relationships between electrical characteristics and their practical implications.
In today’s technologically advanced era, a myriad of variable resistor options flood the market. With such an extensive variety, selecting the most suitable component may at times seem like navigating a complex maze. This is why a detailed examination of a datasheet becomes a fundamental aspect of the decision-making process. Through comprehensive analysis and comparison, one can uncover the most appropriate variable resistor for their specific application, optimizing performance and ensuring a seamless integration that sets the foundation for success.
Understanding the Basics of a Potentiometer

A potentiometer, also known as a variable resistor, is an important electronic component that plays a crucial role in various electrical circuits. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the fundamental concepts associated with potentiometers without delving into specific technical details found in a datasheet.
Working Principle of a Potentiometer

At its core, a potentiometer functions as a three-terminal resistor, where the resistance between two terminals can be adjusted manually. It operates on the principle of a voltage divider, dividing the input voltage into desired proportions. By varying the position of the slider or wiper along the resistor track, the output voltage can be regulated accordingly.
Applications of Potentiometers
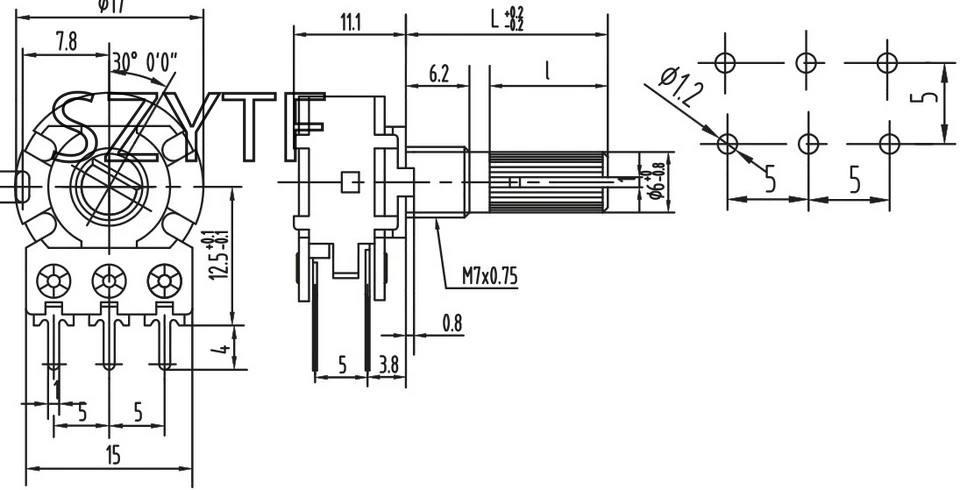
Potentiometers find applications in a wide range of electronic devices and systems. Some common uses include:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Volume Control | In audio systems, potentiometers are used to adjust the volume level, allowing users to control the sound output. |
| Lights Dimming | Potentiometers are employed in lighting systems to regulate the brightness of lights, creating desired ambiance. |
| Instrument Calibration | Potentiometers are crucial in calibrating instruments and sensors to ensure accurate measurements and readings. |
In addition to these applications, potentiometers are utilized in motor speed control, temperature control, and various electronic circuit adjustments.
Understanding the basics of a potentiometer is essential for electronics enthusiasts, hobbyists, and professionals alike. By comprehending its working principle and applications, individuals can gain a solid foundation in utilizing potentiometers in electronics projects and troubleshooting circuit-related issues.
Types of 1k Potentiometers and Their Applications
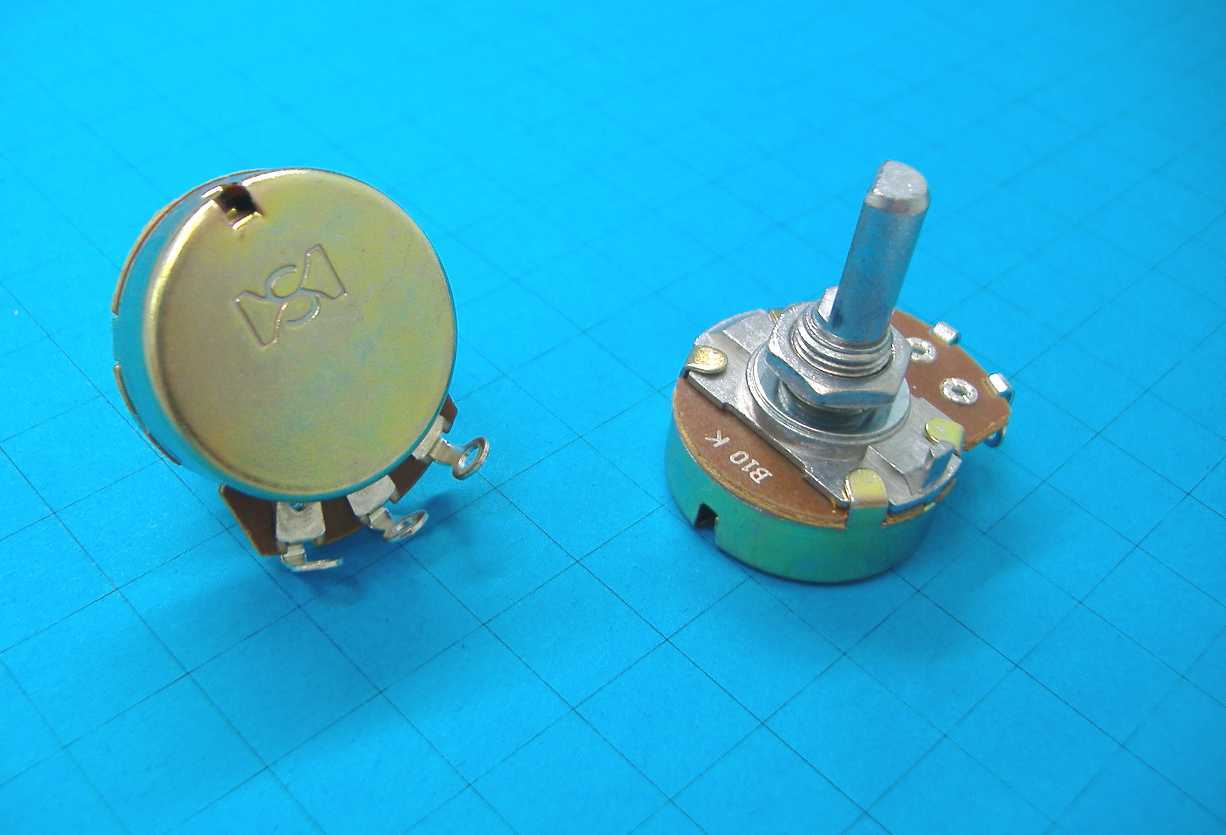
In this section, we will explore different variations of 1k potentiometers and the various applications they can be used for. Potentiometers are versatile electronic components that allow for precise control of electrical currents in a circuit. These devices are essential in a wide range of applications, including audio systems, electrical instrumentation, and industrial automation.
One type of 1k potentiometer is the rotary potentiometer, also known as a rotary variable resistor. As the name suggests, this type of potentiometer consists of a rotating knob that can be adjusted to change the resistance value. Rotary potentiometers are often used in audio systems to control volume or tone levels, as well as in industrial automation for adjusting motor speed or position.
Another type of 1k potentiometer is the slide potentiometer. Instead of a rotating knob, this potentiometer has a sliding mechanism that allows for linear adjustment of the resistance. Slide potentiometers are commonly used in audio mixing consoles and equalizers, where precise control of individual audio channels is required.
A third type of 1k potentiometer is the multiturn potentiometer. Unlike rotary and slide potentiometers, multiturn potentiometers offer greater precision by providing multiple revolutions of the knob for fine-tuning the resistance value. These potentiometers are widely used in electrical instrumentation and calibration devices, where high accuracy is crucial.
1k potentiometers find applications in various industries such as automotive, telecommunications, and consumer electronics. For example, they are commonly used in automotive dashboards to control screen brightness or HVAC settings. In telecommunications, 1k potentiometers are utilized in control panels for adjusting signal strength or channel selection. Additionally, they can be found in consumer electronics like TVs, amplifiers, and home appliances for user-adjustable settings.
In conclusion, the different types of 1k potentiometers provide a wide range of options for controlling electrical currents in various applications. From rotary potentiometers for volume control to multiturn potentiometers for precision calibration, these components play a vital role in electronic systems, ensuring accurate and reliable operation.
Exploring the Different Varieties of 1k Potentiometers
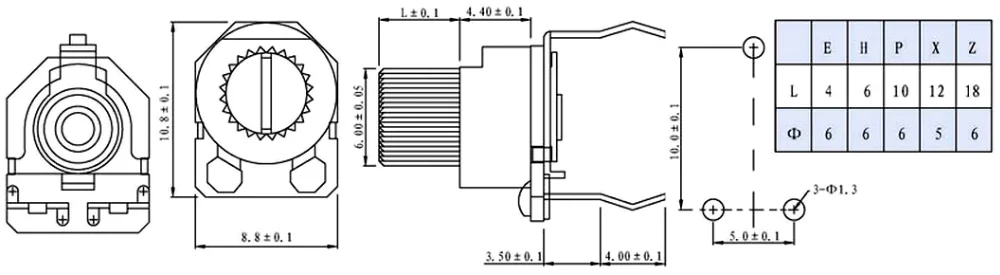
In the realm of electrical components, there exists a wide array of devices that allow for precision control and adjustment of electric signals. One such device, often referred to as a variable resistor, can be found in various forms and sizes, each tailored for different applications. In this article, we will delve into the world of 1k potentiometers, exploring the diverse range of options available and the unique characteristics they possess.
1. Precision 1k Potentiometers: These potentiometers are designed to provide highly precise and accurate adjustment of resistance values, allowing for meticulous control over electrical signals. Their construction often includes high-quality materials and precise engineering, ensuring minimal deviations in resistance and reliable performance.
2. Compact 1k Potentiometers: As the name suggests, these potentiometers prioritize size and space efficiency, making them ideal for applications with limited physical dimensions. With their compact design, these potentiometers offer a space-saving solution without compromising functionality.
3. Digital 1k Potentiometers: In the modern age of digital technology, these potentiometers have emerged as a popular choice for applications requiring precise digital control. Equipped with digital interfaces and controls, these potentiometers offer the ability to directly input desired resistance values, eliminating the need for manual adjustment.
4. Temperature-Compensated 1k Potentiometers: Temperature fluctuations can often impact the performance of electronic components, including potentiometers. To combat this, temperature-compensated potentiometers are engineered with materials and design features that minimize the effect of temperature changes on resistance values. This ensures consistent and reliable performance regardless of environmental conditions.
5. Cermet 1k Potentiometers: Cermet potentiometers are designed with a resistive element composed of a ceramic and metal mixture, offering excellent stability, durability, and resistance to environmental factors such as humidity and dust. These potentiometers are widely used in applications where reliability and long-term performance are essential.
By understanding the different varieties of 1k potentiometers available, engineers and enthusiasts can select the most suitable option for their specific requirements. Whether it’s precision adjustment, compact size, digital control, temperature compensation, or durability and stability, there is a 1k potentiometer to meet every need.
How to Read and Interpret a 1k Potentiometer Datasheet

Understanding the specifications and details provided in a datasheet is crucial when working with a 1k potentiometer. By learning how to effectively read and interpret the information presented, you can gain valuable insights into the performance and characteristics of the potentiometer.
1. Overview:
Begin by familiarizing yourself with the overall structure and layout of the datasheet. Look for sections or headings that provide a summary or introduction to the potentiometer, such as product description or features. This will give you a general understanding of what the potentiometer is designed for and its key attributes.
2. Electrical Characteristics:
Pay close attention to the electrical characteristics section, as this provides important information about the potentiometer’s performance. Look for values related to resistance, tolerance, and power rating. These details will help you determine the potentiometer’s suitability for your specific application and ensure it can handle the desired voltage and current levels.
3. Mechanical and Environmental Specifications:
Another essential section to review is the mechanical and environmental specifications. Here, you’ll find information about the potentiometer’s physical dimensions, terminal layout, and mounting options. Additionally, look for details regarding the potentiometer’s operating temperature range, humidity tolerance, and any certifications it may have, ensuring it can withstand the intended operating conditions.
4. Electrical Diagram:
Many datasheets include an electrical diagram of the potentiometer, illustrating the connection points and pinout. Take note of the terminal designations and their corresponding functions, such as the wiper, terminal 1, and terminal 2. This diagram will help you correctly wire and utilize the potentiometer in your circuit.
5. Application Information:
Look for any application information or examples provided in the datasheet. This can include circuit diagrams, formulas, or recommended usage scenarios. Understanding how the potentiometer can be effectively integrated into a circuit will give you ideas and inspiration for your own applications.
6. Additional Considerations:
Finally, be sure to check for any additional considerations or notes provided in the datasheet. This could include details about storage conditions, handling precautions, or special instructions for programming or calibrating the potentiometer. Paying attention to these details will help you maximize the potentiometer’s performance and lifespan.
By following these steps and carefully examining the information presented in a 1k potentiometer datasheet, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of the potentiometer’s capabilities and confidently incorporate it into your projects.
Key Parameters and Specifications in a 1k Potentiometer Datasheet
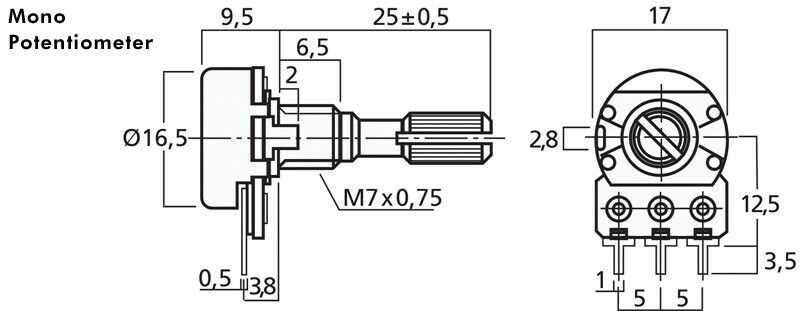
In the datasheet of a 1k potentiometer, there are several important parameters and specifications that provide crucial information about its performance and usage. Understanding these key parameters is essential for effectively integrating the potentiometer into your electronic circuit designs.
One of the fundamental parameters to consider is the resistance value, which indicates the overall resistance range that the potentiometer can provide. This value is usually expressed in ohms and can vary for different potentiometer models. It determines the range of control or adjustment that can be achieved by the potentiometer.
Another essential parameter is the tolerance, which defines the permissible deviation from the specified resistance value. Tolerance is expressed as a percentage, with a lower percentage indicating a higher precision potentiometer. Therefore, a potentiometer with a lower tolerance will have a narrower range of resistance values within the specified rating.
The power rating is also vital, as it determines the maximum power that the potentiometer can safely handle without overheating or damaging its internal components. It is typically measured in watts and helps ensure the potentiometer’s reliability and longevity in a given application.
Furthermore, the operating temperature range specifies the temperature limits within which the potentiometer can function correctly. It is essential to consider this parameter to avoid potential malfunctions or performance degradation due to extreme temperatures or temperature fluctuations.
Other important specifications to evaluate include the mechanical dimensions, such as the physical size and shape of the potentiometer, as well as any mounting requirements. Additionally, the datasheet may provide information about the potentiometer’s shaft type, rotational life, linearity, and noise level, which are crucial factors to consider depending on the intended application and desired performance.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Resistance Value | The overall resistance range provided by the potentiometer. |
| Tolerance | The permissible deviation from the specified resistance value. |
| Power Rating | The maximum power that the potentiometer can handle. |
| Operating Temperature Range | The temperature limits within which the potentiometer can function correctly. |
| Mechanical Dimensions | The physical size, shape, and mounting requirements of the potentiometer. |
| Shaft Type | The type of shaft used in the potentiometer. |
| Rotational Life | The expected lifespan of the potentiometer under normal usage. |
| Linearity | The degree of linearity in the variation of resistance with the potentiometer’s rotation. |
| Noise Level | The amount of electrical noise generated by the potentiometer during operation. |