
Embarking on a journey through the intricate realm of electronic components unveils a labyrinth of innovation and precision engineering. Within this labyrinth lies a particular gem, brimming with potential to revolutionize electronic designs and elevate performance benchmarks. In this exploration, we delve into the intricacies of a versatile electronic marvel, delving into its capabilities and applications.
Unveiling the Intricacies: At the heart of modern electronics lies a myriad of components, each bearing unique characteristics and functionalities. Among these, one component stands out for its versatility and adaptability, offering a plethora of features tailored to meet the demands of diverse applications. This component, shrouded in complexity yet brimming with potential, serves as the cornerstone of innovation in electronic design.
Unlocking Innovation: Within the vast landscape of electronic components, innovation serves as the driving force propelling progress forward. Our exploration takes us into the realm of a component renowned for its ability to unlock new possibilities and push the boundaries of what is achievable. Through a meticulous examination of its features and specifications, we unravel the intricacies of this component and uncover its potential to redefine electronic systems.
The Fundamentals of Understanding Technical Documentation

In this section, we delve into the foundational aspects of comprehending vital technical literature pertinent to electronic components. Exploring the intricacies of deciphering specifications and comprehending essential details is paramount for effectively utilizing electronic components in various applications.
Deciphering Technical Specifications

Understanding the intricacies of technical specifications is akin to deciphering the blueprint of a complex structure. It involves unraveling the intricately woven threads of information to grasp the core functionalities and limitations of a component.
Interpreting Performance Characteristics

Delving deeper, one encounters a plethora of performance characteristics that delineate the behavior of the component under various operating conditions. Deciphering these characteristics empowers engineers to make informed decisions regarding component selection and integration.
Embarking on this journey of understanding technical documentation not only enhances proficiency in utilizing electronic components but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of modern technology.
Understanding Key Specifications

Exploring the intricacies of electronic components involves delving into their core specifications, elucidating the essential characteristics that dictate their performance and functionality. Within the realm of semiconductor devices, comprehending the key specifications lays the foundation for informed decision-making and effective utilization.
Parameter Significance

Each specification encapsulates a distinct aspect of the component’s behavior, encompassing factors such as operational range, power consumption, and signal integrity. Understanding the significance of these parameters provides invaluable insights into the component’s capabilities and limitations.
Interpretation and Application

Interpreting specifications entails deciphering technical jargon and numerical values to extract meaningful information regarding the component’s behavior under various operating conditions. Armed with this knowledge, engineers can judiciously apply the component within their designs, optimizing performance and reliability.
Pin Configuration and Operational Features
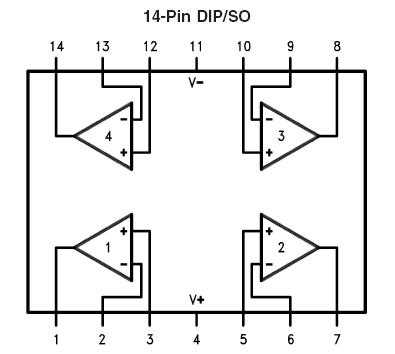
In this section, we delve into the arrangement and operational characteristics of the electronic components contained within the LMC6484IM integrated circuit. Understanding the layout and functionalities of its pins is fundamental for comprehending the device’s operational principles and leveraging its capabilities effectively.
Pin Configuration: The pin configuration of the LMC6484IM embodies a strategically organized layout that facilitates seamless integration into various electronic circuits. Each pin serves a distinct purpose, contributing to the overall functionality of the device.
Functionality Overview: The operational features of the LMC6484IM, encapsulated within its pin configuration, encompass a spectrum of functionalities essential for signal processing and amplification. These functionalities include but are not limited to signal input, output, power supply, and configuration settings, each playing a crucial role in the device’s performance.
Input and Output Pins: Among the array of pins, those designated for signal input and output form the primary conduits for electrical signals within the circuit. These pins enable the transfer of signals between the LMC6484IM and external components, facilitating signal processing and amplification.
Power Supply Pins: The power supply pins constitute the vital interface between the LMC6484IM and the external power source. Proper connection and management of these pins ensure the provision of stable power, essential for the consistent operation of the integrated circuit.
Configuration Pins: Configurable pins offer the flexibility to tailor the operational characteristics of the LMC6484IM to specific application requirements. By configuring these pins according to predefined parameters, users can optimize the performance of the device for diverse tasks.
Conclusion: Understanding the pin configuration and functionality of the LMC6484IM is pivotal for harnessing its capabilities effectively in electronic circuit design. By comprehending the roles and interplay of each pin, engineers can leverage the integrated circuit to its full potential, achieving desired performance outcomes.
Exploring Application Circuits with Lmc6484im

In this section, we delve into various practical circuits where the versatile Lmc6484im integrated circuit plays a pivotal role. These circuits showcase the adaptability and efficiency of this component in diverse applications, offering insights into its potential utility across different electronic systems.
Signal Conditioning Circuits
Signal conditioning is essential in many electronic systems to optimize signal quality for further processing or transmission. Within this domain, the Lmc6484im facilitates precise amplification, filtering, and modulation of signals, ensuring fidelity and reliability in data acquisition, communication, and control systems.
Control and Automation Systems

The Lmc6484im’s robust performance and low noise characteristics make it an ideal choice for control and automation applications. By interfacing with sensors, actuators, and feedback mechanisms, this integrated circuit enables the implementation of sophisticated control algorithms, enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of automated processes across various industries.
Exploring the realm of application circuits with the Lmc6484im unveils a realm of possibilities, where innovation meets functionality to address the evolving demands of modern electronics.
Design Considerations for Amplifier Circuits

When delving into the intricacies of crafting amplifier circuits, meticulous attention to various factors is paramount for optimal performance and reliability. This section explores key aspects to ponder, ensuring robust designs that fulfill desired specifications and functionality.
First and foremost, the choice of amplification topology significantly influences circuit behavior, affecting parameters such as gain, bandwidth, and distortion. Selecting the appropriate configuration, whether it be voltage, current, or transconductance amplifiers, demands a comprehensive understanding of their inherent characteristics and application requirements.
Moreover, considerations regarding signal integrity and noise management hold substantial importance in amplifier design. Strategies for minimizing noise sources, such as thermal, shot, and flicker noise, necessitate judicious component selection, layout optimization, and shielding techniques to uphold signal fidelity and mitigate undesirable artifacts.
Furthermore, impedance matching emerges as a critical aspect in interfacing amplifier circuits with preceding and subsequent stages or load elements. Achieving impedance compatibility ensures maximum power transfer, minimizes signal reflection, and forestalls degradation in overall system performance.
Temperature stability constitutes another pivotal consideration, particularly in applications subjected to varying environmental conditions or demanding stringent accuracy requirements. Employing temperature-compensated components, thermal management techniques, and robust circuit architectures mitigates the detrimental effects of temperature-induced variations, ensuring consistent amplifier operation over a wide temperature range.
In addition to these core considerations, factors such as power supply rejection ratio (PSRR), slew rate, and output impedance warrant careful evaluation to ascertain amplifier suitability for specific applications. Adhering to these design principles fosters the development of amplifier circuits characterized by high performance, reliability, and adaptability to diverse operational scenarios.
| Design Considerations | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Amplification Topology | Choice influences gain, bandwidth, and distortion. |
| Noise Management | Minimize thermal, shot, and flicker noise for signal fidelity. |
| Impedance Matching | Ensure compatibility for optimal power transfer. |
| Temperature Stability | Address temperature-induced variations for consistent operation. |
| Additional Considerations | PSRR, slew rate, output impedance for application suitability. |