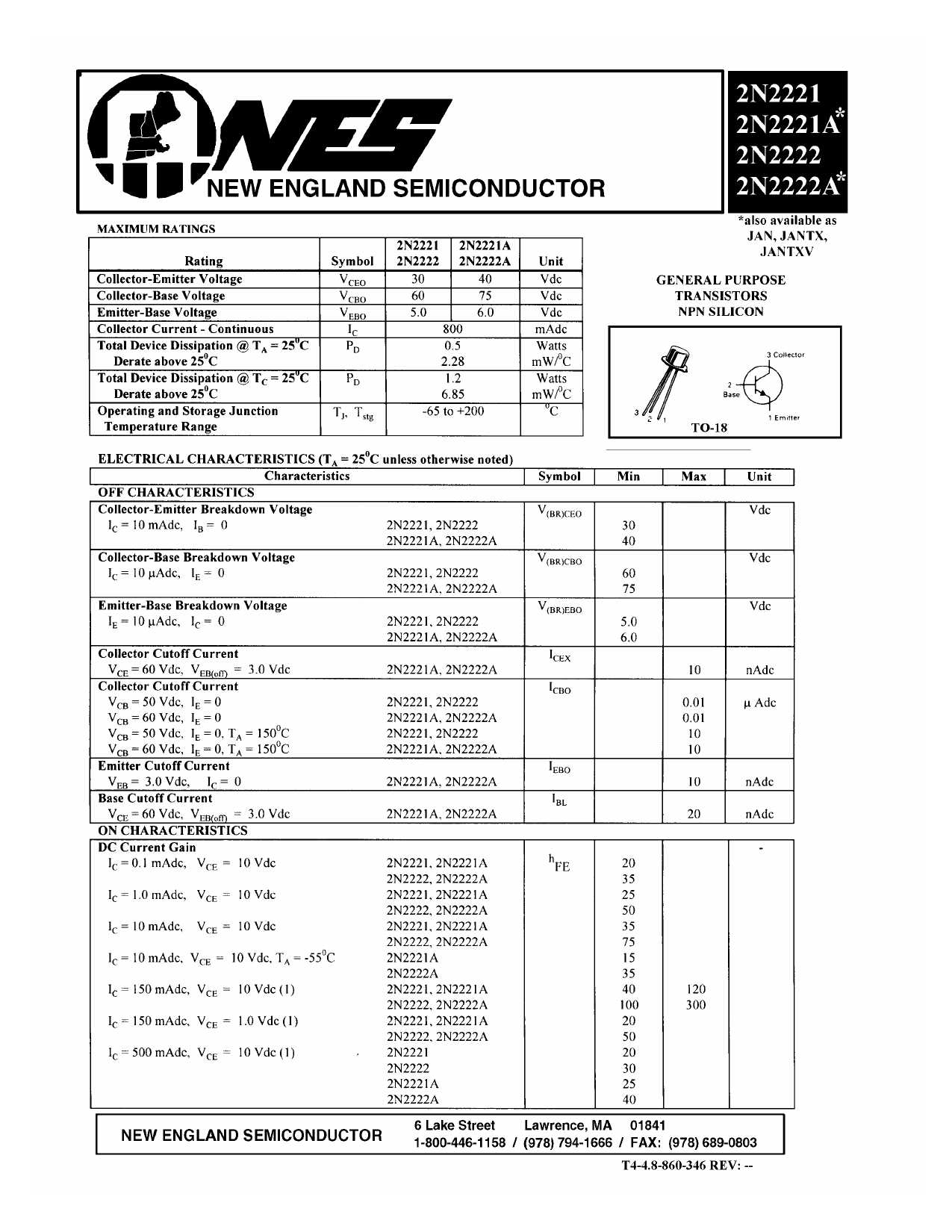
In the realm of electronic components, there’s always a need for efficient and reliable transistors to facilitate the flow of current and amplify signals. And when it comes to NPN transistors, one name stands out: the 2N2222B. This tiny yet powerful device has become a staple in countless electronic applications, making it crucial for every electronics enthusiast and professional to understand its datasheet thoroughly.
The datasheet of the 2N2222B provides a comprehensive overview of its key specifications and performance characteristics. From its electrical ratings to its thermal properties, this document serves as a roadmap for engineers and hobbyists alike. However, deciphering the technical jargon and deciphering the intricate details can be a daunting task for beginners. That’s where this article comes in – to demystify the complexities and help you make sense of the 2N2222B datasheet.
Throughout this article, we will explore the crucial parameters found in a typical datasheet, such as maximum ratings, DC current gain, collector-emitter saturation voltage, and much more. By understanding these specifications and their implications, you’ll be able to design circuits with the 2N2222B more effectively and optimize its performance.
Disclaimer: It’s important to note that while this article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the 2N2222B datasheet, it is always recommended to refer to the official documentation provided by the manufacturer for the most accurate and up-to-date information. This article serves as a guide and should not be solely relied upon for critical design decisions.
Now, let’s dive into the intricacies of the 2N2222B datasheet and unlock the potential of this versatile NPN transistor!
The Basics of the 2N2222B Transistor
In the world of electronics, the 2N2222B transistor holds a significant place. It is a versatile and widely used component that plays a vital role in various electronic circuits. Understanding the basics of the 2N2222B transistor is essential for anyone involved in electronics, whether you are a hobbyist or a professional.
What is a Transistor?

Before delving into the specifics of the 2N2222B transistor, it is important to understand the concept of a transistor. A transistor is a semiconductor device that is capable of amplifying or switching electronic signals and electrical power. It acts as a crucial building block in countless electronic devices, including computers, televisions, and radios.
The Features and Applications of the 2N2222B Transistor
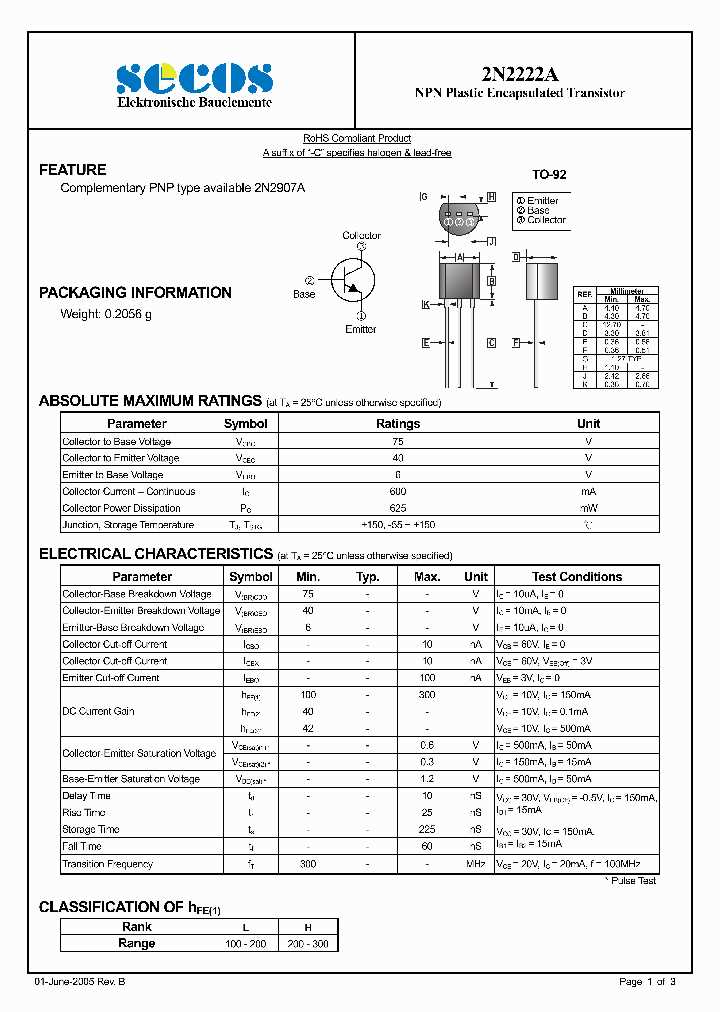
The 2N2222B transistor is a popular and widely used NPN transistor. It is characterized by its low power loss, high gain, and excellent switching performance. The transistor’s small size and rugged construction make it suitable for various applications.
One of the primary applications of the 2N2222B transistor is amplification. It allows weak electrical signals to be boosted to a higher power level, enabling the efficient operation of audio amplifiers, RF amplifiers, and many other circuits where signal amplification is crucial.
Moreover, the 2N2222B transistor is commonly employed in switching circuits. Its ability to rapidly turn on or off electrical current flow makes it ideal for applications such as digital logic gates, motor control, and signal switching.
The Importance of Understanding the 2N2222B Transistor
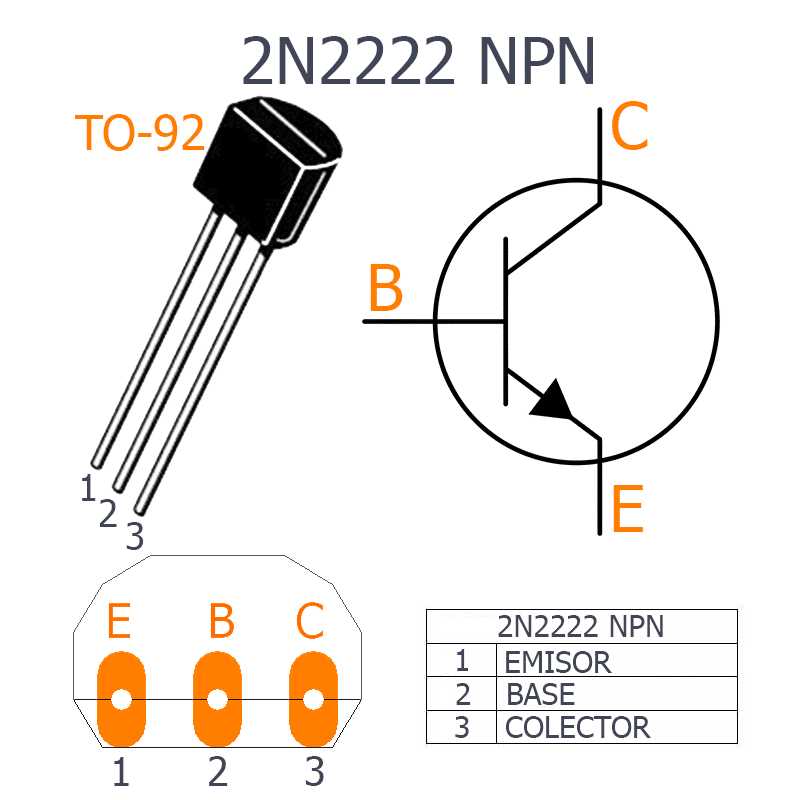
Having a solid understanding of the 2N2222B transistor is paramount for anyone working with electronic circuits. To successfully design and troubleshoot circuits, one must comprehend the transistor’s specifications, pin configuration, and operating characteristics. Additionally, being aware of the proper handling and storage precautions associated with the transistor is essential for ensuring its longevity and reliable performance.
In conclusion, the 2N2222B transistor is an integral part of the electronics world, serving various purposes in amplification and switching applications. Gaining a fundamental understanding of this versatile component is pivotal for anyone aspiring to excel in the field of electronics.
Understanding the Specifications
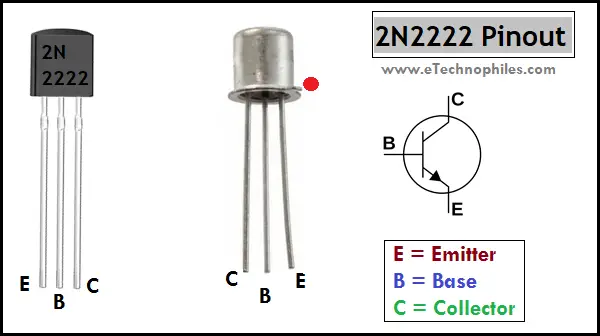
In order to effectively utilize electronic components, it is essential to have a clear understanding of their specifications. Specifications provide detailed information about the performance, capabilities, and limitations of a component.
By comprehending the specifications, engineers and electronics enthusiasts can make informed decisions regarding the selection and usage of the component best suited for their specific application. Understanding the terminology and parameters used in the specifications is crucial for successful integration of the component into a circuit design.
Specifications often include information about electrical characteristics, such as voltage ratings, current ratings, and power dissipation. These specifications help determine the maximum and minimum values that a component can handle, ensuring safe operation and preventing damage.
In addition to electrical characteristics, specifications may also cover thermal and mechanical properties. This includes details about the component’s operating temperature range, thermal resistance, and physical dimensions. Understanding these specifications aids in proper placement and cooling of the component to avoid overheating and mechanical stress.
Furthermore, specifications may provide information on the component’s performance parameters, such as gain, frequency response, and noise level. These specifications are crucial for determining the component’s suitability for a particular application, ensuring optimal performance and desired functionality.
Overall, understanding the specifications of electronic components allows engineers and hobbyists to make informed decisions, select appropriate components, and design circuits that meet the desired performance requirements. By closely examining the specifications and considering their implications, one can ensure successful integration of the component and achieve the desired outcomes in electronic designs.
Applications and Uses
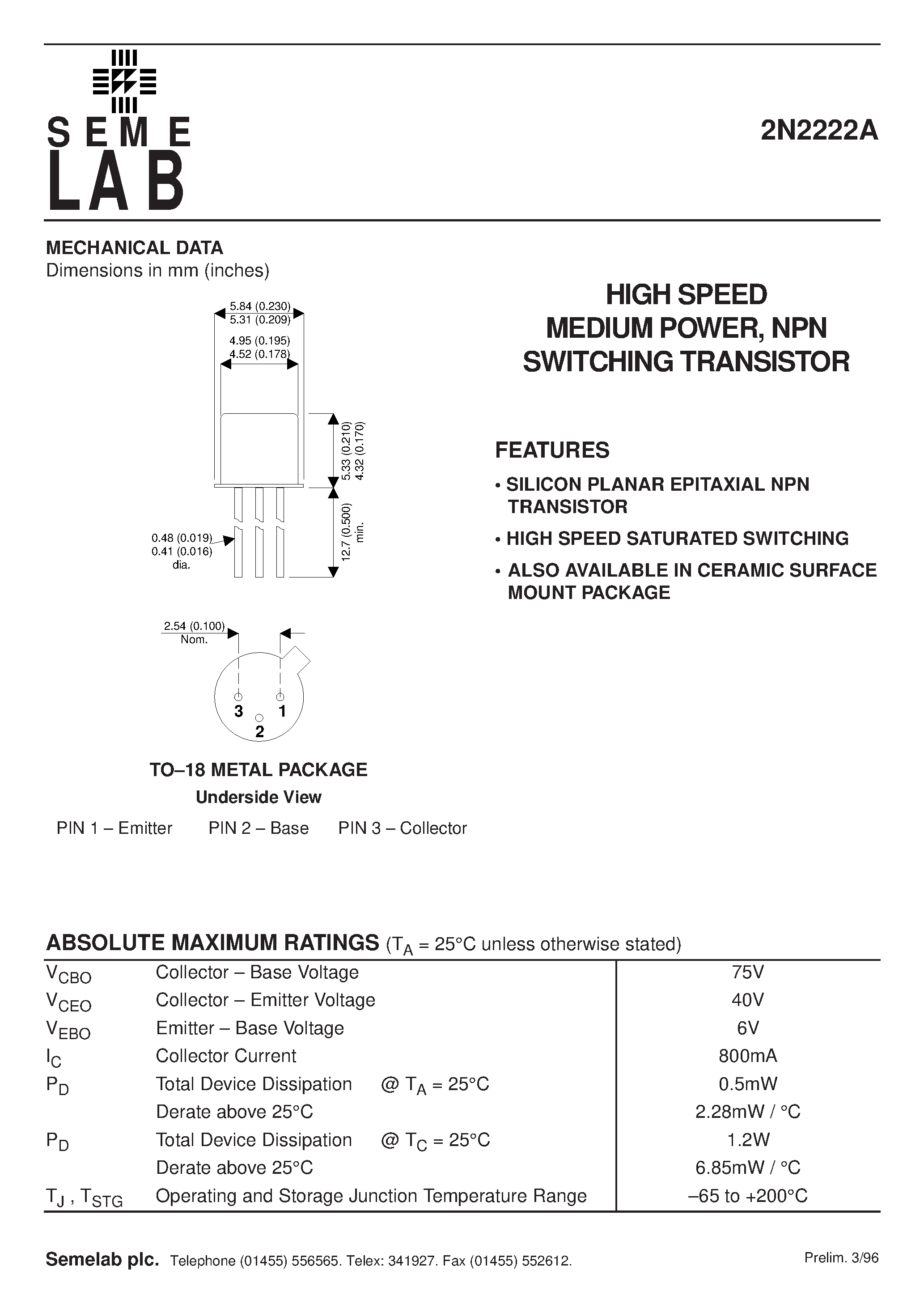
The 2n2222b transistor, known for its versatile and reliable performance, finds applications and uses in a wide range of electronic devices and circuits. This transistor, commonly referred to as a general-purpose NPN bipolar junction transistor, offers functionality across multiple domains, making it a popular choice for engineers and hobbyists alike.
One of the primary applications of the 2n2222b transistor is in amplification circuits. Its ability to amplify small electrical signals accurately and efficiently makes it suitable for use in audio amplifiers, communications systems, and audio/video equipment. With its low noise characteristics and high gain, the transistor ensures the faithful reproduction of sound and signals, delivering clear and distortion-free audio and video output.
Additionally, the 2n2222b transistor is widely used in switching applications. Its ability to control the flow of current from a source to a load makes it ideal for digital logic circuits, switching power supplies, and motor control circuits. The transistor’s fast switching speed and high current capacity enable seamless and precise control, ensuring efficient operation of these electronic systems.
Furthermore, the 2n2222b transistor is employed in oscillator circuits, where it generates and maintains a stable oscillating output. This makes it suitable for applications such as clock circuits, frequency generators, and waveform generators. The transistor’s ability to produce precise and consistent oscillations ensures the accurate timing and synchronization of electronic systems.
In addition to these primary applications, the 2n2222b transistor is used in various other domains, including RF amplification, LED driving, voltage regulation, and sensor circuits. Its versatility and reliability, coupled with its cost-effectiveness, have made it a preferred choice for numerous electronic applications and designs.
| Key Applications | Key Uses |
|---|---|
| Amplification circuits | Audio amplifiers, communications systems, audio/video equipment |
| Switching applications | Digital logic circuits, switching power supplies, motor control circuits |
| Oscillator circuits | Clock circuits, frequency generators, waveform generators |
| RF amplification | Wireless communication systems, radio transmitters |
| LED driving | Lighting systems, display panels, signage |
| Voltage regulation | Power supplies, battery charging systems |
| Sensor circuits | Proximity sensors, temperature sensors, light sensors |