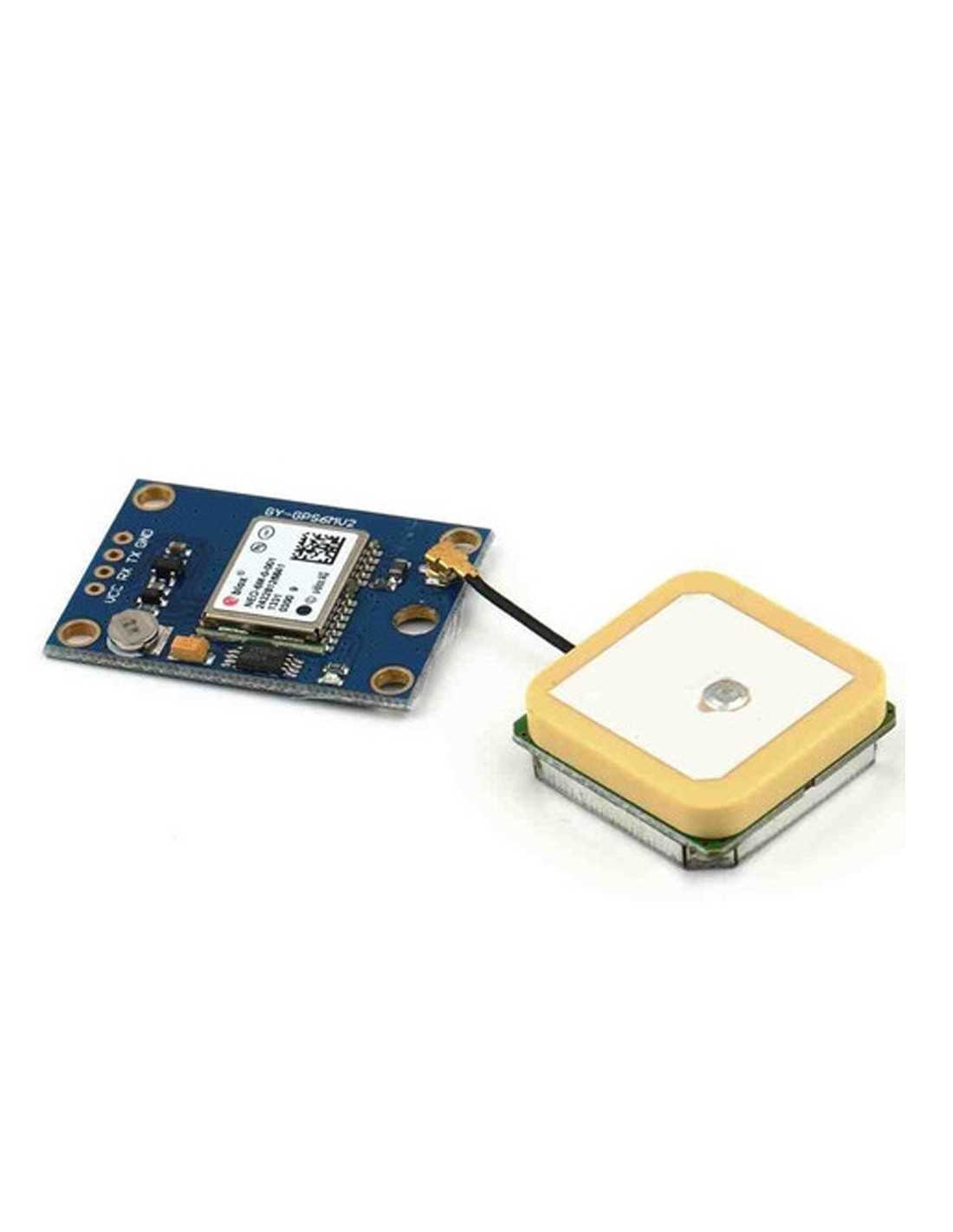

In the realm of cutting-edge positioning technologies, there lies a realm of compact and intricate components that underpin the functionality of modern GPS systems. Within this domain, lies a pivotal element that serves as the bedrock of accurate location tracking and navigation. This foundational piece, akin to a miniature technological marvel, embodies precision, efficiency, and reliability.
Delving into the heart of satellite-based navigation, we uncover a petite yet potent component that orchestrates the seamless synchronization between satellites hovering above and our terrestrial devices below. This technological enigma, embodying the essence of precision engineering and computational prowess, silently powers the GPS modules found within our smartphones, vehicles, and myriad other applications.
Embark with us on an exploration into the inner workings of this remarkable cornerstone, as we navigate through its intricate circuitry, decoding the language of signals and coordinates that shape our understanding of location in the digital age. Through this voyage, we shall unravel the mysteries of connectivity and orientation, gaining insight into the mechanics that bridge the gap between space and place.
Understanding GPS Receiver Specifications
In this section, we delve into the intricate details of the specifications of a cutting-edge global positioning system (GPS) receiver. By comprehending these specifications, users can gain a profound insight into the capabilities and performance metrics of the GPS receiver unit.
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Sensitivity | The ability of the receiver to capture weak satellite signals and accurately determine the position. |
| Accuracy | The degree of closeness between the measured position and the actual position on the Earth’s surface. |
| Time to First Fix (TTFF) | The duration taken by the receiver to acquire satellite signals and calculate the initial position fix after power-up. |
| Update Rate | The frequency at which the receiver calculates and updates the position information. |
| Operating Voltage | The range of voltage within which the receiver operates efficiently. |
| Interface | The communication protocol and physical connectors used for interfacing the receiver with other devices. |
By understanding these specifications in depth, users can make informed decisions regarding the suitability of the GPS receiver for their specific applications, whether it be in navigation, tracking, or geolocation-based services.
Key Features and Performance Metrics
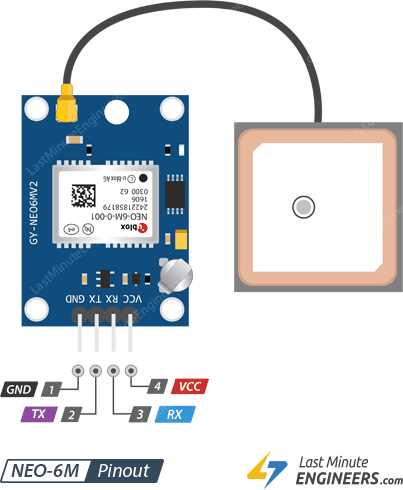
In this section, we delve into the core attributes and operational capabilities of the innovative positioning technology. Highlighting its distinctive characteristics and operational prowess, this segment elucidates the fundamental functionalities and efficiency benchmarks of the cutting-edge solution.
Key Attributes:
The technology encapsulates a myriad of distinctive attributes, ensuring unparalleled precision and reliability in positioning endeavors. From robust signal reception to swift data processing, it embodies a spectrum of features tailored to enhance navigational accuracy and efficiency.
Performance Metrics:
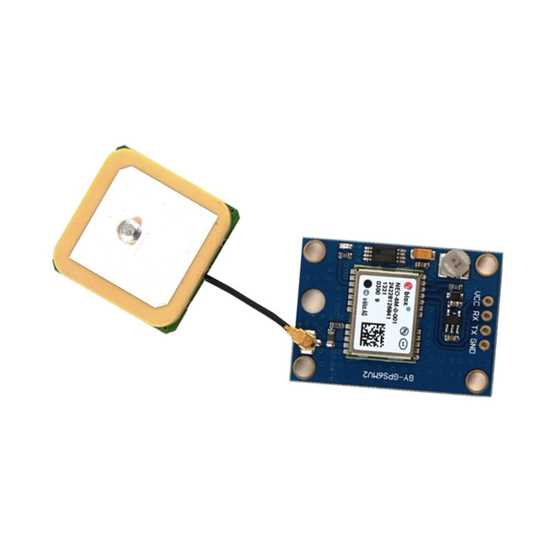

Quantifying the prowess of this advanced solution necessitates a comprehensive assessment of its performance metrics. From acquisition sensitivity to tracking accuracy, each metric delineates the system’s proficiency in delivering precise positioning information across diverse operational scenarios.
| Metric | Description | Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Acquisition Sensitivity | The module’s ability to swiftly acquire satellite signals upon initialization. | High, facilitating rapid position fix under varying environmental conditions. |
| Tracking Accuracy | The precision with which the module maintains satellite signal tracking over time. | Exceptional, ensuring consistent and reliable positioning data even in dynamic environments. |
| Time to First Fix (TTFF) | The duration required for the module to compute its initial position fix upon power-up. | Minimal, expediting time-sensitive navigation tasks with swift initialization. |
| Power Consumption | The amount of power consumed by the module during operation. | Optimized, minimizing energy consumption for prolonged usage and enhanced sustainability. |
Practical Applications and Integration Tips
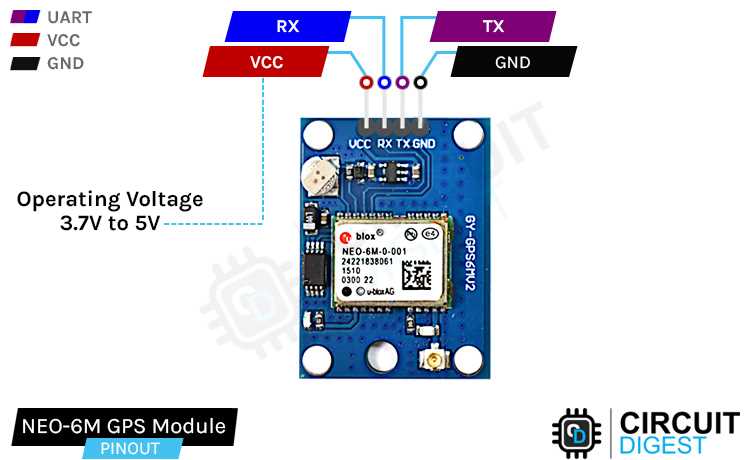
In this section, we delve into the real-world scenarios where the functionalities of the Neo-6m component can be effectively harnessed, offering insightful tips for seamless integration into various systems. Understanding the practical applications and integration nuances is crucial for maximizing the utility of this cutting-edge technology.
One practical application lies in the realm of navigation systems, where precision and reliability are paramount. By leveraging the capabilities of the Neo-6m module, developers can craft navigation solutions that offer unparalleled accuracy and robustness, enhancing user experience across diverse environments.
Furthermore, the integration of this advanced component extends beyond navigation-centric applications. Its versatility lends itself well to a spectrum of projects, ranging from asset tracking and fleet management to IoT deployments and beyond. By incorporating the Neo-6m module intelligently, developers can unlock a myriad of possibilities, driving innovation and efficiency.
| Integration Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Optimizing Antenna Placement | Ensuring optimal positioning of the antenna can significantly enhance the performance of the Neo-6m module, mitigating signal interference and maximizing signal strength. |
| Utilizing External Power Sources | Integrating external power sources, such as batteries or solar panels, can augment the module’s power supply, ensuring consistent operation even in remote or challenging environments. |
| Implementing Data Filtering Algorithms | Employing sophisticated data filtering algorithms can help mitigate noise and improve signal stability, enhancing the accuracy and reliability of location-based applications. |
| Exploring Data Logging Capabilities | Exploring the data logging capabilities of the Neo-6m module enables the capture and analysis of location data over time, facilitating insightful decision-making and trend analysis. |
By adhering to these integration tips and exploring the diverse practical applications, developers can harness the full potential of the Neo-6m module, paving the way for transformative innovations across industries.
Troubleshooting and Common Issues
When integrating the cutting-edge positioning technology represented by the Neo-6m module into your project, encountering hurdles is not uncommon. In this section, we address common challenges that may arise during implementation, offering insights and solutions to streamline your development process.
1. Connectivity Problems
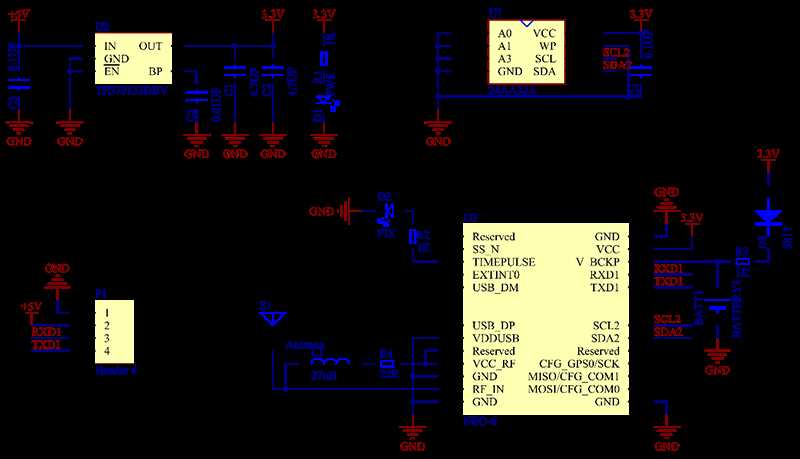
One of the primary hurdles engineers may face is establishing stable connectivity with the positioning system. This issue could manifest in erratic data transmission, intermittent signal reception, or outright connection failures. Factors such as environmental interference, hardware compatibility, or improper wiring might contribute to these connectivity woes. Referencing the following table, we outline potential causes and corresponding troubleshooting steps to rectify connectivity issues.
| Issue | Possible Cause | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Erratic Data Transmission | Interference from nearby electronic devices | Reposition the module away from potential sources of interference or shield sensitive components. |
| Intermittent Signal Reception | Weak antenna connection | Ensure a secure connection between the antenna and the module, checking for loose connections or damaged components. |
| Connection Failures | Compatibility issues between hardware components | Verify compatibility between the Neo-6m module and other hardware components, ensuring they adhere to the required specifications. |
2. Data Interpretation Challenges

Beyond establishing a stable connection, interpreting and utilizing the positioning data provided by the Neo-6m module effectively can present its own set of challenges. Engineers may encounter difficulties in parsing the data format, calibrating accuracy, or integrating the data into their applications seamlessly. Referencing the following table, we outline common data interpretation challenges along with recommended strategies to overcome them.
| Challenge | Possible Solution |
|---|---|
| Data Format Parsing | Implement robust parsing algorithms to extract relevant information from the raw data stream, ensuring compatibility with your application’s data processing pipeline. |
| Accuracy Calibration | Calibrate the module according to environmental conditions and desired precision levels, utilizing available tools and calibration techniques. |
| Integration Complexity | Streamline data integration by developing clear interface protocols and leveraging existing libraries or frameworks tailored to your development environment. |
By addressing these common challenges proactively and implementing the recommended solutions, developers can navigate potential obstacles with greater confidence, ensuring the successful integration and utilization of the Neo-6m module within their projects.