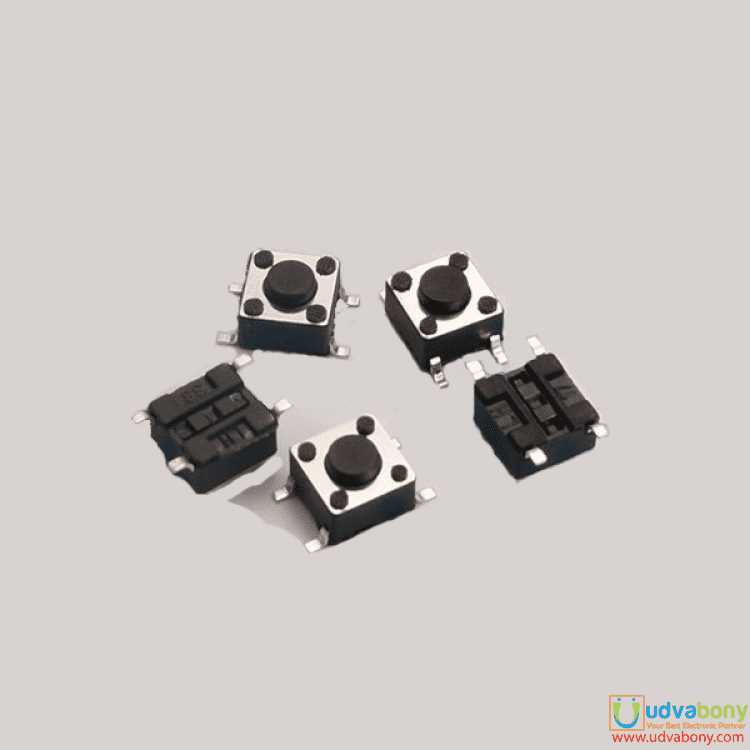

Embark on a journey into the intricate anatomy of modern electronic devices, where every actuator, interface, and technical blueprint holds the key to functionality. In this exploration, we delve into the heart of hardware, dissecting the essence of 6-pin components without merely skimming the surface of technical documentation.
Within the enigmatic realm of hardware design, lies a labyrinth of specifications and standards, each thread intricately woven into the fabric of innovation. Beneath the surface of these complexities, lies the soul of engineering, where precision meets purpose in the subtleties of design.
Unlocking the potential of electronic marvels necessitates a keen understanding of component intricacies. In this voyage, we navigate through the blueprints of 6-pin configurations, deciphering their functional roles and integrated synergies within the broader framework of circuitry.
Understanding the Basics of Six-Pin Button Documentation
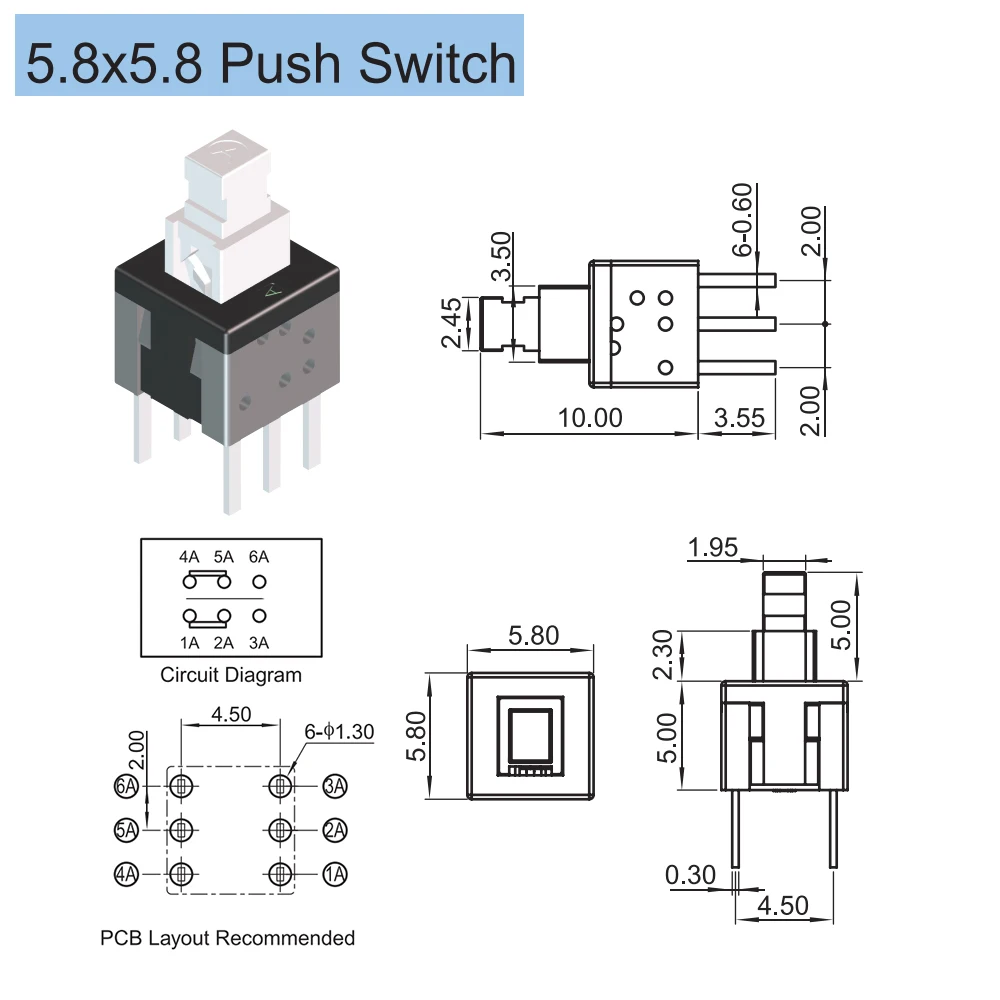
In the realm of electronic components, navigating the intricacies of technical documentation is akin to deciphering a blueprint for innovation. Delving into the realm of six-pin button datasheets unveils a wealth of vital information crucial for understanding functionality, integration, and optimization.
Deciphering Functional Elements
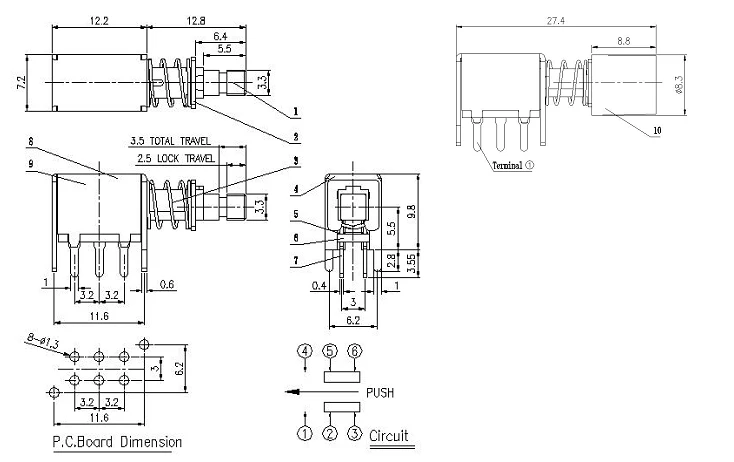
- Identifying Core Features
- Analyzing Configuration Options
- Understanding Performance Metrics
Embarking on this journey entails unraveling the functional elements embedded within the documentation. Unveiling the core features, analyzing configuration options, and understanding performance metrics serve as foundational steps towards harnessing the full potential of these intricate components.
Interpreting Integration Guidelines
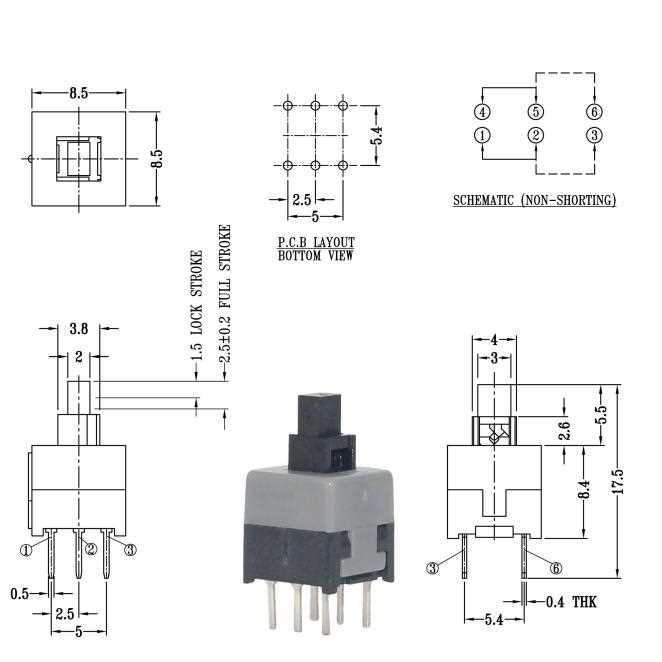
- Exploring Compatibility Considerations
- Assessing Interfacing Requirements
- Implementing Best Practices
Furthermore, interpreting integration guidelines proves paramount in seamlessly incorporating six-pin button functionalities into broader electronic systems. Exploring compatibility considerations, assessing interfacing requirements, and implementing best practices pave the path towards optimal integration and operational efficiency.
The Significance of Connector Configuration
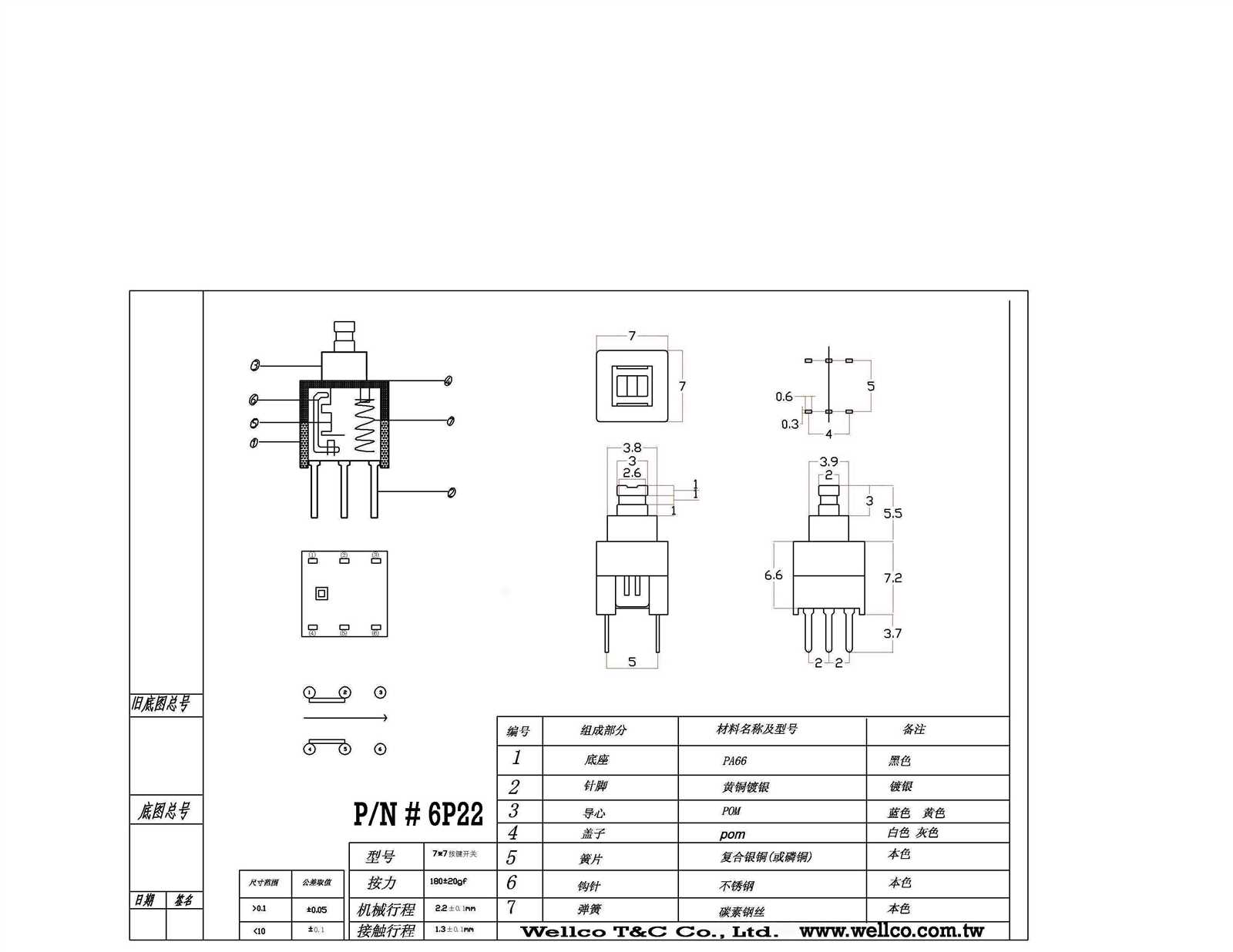
In the realm of electronic componentry, the arrangement of connectors plays a pivotal role in determining the functionality and compatibility of devices. It serves as the foundational blueprint upon which intricate circuits and systems are constructed, influencing the seamless transmission of signals and data across various interfaces.
Enhancing Interoperability
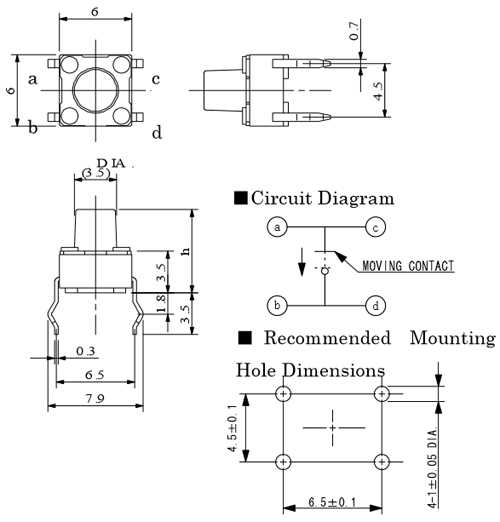
By meticulously configuring pins and connectors, engineers harness the potential to bolster interoperability between diverse components within a networked ecosystem. This meticulous alignment fosters harmonious interaction, enabling fluid communication pathways and minimizing impedance mismatches.
Optimizing Signal Integrity
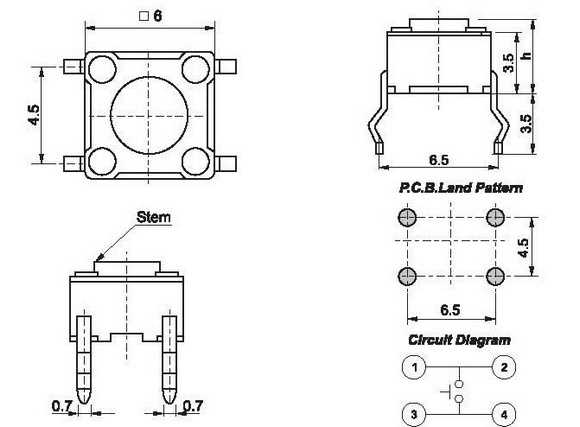
Delving deeper, the precise arrangement of pins within a connector facilitates the preservation of signal integrity, safeguarding against signal degradation and distortion. This strategic layout mitigates the onset of electrical noise and interference, preserving the fidelity of transmitted data and sustaining optimal performance levels.
Interpreting Electrical Characteristics
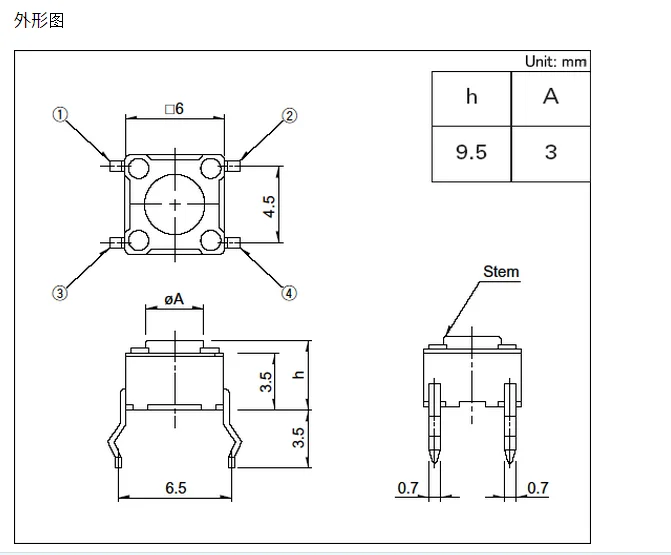
Understanding the intricate specifications and parameters outlined in technical documentation is pivotal for comprehending the operational dynamics of electronic components. In this section, we delve into elucidating the nuanced electrical attributes, shedding light on the underlying performance metrics and functional intricacies.
Electrical characteristics encapsulate a plethora of vital information crucial for assessing the functionality and compatibility of electronic devices. These parameters encompass a spectrum of properties, ranging from voltage thresholds to current capacities, impedance profiles to frequency response, delineating the operational boundaries and constraints.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Threshold Voltage | The minimum voltage required to initiate a specified action or response within the electronic circuitry. |
| Current Capacity | The maximum amount of electrical current that the component can safely handle without compromising its integrity. |
| Impedance | The measure of opposition to the flow of alternating current, influenced by resistance, inductance, and capacitance. |
| Frequency Response | The range of frequencies over which the component can effectively transmit or process signals with minimal distortion. |
Deciphering these electrical characteristics necessitates a holistic understanding of their implications on system performance and reliability. By meticulously analyzing and interpreting these specifications, engineers and designers can optimize component selection, ensure compatibility, and mitigate operational risks.
Application Examples and Considerations
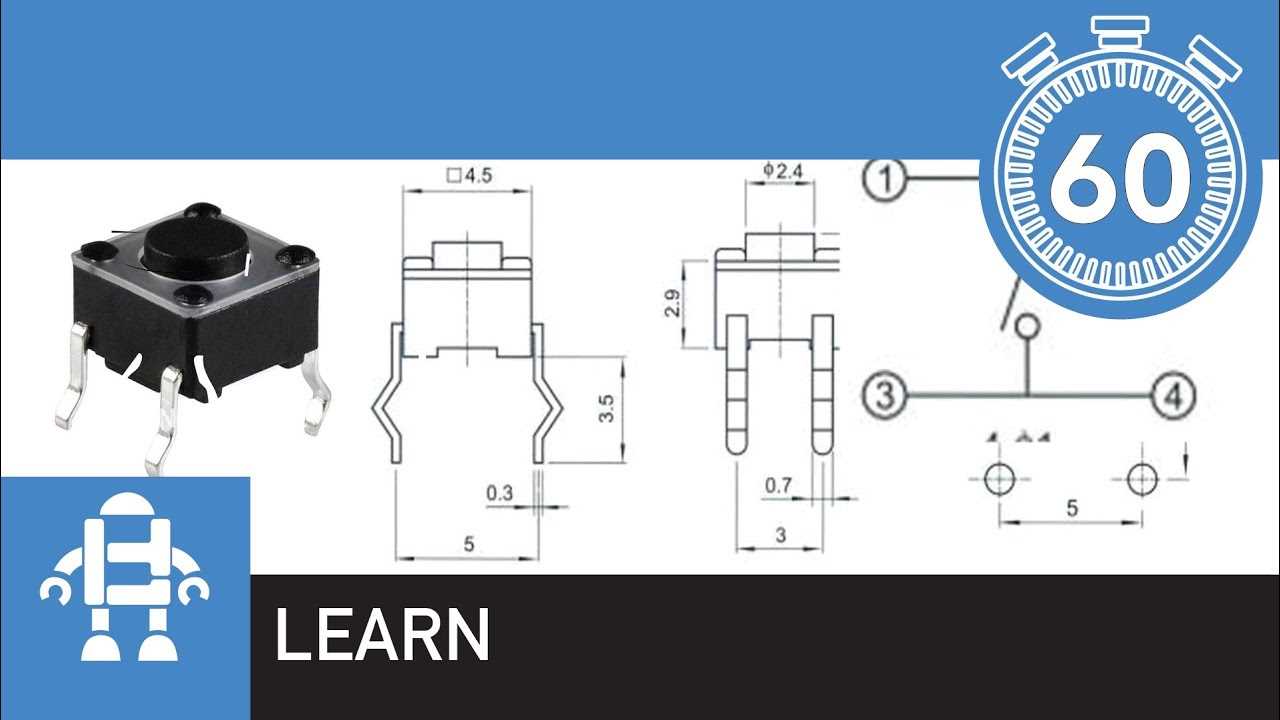
In this section, we delve into various scenarios where the integration of a tactile switch with six connection points proves instrumental, offering insight into its diverse utility across multiple contexts. We explore practical instances where this component facilitates seamless interaction within electronic systems, highlighting its versatility and adaptability.
Interfacing with Microcontrollers: One prevalent application involves integrating the tactile switch with microcontrollers to enable user input in embedded systems. By leveraging the switch’s inherent responsiveness and reliability, developers can design intuitive interfaces for devices ranging from consumer electronics to industrial machinery.
Control Mechanisms in Automotive Systems: Within automotive engineering, the tactile switch finds its place in various control mechanisms, ensuring precision and durability in critical functions such as steering wheel controls, dashboard interfaces, and auxiliary systems. Its robust construction and tactile feedback contribute to enhanced driver experience and operational safety.
Integration into Wearable Technology: The compact nature of the tactile switch makes it well-suited for integration into wearable devices, where space constraints and user comfort are paramount. Whether incorporated into smart garments or fitness trackers, the switch enhances user interaction, allowing for seamless control and functionality without compromising on design aesthetics.
Medical Devices and Accessibility Solutions: Tactile switches with six connection points play a pivotal role in the development of medical devices and accessibility solutions, facilitating user input in assistive technologies such as prosthetics, mobility aids, and communication devices. Their tactile feedback and reliable operation are instrumental in empowering users with diverse needs.
Consumer Electronics and Home Automation: From remote controls to smart home devices, the tactile switch serves as a fundamental component in consumer electronics and home automation systems. Its responsive tactile feedback and longevity ensure consistent performance in everyday devices, enhancing user convenience and operational efficiency.
Considerations for Optimal Performance: While the tactile switch offers versatility and reliability, several considerations influence its optimal performance within specific applications. Factors such as actuation force, tactile feedback, environmental conditions, and lifespan expectations must be carefully evaluated during the design phase to ensure seamless integration and long-term functionality.
Conclusion: Through these diverse application examples and considerations, it becomes evident that the tactile switch with six connection points transcends its traditional role, emerging as a cornerstone component in various electronic systems across industries. Its inherent versatility, coupled with meticulous attention to application-specific requirements, paves the way for innovative solutions and enhanced user experiences in the ever-evolving landscape of technology.