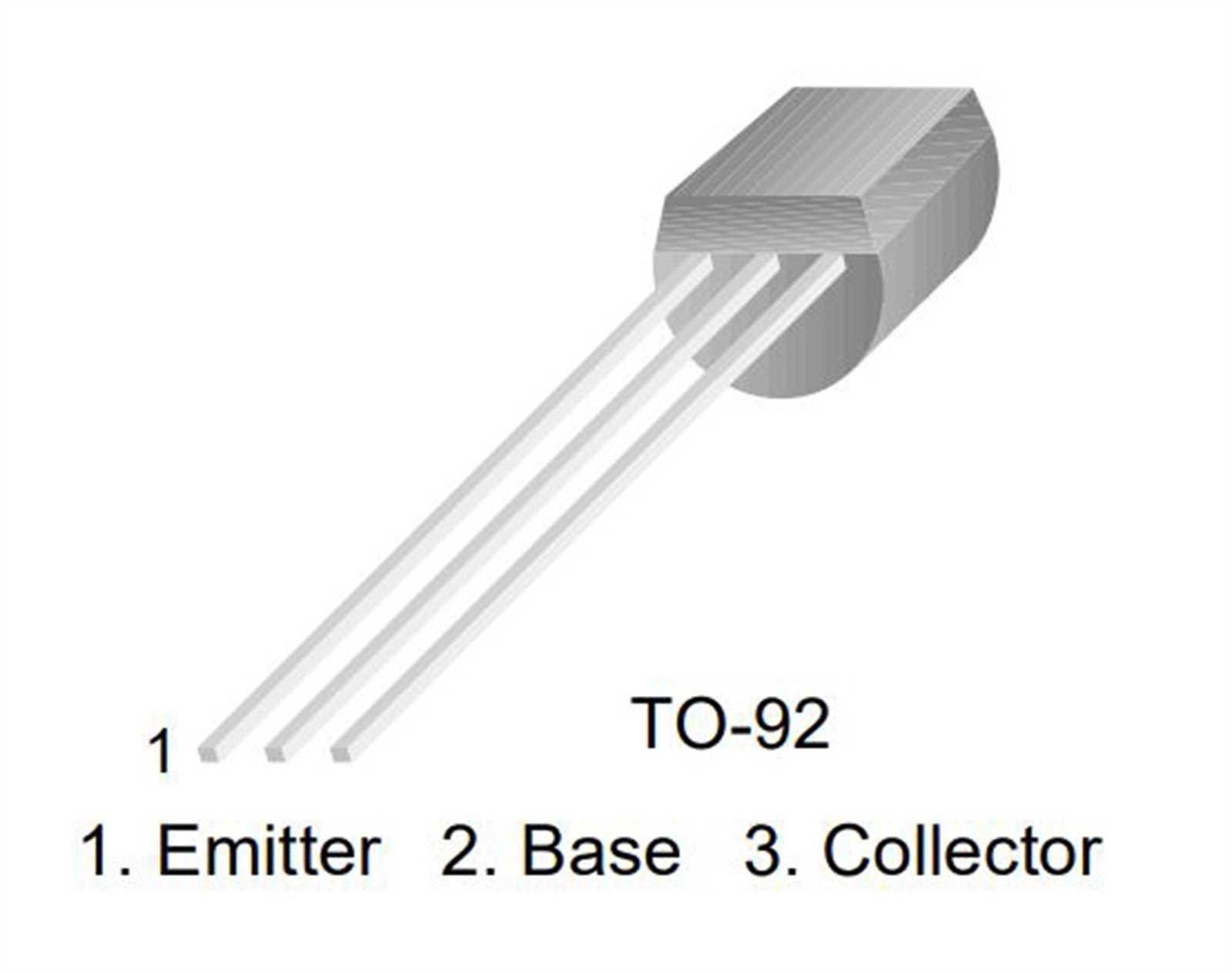

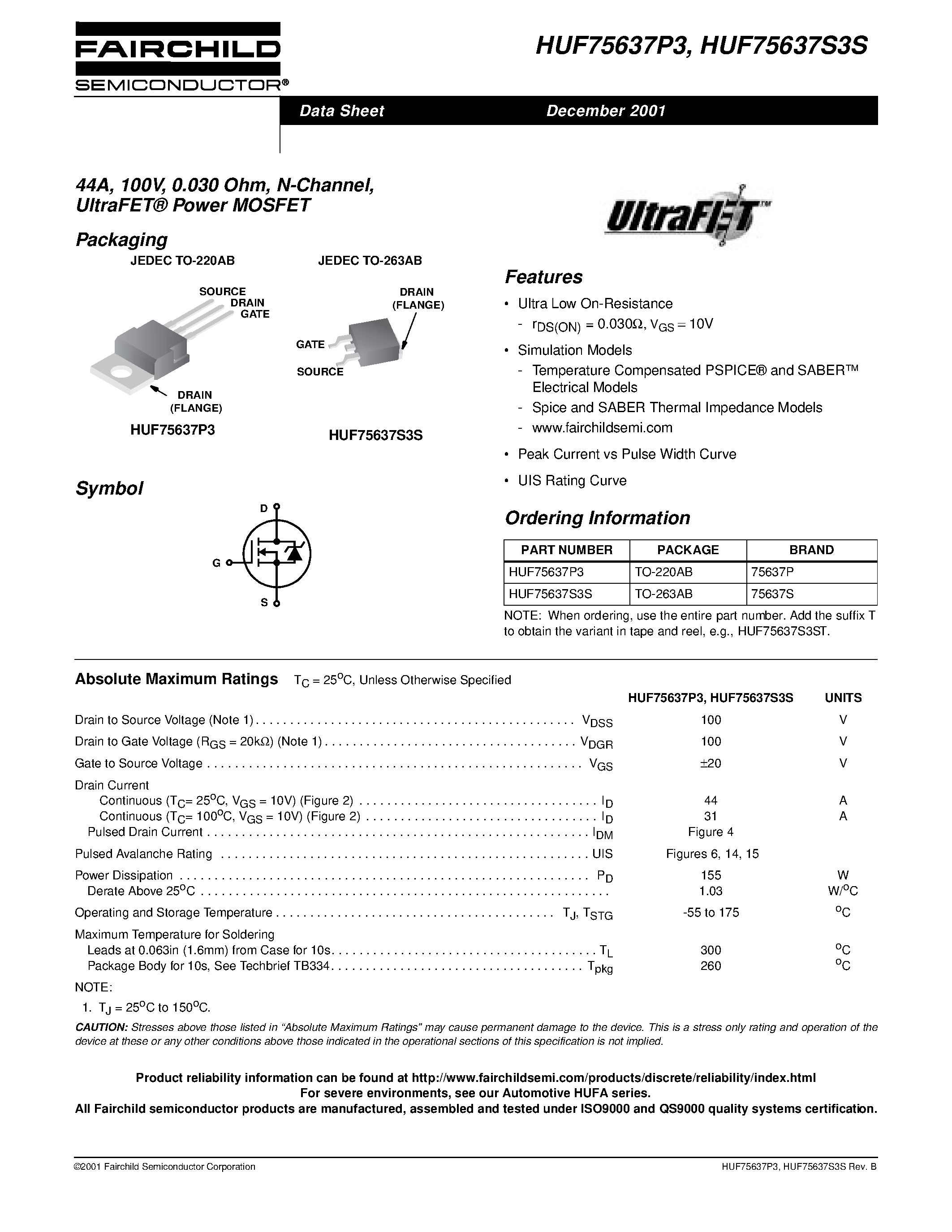
Unlocking the intricacies of electronic components is akin to deciphering the language of innovation. Within the labyrinth of technical documentation lies a wealth of insights, guiding engineers and enthusiasts towards profound understanding and application. In this journey of exploration, one encounters a realm where parameters speak volumes, and specifications unveil the essence of functionality.
Delving into the depths of electronic component specifications illuminates the path towards mastery, offering a glimpse into the soul of innovation. Amidst the myriad of technical intricacies lie clues to performance, functionality, and compatibility. Each specification serves as a beacon, guiding the curious towards a deeper comprehension of the component’s capabilities and limitations.
Embark on a voyage through the corridors of technical documentation, where parameters dance in symphony, orchestrating the melody of design and engineering. Here, amidst the realm of specifications, lies the gateway to innovation, where understanding transcends mere comprehension, and insight heralds the dawn of creativity.
The Basics of Understanding Semiconductor Specifications

When delving into the intricacies of semiconductor components, it’s imperative to grasp the fundamental aspects that govern their functionality and application. In this section, we will navigate through essential insights into deciphering the specifications of a particular semiconductor device, shedding light on its performance characteristics, operational parameters, and potential applications.
1. Terminology Deciphered
Before delving into the specifics of a semiconductor datasheet, it’s crucial to acquaint oneself with the terminology commonly employed within such documents. By understanding the nuanced meanings of key terms and parameters, one can effectively interpret the datasheet’s contents and make informed decisions regarding component selection and integration.
- Performance Metrics: Explore the various performance metrics such as gain, frequency response, and noise figure, which delineate the device’s operational capabilities under different conditions.
- Electrical Characteristics: Dive into the electrical characteristics encompassing parameters like voltage ratings, current consumption, and impedance, elucidating the device’s behavior within an electrical circuit.
- Application Notes: Pay heed to application-specific recommendations and guidelines provided within the datasheet, offering insights into optimal usage scenarios and circuit configurations.
2. Understanding Operational Parameters
Every semiconductor device operates within predefined parameters, delineating its safe and optimal performance envelope. By comprehending these operational parameters, engineers can tailor their designs to harness the full potential of the component while ensuring reliability and longevity.
- Operating Conditions: Familiarize yourself with the specified operating conditions encompassing temperature range, supply voltage, and biasing requirements, which dictate the device’s performance and stability.
- Environmental Considerations: Take into account environmental factors such as humidity, vibration, and electromagnetic interference, which may influence the device’s behavior and necessitate appropriate mitigation strategies.
- Stress Ratings: Exercise caution when operating the semiconductor device near or beyond its specified stress ratings, as exceeding these limits can compromise performance, reliability, and even lead to irreversible damage.
By assimilating these foundational principles and insights, one can navigate through semiconductor datasheets with confidence, unraveling the intricacies of device specifications and harnessing their full potential in diverse engineering applications.
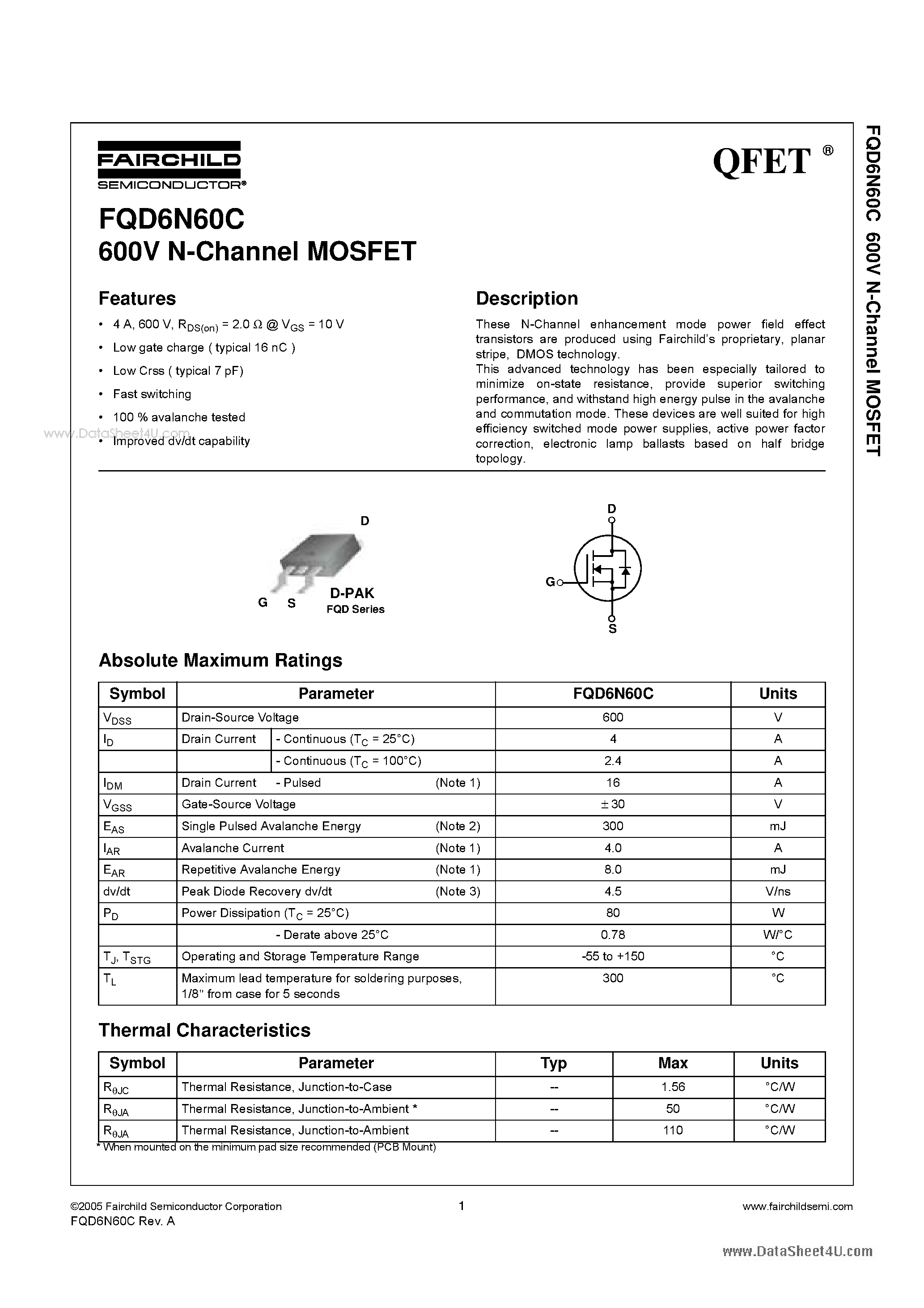
Understanding the Key Specifications
In this section, we delve into comprehending the essential specifications that characterize the performance and functionality of the component under consideration. By dissecting these critical parameters, we aim to provide a clear insight into its operational capabilities and limitations, facilitating informed decision-making in its application.
Electrical Characteristics
The electrical specifications delineate the fundamental properties governing the device’s behavior within a circuit. These metrics encompass parameters such as voltage ratings, current handling capacities, impedance characteristics, and frequency response, among others. Understanding these specifications is imperative for ensuring compatibility with the intended circuit design and operational requirements.
Performance Metrics
Performance metrics encapsulate the quantitative measures of the component’s efficacy and efficiency in various operational scenarios. These include metrics such as gain, noise figure, signal-to-noise ratio, and dynamic range, which dictate the device’s ability to amplify, process, or modulate signals while maintaining fidelity and integrity. A profound comprehension of these metrics enables precise evaluation and optimization of the component’s performance in diverse applications.
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Voltage Ratings | The maximum and minimum voltage levels the component can withstand or operate within without exceeding its specified limits. |
| Current Handling Capacities | The maximum current the component can safely carry or switch under specified conditions without detrimental effects. |
| Impedance Characteristics | The complex relationship between voltage and current in the component, often represented as resistance, capacitance, and inductance. |
| Frequency Response | The range of frequencies over which the component can adequately amplify, process, or transmit signals with minimal distortion or attenuation. |
By comprehensively understanding these key specifications, engineers and designers can effectively leverage the component’s capabilities to optimize circuit performance, ensure reliability, and meet the desired functionality requirements.
Exploring Applications of Semiconductor Component Specifications
In this section, we delve into the practical utilization of detailed specifications for a specific semiconductor component. Understanding the intricacies and potentials of such specifications enables engineers and enthusiasts to innovate and implement various electronic designs and circuits efficiently.
By delving into the practical applications of comprehensive semiconductor documentation, we uncover a realm of possibilities in electronic circuit design. These specifications serve as blueprints for engineers, providing insights into the component’s behavior, limitations, and optimal operating conditions.
- Utilizing the inherent characteristics outlined in the specifications, engineers can devise efficient amplification circuits for audio applications.
- Exploring the voltage and current parameters allows for the creation of precise voltage regulators, ensuring stable power supplies in diverse electronic systems.
- Understanding the frequency response and impedance characteristics aids in the design of robust radio frequency (RF) circuits for communication devices.
- By leveraging the noise figure and gain specifications, engineers can develop sensitive receivers for detecting weak signals in various electronic systems.
Moreover, the thermal characteristics provided in the documentation facilitate the design of heat management solutions, ensuring the longevity and reliability of electronic systems in demanding environments.
Exploring the myriad applications of semiconductor component specifications underscores the crucial role they play in driving innovation and advancing electronic technologies.
From Amplifiers to RF Circuits
Transitioning from the realm of amplifiers to the intricacies of RF circuits marks a journey through the spectrum of electronic signal processing. This progression encompasses the evolution from devices primarily focused on signal boosting and conditioning to those finely tuned for radio frequency applications. Exploring this continuum unveils the nuanced design considerations, ranging from signal fidelity and bandwidth management to impedance matching and noise suppression.
Amplifying Signals: A Foundation
Amplifiers serve as the cornerstone in signal processing, magnifying input signals while preserving their essential characteristics. This section delves into the principles governing amplifier design, emphasizing factors such as gain, bandwidth, and distortion. Understanding these fundamentals lays the groundwork for delving deeper into more specialized applications.
Navigating the RF Spectrum

As the frequency spectrum extends into the RF domain, new challenges and opportunities emerge. RF circuits operate amidst a cacophony of electromagnetic signals, requiring meticulous attention to filtering, tuning, and transmission line theory. This section navigates through the complexities of RF circuit design, addressing topics such as frequency modulation, antenna theory, and impedance matching.
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Bandwidth | The range of frequencies over which a circuit or device can operate effectively. |
| Impedance Matching | Optimizing the load impedance to maximize power transfer and minimize signal reflection. |
| Noise Suppression | Techniques employed to minimize unwanted signals, enhancing the signal-to-noise ratio. |
Tips and Tricks for Navigating the Mpf102 Component Reference
When delving into the intricacies of electronic components, mastering the art of interpreting technical documentation is paramount. In this section, we’ll explore some invaluable insights and strategies for effectively utilizing the reference material associated with the Mpf102 component. By honing these skills, you can streamline your workflow and enhance your understanding of this essential element in electronic circuitry.
1. Deciphering Specifications
Unraveling the intricacies of component specifications can often feel like deciphering a complex code. However, by adopting a systematic approach, you can unlock valuable information hidden within the datasheet. Pay close attention to key parameters such as voltage ratings, frequency response, and gain characteristics. Utilize analogs, equivalents, and substitutes to broaden your understanding and identify alternative components that may suit your needs.
2. Maximizing Application Insights
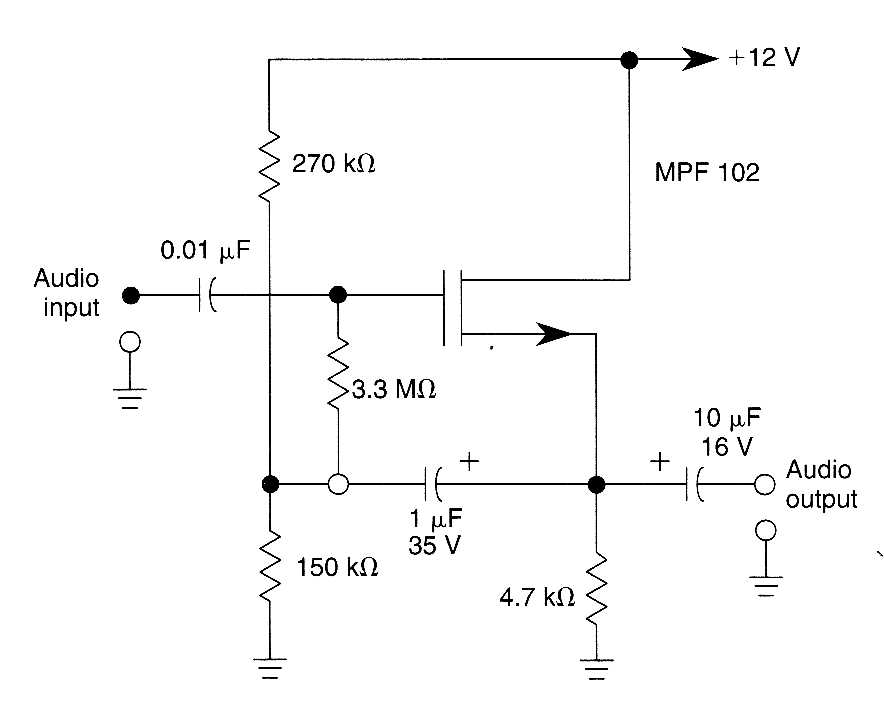
Beyond its technical specifications, the datasheet offers invaluable insights into the practical application of the Mpf102 component. Explore application notes, circuit diagrams, and recommended usage scenarios to gain a comprehensive understanding of how this component fits into broader circuit designs. Look for tips on layout considerations, biasing configurations, and performance optimization techniques to harness the full potential of the Mpf102 in your projects.
By approaching the Mpf102 datasheet with a blend of analytical rigor and practical intuition, you can empower yourself to navigate the complexities of electronic design with confidence and precision.