Unlocking the potential of electronic devices hinges on understanding the intricate details of their constituent parts. Delving into the intricacies of a pivotal component, often referred to as a cornerstone in electrical engineering, reveals a realm where precision and efficiency converge seamlessly. Embracing the essence of this component entails an exploration into its defining characteristics, deciphering its operational parameters, and envisaging its myriad applications. As we embark on this journey of comprehension, we navigate through a realm where currents flow with purpose, guided by the directives of an unassuming yet indispensable element.
The pursuit of mastery in electronics demands a keen grasp of every facet, from the fundamental to the nuanced. Within the realm of rectifying components lies a piece that epitomizes resilience and versatility. Its presence not only rectifies electrical currents but also serves as a beacon of reliability amidst the flux of electrical phenomena. Through meticulous analysis and scrutiny, we unravel the mysteries veiled within its specifications, discerning the subtle variations that dictate its performance under diverse conditions.
In the domain of electrical engineering, where precision reigns supreme, this component emerges as a stalwart companion, orchestrating the flow of energy with unwavering resolve. Beyond its utilitarian function lies a trove of insights awaiting discovery, offering engineers and enthusiasts alike a glimpse into the intricate dance of electrons and the structured chaos they command. Through the lens of its specifications, we glimpse the blueprint of innovation, paving the path towards groundbreaking advancements and technological marvels.
Understanding the Specifications of the 6A10 Diode

In the realm of electronic components, comprehensive comprehension of product documentation is paramount. Exploring the intricacies of the 6A10 diode’s technical specifications unveils a roadmap to its functionality, performance, and compatibility within various circuit configurations.
Deciphering Electrical Characteristics
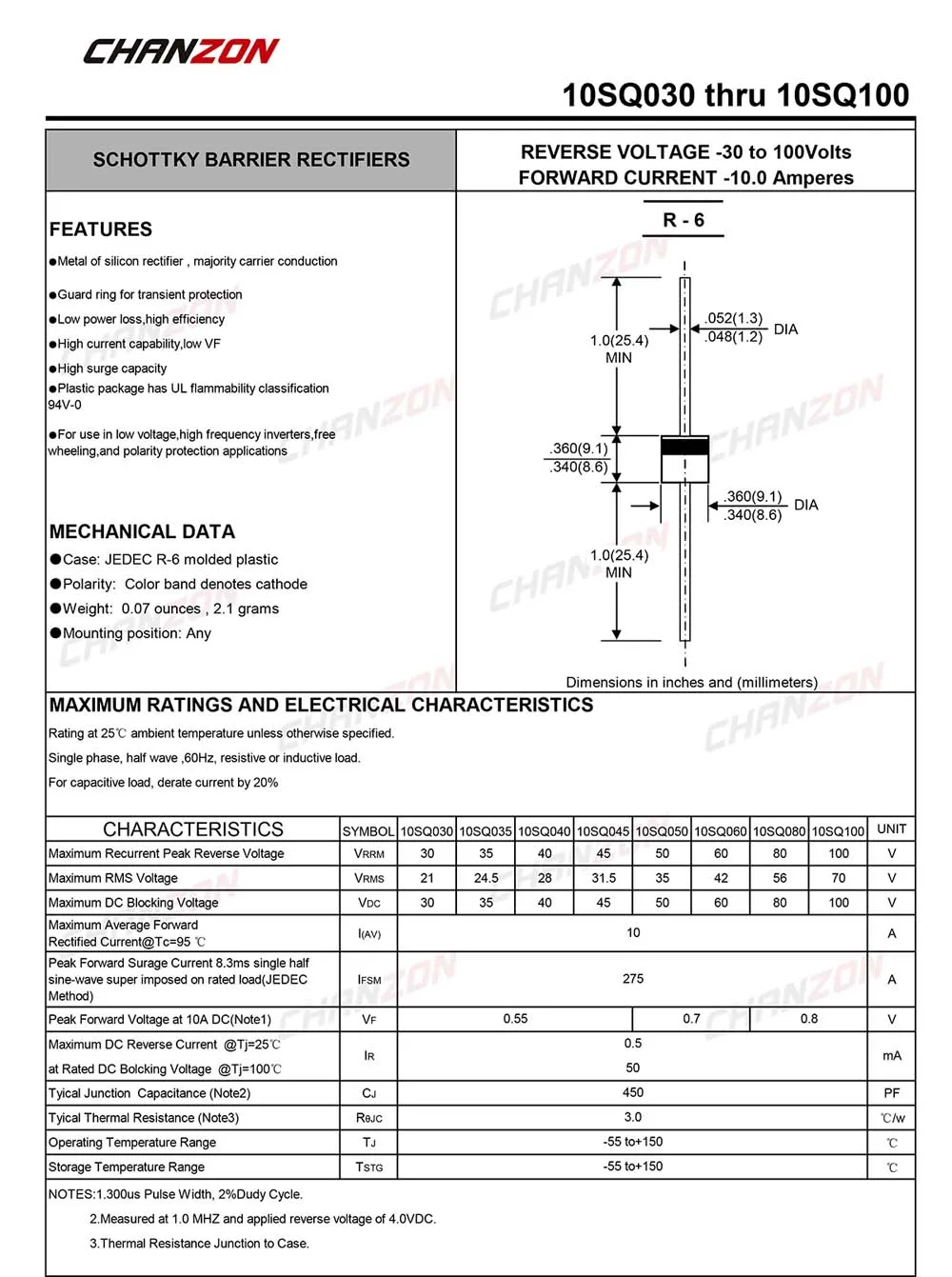
Within the labyrinth of figures and parameters lie the electrical characteristics, delineating the diode’s behavior under different operational conditions. From forward voltage drop to reverse leakage current, each metric provides insights into the diode’s efficiency and reliability in rectification and protection circuits.
Interpreting Mechanical Dimensions
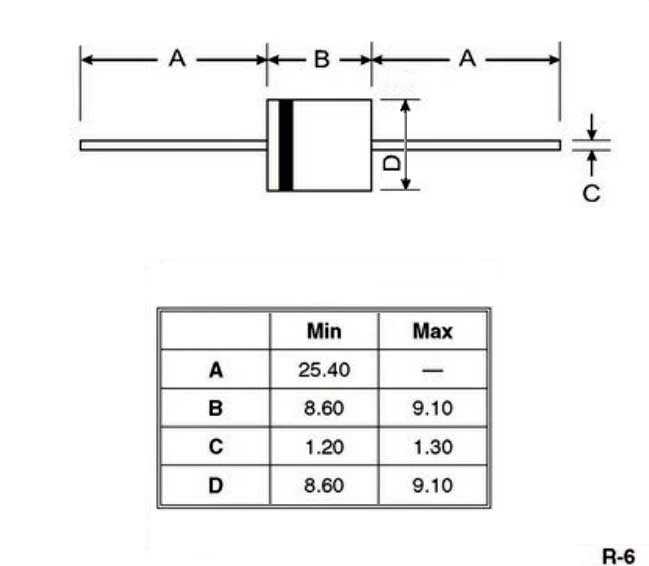
Beyond its electrical prowess, the 6A10 diode’s mechanical dimensions delineate its physical footprint and structural integrity. Understanding package type, lead configurations, and mounting specifications empowers engineers to seamlessly integrate the diode into diverse electronic assemblies, ensuring optimal performance and durability.
Key Specifications to Look for

When delving into the intricacies of electronic components, understanding the fundamental characteristics becomes paramount. In exploring the technical details of the component in question, several key specifications emerge as crucial focal points. These specifications serve as the guiding metrics for assessing the performance and compatibility of the component within a circuit.
- Forward Voltage Drop: This parameter signifies the voltage required for the diode to conduct current in the forward direction. It directly influences the efficiency and functionality of the diode within a circuit.
- Reverse Leakage Current: The reverse leakage current denotes the amount of current that flows through the diode when it is in the reverse-biased state. Minimizing this current ensures the diode’s effectiveness in blocking reverse current flow.
- Maximum Reverse Voltage: Also referred to as the peak reverse voltage, this specification defines the maximum voltage that can be applied across the diode in the reverse direction without causing breakdown.
- Maximum Forward Surge Current: This parameter delineates the maximum instantaneous current that the diode can withstand during transient conditions, such as power surges or spikes.
- Operating Temperature Range: The range of temperatures within which the diode can function optimally without experiencing performance degradation or failure. Understanding this range is crucial for applications subjected to varying environmental conditions.
- Package Type: The physical encapsulation of the diode, determining its mechanical and thermal properties, as well as its compatibility with different circuit layouts and mounting options.
By scrutinizing these key specifications, engineers and enthusiasts can make informed decisions regarding the selection and integration of diodes into their electronic designs. Each specification plays a vital role in ensuring the diode’s reliability, efficiency, and suitability for its intended application.
Interpreting Graphs and Diagrams

Understanding visual representations is paramount when delving into technical documentation. Within the realm of electronic components, the ability to interpret graphs and diagrams serves as a foundational skill, facilitating comprehension of device characteristics and operational behaviors. In this section, we explore the art of deciphering graphical data, elucidating patterns, trends, and crucial insights without reliance on explicit nomenclature.
Graphs and diagrams encapsulate multifaceted information, encapsulating trends, relationships, and performance metrics pertinent to electronic components. Through adept interpretation, one can discern the intrinsic qualities of components, discerning operational thresholds, response dynamics, and efficiency profiles. By navigating these visual depictions, one transcends the limitations of mere textual descriptions, delving into the essence of component behavior and functionality.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Trends | Identifying overarching patterns and tendencies elucidated by the graphical representation. |
| Relationships | Discerning correlations between different parameters or variables portrayed within the graph. |
| Performance Metrics | Extracting quantitative data regarding device performance, such as efficiency, response time, and operational limits. |
| Operational Thresholds | Recognizing critical points or boundaries delineated by the graphical depiction, indicating operational limits or optimal operating regions. |
Moreover, the interpretation of graphs and diagrams transcends linguistic barriers, providing a universal language for conveying technical information. Regardless of one’s proficiency in textual comprehension, visual representations offer a tangible medium for grasping complex concepts, fostering inclusivity and accessibility within the realm of technical discourse.
As we delve deeper into the nuances of graphical interpretation, we equip ourselves with indispensable tools for navigating the intricacies of electronic component documentation. By honing our ability to discern trends, relationships, and performance metrics from visual representations, we unlock a deeper understanding of device characteristics and functionalities, empowering us to harness the full potential of electronic components.
Practical Application Considerations
In this section, we delve into the pragmatic aspects of integrating and utilizing the specified component, focusing on real-world scenarios and operational nuances. Understanding the contextual implications of employing such technology is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring seamless functionality.
Operating Conditions: Before deployment, meticulous attention to operational parameters is imperative. Factors such as voltage ratings, temperature thresholds, and current limitations dictate the diode’s viability within diverse environments. Ensuring alignment with these criteria mitigates the risk of suboptimal performance or premature failure.
Mounting and Packaging: The efficacy of the diode hinges not only on its intrinsic properties but also on the precision of its installation. Proper mounting techniques, encompassing considerations like thermal management and mechanical stability, safeguard against performance degradation and enhance longevity.
Interfacing and Compatibility: Seamless integration with existing circuitry necessitates a comprehensive understanding of interface dynamics and compatibility constraints. Adhering to specified electrical parameters and employing suitable coupling mechanisms facilitate harmonious interaction within the broader system architecture.
Protection and Reliability: Beyond functionality, safeguarding against unforeseen contingencies is paramount. Implementing robust protection mechanisms, such as transient voltage suppressors and reverse polarity safeguards, bolsters reliability and fortifies the system against potential anomalies.
Performance Optimization: Iterative refinement is pivotal in unlocking the full potential of the diode within its designated application. Fine-tuning operational parameters, optimizing circuit layout, and leveraging advanced signal processing techniques culminate in enhanced performance metrics and augmented efficiency.
Environmental Considerations: Acknowledging the impact of environmental factors on device performance is indispensable. From humidity fluctuations to ambient temperature variations, preemptive measures and material selection strategies mitigate degradation risks, ensuring sustained functionality across diverse operating conditions.
End-user Considerations: Ultimately, user experience encompasses paramount significance. Streamlining installation procedures, offering comprehensive documentation, and facilitating intuitive troubleshooting mechanisms empower end-users to leverage the diode’s capabilities optimally, fostering satisfaction and confidence in the product.
By adhering to these pragmatic guidelines and conscientiously addressing contextual intricacies, the integration and utilization of the specified component are poised for success, culminating in enhanced reliability, performance, and user satisfaction.