
Delving into the intricacies of electronic components opens a gateway to understanding their functionalities and applications. Within this realm lies a key player, known for its versatile performance and reliability, offering a myriad of possibilities in various circuit designs.
Embark on a journey through the realms of semiconductor devices, where the 97a6 Triac stands as a beacon of innovation. Through meticulous analysis and comprehension, we uncover the fundamental characteristics and specifications that define its prowess.
Peering beyond the surface, we unravel the intricacies of this electronic marvel, exploring its electrical properties, operational parameters, and practical implementations. Join us as we decode the essence of this component, shedding light on its potential in diverse applications.
Understanding the Documentation for the 97a6 Semiconductor Device
In delving into the intricacies of comprehending the technical literature associated with the 97a6 semiconductor component, it’s pivotal to embark on a journey of deciphering its comprehensive documentation. This endeavor entails unraveling the nuanced specifications, operational characteristics, and performance parameters encapsulated within.
Deciphering Technical Specifications
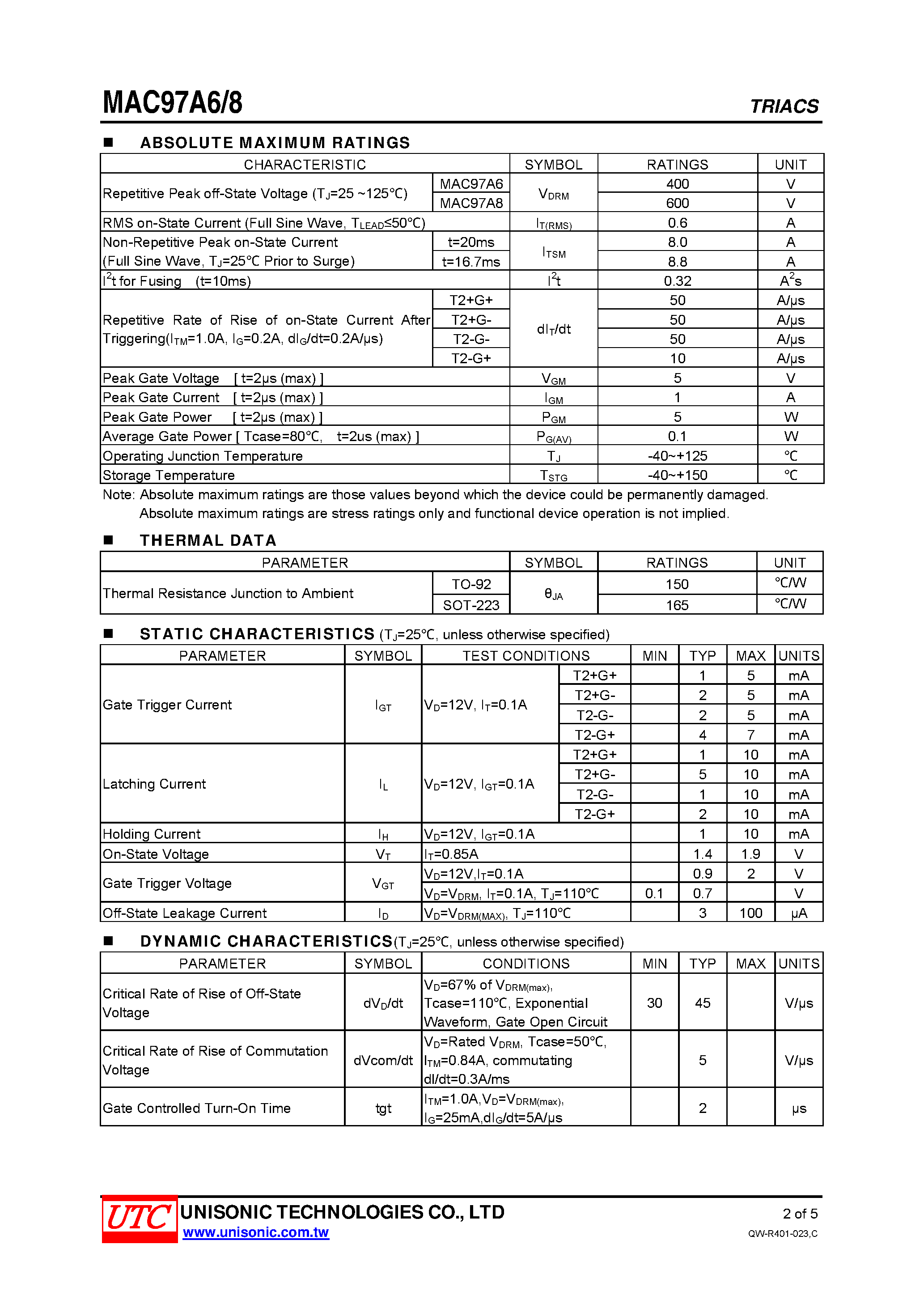
At the core of understanding the functionality of the 97a6 lies the dissection of its technical specifications. These specifications serve as a roadmap, delineating the device’s operational boundaries, electrical characteristics, and application-specific guidelines. By dissecting these specifications with precision, one can glean insights into the device’s capabilities and limitations, facilitating informed decision-making in its utilization.
Analyzing Performance Characteristics
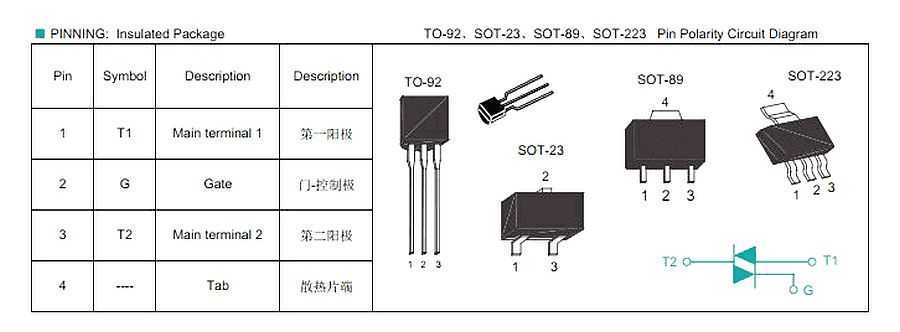
Beyond mere technical specifications, delving into the performance characteristics of the 97a6 offers a deeper understanding of its behavior under varied operating conditions. From conducting transient analysis to scrutinizing thermal performance, a comprehensive evaluation of the device’s performance metrics elucidates its efficacy in diverse application scenarios. By scrutinizing these performance parameters, engineers can optimize circuit designs, mitigate potential risks, and enhance overall system reliability.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Electrical Characteristics | Includes parameters such as voltage ratings, current ratings, and gate trigger characteristics. |
| Application Guidelines | Provides insights into recommended circuit configurations, load considerations, and compatibility with peripheral components. |
| Thermal Performance | Explores the device’s thermal resistance, junction temperature limits, and heat dissipation mechanisms. |
| Transient Analysis | Evaluates the device’s response to transient phenomena such as dv/dt and di/dt, crucial for robust circuit design. |
Key Specifications and Parameters

In this section, we delve into the fundamental characteristics and essential metrics that define the performance and functionality of the aforementioned electronic component. We explore its intrinsic attributes, operational thresholds, and critical parameters that shape its behavior and application potential.
We elucidate the pivotal figures, thresholds, and performance indicators that delineate the capabilities and limitations of this electronic device. From operational parameters to environmental considerations, we unveil the intricate details crucial for comprehending its utilization and integration within various electronic systems.
Furthermore, we examine the nuanced specifications and intrinsic properties that underscore its functionality and suitability for diverse applications. Through a meticulous analysis of its electrical characteristics and performance metrics, we offer insights into its operational versatility and potential implications in practical scenarios.
Application Notes and Circuit Design Tips
In this section, we delve into practical insights and strategies for optimizing the performance and reliability of electronic systems utilizing semiconductor switching components. Explore recommendations and guidelines for circuit design, operational considerations, and integration techniques to enhance the efficiency and functionality of your applications.
Understanding Semiconductor Switching

Before delving into specific circuit design tips, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamental principles underlying semiconductor switching. Gain insights into the behavior of these devices in various operating conditions, including triggering mechanisms, voltage and current ratings, and thermal management strategies.
Optimizing Circuit Performance

Discover strategies for maximizing the efficiency and reliability of your circuits by implementing appropriate component selection, layout techniques, and signal conditioning methods. Learn how to mitigate common issues such as electromagnetic interference (EMI), voltage transients, and thermal stress to ensure robust operation in diverse applications.
Troubleshooting and Common Issues
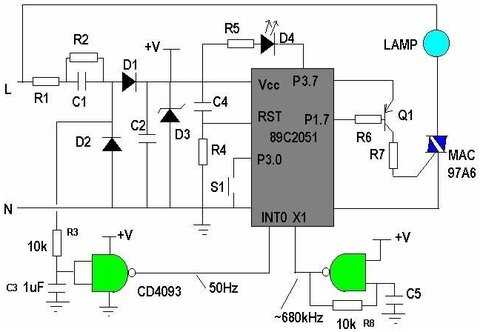
When encountering challenges with the 97a6 triac, it’s essential to navigate through potential stumbling blocks effectively. Understanding common issues and troubleshooting methods can streamline the process of resolving technical hitches and ensuring optimal performance.
1. Operational Anomalies: In the realm of semiconductor devices like the 97a6 triac, operational irregularities may arise, leading to suboptimal functionality. Identifying these discrepancies promptly is paramount for maintaining operational integrity.
2. Performance Fluctuations: Fluctuations in performance can stem from various factors, ranging from environmental conditions to circuit configurations. Pinpointing the root cause of performance deviations is crucial for restoring consistent operation.
3. Overheating Concerns: Excessive heat generation poses a significant risk to the longevity and reliability of electronic components. Implementing effective cooling measures and monitoring thermal profiles are essential strategies for mitigating overheating concerns.
4. Compatibility Issues: Compatibility discrepancies between the 97a6 triac and associated components can hinder seamless integration within electronic systems. Conducting comprehensive compatibility assessments and addressing compatibility issues promptly are pivotal for ensuring smooth operation.
5. Noise and Interference: Noise and interference can compromise signal integrity and disrupt the functionality of the 97a6 triac. Employing appropriate shielding techniques and filtering mechanisms can help attenuate noise and interference, preserving signal integrity.
6. Failure Analysis: When faced with component failure, conducting thorough failure analysis is imperative for identifying failure modes and implementing corrective actions. Leveraging diagnostic tools and methodologies can facilitate efficient failure analysis and resolution.
By proactively addressing common issues and employing effective troubleshooting techniques, users can enhance the reliability and performance of the 97a6 triac in diverse applications.