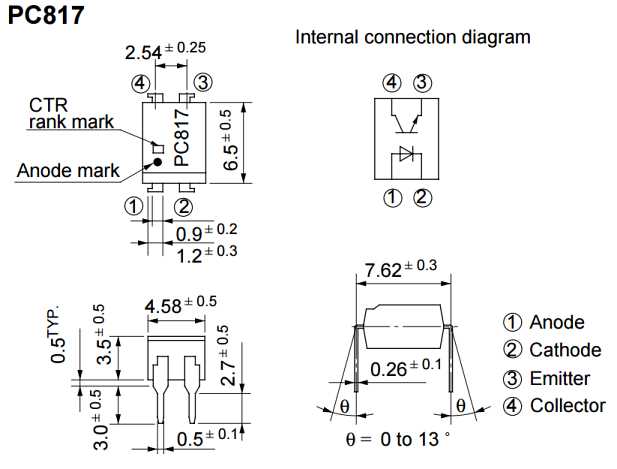
In the vast realm of modern technology, there exists a multitude of electronic components that enable the seamless functioning of various devices and systems. One such component, often overlooked yet highly significant, is the 814 optocoupler. With its ability to transmit signals between electronic circuits by using light as a means of isolation, this device plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficiency and reliability of countless electronic applications.
Delving into the realm of technical specifications, it is vital to understand the various characteristics and features that define the performance capabilities of the 814 optocoupler. These parameters encompass an extensive array of data points, ranging from input and output current ratings to voltage isolation and speed of operation. Each of these specifications holds immense importance in determining the suitability of the optocoupler for specific applications, making a thorough examination of the datasheet an essential task for engineers and enthusiasts alike.
The datasheet of the 814 optocoupler serves as a valuable resource, providing a comprehensive overview of the component’s capabilities and limitations. Within its pages lie detailed graphs, charts, and tables that illustrate the input and output characteristics, forward current transfer ratio, and various other critical parameters. Additionally, the datasheet serves as a guide, offering insights into temperature ratings, moisture sensitivity, and the necessary precautions to be taken during installation and operation.
As technologists and engineers, it is crucial to grasp the significance of thoroughly analyzing the specifications outlined in the datasheet of the 814 optocoupler. By harnessing the knowledge presented within, we gain the ability to make informed decisions regarding the integration of this component into our electronic designs, ensuring optimal performance and longevity for our creations. In the following sections, we will embark on a comprehensive exploration of the various datasheet parameters, shedding light on the possibilities and limitations offered by the 814 optocoupler in our ever-evolving world of technology.
Understanding the 814 Optocoupler Datasheet: An Overview of Specifications and Features
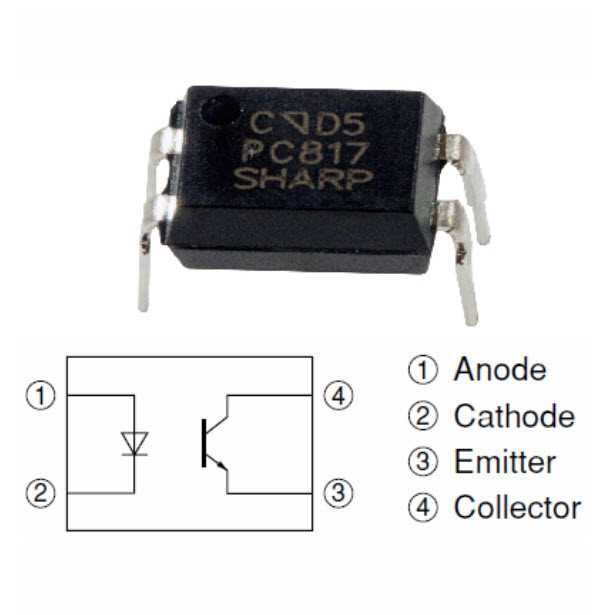
In this section, we will take a closer look at the specifications and features detailed in the datasheet of the 814 optocoupler. By understanding these key aspects, users can gain valuable insights into the capabilities and potential applications of this optocoupler model.
The datasheet serves as a comprehensive guide, providing in-depth information on various parameters that define the performance of the 814 optocoupler. It presents a thorough analysis of its specifications, enabling users to make informed decisions regarding its implementation.
One of the significant aspects covered in the datasheet is the electrical characteristics of the 814 optocoupler. This includes details on voltage, current, and power ratings, as well as input and output impedance. By examining these specifications, users can determine the suitable operating conditions for the optocoupler in their specific application.
Another crucial part of the datasheet is the optocoupler’s performance specifications, which outline its response time, propagation delay, and bandwidth. These parameters are essential in evaluating the speed and efficiency of the device, allowing users to tailor its usage to their particular requirements.
Furthermore, the datasheet provides information on various features of the 814 optocoupler, such as its optically coupled isolator configuration and its compatibility with different input and output systems. Understanding these features aids users in comprehending the optocoupler’s versatility and integrating it seamlessly into their electronic circuits.
Additionally, the datasheet may offer application notes and recommended usage guidelines. These valuable resources provide insights into the optimal utilization of the 814 optocoupler, offering practical suggestions for its incorporation in different electronic designs.
Overall, a thorough review of the 814 optocoupler datasheet equips users with the necessary knowledge to harness the full potential of this component. By exploring its specifications and features, users can make informed decisions, select appropriate operating conditions, and optimize the performance of the 814 optocoupler within their electronic systems.
Key Specifications: Unraveling the Technical Details of the 814 Optocoupler
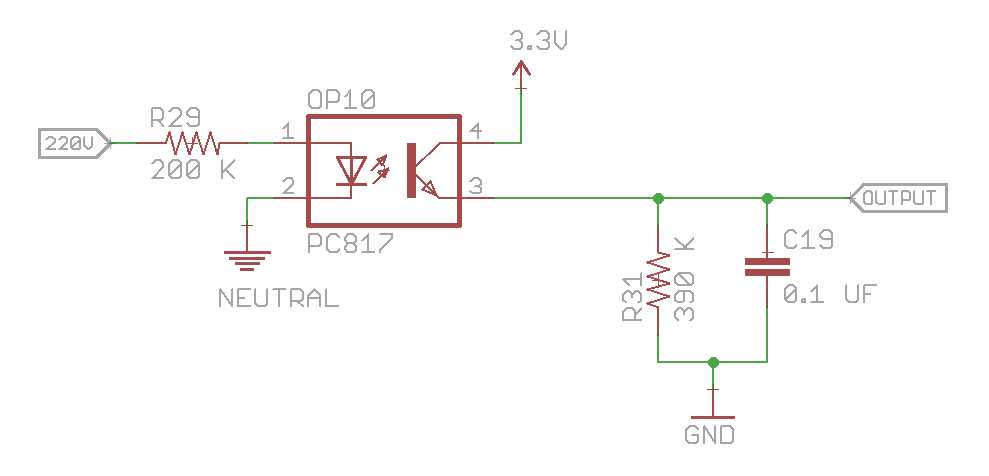
In this section, we will delve into the intricate technical aspects of the advanced electronic component known as the 814 Optocoupler. By exploring its key specifications, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of its capabilities and functionality, shedding light on its potential applications in various fields.
1. Performance Metrics
- Signal Transfer Ratio: The measure of efficiency in transferring an input signal to the output side, indicative of the device’s amplification capabilities.
- Isolation Voltage: The maximum voltage that can be safely applied between the input and output sides, ensuring proper electrical isolation.
- Rise and Fall Time: The time taken for the output signal to transition from low to high state or vice versa, determining the device’s speed of operation.
- Dynamic Current Transfer Ratio: The ratio of output current to input current, playing a crucial role in accurately replicating the input signal.
2. Electrical Characteristics
- Forward Voltage: The voltage drop across the input side LED, influencing the overall power consumption of the optocoupler.
- Collector-Emitter Breakdown Voltage: The maximum voltage that can be safely applied across the output side of the optocoupler, preventing damage to the device.
- Input-Output Capacitance: The inherent capacitance between the input and output sides, affecting the device’s frequency response and ability to handle dynamic signals.
- Power Dissipation: The maximum amount of power that can be safely dissipated by the optocoupler without causing thermal issues.
3. Mechanical Specifications
- Package Type: The physical housing of the optocoupler, available in different forms such as through-hole or surface mount packages.
- Dimensions: The overall dimensions of the optocoupler’s package, allowing for proper integration and compatibility with existing designs.
- Lead Configuration: The arrangement and pinout of the optocoupler’s leads, determining the correct orientation and connection during installation.
- Operating Temperature Range: The range of ambient temperatures within which the optocoupler can reliably function, crucial for its deployment in different environments.
By closely examining these key specifications, engineers and designers can make informed decisions regarding the suitability of the 814 Optocoupler for their specific applications. Understanding the technical intricacies ensures optimal utilization of the device’s capabilities, leading to enhanced performance and reliability in electronic designs.
Applications and Benefits: Exploring the Versatile Uses and Advantages of the 814 Optocoupler
In this section, we will delve into the wide range of applications and advantages offered by the 814 optocoupler, a versatile component that finds use in various industries. We will explore how this device facilitates reliable isolation and signal transmission between different electrical circuits, and how it can enhance safety and performance in diverse systems.
One of the key applications of the 814 optocoupler is in the field of industrial automation. With its ability to provide galvanic isolation, this component enables secure communication and control between different parts of a system. By preventing unwanted electrical interference and voltage spikes, the 814 optocoupler ensures the smooth operation of machinery and equipment. It can be employed in motor drives, power supplies, and PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) systems, enhancing the reliability and efficiency of industrial processes.
Another area where the 814 optocoupler shines is in medical devices and equipment. With its ability to transmit signals without the need for direct electrical contact, this component ensures patient safety and reduces the risk of electrical shocks. It finds applications in devices such as patient monitoring systems, electrocardiographs, and defibrillators. The 814 optocoupler not only guarantees accurate signal transmission but also provides electrical isolation, protecting both the patient and medical personnel.
The versatility of the 814 optocoupler is further demonstrated in its use in telecommunications. From high-speed data transmission to telecommunication network equipment, this component plays a vital role in maintaining signal integrity and minimizing noise interference. By effectively isolating the different circuitry within communication systems, the 814 optocoupler ensures reliable data transfer, enhancing the overall performance and stability of telecommunication networks.
In addition to its applications in industrial automation, medical devices, and telecommunications, the 814 optocoupler also finds use in consumer electronics and automotive systems. In consumer electronics, it can be employed in devices such as audio amplifiers, photocopiers, and infrared remote control systems. Within the automotive industry, the 814 optocoupler can be utilized in applications such as automotive lighting, battery management systems, and electric vehicle charging stations.
The benefits of utilizing the 814 optocoupler in these various applications are numerous. Not only does it provide reliable electrical isolation, but it also offers high-speed data transmission, resistance to environmental disturbances, and long lifespan. Its compact size and ease of integration make it a favored choice among designers and engineers. Moreover, the use of the 814 optocoupler can lead to improved system performance, enhanced safety, and cost savings.
In conclusion, the 814 optocoupler is a highly versatile component that finds applications in a wide range of industries. Its ability to provide reliable electrical isolation and signal transmission offers significant benefits in terms of safety, performance, and cost-effectiveness. Whether in industrial automation, medical devices, telecommunications, consumer electronics, or automotive systems, the 814 optocoupler proves its value as a reliable and efficient component.
Interpreting the Pinout and Functional Diagram: A Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding the 814 Optocoupler’s Connection and Operation

In this section, we will explore the pinout and functional diagram of the 814 optocoupler, providing a comprehensive guide to understanding its connection and operation. By breaking down the various components and their functions, we will demystify the inner workings of the optocoupler, enabling you to make informed decisions about its implementation in your circuits.
Pins and their Functions
- Pin 1: Input Emitter – This pin is responsible for receiving the input signal that needs to be isolated. It works in conjunction with the input detector to transmit the signal across the isolation barrier.
- Pin 2: Input Detector – Serving as the counterpart to the input emitter, this pin detects the input signal and converts it to an electrical current that can be transmitted.
- Pin 3: Output Collector – Once the input signal is transmitted across the isolation barrier, it is received by the output collector, which converts it back to a usable form.
- Pin 4: Output Emitter – This pin works in tandem with the output collector and serves as the connection point for the converted output signal.
- Pin 5: Control Current – The control current pin regulates the flow of current through the optocoupler, controlling its overall performance.
Functional Diagram
The functional diagram of the 814 optocoupler illustrates how the various pins and components interact with each other to achieve the desired isolation and signal transmission. At its core, the optocoupler consists of an input emitter-detector pair, an output collector-emitter pair, and a control current pin.
The input emitter and input detector work together to transmit the input signal across the isolation barrier, which separates the input and output sides of the optocoupler. Once the signal is received by the output collector, it is then transmitted through the output emitter as the converted output signal.
Throughout this process, the control current pin ensures that the optocoupler operates within its desired parameters, regulating the flow of current and maintaining optimal performance.
By understanding both the pinout and functional diagram of the 814 optocoupler, you will be equipped with the knowledge necessary to effectively incorporate it into your circuit designs. Consider the unique requirements of your application, and utilize this understanding to maximize the benefits offered by the optocoupler’s connection and operation.