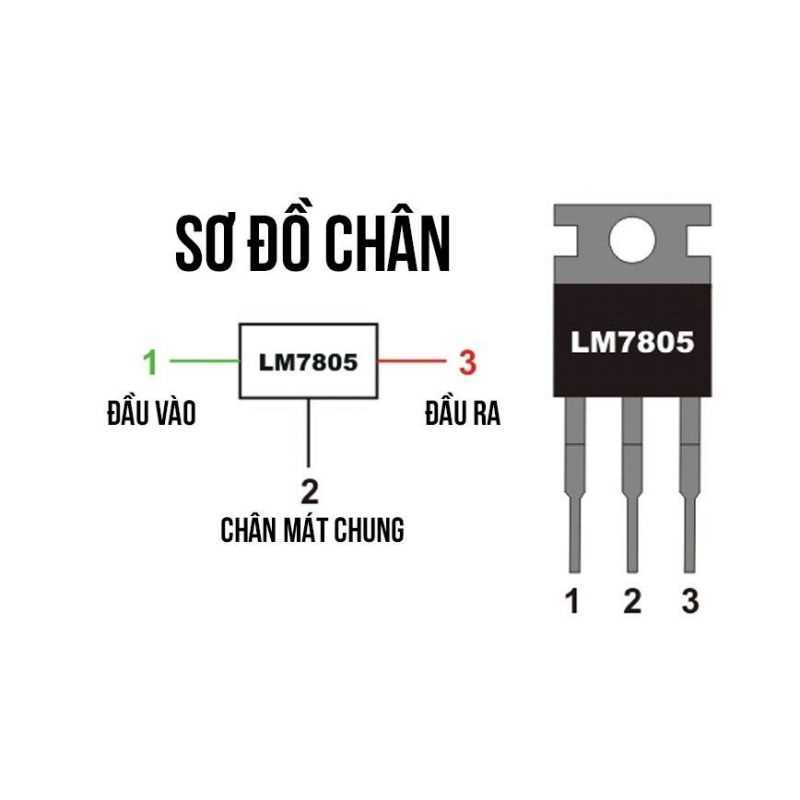
In the labyrinth of electronic components, nestled amidst the intricate circuits and voltage regulations, lies a quintessential cornerstone of power management, akin to the maestro orchestrating a symphony of electrons. This pivotal entity, meticulously crafted to ensure seamless functionality and reliability, embodies the essence of precision engineering.
Embark on a journey where voltages are tamed, currents regulated, and stability is paramount. Within the enigmatic realm of semiconductor technology, this enigmatic gem serves as the fulcrum upon which myriad electronic systems hinge. Through a delicate dance of currents and voltages, it wields influence, steering the trajectory of electronic endeavors with finesse.
Within the folds of its design lies the culmination of years of innovation and refinement, a testament to the ceaseless pursuit of perfection within the electronic domain. Experience the epitome of reliability, where each electron finds its path guided by the hand of precision.
Understanding the Regulator Documentation: Essential Parameters Deciphered
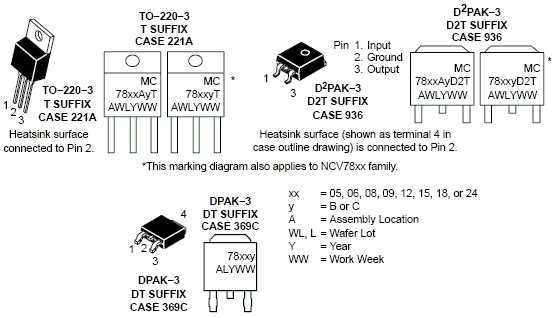
In the realm of electronic components, comprehending the technical documentation can be akin to deciphering a complex code. Within the intricate maze of specifications lie crucial insights into the performance and functionality of a voltage regulator. This section aims to demystify the labyrinth of figures and abbreviations found in the datasheet, shedding light on the vital parameters necessary for an informed design process.
The Power of Input Voltage:
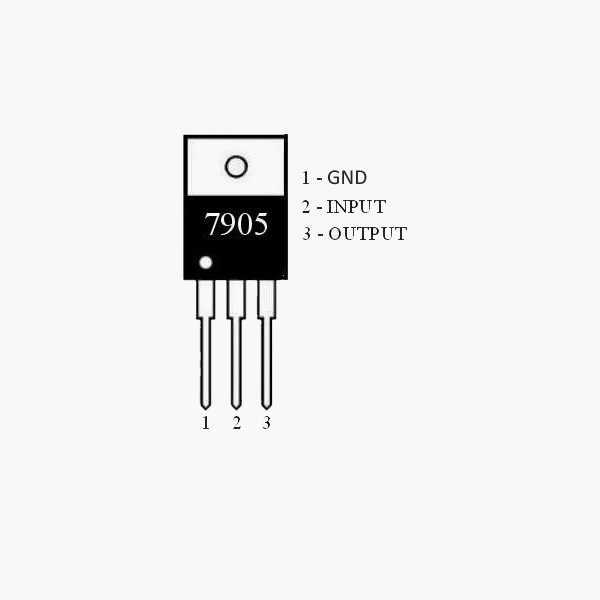
One of the fundamental pillars of regulator operation resides in its ability to tame varying input voltages into a stable output. Exploring the input voltage range, dropout voltage, and maximum input voltage elucidates the regulator’s capacity to withstand fluctuations while maintaining its intended function.
Stability and Output Characteristics:
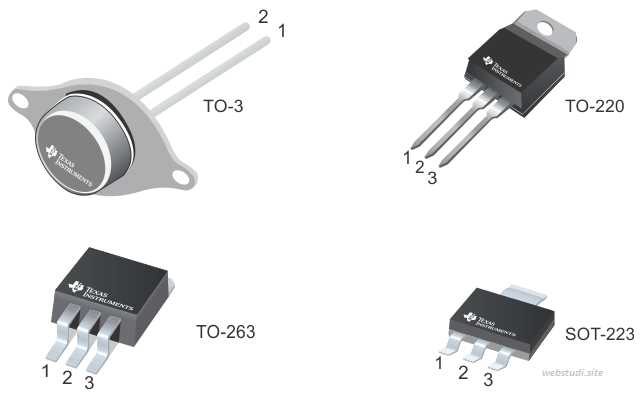
Beneath the veneer of stability lies a plethora of specifications dictating the regulator’s ability to deliver consistent output under diverse load conditions. Parameters such as output voltage accuracy, line regulation, and load regulation provide insight into the regulator’s resilience against external disturbances, ensuring a reliable power supply for the system at hand.
Voltage Regulation: Unveiling the Core Functionality

In the realm of electrical engineering, understanding the fundamental principles of voltage regulation constitutes a cornerstone of proficiency. Delving into the intricacies of this pivotal aspect unveils the essence of ensuring stable and consistent voltage levels, crucial for the reliable operation of electronic circuits.
At its core, voltage regulation entails the meticulous control and maintenance of voltage within prescribed limits, safeguarding electronic components from potential damage due to overvoltage or undervoltage conditions. This pivotal function serves as the bedrock for a myriad of applications across various industries, ranging from telecommunications to power distribution.
Exploring the underlying mechanisms reveals a dynamic interplay of components and concepts, encompassing voltage regulators, feedback loops, and error correction mechanisms. These elements synergize to orchestrate a delicate balance, harmonizing voltage fluctuations and deviations to uphold system integrity.
Moreover, voltage regulation transcends mere static stabilization, embracing dynamic responsiveness to accommodate transient load variations and environmental influences. This adaptive characteristic underscores the resilience of voltage regulation systems in the face of fluctuating operational conditions.
Embarking on an exploration of voltage regulation unveils not only its technical intricacies but also its indispensable role in fostering the seamless functionality of electronic systems. Through a nuanced comprehension of its core functionality, engineers can navigate the complexities of circuit design with confidence, poised to address the dynamic demands of modern technology.
Thermal Considerations: Ensuring Stable Performance
Within the realm of electronic components, the reliability and efficiency of operation hinge significantly upon the management of thermal conditions. This section delves into the critical importance of thermal considerations in fostering consistent and reliable performance.
Temperature regulation plays a pivotal role in sustaining the functionality and longevity of electronic devices. Proper thermal management mitigates the adverse effects of overheating, ensuring optimal operation and preventing potential damage or malfunction.
Effective thermal design encompasses various strategies aimed at dissipating heat generated during operation. From heat sinks to thermal vias, each method serves to maintain components within their specified temperature thresholds, safeguarding against performance degradation and premature failure.
- Heat sinks: These passive cooling solutions efficiently transfer heat away from sensitive components, promoting thermal equilibrium and enhancing overall reliability.
- Thermal vias: By facilitating the conduction of heat through circuit boards, thermal vias aid in dispersing thermal energy and averting localized hotspots that could compromise performance.
- Thermal pads: These interface materials ensure optimal contact between components and heat sinks, maximizing heat transfer efficiency and minimizing thermal resistance.
Furthermore, comprehensive thermal analysis and simulation techniques empower engineers to anticipate and address potential thermal issues during the design phase, preemptively optimizing system performance and reliability.
In conclusion, meticulous attention to thermal considerations is indispensable in upholding the stability and longevity of electronic components, underscoring the imperative for proactive thermal management practices throughout the design and deployment lifecycle.
Application Notes: Enhancing Circuit Performance with the 7805
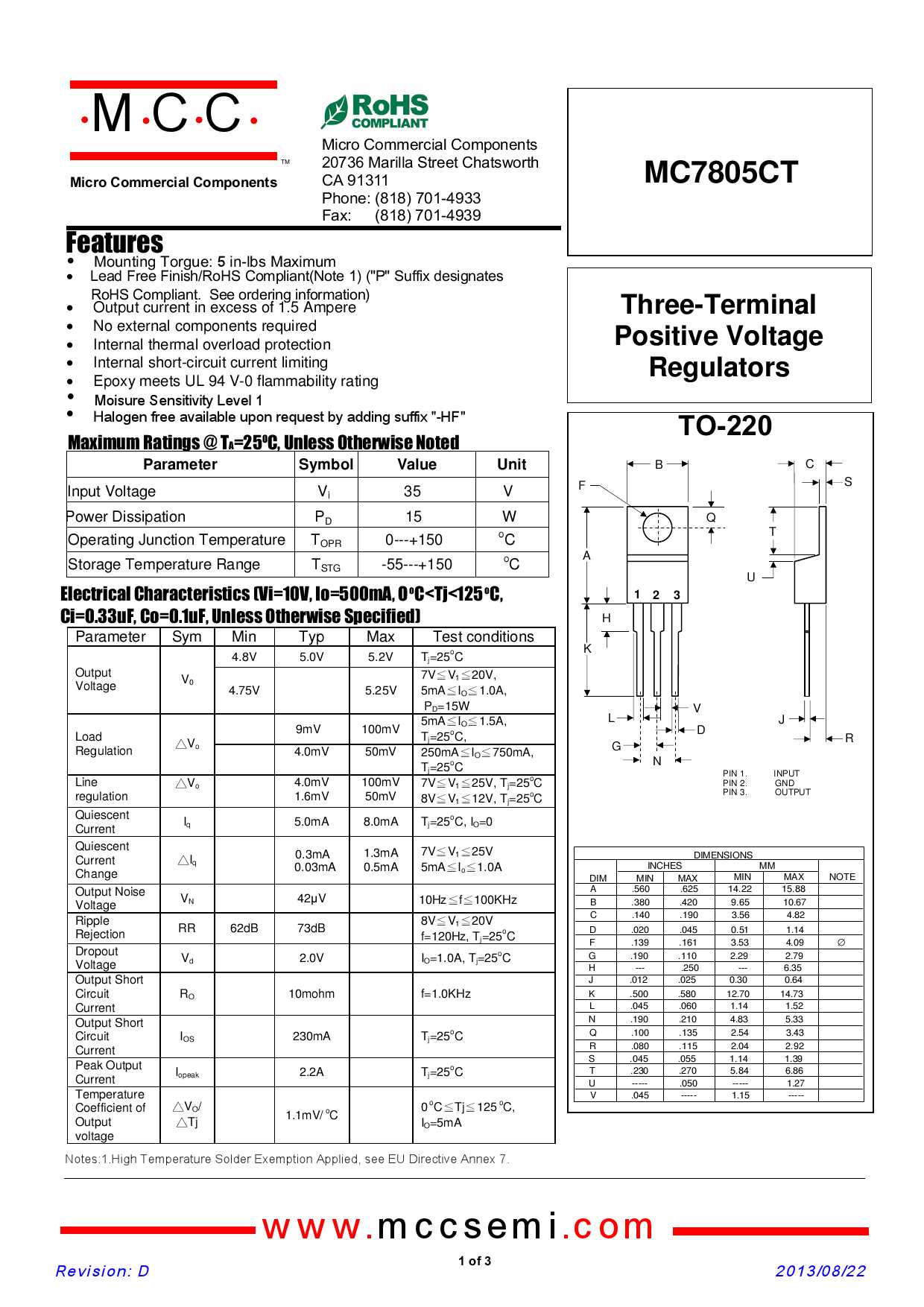
In this section, we delve into strategies for maximizing the efficacy of a ubiquitous voltage regulator component without explicit reference to its technical specifications. The focus lies on optimizing circuitry to achieve superior performance and efficiency, thereby leveraging the full potential of the component in question.
| Enhanced Heat Dissipation | Efficient management of thermal dissipation is pivotal for sustained performance. By implementing effective heat sinking techniques and ensuring proper airflow, the circuit’s reliability and longevity can be significantly enhanced. |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage Stability | Maintaining stable input voltage is imperative for the consistent operation of electronic devices. Through judicious selection of input capacitors and noise filtering mechanisms, voltage fluctuations can be minimized, fostering a more reliable circuit environment. |
| Output Capacitor Optimization | Optimizing the characteristics of the output capacitor plays a crucial role in mitigating transient response issues and minimizing output voltage ripple. Careful consideration of capacitance values and equivalent series resistance (ESR) facilitates smoother voltage regulation. |
| Load Regulation Enhancement | Enhancing load regulation capabilities is instrumental in ensuring consistent voltage output across varying load conditions. By fine-tuning feedback mechanisms and employing appropriate compensation techniques, deviations in output voltage can be minimized, bolstering overall circuit stability. |
| Noise Reduction Techniques | Noise interference can compromise circuit performance and introduce inaccuracies in voltage regulation. Employing effective noise suppression methods, such as shielding, filtering, and layout optimization, helps attenuate extraneous signals, preserving the integrity of the regulated output. |
By implementing these optimization strategies judiciously, circuit designers can harness the full potential of the voltage regulator component, elevating the efficiency, reliability, and performance of their electronic systems.