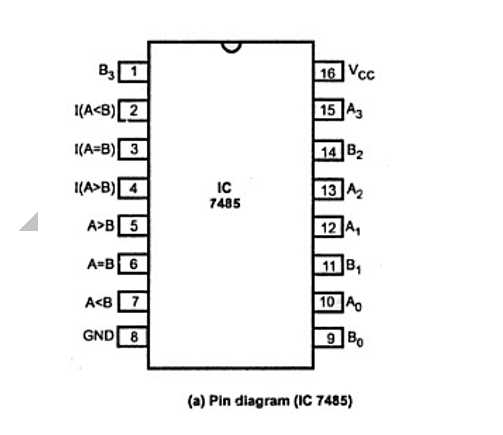
Modern electronic devices are powered by a myriad of integrated circuits, each designed to perform specific functions crucial to their overall operation. One such component that plays a pivotal role in signal processing is the 7485 comparator. With its versatility and reliability, this device has become an indispensable element in numerous applications across various industries.
The 7485 comparator, also referred to as a voltage comparator, is an electronic component widely utilized in circuitry where precise comparisons between two input voltages are essential. This high-performance device enables engineers and technicians to analyze the relationship between different voltage levels, aiding in decision-making and control processes.
The unique distinguishing characteristic of the 7485 comparator lies in its ability to accurately determine the relative magnitudes of two input voltages, efficiently producing an output signal that reflects the result of this comparison. With a vast array of specifications and features to cater to different design requirements, this device offers engineers the flexibility they need to implement tailored solutions in a diverse range of electronic systems.
Throughout this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the 7485 comparator’s technical specifications, shedding light on its various performance metrics such as input offset voltage, input bias current, and output voltage swing. By understanding these critical details, designers can make informed decisions when incorporating the 7485 comparator into their circuit designs, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Understanding the Basics of a 7485 Comparator: A Comprehensive Datasheet
Exploring the Fundamental Concepts of a 7485 Comparator
When it comes to electronic circuits, understanding the essential building blocks is crucial. In this section, we will delve into the fundamental principles behind a highly versatile component known as the 7485 comparator. By grasping the underlying concepts of this device, you will gain a comprehensive understanding of its functionality and potential applications.
An Overview of Comparator Functionality
A comparator, also referred to as a voltage comparator, is an electronic device that examines the voltage levels of two input signals and outputs a corresponding comparison result. It acts as a decision-making component, determining whether one signal is greater, lesser, or equal to the other. The 7485 comparator is renowned for its precision and speed, making it a favored choice in various electronic systems.
Understanding Input Signal Interpretation
One crucial aspect of comprehending the 7485 comparator is understanding how it interprets input signals. It is essential to recognize that the device operates based on the voltage levels present in the input signals. By analyzing the polarity and magnitude of these signals, the comparator generates an appropriate output, allowing for further circuit interactions.
Exploring Comparator Output Modes
The 7485 comparator offers multiple output modes, enhancing its versatility and adaptability. Within this section, we will examine the various possible output configurations and how they can be utilized to meet specific circuit requirements. By understanding these modes, you will be able to optimize the 7485 comparator’s performance and ensure seamless integration within your electronic designs.
Utilizing the 7485 Comparator in Practical Applications
In addition to understanding the theoretical aspects of the 7485 comparator, it is crucial to recognize its practical applications. This section will showcase real-world scenarios where the comparator excels, including voltage level detection, digital-to-analog conversion, and waveform shaping. By gaining insights into these applications, you will be able to harness the full potential of the 7485 comparator in your design projects.
Conclusion
By delving into the basics of the 7485 comparator, you have obtained a comprehensive overview of this multifunctional component. By understanding its fundamental principles, input signal interpretation, output modes, and practical applications, you are now well-equipped to leverage the capabilities offered by the 7485 comparator and explore its endless possibilities in electronic circuits.
Functional Overview of the 7485 Comparator
The functional overview of the 7485 comparator explores the key aspects and capabilities of this electronic component without directly referencing its specific model or functionality. In this section, we will delve into the operational features and applications of this device, shedding light on its utilization in various electronic circuits.
One significant aspect of the 7485 comparator is its ability to compare analog voltages and determine their relative magnitudes. This essential function enables the comparator to make decisions based on input voltage levels, making it an integral part of many electronic systems.
- The comparator’s output swings to a high or low state based on the comparison result, making it ideal for digital logic applications.
- It can be used to implement different logic functions, such as AND, OR, and NOT gates, providing great versatility in circuit design.
- The device exhibits fast response times, allowing for real-time voltage comparisons in dynamic systems.
- Low power consumption makes the 7485 comparator suitable for battery-powered applications, without draining excessive energy.
The 7485 comparator also offers configurable hysteresis, allowing users to define a range within which the device will maintain a stable output. This capability helps prevent unexpected output fluctuations caused by noise or small voltage variations.
Furthermore, the 7485 comparator is designed to be compatible with a wide range of supply voltages, providing flexibility in both low and high power operation.
Considering its various features and flexible usage options, the 7485 comparator finds applications in a multitude of fields, such as digital electronics, instrumentation, communications, and control systems. Its reliability and efficiency make it a popular choice for engineers and hobbyists alike.
Key Specifications and Features of the 7485 Comparator
The section below highlights the essential specifications and noteworthy features of the 7485 comparator component. This information aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the key aspects of the component without specifically referring to its model number or function.
| Specifications | Features |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage Range | Wide input voltage compatibility |
| Output Voltage Swing | High output voltage range |
| Supply Voltage | Wide voltage supply options |
| Input Offset Voltage | Precise input circuitry for accurate comparisons |
| Response Time | Fast response for rapid comparison operations |
| Input Bias Current | Low input bias current for improved efficiency |
| Low Power Consumption | Efficient power management for reduced energy usage |
| Noise Immunity | Enhanced noise rejection for reliable performance |
| Operating Temperature Range | Wide operating temperature range for various environments |
This collection of specifications and features illustrates the versatility and capabilities of the 7485 comparator. Its wide input voltage range, high output voltage swing, and various supply voltage options allow it to be integrated into diverse electronic systems. The precise input circuitry with low input offset voltage ensures accurate and reliable comparison operations. Additionally, the fast response time, low input bias current, and low power consumption contribute to the component’s efficiency and performance. Lastly, the enhanced noise immunity and wide operating temperature range further enhance the reliability and adaptability of the 7485 comparator.