
When it comes to the realm of precision and control in mechanical systems, one cannot overlook the profound importance of high-performance motion control components. Among the various options available, the 42 step motor stands as a noteworthy contender. This component embodies the epitome of efficiency, delivering reliable and precise rotational motion in a wide range of applications.
Embracing the concept of synchronization and accuracy, the 42 step motor provides an essential link between computational instructions and mechanical execution. This integral part boasts a remarkable ability to transform electrical signals into exact mechanical movements, making it a token of precision engineering.
With its distinct set of features and technical specifications, the 42 step motor paves the way for a multitude of applications in various industries. The heart and soul of robotics, this component enables robotic systems to accomplish precise tasks with utmost accuracy and repeatability. Additionally, it finds its application in CNC machines, 3D printers, and other automated systems that require controlled and synchronized motion.
Understanding the Basics of Stepper Motors
In this section, we will delve into the fundamental principles and concepts behind the operation and functionality of a commonly used type of electric motor. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the inner workings and terminology associated with these devices, you will be well-equipped to harness their capabilities effectively in various applications.
At their core, stepper motors are innovative electromechanical devices that ensure accurate positioning and rotational control without relying on traditional feedback mechanisms. Their uniqueness lies in their ability to divide a full rotation into a precise number of equidistant steps. Each step corresponds to a discrete position, giving stepper motors unparalleled precision and repeatability.
Advantages of Stepper Motors
Stepper motors offer several advantages over other types of motors. First and foremost, they excel in applications requiring precise control, such as robotics, 3D printers, and CNC machines. Their ability to move in predetermined increments with high precision makes them ideal for applications where accuracy is critical.
Another advantage of stepper motors is their ease of use. Unlike other motors that require complex control mechanisms, stepper motors simplify the driving process by using pulse signals. These signals, generated by specialized control circuits called drivers, dictate the number and direction of steps the motor takes. This straightforward operation makes stepper motors popular in both hobbyist and professional environments.
Distinguishing Characteristics
Understanding the distinguishing characteristics of stepper motors is crucial for their successful implementation. One key aspect is their torque-speed curve, which describes the motor’s ability to produce torque at different speeds. This curve typically exhibits a drop-off in torque as motor speed increases, indicating the motor’s limitations in high-speed applications.
Additionally, stepper motors offer a range of options in terms of step size and holding torque. The step size determines the angular movement per step, with smaller step sizes allowing for finer control. Holding torque refers to the motor’s ability to hold a position when stopped – a critical consideration in applications that require maintaining position without power.
By comprehending these fundamental principles and characteristics of stepper motors, you are better equipped to select, operate, and optimize the performance of these versatile devices. The following sections will delve deeper into the specific technical details and considerations unique to stepper motors, ensuring that you can harness their benefits to their full potential.
Exploring the Key Features of 42 Stepper Motors
Powerful and reliable, 42 stepper motors are a popular choice for a wide range of industrial and consumer applications. These advanced motion control devices offer an array of impressive features that make them versatile and efficient for various tasks.
- Precision and Accuracy: 42 stepper motors are known for their high precision and accurate positioning capabilities. With their precise step angle and microstepping options, they ensure smooth and consistent motion control without any slippage or loss of steps.
- Torque and Performance: These motors deliver robust torque at low speeds, making them ideal for applications requiring high torque output. Whether it’s handling heavy loads or precise movements, 42 stepper motors excel in delivering exceptional performance.
- Versatility: With their compact size and flexible mounting options, 42 stepper motors can be easily integrated into various systems and devices. They can be used in CNC machines, 3D printers, robotics, medical equipment, and many other applications that require precise and controlled motion.
- Quiet Operation: Thanks to their design and construction, 42 stepper motors operate quietly even when running at high speeds. This makes them suitable for applications where noise reduction is essential, such as in office environments or residential settings.
- Reliability and Durability: Built with high-quality materials and advanced engineering, 42 stepper motors are known for their reliability and durability. They can withstand harsh industrial environments and continuous operation without compromising performance.
From their precision and versatility to their quiet operation and durability, 42 stepper motors offer an outstanding range of features that make them an excellent choice for various applications. Whether you need precise control over motion or robust torque output, these motors deliver exceptional performance and reliability.
A Deep Dive into the Technical Specifications of 42 Stepper Motors
Understanding the intricacies of 42 stepper motors requires a thorough examination of their technical specifications. In this article, we will explore the various parameters and characteristics that define these motors, without directly referring to them as “stepper” or “motor”. By providing a comprehensive overview, we aim to shed light on the essential elements that make these devices pivotal in a plethora of applications.
1. Torque
One of the fundamental aspects to consider when evaluating the performance of 42 stepper motors is their ability to generate rotational force. Commonly known as torque, this parameter determines the motor’s capacity to exert a twisting motion. The torque specification for these motors is a critical factor in determining their suitability for different applications, as it directly influences their ability to overcome resistance and maintain precise control.
2. Step Angle
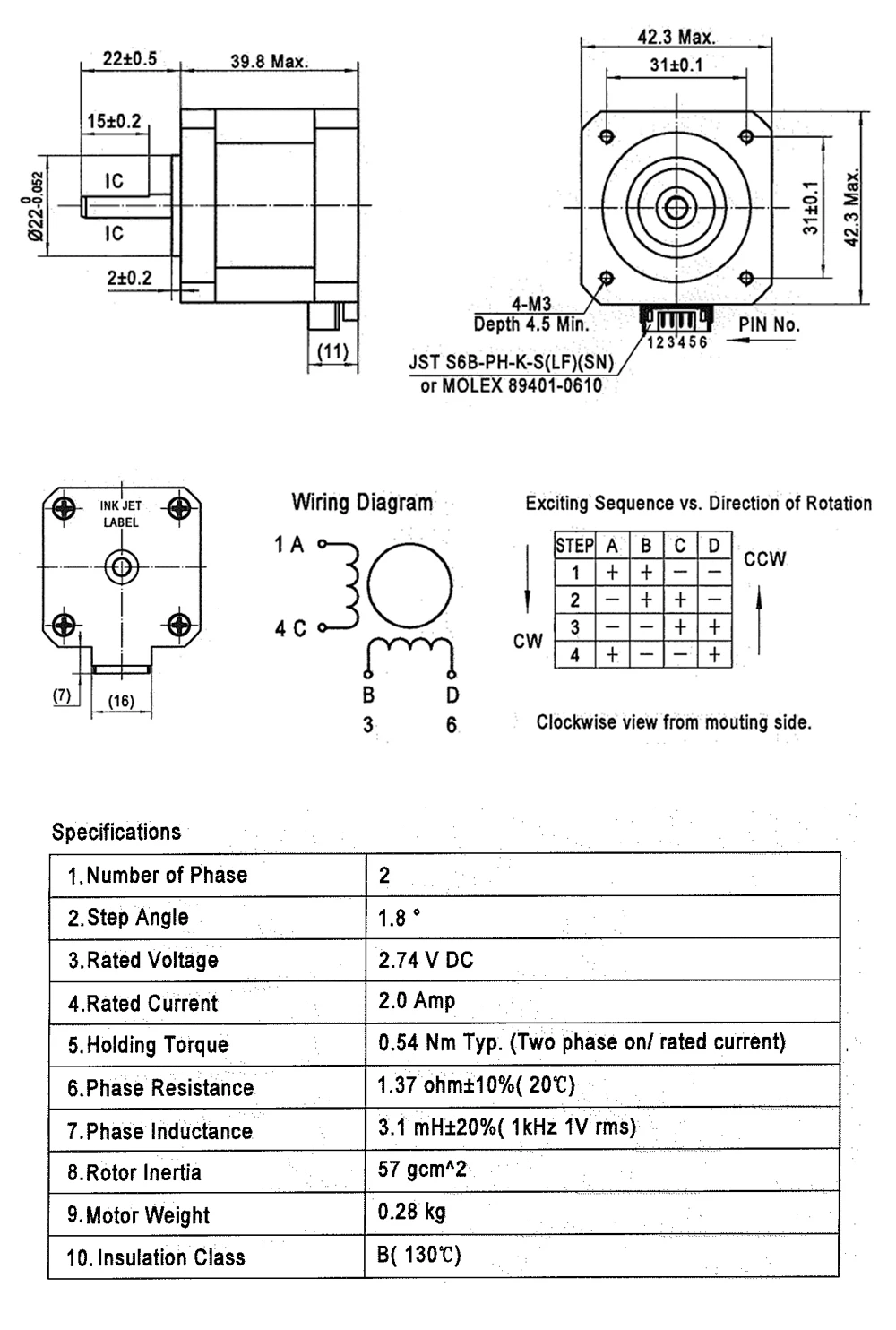
Another crucial characteristic that sets 42 stepper motors apart is their step angle. The step angle refers to the angle the motor rotates for each step of its operation. Measured in degrees, this specification plays a pivotal role in determining the motor’s precision and ability to achieve accurate positioning. A smaller step angle typically translates to finer motion control, making it crucial in applications that require intricate movements.
Furthermore, the step angle also affects the motor’s resolution, which refers to the smallest incremental movement it can achieve. A smaller step angle correlates to higher resolution, enabling the motor to achieve fine-grained positioning and smoother operation.
- 3. Holding Torque: The force exerted by the motor when stationary, ensuring it maintains position without external assistance.
- 4. Inductance: The property that determines the motor’s ability to resist changes in current flow. Lower inductance results in faster response times and improved high-speed control.
- 5. Voltage: The electrical potential required to power the motor and generate motion.
- 6. Current: The flow of electric charge that drives the motor’s operation. Proper current settings are crucial for optimal motor performance and longevity.
- 7. Resistance: The opposition to the flow of electrical current within the motor’s coils.
- 8. Detent Torque: The small force that prevents the motor from freely rotating when not powered, contributing to its ability to hold position.
By delving into these technical specifications, we gain a comprehensive understanding of the capabilities of 42 stepper motors. From their torque and step angle to other parameters such as holding torque, inductance, voltage, current, resistance, and detent torque, each specification plays a crucial role in determining the motor’s performance in specific applications. Armed with this knowledge, engineers and enthusiasts can make informed decisions when selecting and implementing these motors, unlocking their full potential in a wide range of innovative projects.
Tips for Choosing and Implementing 42 Stepper Motors
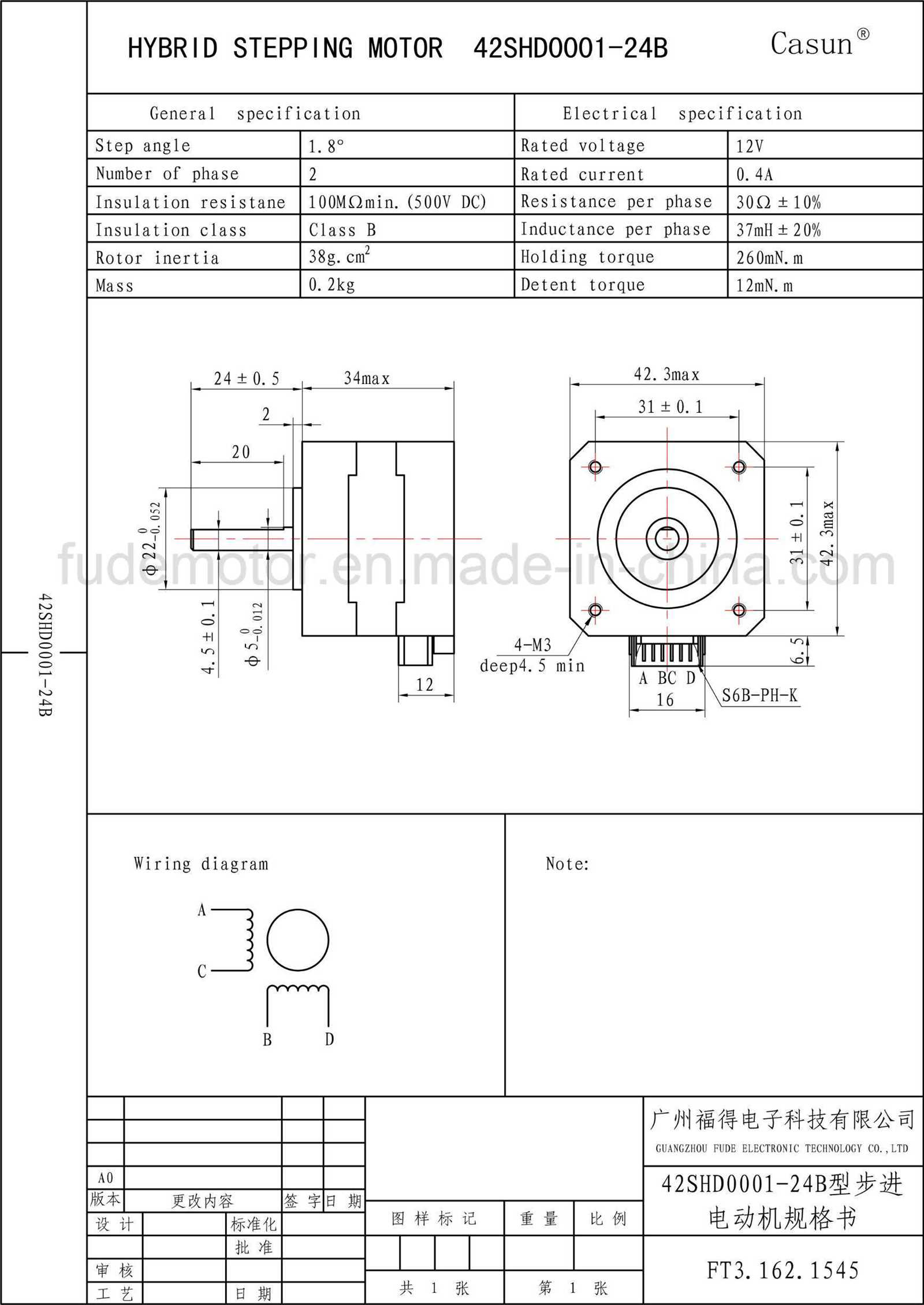
Selecting the right stepper motor for your application and successfully implementing it can greatly impact the performance and efficiency of your system. In this article, we will provide valuable insights and tips to help you make informed decisions when choosing and utilizing 42 stepper motors.
1. Understand Your Application Requirements

Before diving into the selection process, it is crucial to have a clear understanding of your application’s specific needs. Consider factors such as torque requirements, speed range, accuracy, and power consumption. By defining these requirements upfront, you can narrow down your choices and ensure a more precise selection.
2. Explore Different Motor Configurations

When it comes to 42 stepper motors, there are various configurations available, including bipolar and unipolar options. Bipolar motors offer higher torque and efficiency, while unipolar motors are typically easier to control. Understanding the differences between these configurations can help you choose the motor that aligns best with your application’s requirements.
3. Evaluate the Motor’s Holding Torque

Holding torque is a critical parameter that determines the stepper motor’s ability to maintain its position without external force. It is especially important for applications that require precise positioning or holding mechanisms. Be sure to compare the holding torque values of different motors to find the one that offers optimal performance for your specific application.
4. Consider Motor Sizing and Weight
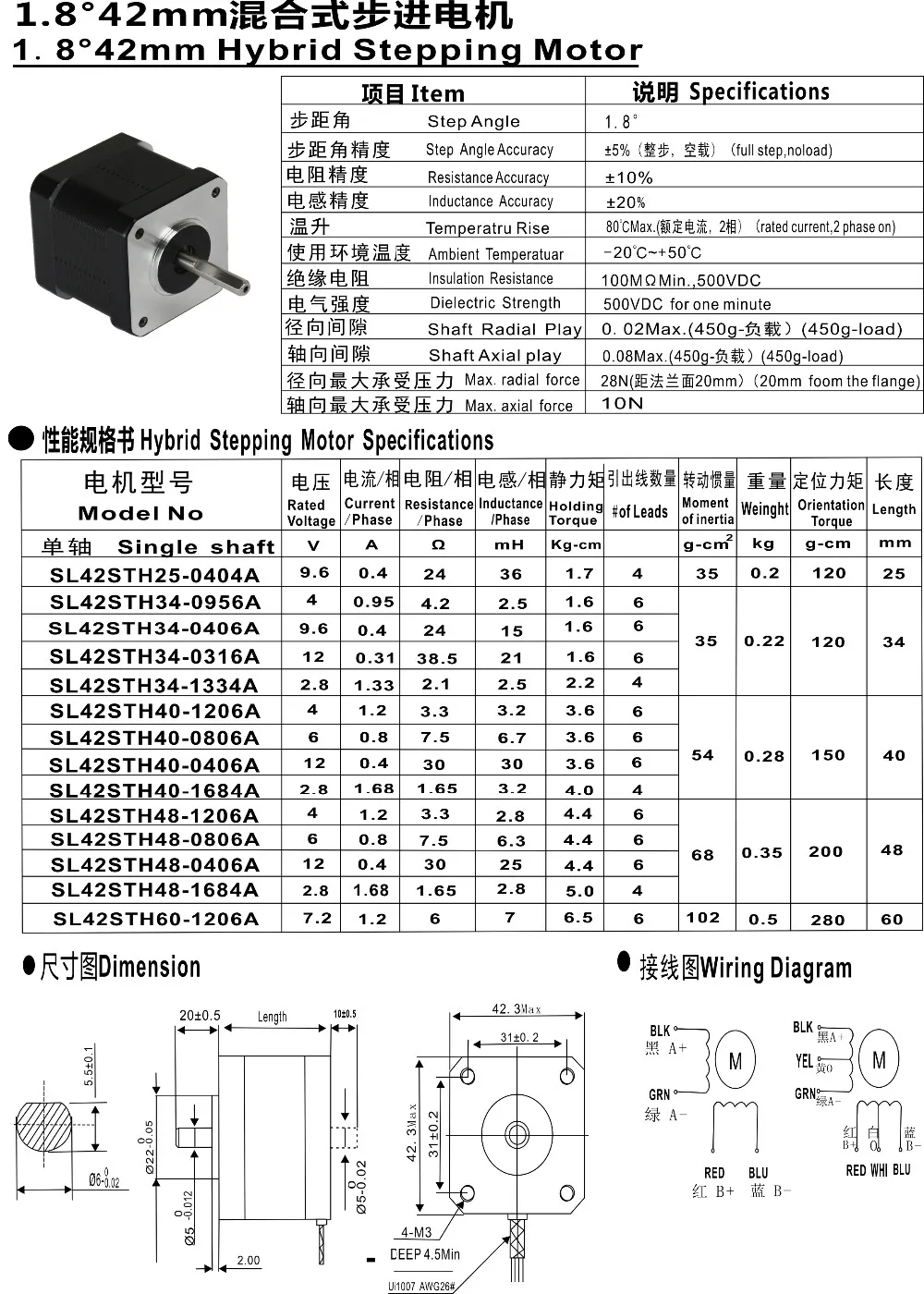
The physical dimensions and weight of the motor can impact your system’s overall size, weight, and design constraints. Ensure that the stepper motor you select fits within the available space and aligns with your system’s weight limitations. Additionally, consider any mounting requirements and compatibility with existing mechanical components.
5. Evaluate Motor Control Options
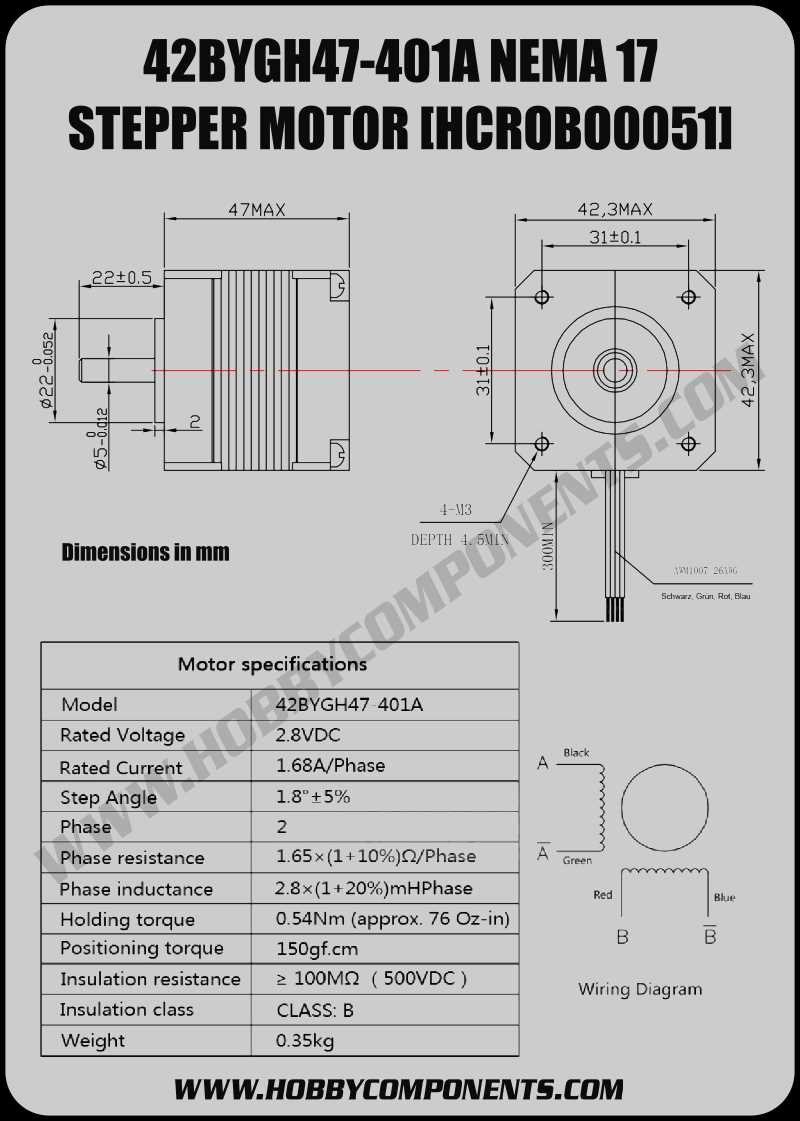
42 stepper motors can be controlled using various methods, such as open-loop or closed-loop systems. Open-loop control is simpler and more cost-effective but may result in less precise positioning. Closed-loop control, on the other hand, provides feedback for enhanced accuracy but can be more complex and costly. Assess your application’s control requirements and choose the appropriate motor control method accordingly.
Conclusion
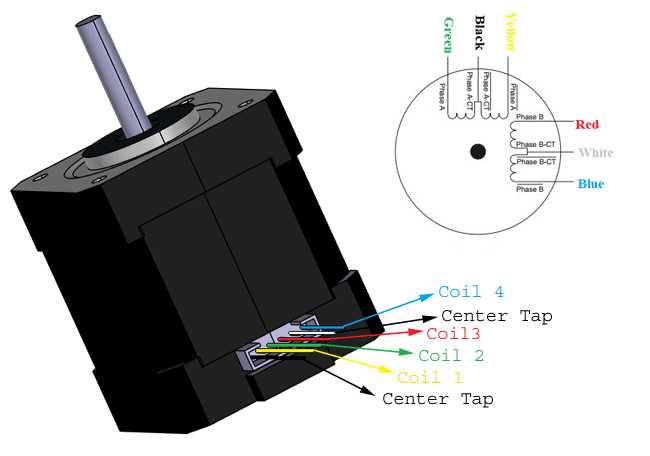
Choosing and implementing 42 stepper motors requires careful consideration of your application’s specific requirements. By understanding these tips and conducting thorough research, you can identify the ideal motor that will optimize the performance and efficiency of your system.
Factors to Consider and Best Practices for Optimal Performance

When it comes to maximizing the efficiency and effectiveness of any device, there are key factors that must be taken into consideration. By understanding these factors and implementing best practices, users can ensure optimal performance without relying solely on technical specifications or product datasheets.
One crucial aspect to evaluate is the overall design and configuration of the system in which the device operates. By properly aligning components and understanding the interplay between various elements, users can optimize performance and minimize potential issues.
Another vital factor is the choice of materials and components used. Selecting high-quality materials that are compatible with the device’s intended application can greatly influence its performance. Additionally, opting for components that are known for their reliability and durability can enhance long-term functionality.
Efficient power management is also a key consideration. By understanding the power requirements and utilizing power-saving techniques, users can maximize the device’s performance while minimizing energy consumption. This can lead to increased efficiency and reduced operating costs.
Regular maintenance and proper care are essential for ensuring optimal performance. Performing routine inspections, cleaning, and lubrication can prevent issues such as mechanical failures or reduced precision. Moreover, implementing preventive measures such as regular calibration or replacing worn-out parts can help maintain peak performance levels.
Lastly, user knowledge and understanding play a crucial role in maximizing the device’s performance. By educating oneself about the device’s capabilities, limitations, and recommended practices, users can make informed decisions and implement optimized operating procedures.
In conclusion, optimizing the performance of any device, including a stepper motor, involves considering various factors and adhering to best practices. By emphasizing system design, material selection, power management, maintenance, and user knowledge, individuals can ensure that their device operates at its peak capacity and delivers reliable results.