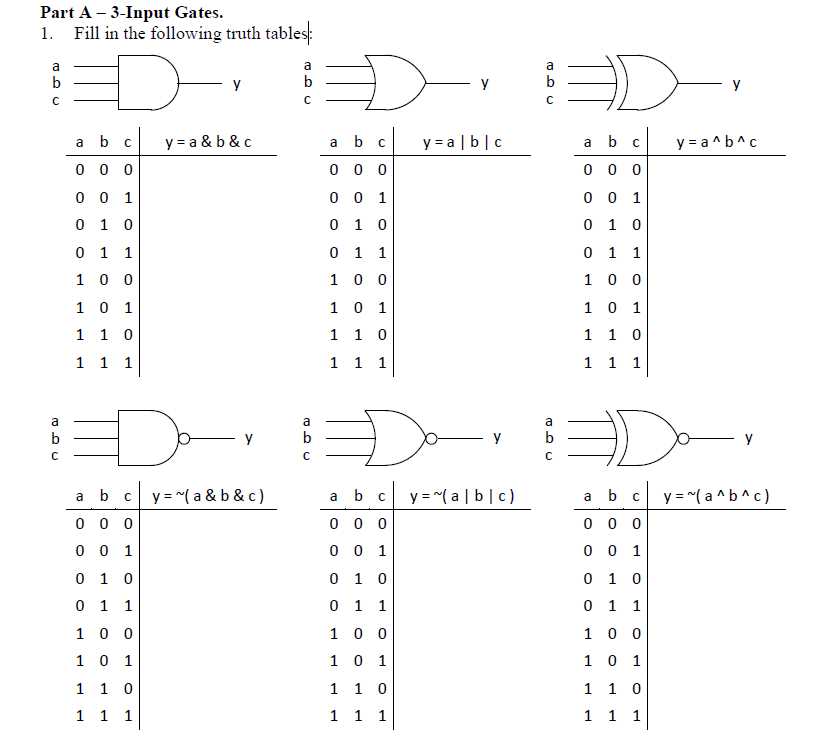
Unlocking the potential of interconnected systems relies on the seamless integration of foundational components. Within the realm of digital electronics, the synergy between multiple inputs and logical operations forms the bedrock of computational processes. In the pursuit of precision and efficiency, engineers delve into the intricacies of component specifications to ensure optimal performance. Here, we embark on a journey to dissect the characteristics and functionalities of a trio of input-driven logical elements, transcending conventional boundaries to unravel their nuanced capabilities.
Embarking on this exploration necessitates a keen understanding of the fundamental principles that govern electronic logic. Through meticulous analysis and rigorous experimentation, these components serve as the building blocks for complex systems, orchestrating the flow of information with precision and reliability. While conventional wisdom may dictate a binary perspective, the fusion of multiple inputs heralds a new era of computational prowess, elevating the discourse from the mundane to the extraordinary.
Amidst the tapestry of digital intricacies lies the domain of logical conjunction, where signals converge to dictate outcomes. As we navigate through the labyrinth of technical specifications, each facet unveils a narrative of efficiency and optimization. Beyond the veneer of simplicity lies a realm teeming with potential, awaiting the discerning eye of the adept engineer to harness its power.
Understanding 3-Port Logical Interconnections
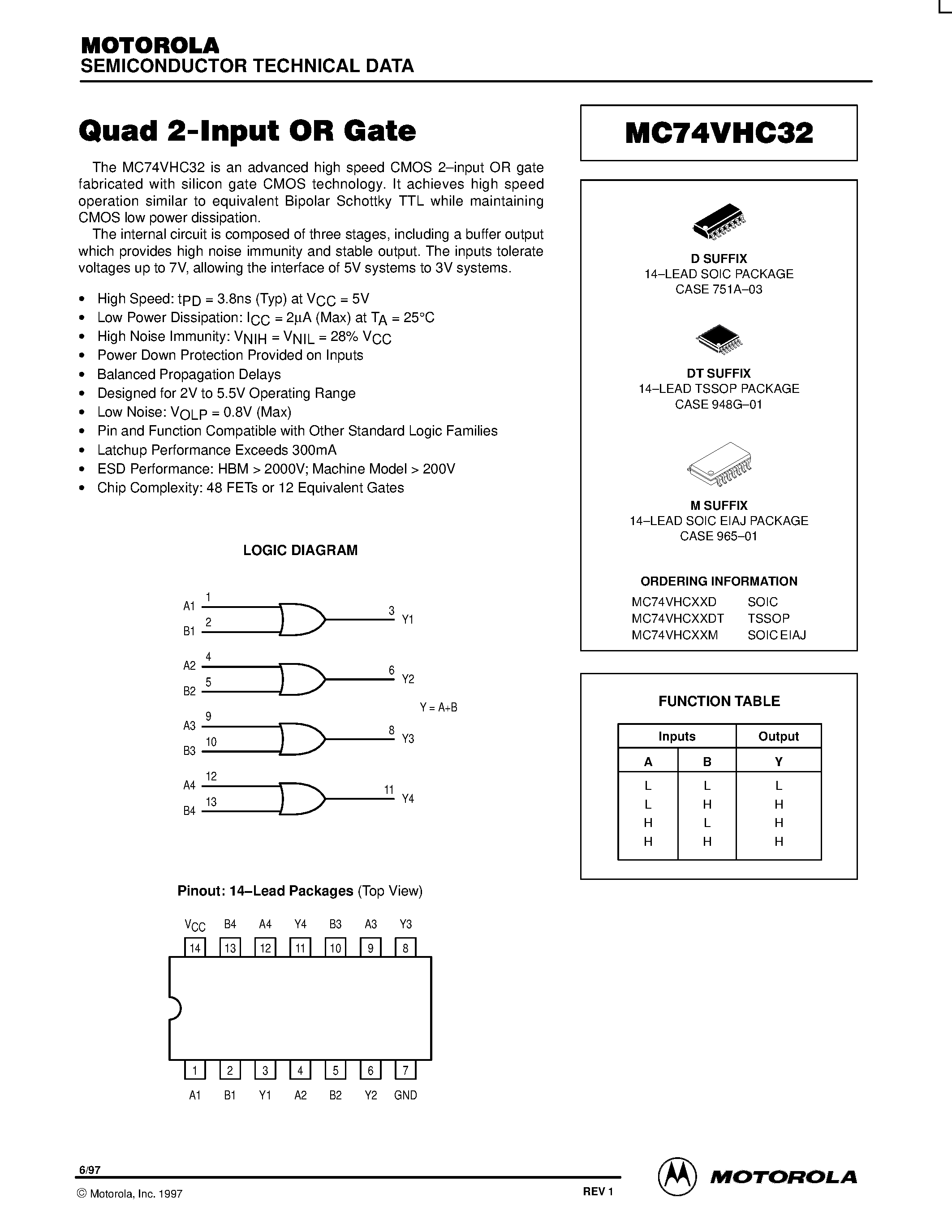
In the realm of digital circuitry, the comprehension of complex logical interconnections is pivotal for engineers and enthusiasts alike. Within the expansive landscape of digital systems, delving into the intricacies of 3-port logical linkages unveils a realm where convergence meets precision.
| Element | Representation |
|---|---|
| Component | Symbolic representation |
| Connector | Interconnect node depiction |
| Conductor | Pathway manifestation |
Exploring the intricacies of these logical junctures unveils not merely the interplay of symbols, but rather the synergy of abstract concepts converging into tangible manifestations. The narrative woven within the annals of these datasheets transcends the mere delineation of connections, offering a portal into the underlying principles governing digital systems.
Key Specifications to Look For
When exploring the intricacies of electronic components, understanding the pivotal characteristics is paramount for informed decision-making. In the realm of logical circuitry, identifying the fundamental attributes ensures optimal performance and compatibility. Here, we delve into the essential metrics guiding selection processes, offering insights into critical facets to consider.
Operating Parameters: Delve into the operational boundaries dictating the functionality of the component. Explore metrics such as voltage thresholds, temperature ranges, and power consumption to ascertain its adaptability across diverse environments.
Response Dynamics: Evaluate the responsiveness and latency of the component in processing signals. Scrutinize parameters like propagation delay and rise/fall times to gauge its efficiency in facilitating swift data transmission.
Reliability Metrics: Assess the reliability indicators encompassing factors like Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF), failure rates, and environmental resilience. Understanding these metrics ensures the longevity and stability of the component in prolonged usage scenarios.
Interfacing Compatibility: Explore the compatibility of the component with other circuitry elements. Examine interface standards, input/output voltage levels, and signal compatibility to ensure seamless integration within the existing system architecture.
Environmental Considerations: Consider the environmental factors influencing the performance and durability of the component. Evaluate parameters such as operating temperature, humidity tolerance, and susceptibility to external interferences to ensure optimal functioning across diverse conditions.
Manufacturing Specifications: Gain insights into the manufacturing intricacies governing the consistency and quality of the component. Scrutinize parameters like process technology, fabrication materials, and production standards to ensure adherence to industry norms and standards.
Cost-Effectiveness: Strike a balance between performance and cost considerations by evaluating the component’s cost-effectiveness. Analyze factors such as pricing models, volume discounts, and lifecycle costs to optimize resource allocation without compromising on quality or functionality.
By delving into these key specifications, stakeholders can navigate the intricate landscape of electronic components with clarity and confidence, facilitating informed decision-making and fostering seamless integration within diverse applications.
Interpreting Timing Diagrams
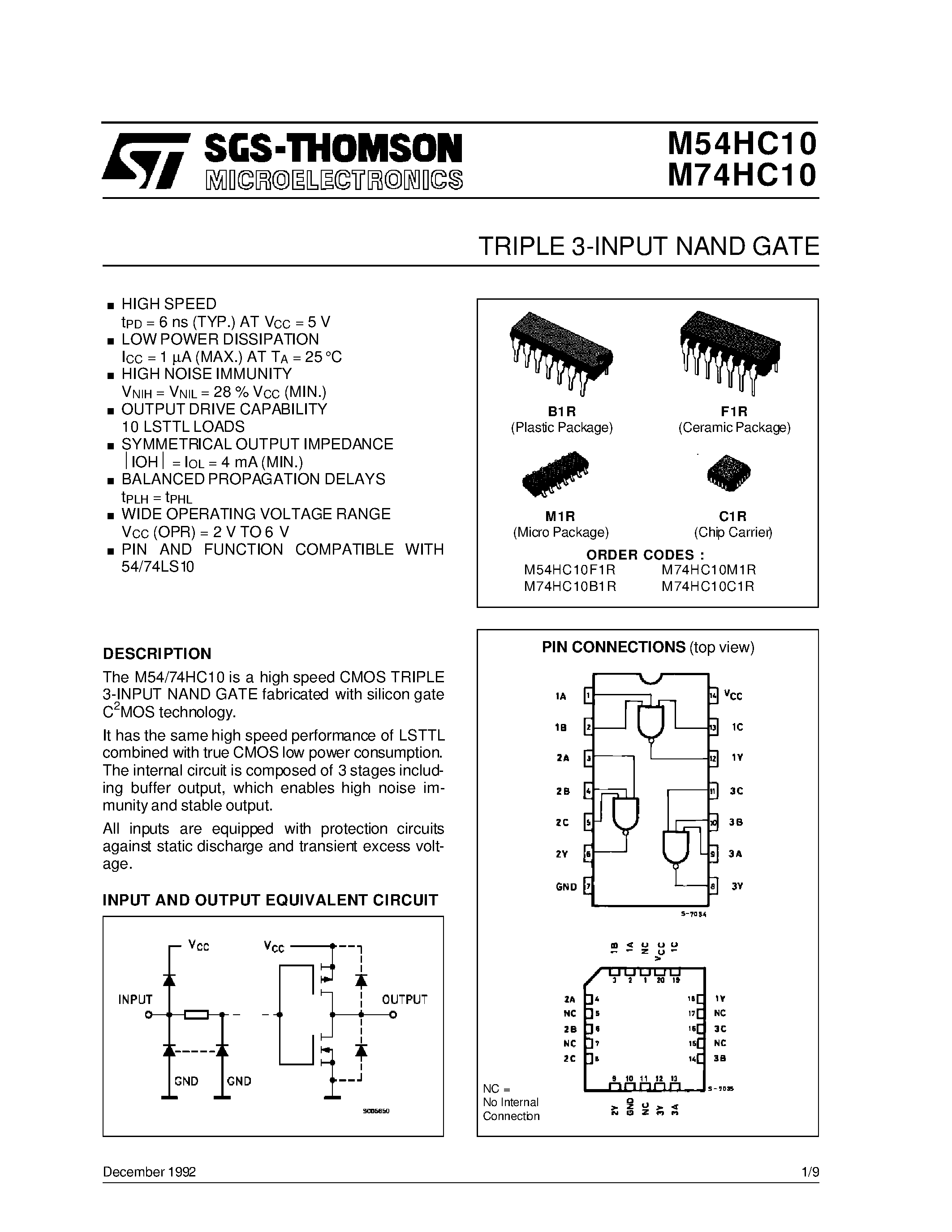
Understanding the temporal characteristics of electronic circuits is crucial for comprehending their functionality and performance. In this section, we delve into the elucidation of temporal patterns illustrated in graphical representations, shedding light on the intricacies of signal propagation and synchronization.
Deciphering Temporal Relationships
Temporal diagrams offer a visual narrative of the temporal dynamics within a circuit, elucidating the sequential progression of signals and their interdependencies. By scrutinizing these diagrams, one can discern the intricate interplay between different components, unveiling the nuances of signal propagation, synchronization, and latency.
Analyzing Waveform Characteristics
Waveforms depicted in timing diagrams encapsulate a wealth of information regarding signal transitions, durations, and logical states. Through meticulous analysis of waveform characteristics such as rise time, fall time, and propagation delay, one can glean insights into the operational efficiency and reliability of the circuit under scrutiny.
| Time | Signal A | Signal B | Signal C |
|---|---|---|---|
| t1 | High | Low | High |
| t2 | Low | Low | High |
| t3 | High | High | Low |