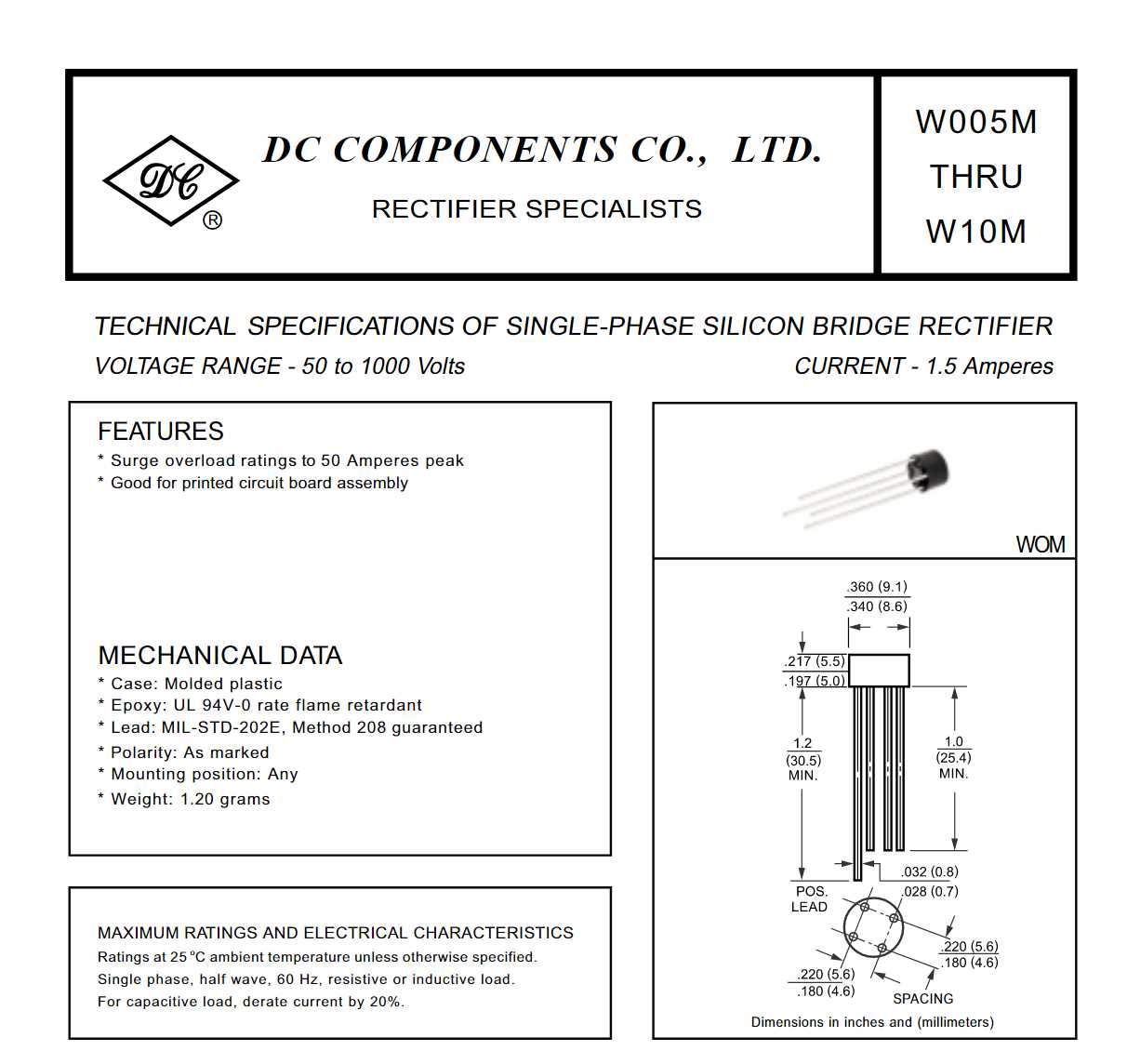
Imagine a world where electrical currents flow seamlessly, enabling our devices to function flawlessly. In this intricate system, various components work harmoniously to convert AC into DC, ensuring stable and efficient power supply. Among these indispensable elements lies a remarkable device, often underestimated yet essential in countless applications.
Welcome to the world of electrical engineering, where the 2w10g bridge rectifier plays a crucial role in powering our technological advancements. Although its name may not ring a bell for many, this small yet mighty component is responsible for converting alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) with utmost precision and efficiency, allowing our devices to operate safely and effectively.
Whether you are an aspiring engineer, a product developer, or simply curious about the inner workings of electronics, a thorough understanding of the specifications of the 2w10g bridge rectifier is vital. This datasheet will provide a comprehensive guide, exploring the detailed specifications and functionalities of this remarkable electronic component, shedding light on its critical role in ensuring the uninterrupted flow of electricity.
Understanding Bridge Rectifiers
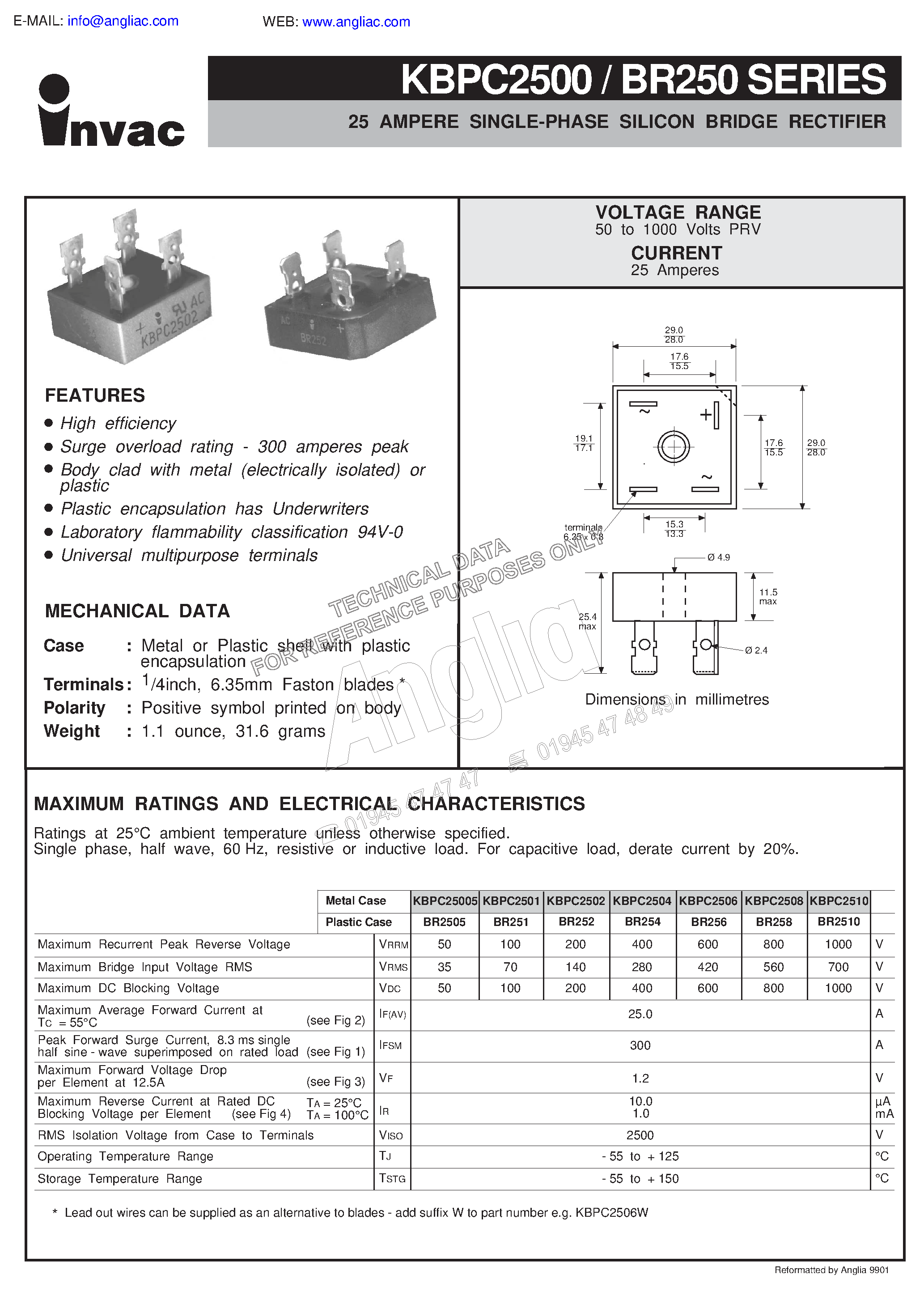
In this section, we will explore the fundamental concepts and principles behind the operation of bridge rectifiers. Bridge rectifiers are electronic devices that play a crucial role in converting alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) in various electrical applications.
Bridge rectifiers, also known as full-wave rectifiers, are widely used in power supplies and electronic circuits to ensure smooth and reliable DC power output. They consist of four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration, allowing for efficient conversion of AC voltage into pulsating DC voltage.
The main function of a bridge rectifier is to rectify the AC input voltage, which means converting it from a fluctuating waveform that alternates between positive and negative cycles to a unidirectional current flow. This rectification process is essential for powering electronic devices and components that require a consistent and stable source of DC power.
| Advantages of Bridge Rectifiers | Disadvantages of Bridge Rectifiers |
|---|---|
| – Efficient conversion of AC to DC | – Voltage drop across diodes |
| – Compact design | – Ripple voltage in output |
| – Wide range of voltage and current ratings | – High heat dissipation |
One of the key advantages of bridge rectifiers is their high efficiency in converting AC power to DC power. This is achieved through the simultaneous use of both the positive and negative cycles of the input AC waveform, maximizing the utilization of power. Additionally, bridge rectifiers have a compact design, making them suitable for a wide range of electrical applications.
However, like any electronic device, bridge rectifiers also have their limitations. One of the drawbacks is the voltage drop across the diodes used in the rectifier circuit, which results in a slight loss of voltage. Another disadvantage is the presence of ripple voltage in the output DC signal, which can cause fluctuations or noise in the powered devices. Furthermore, bridge rectifiers tend to generate significant heat, requiring proper thermal management to prevent damage or performance degradation.
In conclusion, understanding the operation and characteristics of bridge rectifiers is essential for anyone working with electrical circuits and power supplies. By harnessing their advantages and addressing their limitations, bridge rectifiers can provide reliable and efficient conversion of AC to DC power in various applications.
Exploring the Features of 2w10g Bridge Rectifier
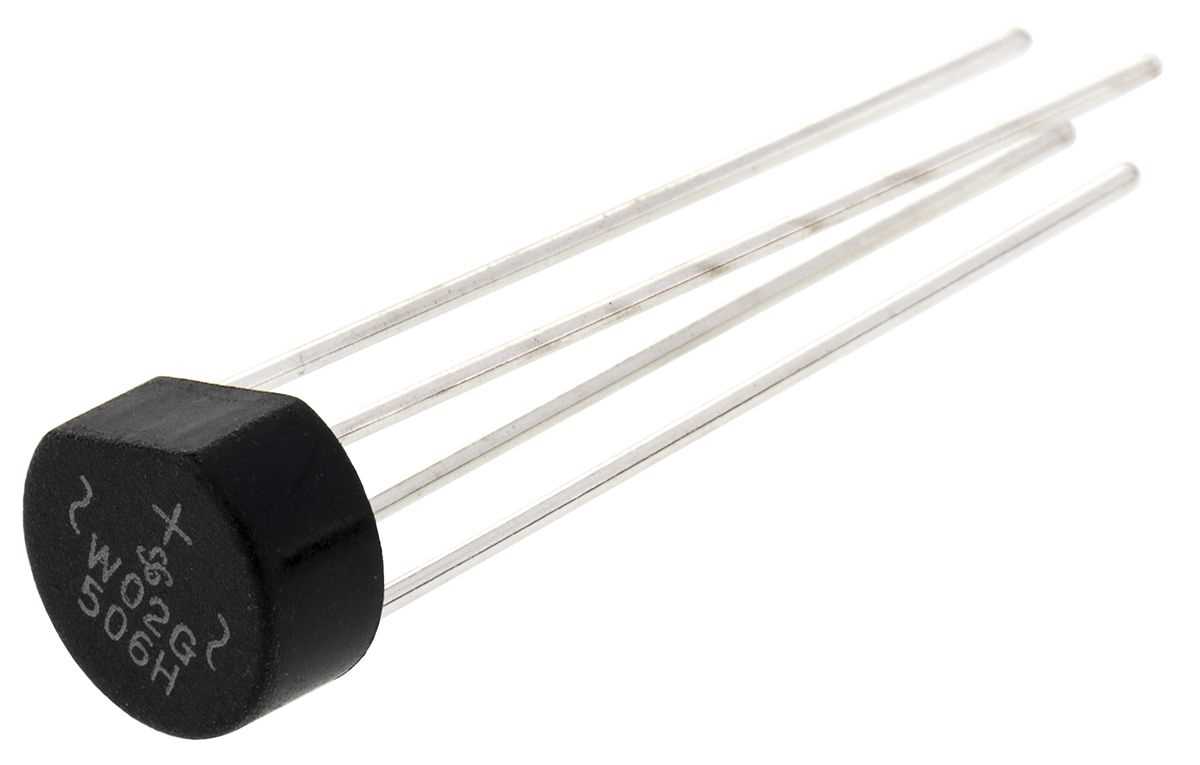

In this section, we will delve into the various characteristics and functionalities offered by the 2w10g bridge rectifier. This essential component plays a crucial role in converting alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) by rectifying the input voltage. By understanding its unique qualities, we can better comprehend its contribution to electronic circuits and systems.
One notable feature of the 2w10g bridge rectifier is its ability to efficiently handle high power levels, making it suitable for applications requiring robust rectification capabilities. Its construction consists of four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration, allowing for a complete conversion of AC to DC. This arrangement also enables the rectifier to effectively handle both positive and negative half-cycles of the input waveform, resulting in a smoother and continuous DC output.
Another advantage of the 2w10g bridge rectifier is its low voltage drop, which ensures minimal power loss during the rectification process. This attribute is particularly important in applications where energy efficiency is paramount. Additionally, the rectifier exhibits excellent thermal stability, enhancing its reliability and performance under challenging operating conditions.
A crucial aspect to consider when utilizing the 2w10g bridge rectifier is its maximum forward current rating, which specifies the maximum current it can handle without compromising its functionality and integrity. This rating is essential for selecting the appropriate rectifier for a given application, ensuring it can safely handle the anticipated currents without the risk of overheating or failure.
| Key Features of 2w10g Bridge Rectifier |
|---|
| Efficient conversion of AC to DC |
| High power handling capabilities |
| Four-diode bridge configuration for complete rectification |
| Minimal voltage drop for optimized power efficiency |
| Excellent thermal stability for reliable operation |
| Maximum forward current rating for safe usage |
In conclusion, the 2w10g bridge rectifier offers various features that make it a valuable component in electronic circuits. Its efficient conversion, high power handling capabilities, low voltage drop, thermal stability, and maximum forward current rating all contribute to its effectiveness in rectifying AC voltage and providing reliable and continuous DC output.