Unlocking the intricacies of cutting-edge electronic components, this section delves into the heart of modern circuitry. Within these pages, delve into the essence of microelectronic mechanisms that power our digital world.
Embark on a journey through the realms of semiconductor intricacies. Discover the enigmatic elements that form the backbone of contemporary electronics, unraveling the mysteries of small-scale electrical engineering.
Here lies a realm where quantum particles dance to the rhythm of coded instructions, where the flow of electrons orchestrates the symphony of technology. It’s a landscape where every junction holds the potential for innovation, every layer a story of progress.
The Basics of 2SC3198 Transistor
Understanding the fundamental principles behind the functionality and application of this electronic component entails delving into its core characteristics and operational mechanisms. This section aims to elucidate the essential aspects of the 2SC3198, shedding light on its role within electronic circuits and its significance in various applications.
Outlined below are key insights into the operational principles and characteristics of the 2SC3198:
- Operating Principle: Explicating the underlying principle guiding the functionality of the 2SC3198 without delving into technical minutiae.
- Functional Role: Exploring the role played by the 2SC3198 within electronic circuits, elucidating its significance in facilitating specific operations.
- Performance Characteristics: Highlighting the performance attributes that distinguish the 2SC3198 and contribute to its efficacy in diverse applications.
- Application Areas: Surveying the broad spectrum of applications where the 2SC3198 finds utility, showcasing its versatility across different domains.
- Integration Considerations: Discussing factors pertinent to the seamless integration of the 2SC3198 within electronic systems, addressing compatibility and optimization concerns.
By grasping the fundamental concepts outlined in this section, one can gain a comprehensive understanding of the 2SC3198 transistor, thereby fostering informed decision-making and effective utilization within electronic designs.
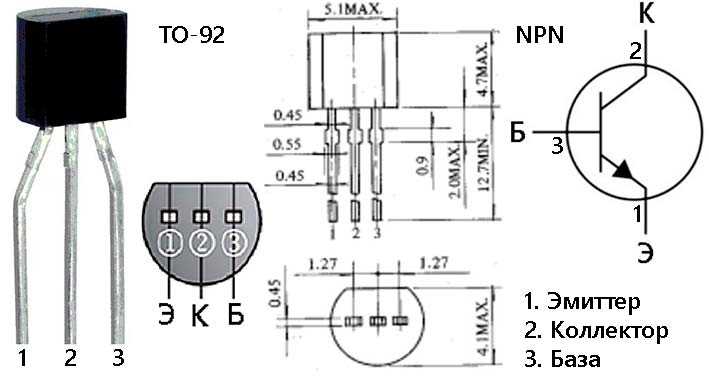
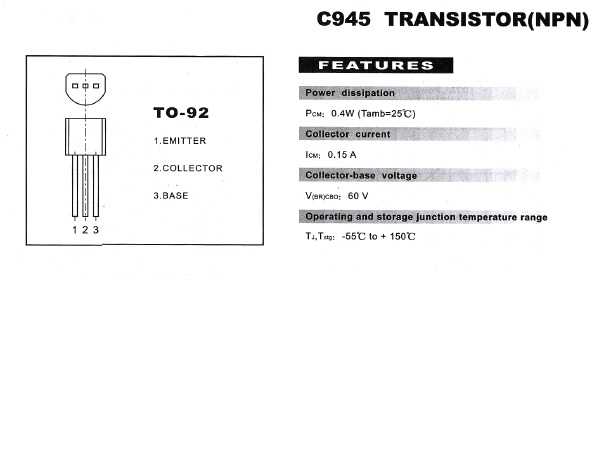
Understanding the Specifications and Pinout

In this section, we delve into comprehending the intricacies of the specifications and pinout configuration of the component in question. We explore the technical parameters and arrangement of connection points, shedding light on its operational characteristics and integration within electronic circuits.
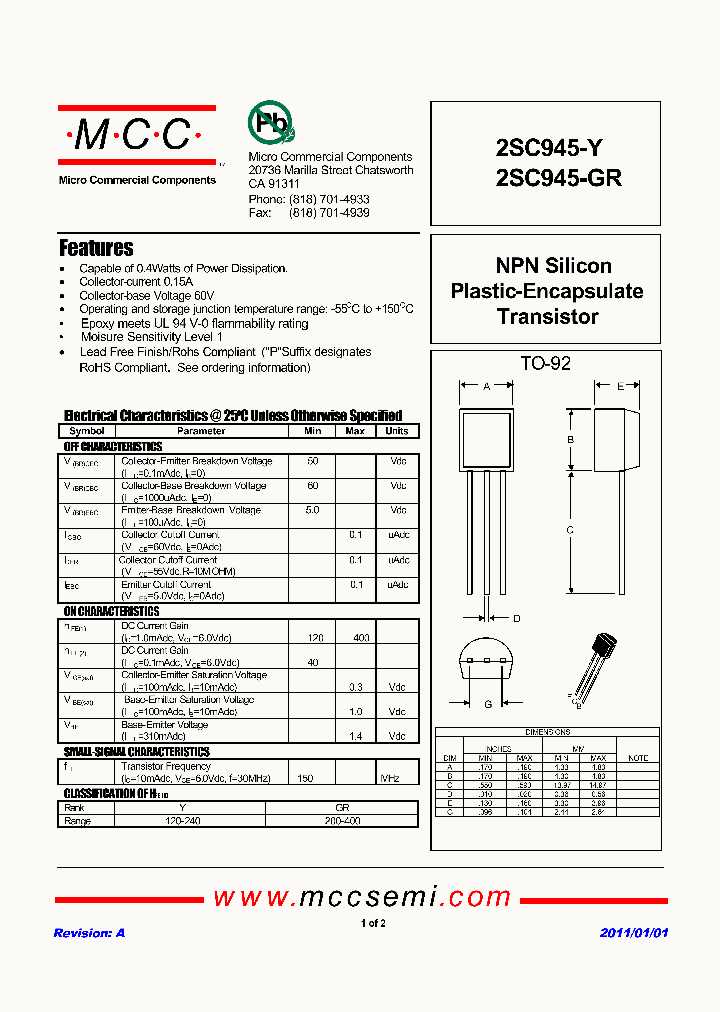
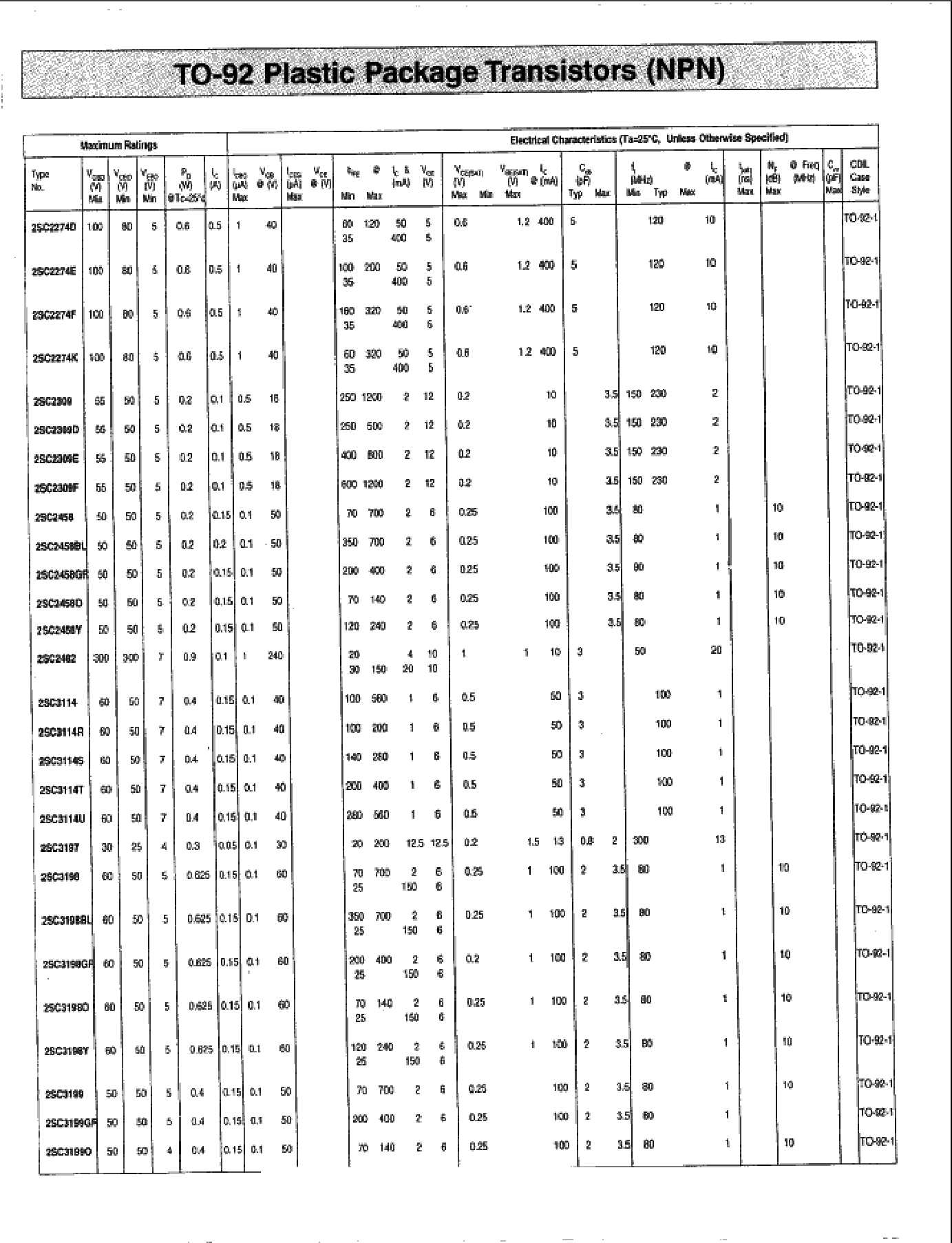
Technical Specifications Overview

Before delving into the specifics of pinout configurations, it’s crucial to grasp the key technical specifications that define the behavior and performance of the device. These specifications encompass a range of electrical characteristics such as voltage ratings, current handling capabilities, frequency response, and power dissipation. Understanding these parameters is essential for selecting the appropriate component for a given application and ensuring optimal circuit performance.
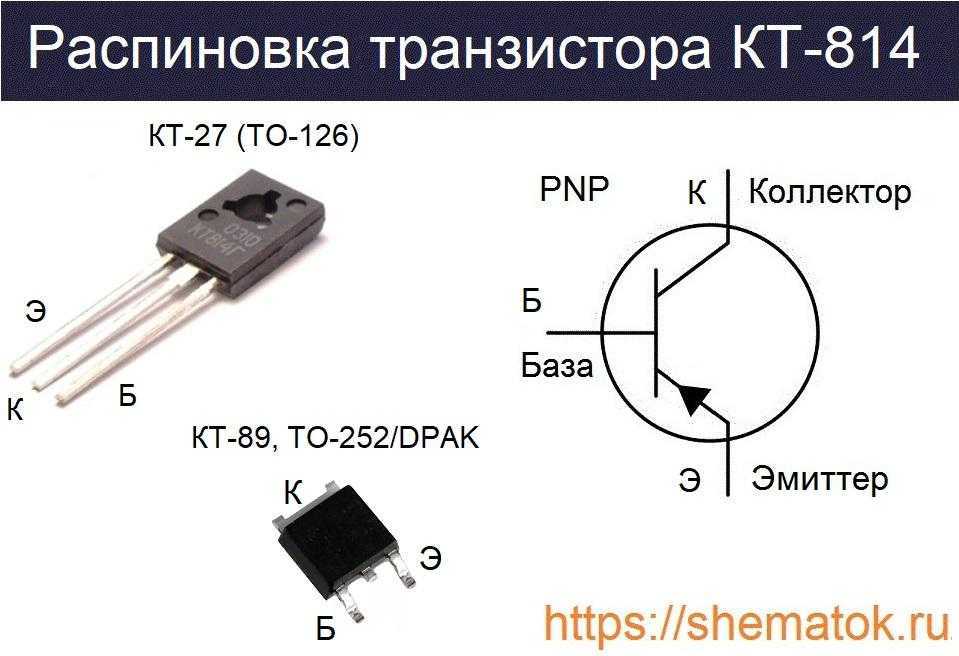
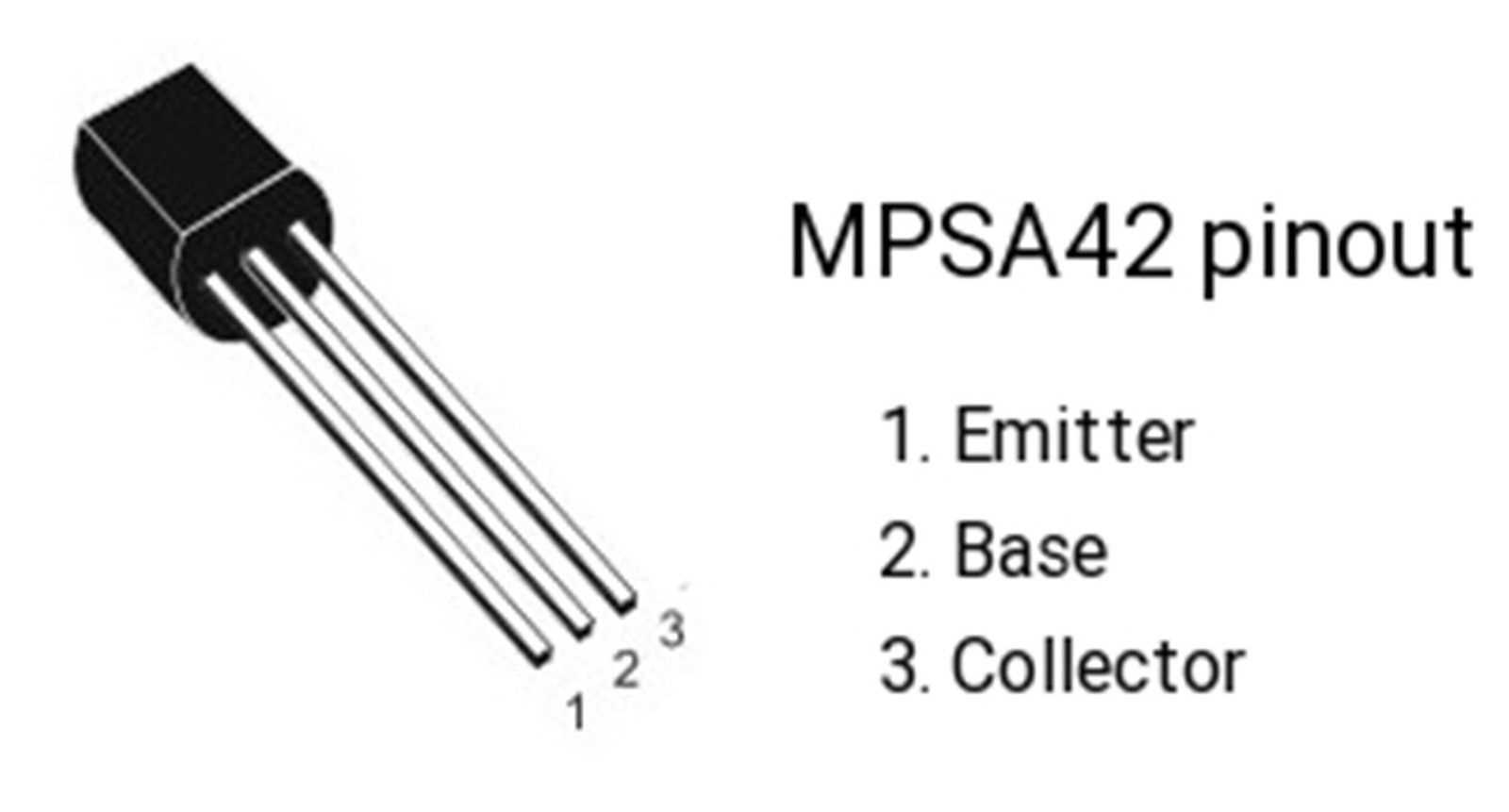
Pinout Configuration
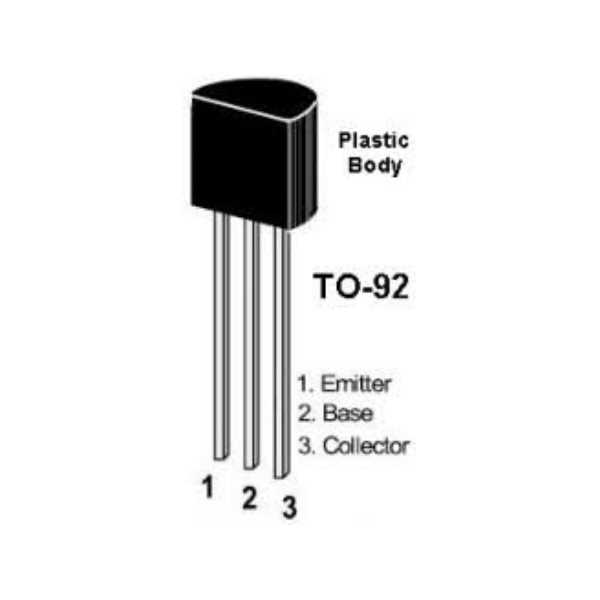
The pinout configuration of a semiconductor device dictates the arrangement of its connection points, facilitating its integration into electronic circuits. By examining the pinout diagram, engineers can identify each pin’s function, including emitter, base, and collector terminals, along with any additional features such as protection diodes or temperature sensing elements. Familiarizing oneself with the pinout layout is vital for correctly connecting the transistor within a circuit, preventing potential errors or malfunctions.
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Emitter Terminal |
| 2 | Base Terminal |
| 3 | Collector Terminal |
Applications and Circuit Design Utilizing 2SC3198
In this section, we explore the myriad applications and circuit design possibilities afforded by the versatile semiconductor device under consideration. From amplification to signal modulation, the 2SC3198 facilitates a broad spectrum of electronic functionalities. Its inherent characteristics lend themselves to a diverse array of electronic circuits, enabling engineers and hobbyists alike to craft innovative solutions for various challenges in electronics.
| Application | Circuit Design |
|---|---|
| Amplification | Utilizing the device’s amplification capabilities to boost signal strength in audio systems, radio frequency transmitters, and instrumentation circuits. Design considerations include biasing arrangements and load impedance matching for optimal performance. |
| Switching | Incorporating the transistor into switching circuits for power management, motor control, and digital logic applications. Techniques such as pulse-width modulation (PWM) and feedback control enhance efficiency and precision in switching operations. |
| Oscillation | Employing the 2SC3198 in oscillator circuits for generating stable clock signals, local oscillators in communication systems, and waveform generation in test equipment. Factors such as feedback network design and component selection influence frequency stability and waveform fidelity. |
| Signal Conditioning | Integrating the transistor into circuits for signal conditioning tasks such as filtering, amplification, and impedance matching. This includes applications in sensor interfacing, data acquisition systems, and telecommunications equipment. |
| Control Systems | Utilizing the transistor in control systems for regulating processes, managing power distribution, and implementing feedback mechanisms. Design considerations encompass stability analysis, control algorithm development, and interface integration. |
These are but a few examples of the diverse applications and circuit design possibilities enabled by the 2SC3198 semiconductor device. Its versatility and reliability make it a cornerstone component in modern electronic systems, empowering engineers to realize innovative solutions across a spectrum of domains.
Explore Practical Implementations and Configurations

In this section, we delve into real-world applications and setups utilizing components akin to the 2SC3198 transistor. Here, we navigate through tangible scenarios where electronic components are employed in various configurations to accomplish diverse tasks, showcasing their versatility and adaptability.
Application Scenarios

Discover how these electronic building blocks are ingeniously integrated into circuits to perform a multitude of functions. From amplification and signal processing to power regulation and switching, explore the myriad ways in which these components are utilized across industries and disciplines.
Configurations and Circuit Designs
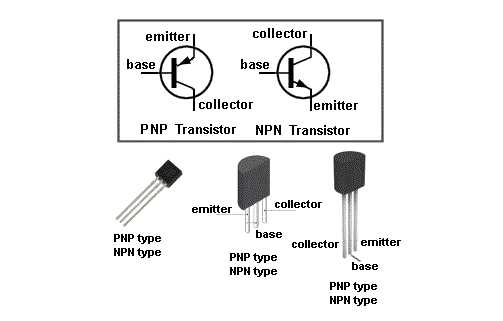
Uncover the intricacies of circuit design as we analyze different configurations incorporating transistors resembling the 2SC3198. Explore the nuances of common emitter, common collector, and common base configurations, understanding their respective advantages and limitations in practical applications. Delve into circuit diagrams and schematic representations to grasp the underlying principles governing their functionality.
Troubleshooting and Common Issues with 2SC3198
When delving into the functionality of this semiconductor component, it’s crucial to navigate potential hurdles that may arise during operation. This section aims to explore prevalent challenges and their resolutions, fostering a deeper understanding of the 2SC3198 transistor’s operational dynamics.
Intermittent Performance
One of the recurring dilemmas encountered with the 2SC3198 involves sporadic functionality, wherein the device exhibits inconsistent behavior over time. This erratic performance may stem from various factors, such as improper connections, inadequate power supply, or temperature fluctuations. Identifying the root cause necessitates meticulous inspection of circuitry, ensuring secure connections and stable power delivery. Additionally, vigilance regarding environmental conditions can mitigate thermal instabilities, thus enhancing the transistor’s reliability.
Signal Distortion and Amplification Issues
In certain scenarios, users may encounter signal distortion or suboptimal amplification capabilities with the 2SC3198. This phenomenon can manifest due to mismatched impedance levels, improper biasing, or inadequate voltage margins. Addressing these concerns entails recalibrating the circuit parameters to align with the transistor’s specifications, optimizing signal integrity and amplification efficiency. Furthermore, employing suitable filtering mechanisms and impedance matching techniques can attenuate distortion effects, facilitating enhanced signal fidelity.