In the realm of electronic engineering, every circuit tells a story, woven intricately with components that serve as the protagonists, each with its unique character and role. Delving into the intricacies of these components is akin to deciphering the language of innovation, where every resistor, capacitor, or semiconductor unveils its tale of functionality and application.
Embark on a journey of discovery as we navigate through the realm of semiconductor marvels, exploring their inner workings and potential applications. Our focus today lies not merely in the nomenclature of specific components, but rather in unraveling the mysteries they harbor, transcending the mere confines of technical documentation.
Let us embark on an expedition into the heart of a particular electronic gem, a beacon of innovation that ignites curiosity and sparks creativity. While it may bear a name and a datasheet, its essence extends far beyond the confines of these labels, beckoning us to delve deeper into its seminal attributes and operational intricacies.
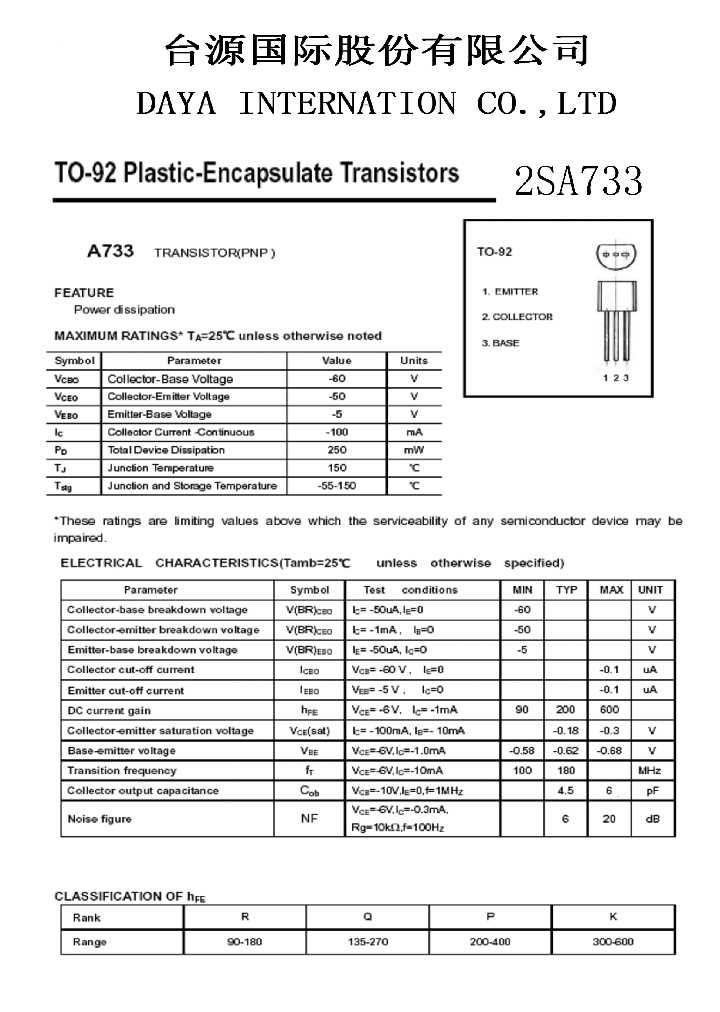
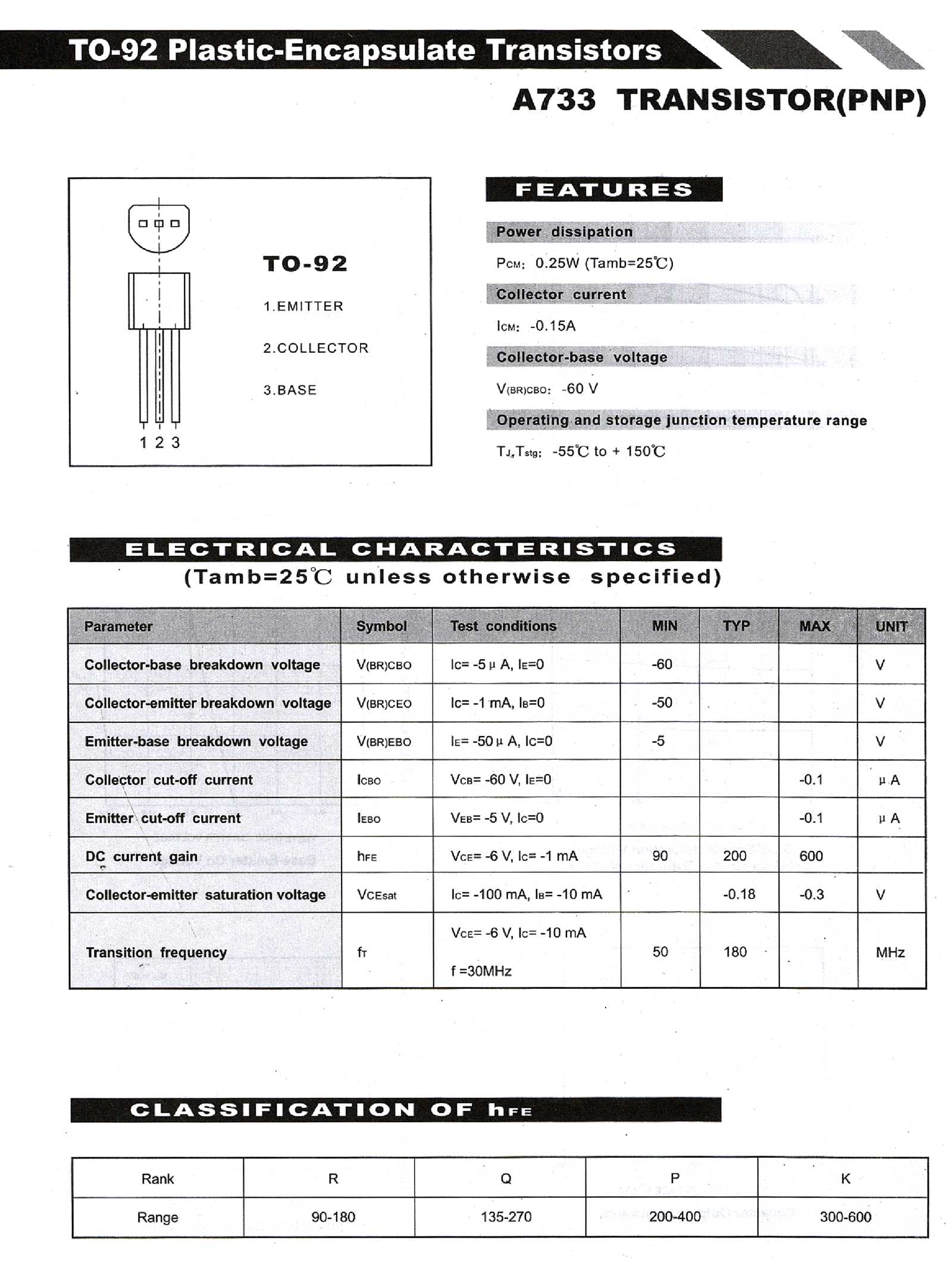
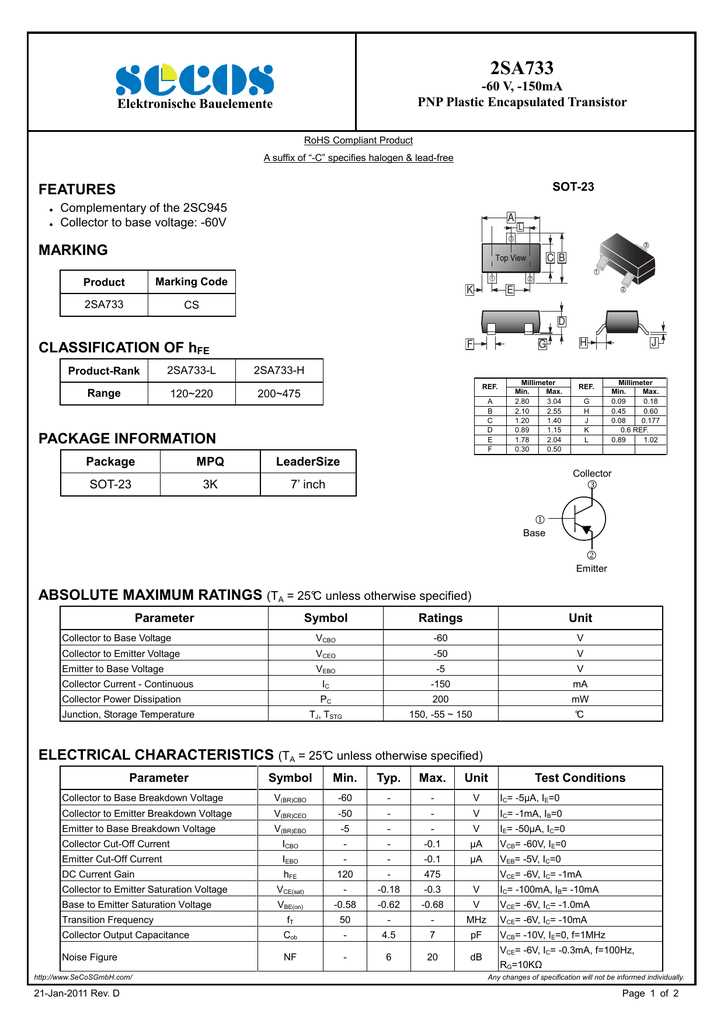
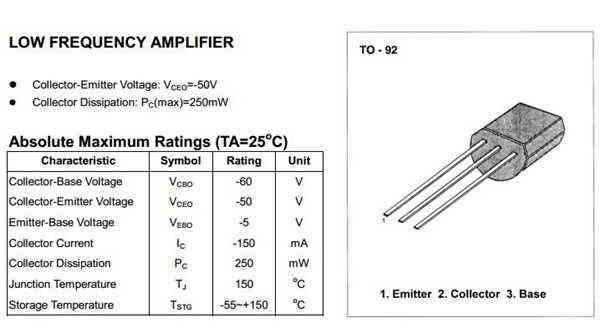
Understanding the 2SA733 Component Documentation
In the realm of electronic components, delving into the intricacies of documentation reveals a trove of valuable insights. This section aims to illuminate the nuances of comprehending the specifications and characteristics of the 2SA733 semiconductor device. By navigating through the detailed records provided, enthusiasts and professionals alike can unlock a deeper understanding of its functionality and applications.
Deciphering Key Parameters
Within the documentation lie essential parameters, each holding significance in discerning the behavior and performance of the component. These descriptors serve as the building blocks for engineers and hobbyists to analyze and predict the transistor’s operation without the need for exhaustive experimentation. Through meticulous examination, one can unveil the intricacies encapsulated within these specifications, guiding the utilization of the 2SA733 in various circuit designs.
Interpreting Graphs and Curves
Beyond mere numerical values, graphical representations enrich the datasheet, offering visual insights into the transistor’s characteristics across different operating conditions. These curves depict the relationship between critical parameters, shedding light on crucial aspects such as voltage-current behavior and frequency response. By adeptly interpreting these graphical depictions, practitioners can refine their design strategies and optimize circuit performance, ensuring efficient utilization of the 2SA733 within their projects.
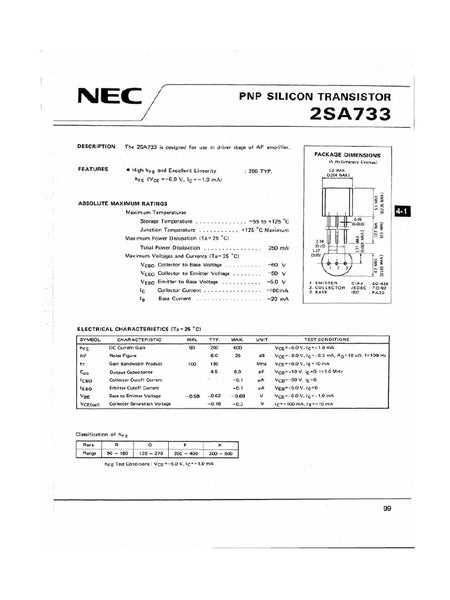
Unveiling Key Specifications and Parameters
Exploring the essential details and characteristics of this electronic component unveils a wealth of vital specifications and parameters. Understanding these foundational elements provides crucial insights into its functionality and potential applications.
Electrical Characteristics: Delving into the electrical properties reveals fundamental aspects such as voltage ratings, current capabilities, and frequency response. These parameters illuminate the component’s behavior within circuits, dictating its performance under various operating conditions.
Physical Attributes: Beyond electrical traits, attention to physical dimensions, material composition, and thermal properties offers valuable context for integration into designs. These attributes influence not only the component’s fit within a layout but also its reliability and longevity.
Environmental Considerations: Assessing environmental specifications sheds light on the component’s resilience to external factors such as temperature fluctuations, humidity, and mechanical stress. Understanding these parameters aids in selecting suitable operating environments and ensuring reliable functionality over time.
Application Guidelines: Unveiling key specifications also involves exploring recommended usage scenarios, including typical circuit configurations and performance expectations. Insight into application-specific considerations enables engineers to leverage the component effectively within their designs, maximizing performance and longevity.
Performance Metrics: Finally, scrutinizing performance metrics such as gain, saturation voltage, and noise characteristics provides a comprehensive understanding of the component’s behavior in amplification and signal processing applications. These parameters serve as benchmarks for evaluating performance and optimizing circuit designs.
By unraveling these essential specifications and parameters, engineers gain the necessary knowledge to effectively utilize this electronic component in diverse applications, driving innovation and advancement in electronic design.
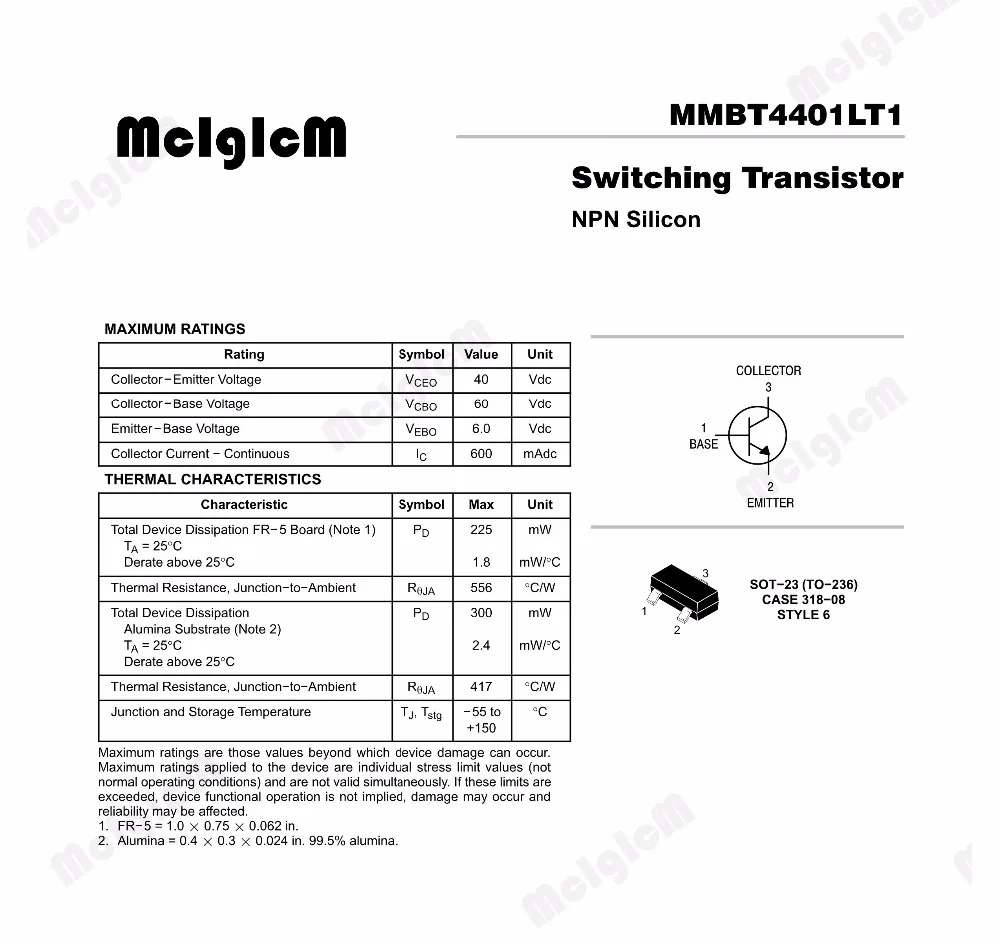
Exploring Application Circuit Examples

In this section, we delve into a variety of practical circuit configurations showcasing the versatile utility of the component under scrutiny. Through illustrative examples, we uncover the diverse applications and operational contexts where this component finds its niche, offering insights into its adaptability and performance across different scenarios.
Example 1: Amplification Circuit
One of the fundamental applications of this electronic element lies in signal amplification, where it serves as a crucial building block in enhancing the strength of input signals. By examining a typical amplification circuit, we uncover the mechanisms through which small input signals undergo significant augmentation, enabling clearer and more robust output signals for various electronic devices.
Example 2: Switching Circuit
Beyond amplification, this component also plays a pivotal role in switching circuits, facilitating the control and manipulation of electrical currents in electronic systems. Through an exploration of a switching circuit example, we elucidate how this component enables the efficient routing of signals, allowing for precise control over the flow of electricity in diverse applications ranging from consumer electronics to industrial automation.
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Amplification | Enhances input signals to produce stronger output signals. |
| Switching | Controls and manipulates electrical currents in electronic systems. |
Interpreting Performance Characteristics and Graphs
In the realm of electronic components, understanding the intricacies of performance characteristics and graphical representations thereof is paramount. This section delves into the nuanced art of deciphering the behavior and capabilities of semiconductor devices through various graphs and metrics. By grasping these fundamental principles, engineers and enthusiasts alike can glean invaluable insights into the operational dynamics of these essential components.
Key Metrics and Parameters
- Gain: This metric encapsulates the amplification prowess of the device, indicating how effectively it boosts the signal.
- Frequency Response: Describes the device’s ability to handle signals across different frequencies, crucial for applications demanding wide bandwidth.
- Noise Figure: Reflects the level of unwanted noise introduced by the device, influencing its suitability for low-noise applications.
Graphical Representation
Graphs serve as visual aids, offering a compact yet comprehensive depiction of a transistor’s behavior under varying conditions. These graphical representations often include plots showcasing parameters such as voltage, current, and frequency response against specified input conditions. By scrutinizing these graphs, one can discern crucial details about the device’s performance across a spectrum of operating scenarios.
Furthermore, graphs facilitate comparative analysis, allowing engineers to juxtapose different transistor models or configurations to determine the most suitable option for a particular application. Understanding how to interpret these graphical representations empowers individuals to make informed decisions, optimizing the performance and reliability of electronic circuits.