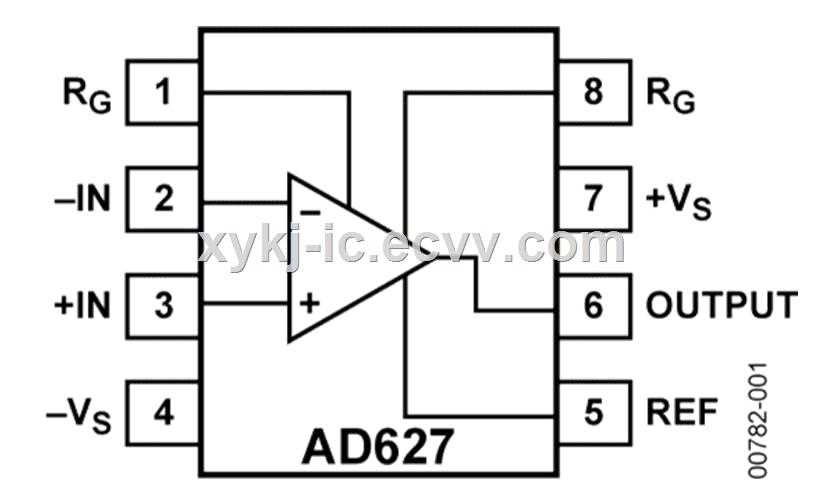
In the realm of electronic components, there exists a wealth of intricate documents that serve as guiding beacons for engineers and enthusiasts alike. These documents, brimming with technical intricacies and performance specifications, form the backbone of innovation in the ever-evolving landscape of technology.
Delving into the intricacies of these documents reveals a treasure trove of insights, guiding the hands of engineers as they navigate the labyrinthine paths of design and implementation. These documents, often veiled in jargon and technical language, hold the keys to unlocking the full potential of electronic components, empowering creators to push the boundaries of what’s possible.
As we embark on a journey of exploration, one such document emerges from the shadows, beckoning us to unravel its mysteries. Through careful analysis and discernment, we aim to uncover the essence of its contents, shedding light on its capabilities and applications.
The Basics of 2SA627 Transistor
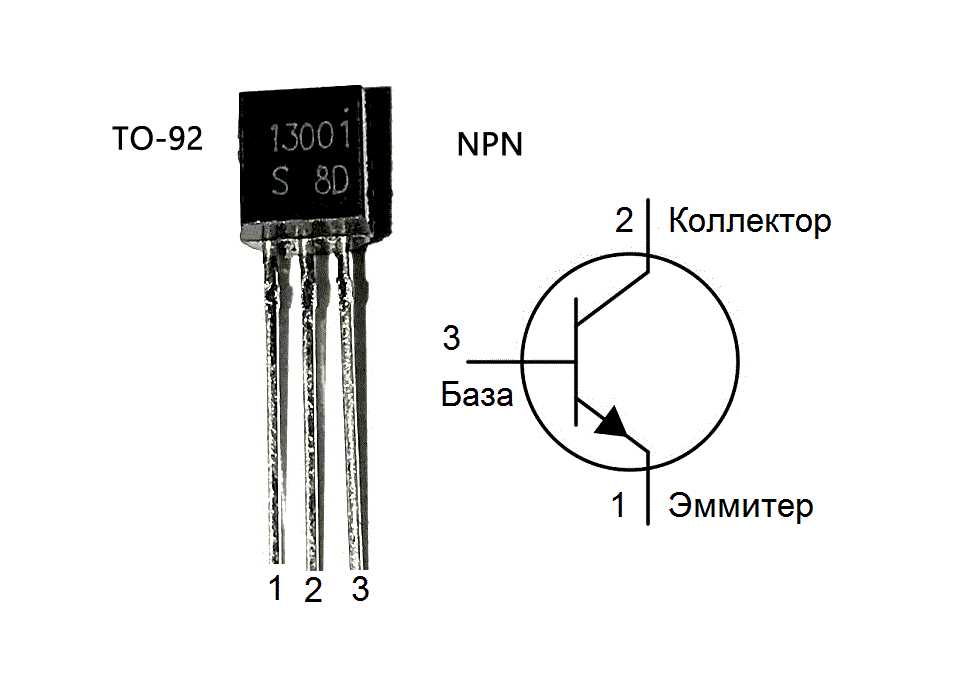
In the realm of electronic components, a small yet mighty device known for its pivotal role in amplification and signal processing emerges–the 2SA627 transistor. This component, integral to numerous electronic circuits, functions as a crucial element in regulating and controlling electrical currents. In this exploration, we delve into the fundamental workings and characteristics of this semiconductor marvel, shedding light on its applications and importance in modern electronics.
Understanding Semiconductor Transistors
Semiconductor transistors stand as cornerstones of contemporary electronics, facilitating the manipulation of electrical signals with remarkable precision and efficiency. These miniature devices operate as amplifiers, switches, or signal modulators, depending on their configuration and application. Within this diverse category, the 2SA627 transistor occupies a significant position, renowned for its versatility and reliability in various circuit designs.
When delving into the intricacies of semiconductor transistors, one encounters a rich tapestry of principles from solid-state physics and electronic engineering. Central to their operation is the modulation of current flow through a semiconductor material, controlled by the application of external voltages or currents. This nuanced interplay between electrical signals forms the basis of transistor functionality, enabling a myriad of applications ranging from audio amplification to digital logic circuits.
Key Characteristics and Applications
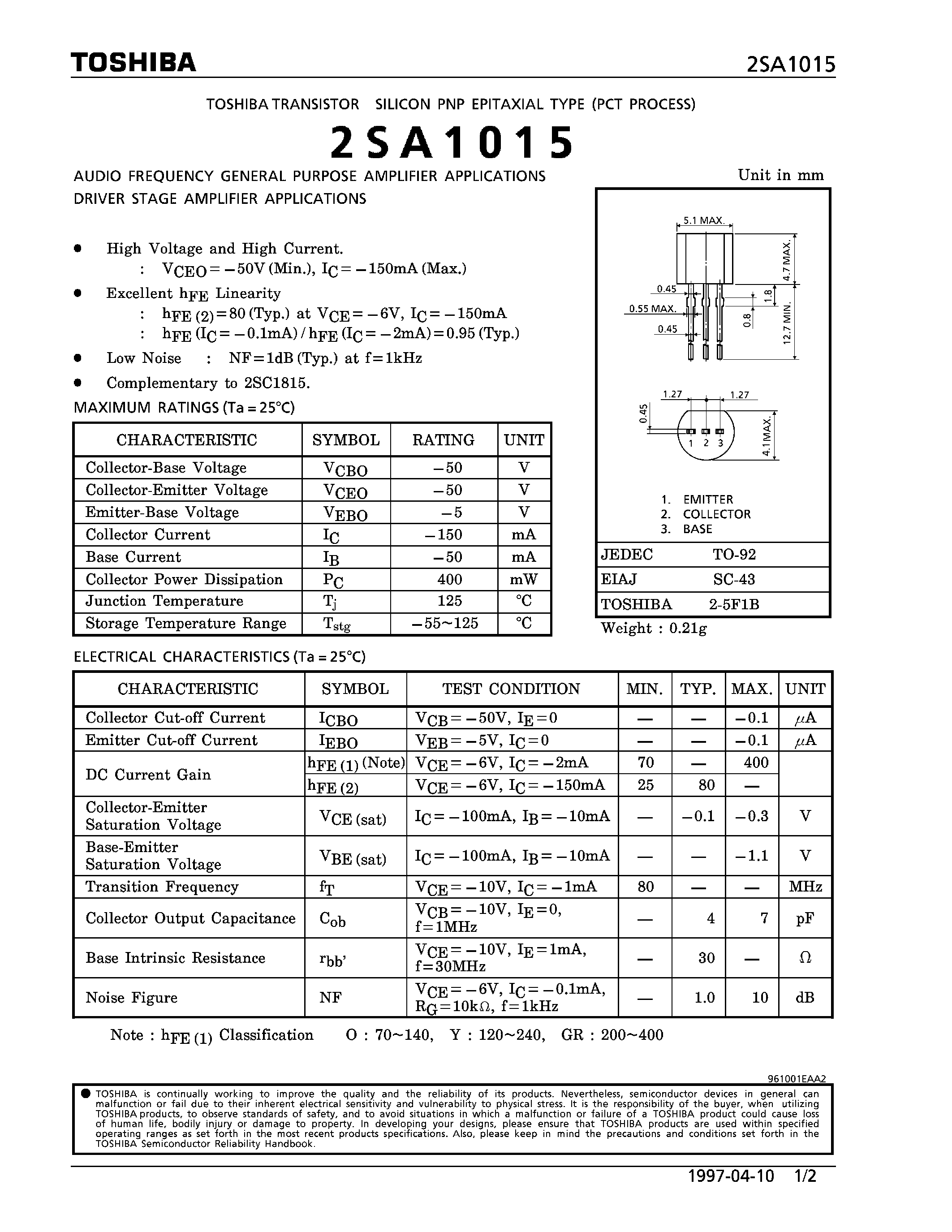
At the heart of the 2SA627 transistor lie distinctive attributes that render it indispensable in electronic design. From its precise voltage regulation capabilities to its high-frequency response, this semiconductor device exhibits traits tailored to specific application requirements. Whether employed in audio amplifiers, voltage regulators, or radio frequency circuits, the 2SA627 transistor showcases its prowess in delivering consistent and reliable performance.
Beyond its technical specifications, the significance of the 2SA627 transistor extends to its role in advancing technological innovation. As an essential building block in electronic systems, its reliability and efficiency contribute to the seamless operation of myriad devices, from consumer electronics to industrial automation. Understanding the fundamentals of this transistor not only empowers engineers and enthusiasts but also underscores its enduring legacy in shaping the landscape of modern electronics.
Understanding the Key Specifications
In this section, we delve into the vital parameters that define the performance and functionality of the component in question. These specifications serve as the cornerstone for assessing its suitability for various applications and understanding its capabilities in diverse operating conditions.
- Electrical Characteristics: Explore the electrical properties that govern the behavior of the component, such as voltage ratings, current handling capacity, and impedance characteristics.
- Performance Metrics: Gain insights into the operational efficiency and effectiveness of the component through key performance indicators like gain, bandwidth, and noise characteristics.
- Environmental Considerations: Assess the component’s resilience to environmental factors such as temperature variations, humidity, and shock resistance, ensuring reliability in challenging conditions.
- Mechanical Specifications: Examine the physical attributes of the component, including dimensions, mounting options, and mechanical tolerances, crucial for integration into systems and assemblies.
- Lifecycle Parameters: Understand the longevity and reliability of the component over its lifecycle, considering factors like mean time between failures (MTBF), operating lifespan, and reliability metrics.
By comprehensively understanding these key specifications, engineers and designers can make informed decisions regarding component selection, integration, and optimization, ultimately contributing to the successful realization of their projects.
Application Notes for 2SA627
In this section, we delve into practical insights and guidance for maximizing the performance and versatility of the component under discussion. Here, you’ll find valuable information and recommendations for effectively integrating this semiconductor device into your electronic designs. Discover tips, best practices, and real-world applications to harness the full potential of this critical component.
Exploring Operational Scenarios: Gain deeper insights into the diverse operational scenarios where the 2SA627 can excel. From amplification tasks to signal conditioning and beyond, understand how this component can be leveraged across various applications.
Optimizing Circuit Configurations: Learn about optimal circuit configurations and layouts to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Explore circuit design principles, including biasing techniques, feedback mechanisms, and impedance matching considerations.
Temperature and Environmental Considerations: Delve into the impact of temperature and environmental factors on the performance of the 2SA627. Discover strategies for mitigating thermal issues and ensuring consistent operation across different environmental conditions.
Interfacing and Compatibility: Uncover compatibility considerations and interfacing guidelines when using the 2SA627 alongside other electronic components. Learn how to integrate this component seamlessly into your existing circuitry for enhanced functionality.
Case Studies and Practical Examples: Explore real-world case studies and practical examples illustrating the application of the 2SA627 in diverse electronic systems. Gain valuable insights from these use cases to inspire innovative design solutions and overcome common challenges.
Performance Optimization Techniques: Discover advanced techniques for optimizing the performance of the 2SA627 in specific applications. From dynamic range enhancement to noise reduction strategies, unlock the full potential of this semiconductor device through expert tips and techniques.
Conclusion: Wrap up your exploration of application notes for the 2SA627 with a concise summary highlighting key takeaways and actionable insights. Reflect on the versatility and significance of this component in modern electronic design and encourage further experimentation and innovation.
Optimizing Circuit Designs with 2SA627
In the pursuit of refining electronic systems, the quest for optimal circuit designs stands paramount. Within this endeavor lies the exploration of components that wield significant influence over circuit performance. In this section, we delve into strategies for enhancing circuitry efficiency and efficacy through the judicious utilization of a specific electronic component, exploring its characteristics and potential applications.
The Role of Component Selection
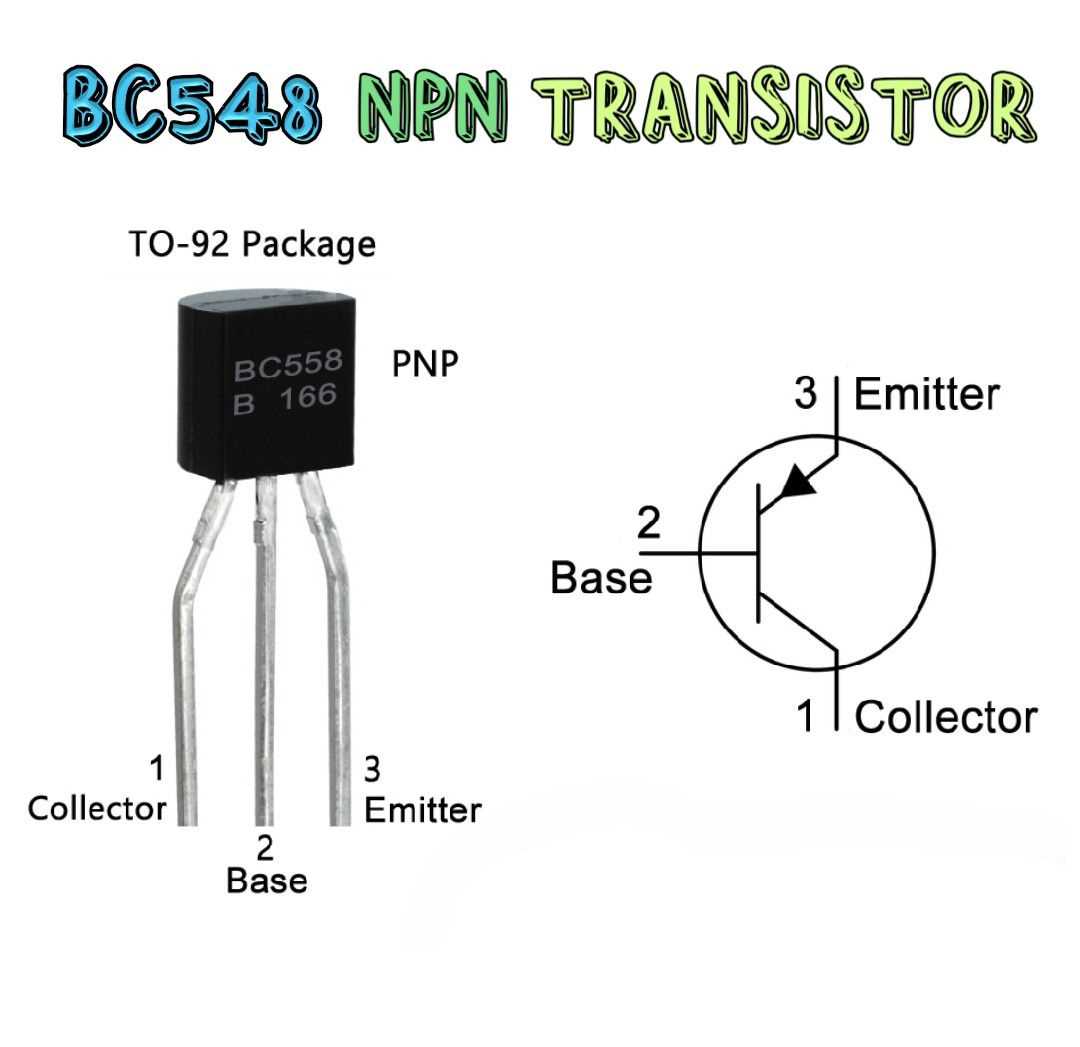
At the core of any circuit lies the careful selection of components, each contributing its unique attributes to the overall functionality. By understanding the nuanced characteristics of individual components, engineers can leverage them to tailor circuit performance to specific requirements. Within this paradigm, the significance of selecting appropriate transistors cannot be overstated. These semiconductor devices play a pivotal role in amplification, regulation, and switching within circuits, thus exerting a profound impact on system behavior.
Exploring the Performance Spectrum
Within the realm of transistor selection, the 2SA627 emerges as a noteworthy candidate, characterized by its distinctive features and versatile applications. Through a comprehensive examination of its performance spectrum, engineers can unlock insights into its operational parameters, including but not limited to gain, bandwidth, and voltage ratings. Armed with this knowledge, circuit designers can strategically integrate the 2SA627 to optimize signal processing, mitigate distortion, or enhance power efficiency, depending on the specific design objectives.
Exploring Alternatives to 2SA627
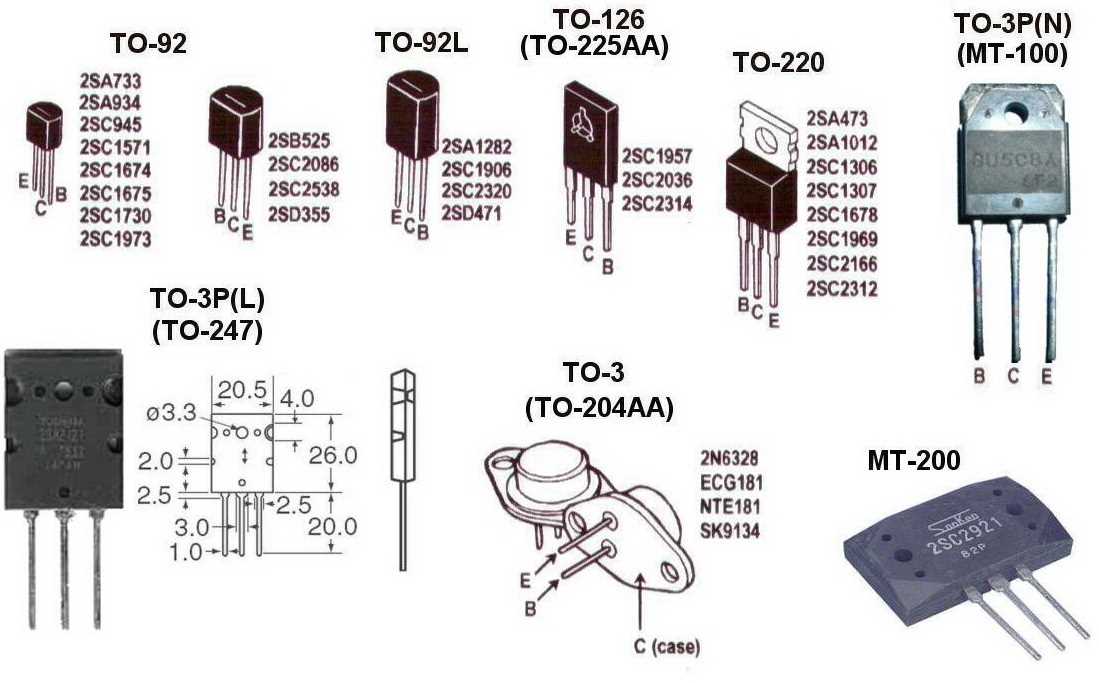
In this section, we delve into potential substitutes for the component under scrutiny, broadening our perspective beyond the confines of the specific model number. Our aim is to uncover alternative options that could fulfill similar roles, considering various technical specifications and performance characteristics.
When seeking alternatives to the component in question, it becomes imperative to conduct a comprehensive assessment of comparable components available in the market. By examining parameters such as voltage ratings, current handling capabilities, and package types, we can identify substitutes that align with the requirements of the intended application.
- Voltage Ratings: Exploring components with analogous voltage ratings ensures compatibility within the circuit design, safeguarding against potential overloads or voltage disparities.
- Current Handling Capabilities: Evaluating alternatives based on their ability to manage current flow effectively is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and reliability.
- Package Types: Considering different package types enables flexibility in terms of PCB layout and space constraints, facilitating seamless integration into existing designs.
Furthermore, delving into datasheets of prospective substitutes allows for a more nuanced comparison, enabling insights into additional features, thermal characteristics, and application notes that may influence the selection process.
By exploring alternatives to the component under examination, we aim to broaden the scope of possibilities, empowering designers to make informed decisions based on a thorough understanding of available options and their suitability for specific applications.